21. Disorders of the mammary gland – tumours (diagnosis of tumours, clinical classification in bitch and queen – staging)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the second most common tumour in female dogs?
Mammary gland tumours
What percentage of mammary gland tumours are benign in dogs?
50%
What is the third most common tumour in female cats?
Mammary gland tumours
What percentage of mammary gland tumours are adenocarcinomas in cats?
80%
Which hormones influence the development of mammary gland tumours?
Oestrogen and progesterone
What factor in feline birth control can increase the risk of mammary tumours?
Birth control pills
What are some risk factors for mammary gland tumours?
Age >6 years, being unspayed, obesity, history of pseudopregnancy
Which mammary glands are more at risk in bitches?
Caudal mammary glands (M4-5)
What is the most effective way to reduce the risk of mammary tumours in bitches?
Spaying after the first heat
What is the effect of spaying after 3-4 heats on mammary tumour risk?
No significant reduction in risk
What are some types of mammary gland tumours in dogs?
Carcinoma, sarcoma, carcinosarcoma, benign adenoma
What are some types of mammary gland tumours in cats?
Carcinoma, sarcoma, mixed mammary tumours, adenocarcinomas
What are the clinical signs of benign mammary tumours?
Small, circumscribed masses
What are the clinical signs of malignant mammary tumours?
Rapid growing, ill-defined boundaries
What is the typical appearance of the cut surface of a mammary tumour?
Lobulated, grey-tan and firm, possibly with fluid-filled cysts
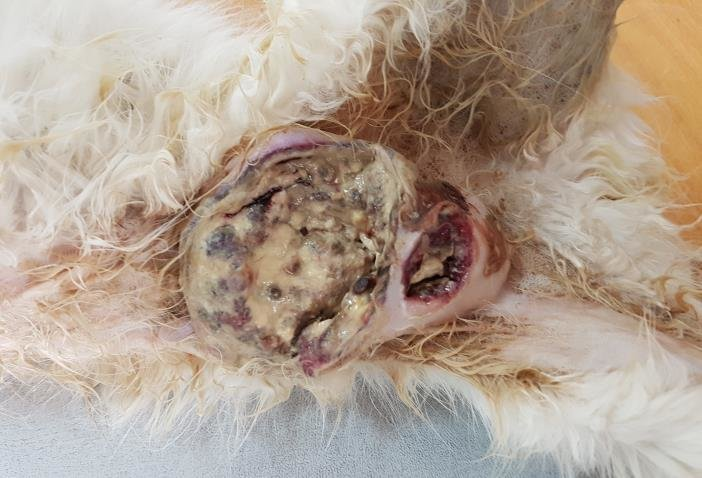
What are the clinical signs of inflammatory mammary carcinoma?
Rapid, multiple, firm, warm, oedematous, red masses
Is surgery recommended for inflammatory mammary carcinoma?
No
What treatments can be considered for inflammatory mammary carcinoma?
NSAIDs and antibiotics, with re-evaluation after the heat cycle
How are mammary gland tumours diagnosed?
History, palpation of glands and lymph nodes, lung X-ray, USG, bloodwork, FNA, biopsy
What information should be included in the history for diagnosing mammary tumours?
Use of progestogen drugs, history of pseudopregnancy, oestrus cycle, time of spay
What is the TNM system used for?
Staging tumours
What does 'T' in the TNM system refer to?
Tumour size
What does 'N' in the TNM system refer to?
Lymph node status
What does 'M' in the TNM system refer to?
Metastasis
What does T0 mean in the TNM system?
Tumour cannot be found
What does N0 mean in the TNM system?
No cancer in nearby lymph nodes
What does M0 mean in the TNM system?
Cancer has not spread to other organs
What do higher numbers in T (T1-T4) indicate?
Larger tumour size
What do higher numbers in N (N1-N3) indicate?
Cancer in more lymph nodes
What does M1 mean in the TNM system?
Cancer has spread to other organs
What diagnostic tool is important for checking for metastasis of mammary tumours?
Lung X-ray
Why is palpation of regional lymph nodes important in mammary tumour diagnosis?
To assess for potential spread of cancer.