WEEK 12 TOPIC: CENTRAL PLACE THEORY
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Christaller's Central Place Theory
The theory was originally published in 1933 by a German geographer Walter Christaller who studied the settlement patterns in southern Germany.
Central Place Theory (CPT)
is an attempt to explain the spatial arrangement, size, and number of settlements.
By examining and defining the functions of the settlement structure and the size of the hinterland he found it possible to model the pattern of settlement locations using geometric shapes.
Central Place
is a settlement which provides one or more services for the population living around it.
Low order
Simple basic services (e.g. grocery stores)
High order
specialized services (e.g. universities)
Having a high order service implies there are _________________, but _____________
low order services around it, but not vice versa.
Low order settlements
Settlements which provide low order services
High order settlements
Settlements that provide high order services
Sphere of influence
is the area under influence of the Central Place.
Central Place Theory Basic Concepts
Threshold
Range of Good or Services
Threshold
the minimum population that is required to bring about the provision of certain good or services
Range of good or services
the average maximum distance people will travel to purchase goods and services
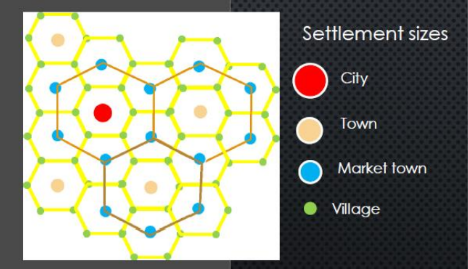
Arrangement of the Central places/ settlements:
As transport is equally easy in all direction, all central place will have a circular market. However, as proposed by Christaller, he suggested the hexagonal shape. There will be equidistance from each other. There will be equidistance. The higher order settlements will be further apart than the lower order ones.
The three principles in the arrangement of the central places
The Marketing Principle (K=3 system)
The Transport Principle (K=4 system)
The Administrative Principle (K=7 system)
The Marketing Principle
Lower is the order, Larger is the number of settlements.
The higher the order, the greater is the area served

The Transportation Principle
Depends on the traffic route. Centers are located at the midpoint of each side of the hexagon rather than at the corner.
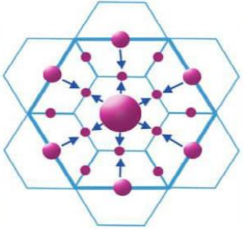
The Administrative Principle
The six lower order centers are full subordinate to the higher order
Evaluation of Central-Place Theory
Production may vary due to economies of scale and natural resource endowments
Transportation costs are not equal in all directions
Rural Markets (Households) are not evenly distributed
Non Economic factors (culture, politics, leadership) important, but not evenly distributed
Competitive practices may lead to freight absorption and phantom freight
Advantages of Central Place Theory
No other economic theory explains why there is a hierarchy or urban centers
Heilbrun wrote: A hierarchy is a systematic arrangement of the classes of an object. THe CP hierarchy provides the relationship between a center place and Tributary areas (higher and lower areas)
Does a good job of describing the location of trade and service activity
Why does Christaller’s model will never be found in the real world?
Changes that happened over time
Large areas of flat lands are rare
People vary their shopping trends, not always going to the nearest center.
People or resources are never perfectly distributed
Application to Economic Development of CPT:
Average transportation cost per purchase are lowered by multipurpose shopping trips
The consumers are more likely to shop at multiple locations on a single trip
Spatial clustering also deals with demographic characteristics
Many producers wanted to locate far from their competitors, but firms recognized the advantages of having your competitor in an adjacent location
The development of central places depends on factors such as transport costs, expenditure shares for relevant goods and cost characteristics of stores
Planning commissions focused more on industrial recruitment rather than retail-sector.
Central Place Theory (Political Boundary)
Who introduced Core Periphery Model
John Friedman
Who is John Friedman
is one of the pioneering urban theorists of the late twentieth century. He founded the Graduate School of Architecture and Planning at UCLA in the late 1960. He is famous for his analysis of world city formation.
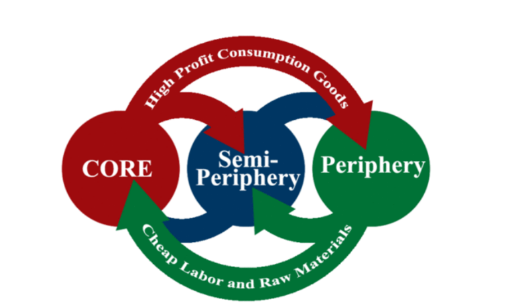
What is Core Periphery Model?
Represents four major stages which works equally with the development of tranportation
Why inner city areas enjoy prosperity, while others urban deprivation and poverty
Four types of Regions in Core Periphery Model
Core Regions
Upward Transition regions
Resource frontier regions
Downward transition regions
Core Regions
Metropolitan, high potential for innovation (improvement) and growth
Upward transition regions
areas of growth, small centers rather than at the core
Resource Frontier Regions
newly colonized regionD
Downward Transition regions
Depleted resources, low agricultural productivity or outdated industry
What is Periphery Role in Wallerstein’s World System Theory Model?
Core Periphery Model Stages of Development
Stage 1: Pre-Industrial
Stage 2: Transitional
Stage 3: Industrial
Stage 4: Post-Industrial
Stage 1: Pre-Industrial Stage
agricultural/ primary sector of society
Small area and a small scale settlement
isolated, dispersed, and low mobility
Stage 2: Transitional
Core Begins
Capital accumulation and Industrial growth
A dominant center emerges
Stage 3: Industrial Stage
Other growth Centers appear
Deconcentration due to increased production cost (labor and land) in the core area
More interactions between elements, and constructions of transport infrastructures
Stage 4: The Post Industrial Stage
Urban System fully integrated, inequalities reduced
Division of labor linked with intense flows along high capacity transport corridors