Upper Extremities - Fingers, Hand, Wrist
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
What should you do before taking an radiograph of extremities.
Remove all artifacts. (Rings, watches etc..
How should you position the pt. for upper limb radiography.
-Seat patient 90 ° to the I.R
-This will decrease gonadal dose and assist in visualizing the joint spaces.
-pt. usually sits at the end of exam table
What should you always do when taking a radiograph?
-Always shield the gonads
-Always Collimate. This will improve image quality
-Place the correct anatomical side marker either laterally or anteriorly
-All extremity work is done at _____''
-Remember that table top is not ____'' to standard detent. Table top is about 3'' different.
-Drop the tube ______" for every _____ degree of tube angulation.
-40"
-40"
-1'' inch, 5 degree
What size focal point is used for extremities? Why does it help?
-Use small focal spot for extremities.
-This will increase recorded detail.
Protocol for R/O Foreign body
-(R/O FB) protocol is 2 projections 90 ° from each other. AP/PA and a lateral.
-(Make sure I.R is cleaned so that an artifact in the cassette does not show up as a FB on your radiograph)
Depending on the institution what will they will require you to do when R/O foreign body?
-that you mark on the I.R the entrance/exit of the FB
-(A soft tissue technique may be achieved by decreasing mAs 1/3 from what you would normally use. For example, if you would use 10 mAs for a particular body part, use 6 mAs for a soft tissue study of that same part.)
Pediatric comparison
Some institutions require AP/PA and lateral to be done on pts. 14 and under. Some institutions do not need comparisons if there is a FX Mark “Comparison” on I.R
Technique for cast
-Wet plaster: ____kVp or increase ____ your mAs
-Wet plaster: +8-10 kVp or 2x (100%) of your mAs
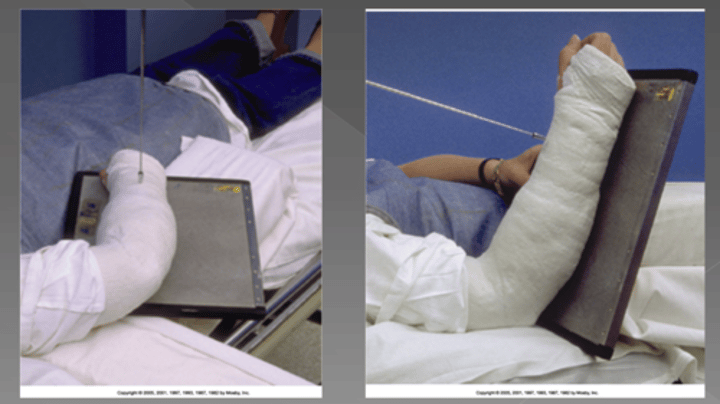
Technique for cast.
-Dry plaster: ___kVp or increase mAs by ____?
-Dry plaster: +5-7 kVp from the "normal" range you use for that part or increase mAs by 50%-60%
Technique for cast
-Fiberglass: ____kVp or increase your mAs
-Fiberglass: +3-4 kVp or increase mas by 25%-30%
Radiography of joints are a minimum of _____ images
min. of 3 images
Radiograph of long bones require how many projections.
2 proj, 90°apart. Include both jts.
Radiograph of a Post Reduction require how many projections and what should you mark on IR?
2 proj, 90° apart, marked POST-REDUCTION
-When is a grid used?
-Where can you use a grid?
-What does using a grid do?
-used when the body part exceeds 10-cm thickness
-could be the table or wall bucky or a portable “snap on” type.
-it absorbs the scatter radiation before it reaches the I.R. and improves image quality (contrast)
Who holds the pt. when they're getting a radiograph?
What question should you always ask before exposure?
-Always try to get a family member to assisting keeping the moving patient still. Remember EVERYONE GETS SHIELDED
-ALWAYS ASK THE PATIENT IF "THERE IS ANY POSSIBILITY, EVEN
A REMOTE ONE, THAT YOU COULD BE PREGNANT?
Which type of pt. should you decrease exposure factors? and why?
-older and younger patients.
-Older patients have less calcium in their bones and younger patients have smaller bones
Golden rule:
Set your panel before you position your patient!!
How many bones in the adult human body.?
How many are appendicular and how many are axial?
206 bones
Appendicular (126 bones) and Axial (80 bones)

Compact bone: (define)
strong dense outer layer (protects)
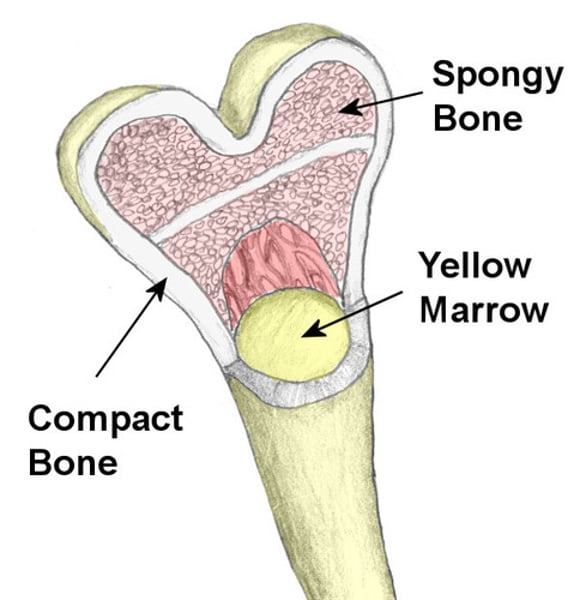
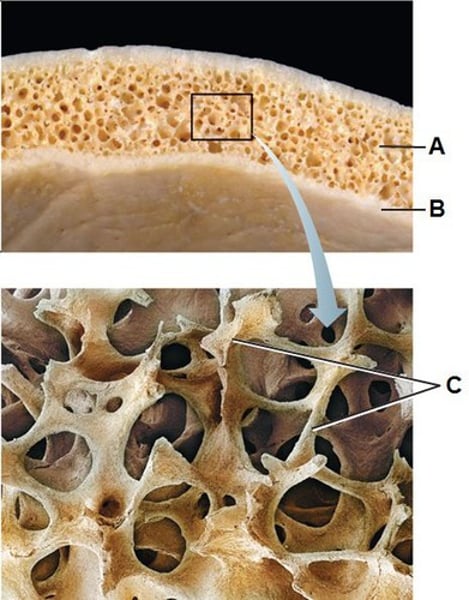
Spongy bone: (define)
less dense inner portion.
(Contains a spiculated network called trabeculae)
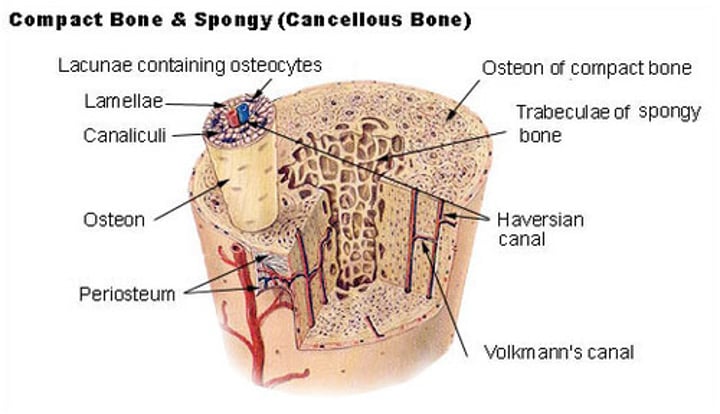
Trabeculae: Define
-interconnecting network of bony tissue filled with with red & yellow bone marrow.
Medullary Cavity: (define)
-central cavity in long bones containing trabeculae
(filled with yellow marrow. In long bones, red marrow concentrates @ ends of the bone.)
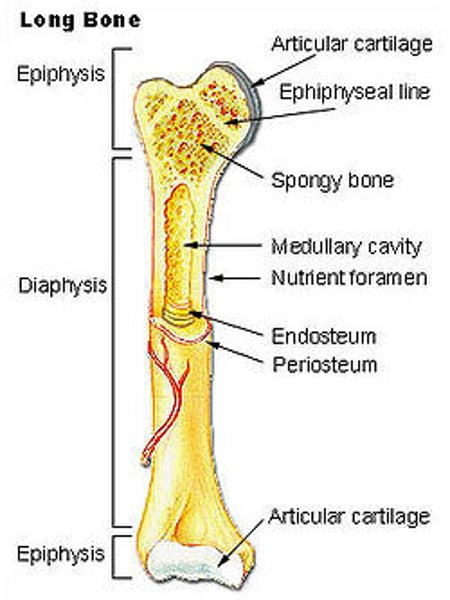
Periosteum (define)
-Covering of bones
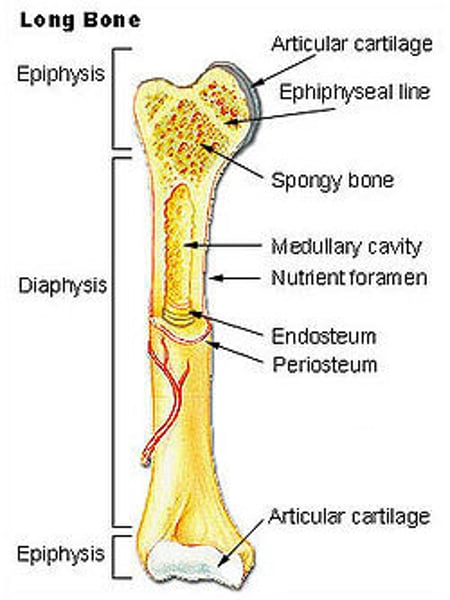
Endosteum (define)
tissue lining medullary cavity
Define Ossification:
development and formation of bones
intermembranous ossification
bones develop from fibrous membranes in the embryo; creates the flat bones, such as (skull, clavicles, mandible, and sternum)
Primary Ossification
-begins before birth
(sort, carpals & tarsals & irregular bones, some facial and pelvis)
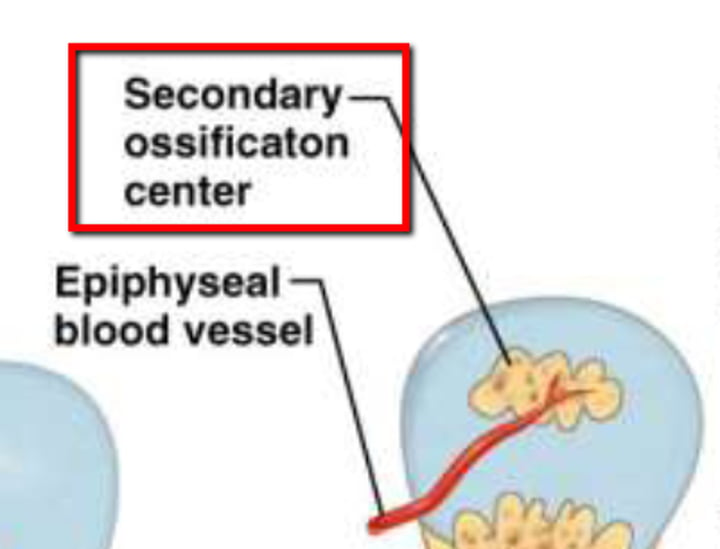
Secondary ossification
-occurs after birth
-Epiphyseal plate, full ossification @/near the age of 21
(Classification of bones)
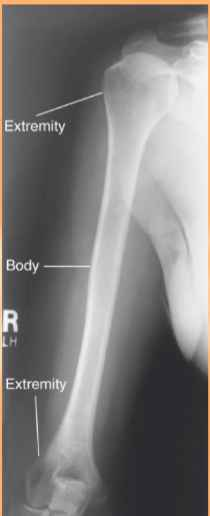
Long bones include
-Limbs
-Compact bone
-Spongy bone
-Periosteum
(Classification of bones)
Short and Flat bones include
-Carpal and tarsal bones
-Calvarium, sternum, ribs, and scapulae
(Classification of bones)
Irregular Bones include
Peculiar shapes (vertebrae, facial
bones, and pelvic bones)
Arthrology (review in textbook)
study of joints
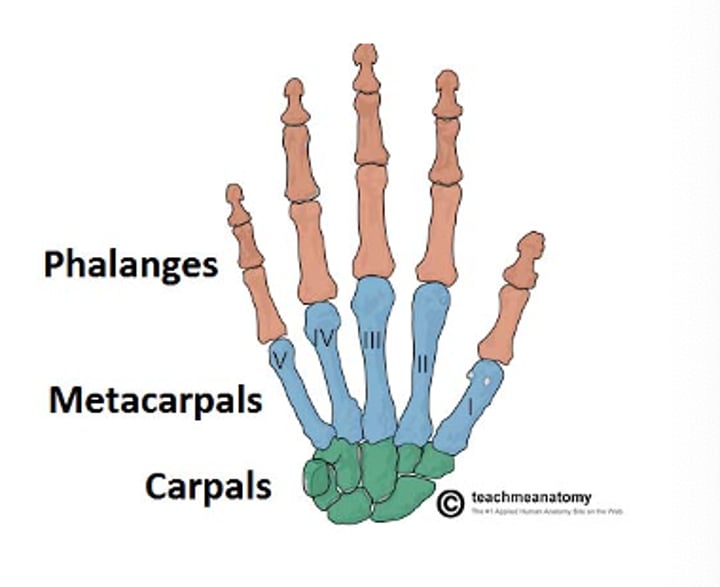
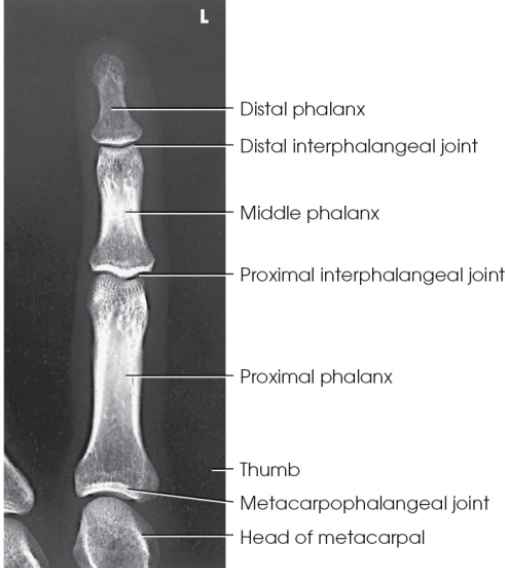
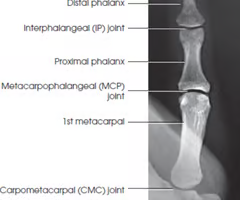
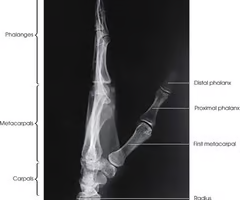
Anatomy of Fingers and hand
How many phalanges does one hand have?
How many Meta carpals?
How many Carpals?
-14 phalanges
-5 metacarpals
-8 carpals
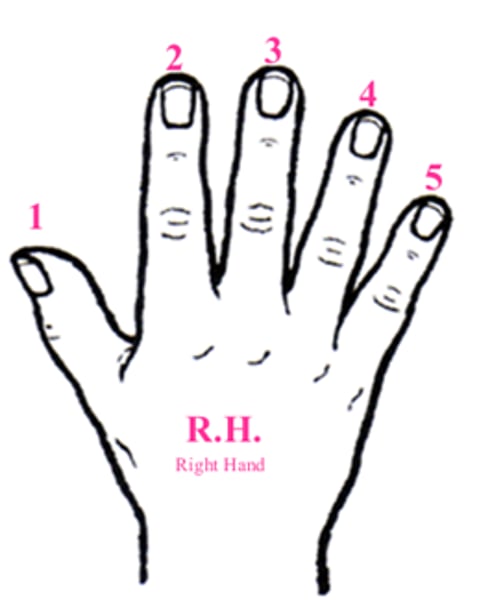
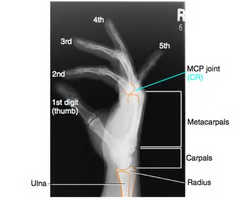
Anatomy of fingers and hand
How do you start to count the digits in hand? and label.
-You start with your thumb being the 1st digit.
-Index finger (2nd digit)
-Middle finger (3rd digit)
-Ring Finger (4th digit)
-Pinky (5th digit)
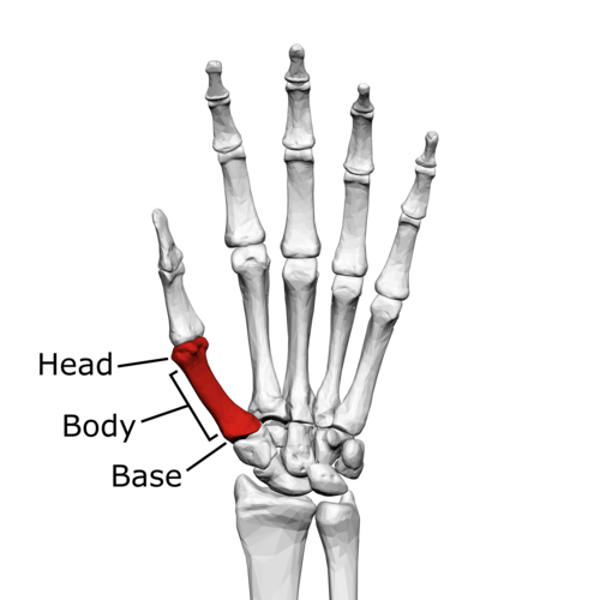
Metacarpals have a … (Anatomy)
-Head, Shaft, Base
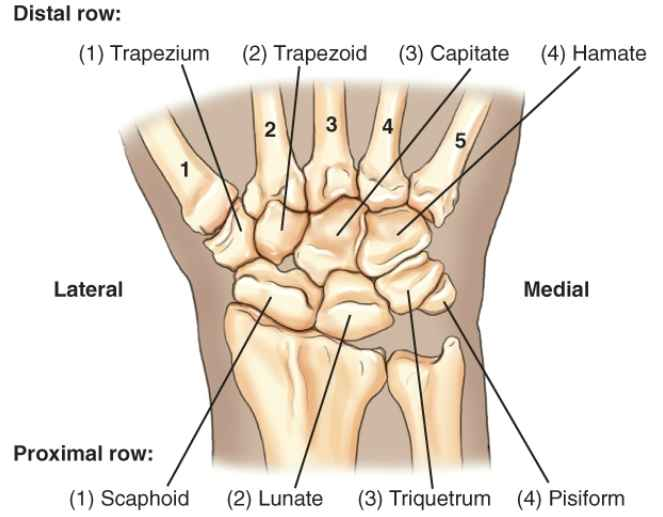
Carpals (Anatomy)
So Long To Pinkie Here Comes The Thumb
Proximal row: (1) Scaphoid, (2) Lunate, (3) Triquetrum, (4) Pisiform
Distal row: (4) Hamate, (3) Capitate, (2) Trapezoid, (1) Trapezium
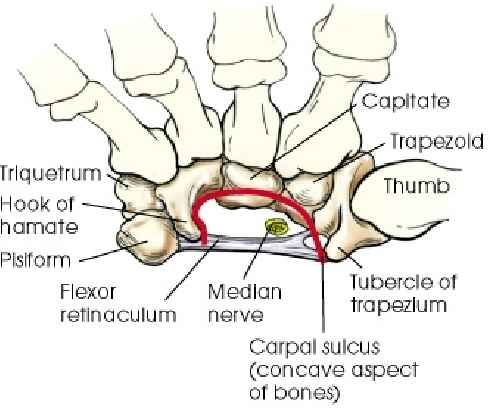
Carpal Sulcus (define)
Carpal Tunnel syndrome (define)
-area between flexor & red line
-compression of median nerve
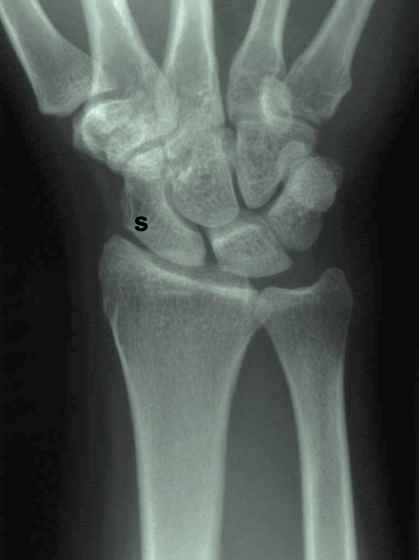
Scaphoid bone also known as...
(where else could it be found and interesting fact about scaphoids)
-Navicular
-also one on the foot
-Commonly Fractured
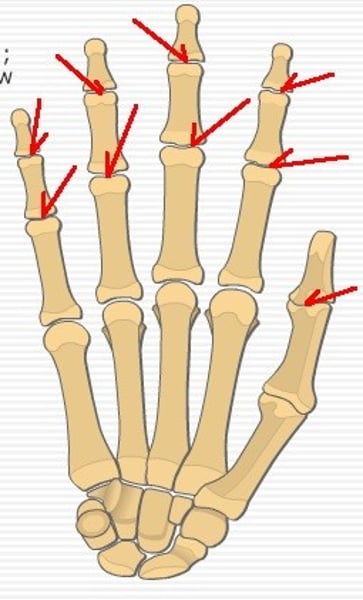
Interphalangeal joints
(Lt or Rt)
-Are the joint spaces in-between phalanges digits
-(also the 1st digit only has an interphalangeal jt. and a metacarpohalangeal jt.)
Proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP) Lt or Rt
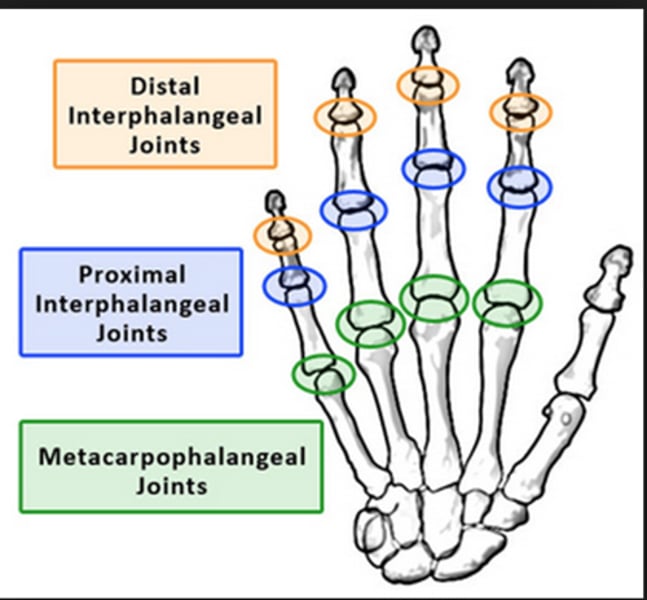
Distal Interphalangeal joint (DIP) Lt or Rt
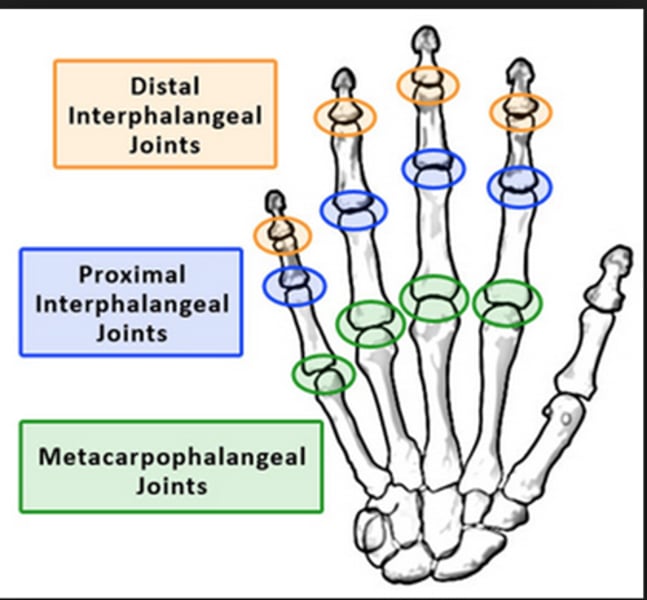
Metacarpophalangeal joint (MCP) Lt or Rt
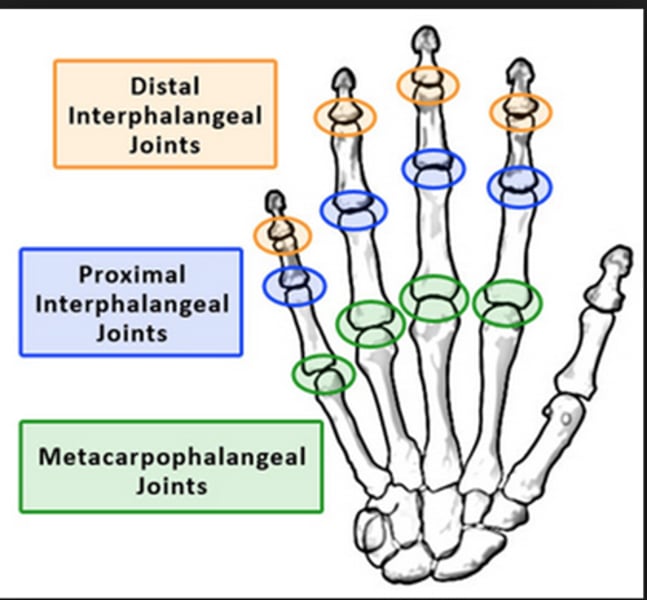
Carpometacarpal joint (CMC)
Lt or Rt
Connects the metacarpals to the distal carpals
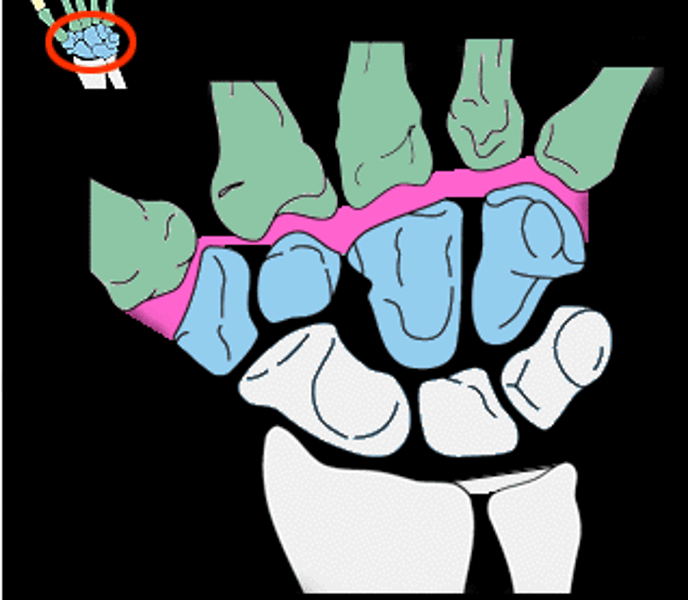
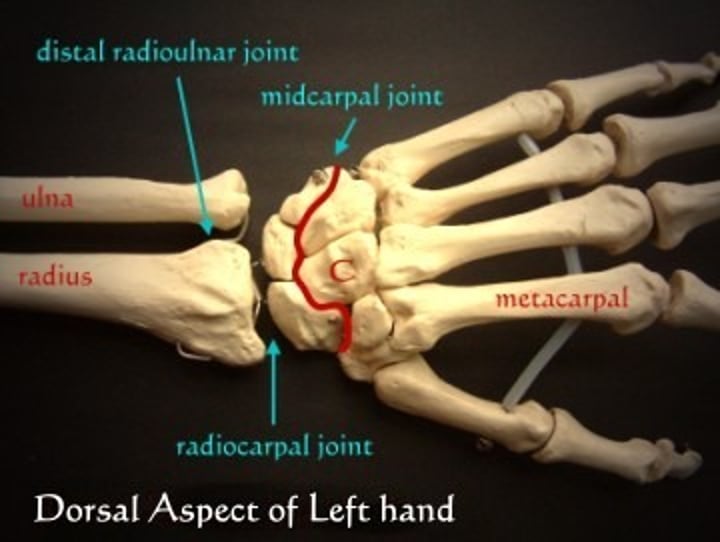
Radiocarpal joint
Lt or Rt
pertaining to the joint between the radius and wrist
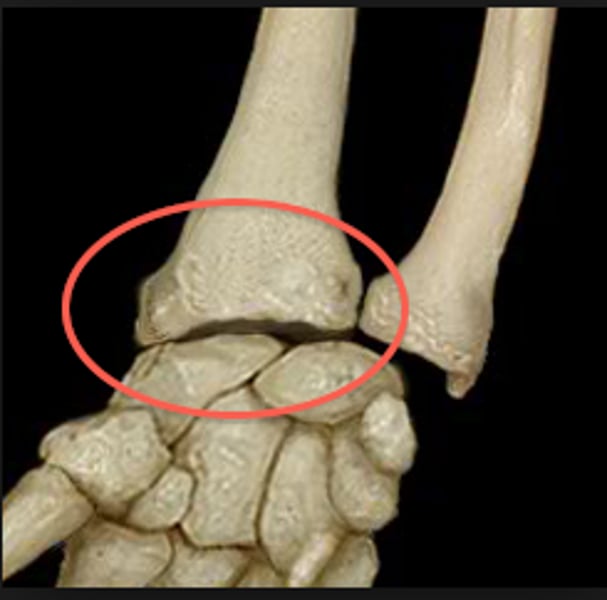
Distal radioulnar Joint
Lt or Rt
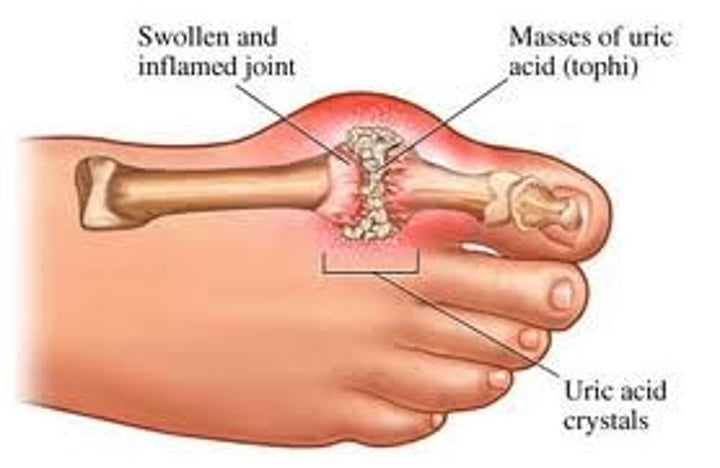
Gout (+)
hereditary form of arthritis in which uric acid is deposited in joints
(Hereditary arthritis)
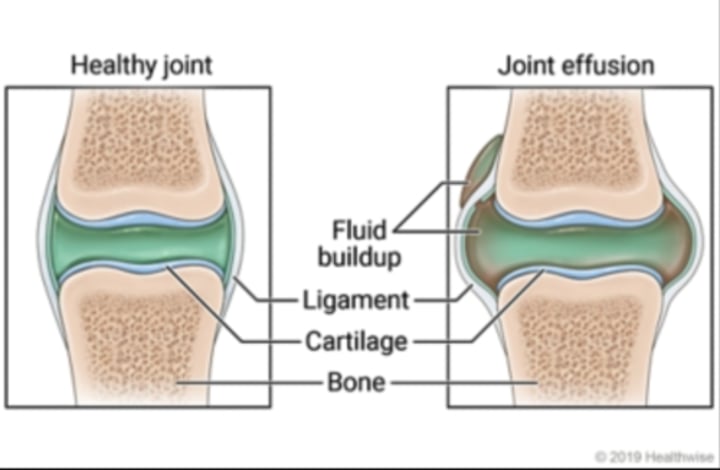
Joint Effusion (+)
Accumulation of fluid in joint associated with underlying condition
Osteoarthritis or Degenerative joint disease (DJD) (-)
-form of arthritis marked by progressive cartilage deterioration in synovial joints and vertebrae
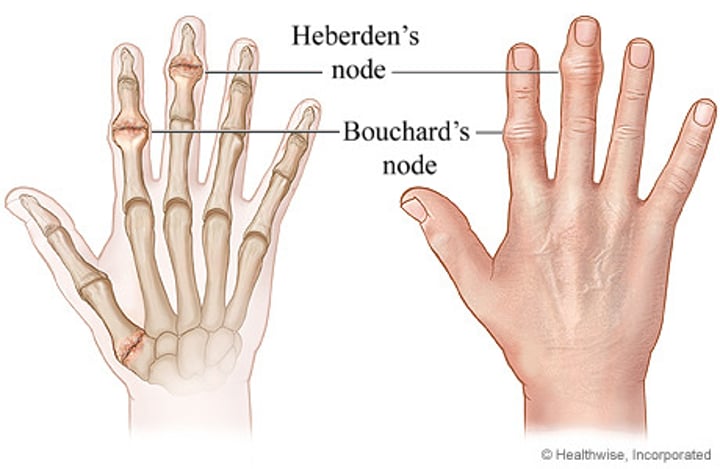
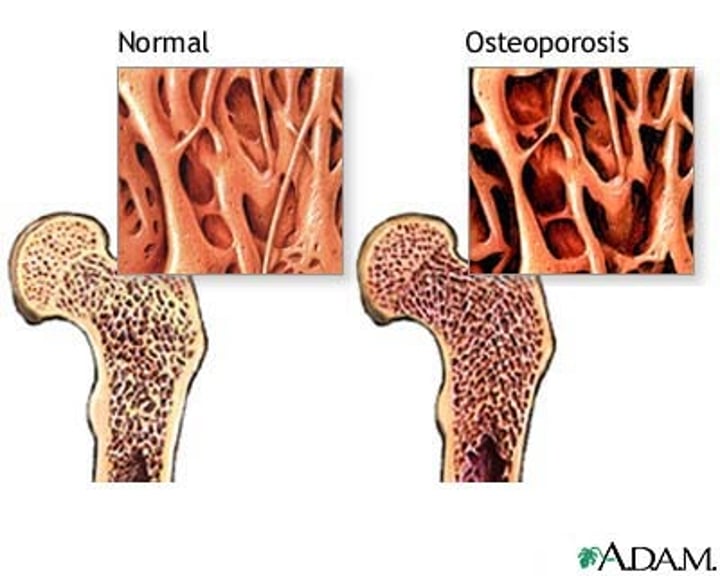
Osteoporosis (-)
loss of bone density
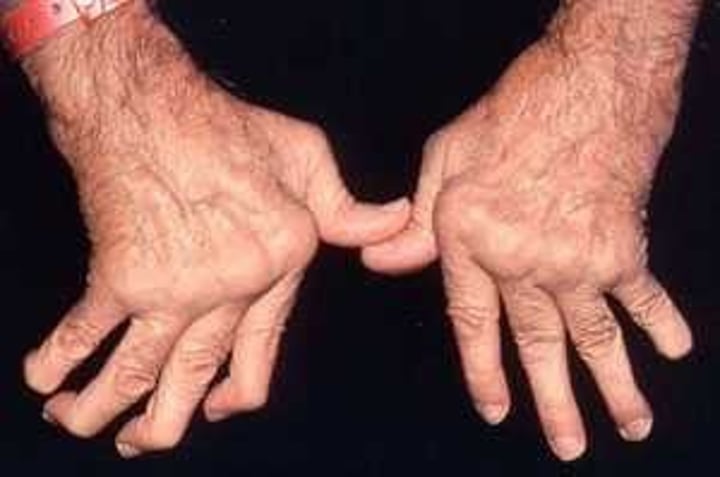
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (-)
chronic, systemic disease, inflammatory collagen disease
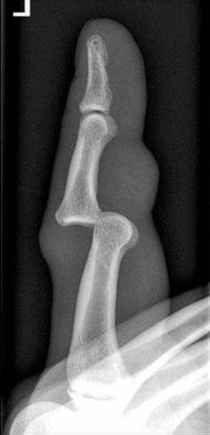
Dislocation
displacement of a bone from its joint
List Fx. Types
-Bennett's fx
-Boxer's fx.
-Colle's fx.
-Smith's fx
-Buckle or Torus fx.
Bennett's fx.
Fx at base of 1st metacarpal
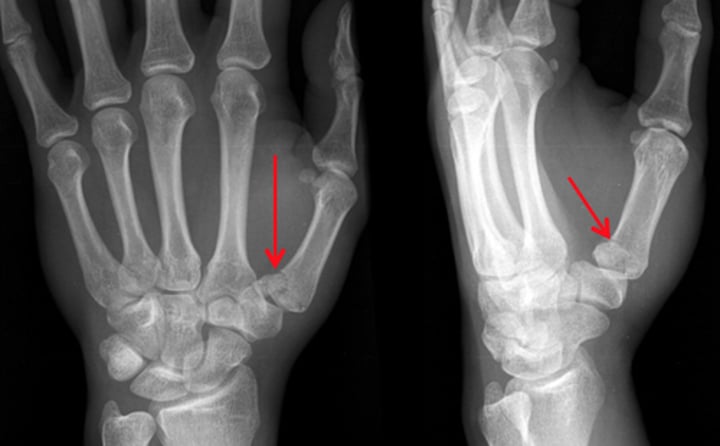
Boxer's fx.
fx of 5th metacarpal neck
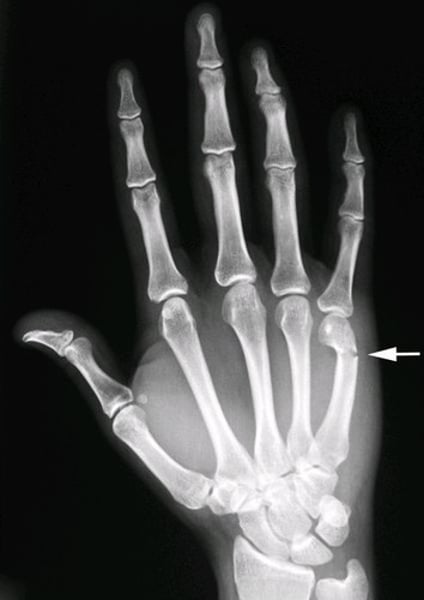
Colles fx.
fx of distal radius with posterior (dorsal) displacement
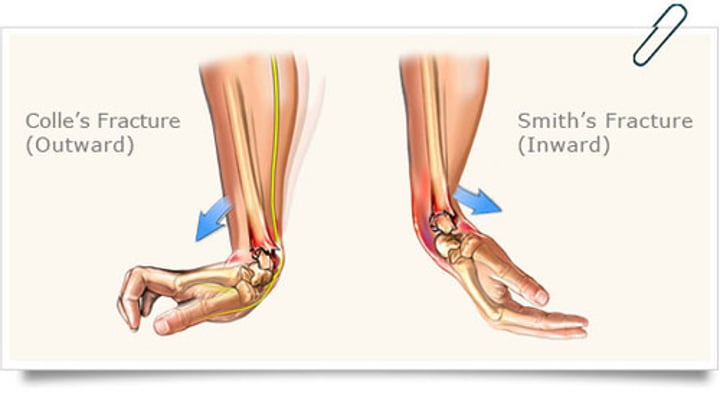
Smith fx.
fx of distal radius with anterior displacement (inward)
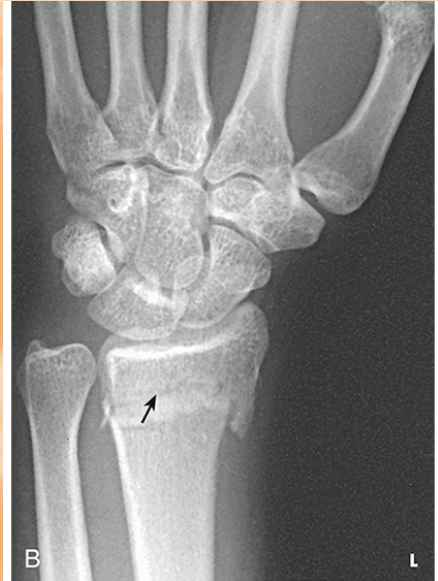
Buckle or Torus fx
impacted fracture with bulging of periosteum
(More often seen in peds.)
Routine Finger Projections/Positions (digits 2-5)
-PA: prone
-PA oblique: lateral rotation
-Mediolateral: Lateral (depends on the area of interest (closer to the IR))
-Lateromedial
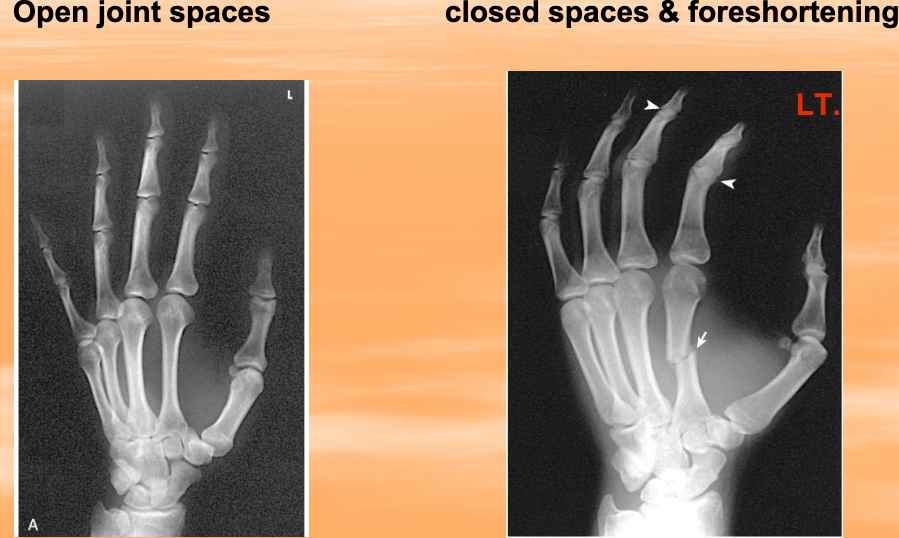
Why keep digits close to the IR?
1. Keeps joint spaces open
2. Prevent foreshortening
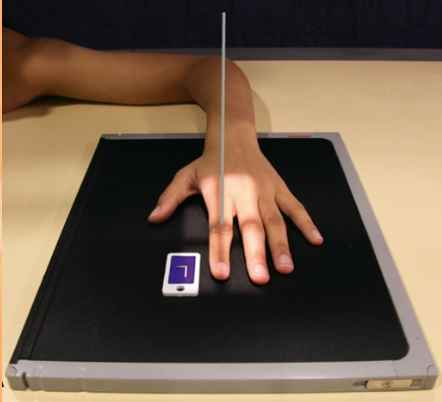
PA Projection (digits 2-5)
Position:
Focal spot:
SID:
pt.seated __, elbow flexed __
digit _____ _____
CR:
Position: prone
Focal spot: small
SID: 40 inches
pt.seated 90 degrees, elbow flexed 90 degrees
digit fully extended (separated)
CR: perp. to PIP of affected joint
ctr. PIP jt. to midpt. of space
No rotation is evaluated on a PA projection (digits 2-5) by:
Equal concavity on both sides of the phalangeal bodies
Equal amount of soft tissue on both sides of phalanges
If fingernails are seen, centered over the distal phalanx
Lateromedial or Mediolateral (2-5)
Position:
pt. seated __, elbow flexed __
digit ____ _____, make ____
CR:
ctr. PIP jt/to midpt. of space
Position: lateral (decrease OID)
pt. seated 90 degrees, elbow flexed 90 degrees
digit fully extended, make fist
CR: perp. to PIP in
ctr. PIP jt/ to midpt. of space

When taking a lateral position radiograph which digits are lateromedial and then mediolateral? (2-5 digits)
digits 2&3 = mediolateral
digits 4&5 = lateromedial
Evaluation Criteria for Lateral Projection of digits 2-5
-Rotation: concave on both sides of phalangeal bodies, fingernail in profile, equal distance of soft tissue
-Open joints (IP)
-No overlap: (superimpositions of other digits)
-Marker side Anteriorly
-Proper collimation
-Entire digit (fingertip to adjoining metacarpal)
-Boney trabecular detail and surrounding soft tissue (enough density)
-Open IP joint spaces
PA Oblique Projection (digits 2-5)
Position:
pt.seated __, elbow flexed __
digit ____ ____, laterally rotate __
CR:
Position: lateral rotation (from prone)
pt.seated 90 degrees, elbow flexed 90 degrees
digit fully extended, laterally rotate 45 degrees
CR: perp. to PIP in affected joint
ctr. PIP jt. to midpt. of space

Evaluation criteria of Oblique Projection of digits 2-5
-Proper Collimation, side marker placed clear of anatomy of interest
-Entire digit (fingertip-adjoining metacarpal)
-Digit rotated 45 degrees demonstrated by concavity of the elevated side of phalangeal bodies
-No superimposition of proximal phalanx and MCP joints by adj. digits
-Open IP/MCP jt. spaces
-Bony trabecular detail and surrounding soft tissues
Routine thumb projections
AP-supine
PA oblique -oblique
Mediolateral - lateral
AP Projection (1st digit)
Position:
pt.seated __ , extend elbow & rotate limb in ____ _____ _____
digit ______
CR:
Rotation seen by:
Position: supine
pt.seated 90 degrees, extend elbow and rotation limb in extreme internal rotation
digit extended
CR: perp to MCP
Ctr. MCP jt. to midpt. of space
Rotation seen by asymmetric concavity

PA Oblique Projection (1st digit)
Position:
pt.seated __, elbow flexed __
place hand ____, 1st digit __
digit ____
CR:
Position: oblique
pt.seated 90 degrees, elbow flexed 90 degrees
place hand prone, 1st digit 45 degrees
digit extended (separated)
CR: perp. to MCP
Ctr. MCP jt. to midpt. of space
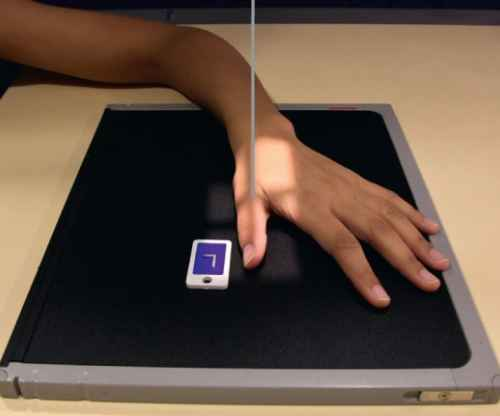

Thumb PA oblique evaluation criteria
-Evidence of proper collimation and side markers laterally
-distal tip to trapezium
-proper rotation: concave surface demonstrated by concave surface of elevated side of the proximal phalanx and metacarpal
-Bony trabecular detail and surrounding tissue
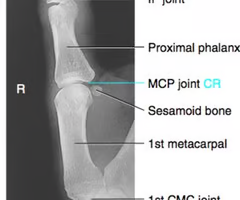
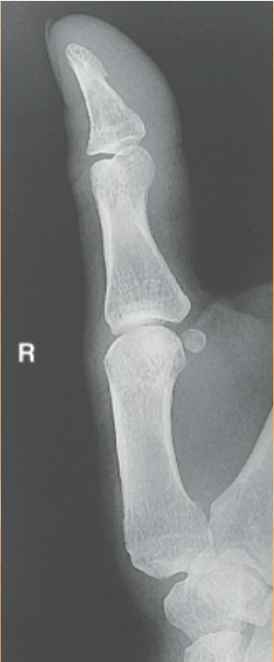
What does this hand have?
dislocation of thumb
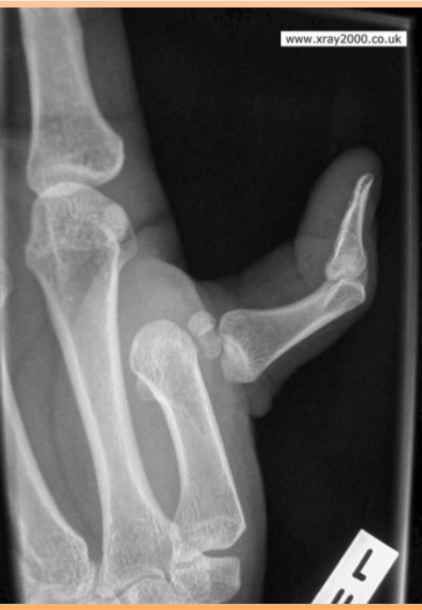
Evaluate this PA thumb
-open joint space
-no foreshortening (digit is parallel to the IR)
-no rotation: concavity and equal amount of soft tissue
Evaluation Criteria for AP and PA Thumb
-Proper collimation, side marker out of anatomy of interest
-Distal tip of side thumb to trapezium
-No rotation: symmetric concavity of phalangeal and metacarpal bodies, equal amount of soft tissue on both sides of phalanges, thumbnail if visualized in center of distal thumb
-overlap of soft tissue profile palm over the midshaft of the first metacarpal
-Open IP and MCP joints without overlap of bones
-Boney trabecular detail
-PA thumb projection will be magnified compared with AP projection
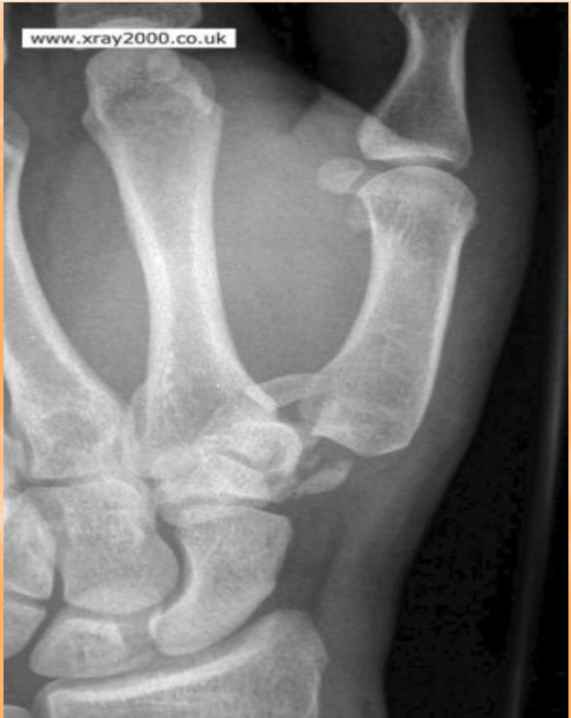
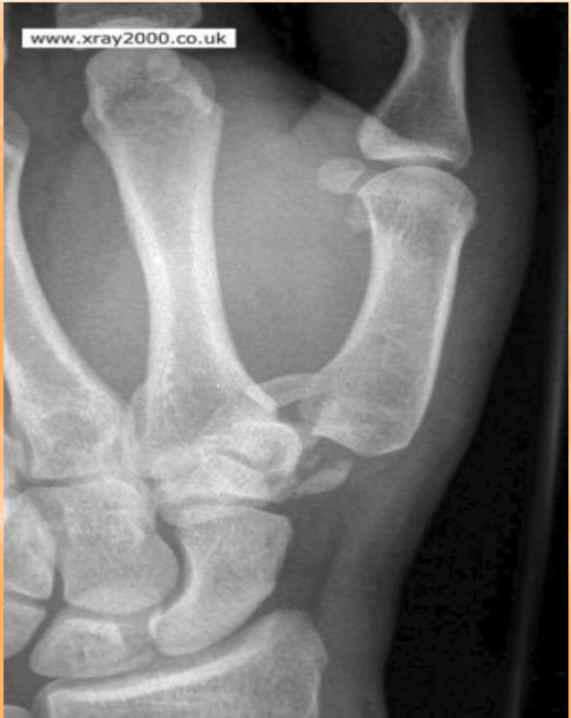
What fracture is this?
“Fun Film” trapezium fracture
Mediolateral Projection (1st digit)
Position:
pt. seated __, elbow flexed __
digit fully _______
Ctr. ____ jt. to midpt. of space
CR:
Position: lateral
pt. seated 90, elbow flexed 90
digit fully extended
Ctr. MCP jt. to midpt. of space
CR: perp. to MCP
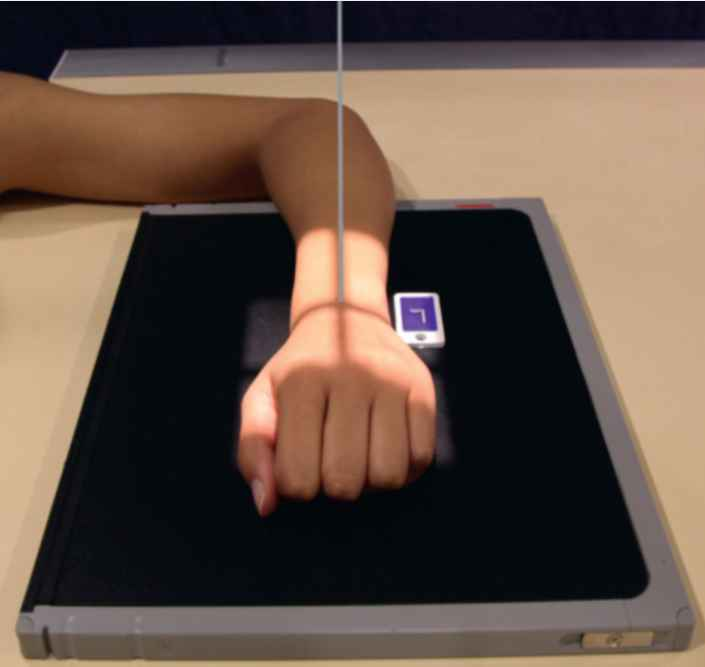
What does it mean when you see certain bones (carpals, radius/ulna) stacked on one another? (you can see the lines)
-able to see through structures
it is penetrated correctly
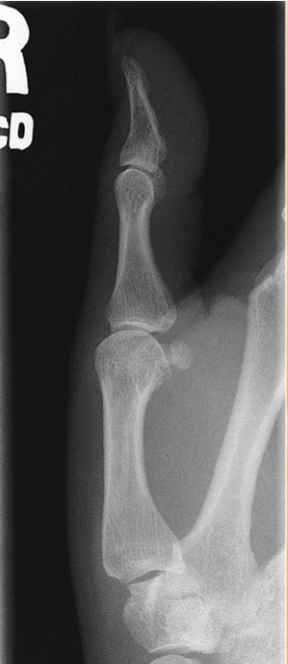
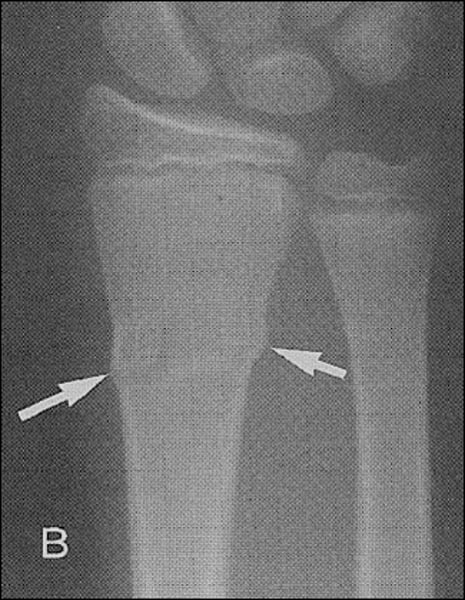
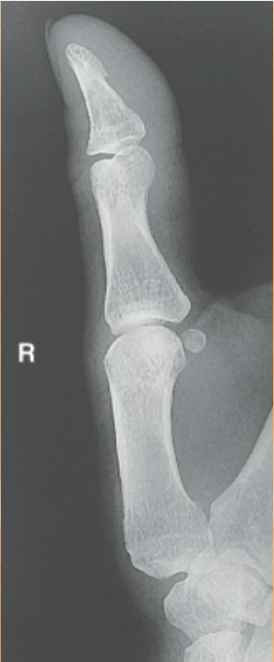
Describe where the fracture is
-shaft of Middle phalanx 2nd digit of left hand
Routine Hand Projections & positions
PA - prone
PA oblique - lateral rotation
Lateromedial - fanned lateral
Optional image - lateral in extension
PA projection (hand)
Position:
pt. seated __, elbow flexed __
digit fully _______
Ctr. ____ jt. to midpt. of space
CR:
Position prone
pt. seated 90, elbow flexed 90
digits fully extended
Ctr. 3rd MCP jt. to midpt. of space
CR: perp to 3rd MCP
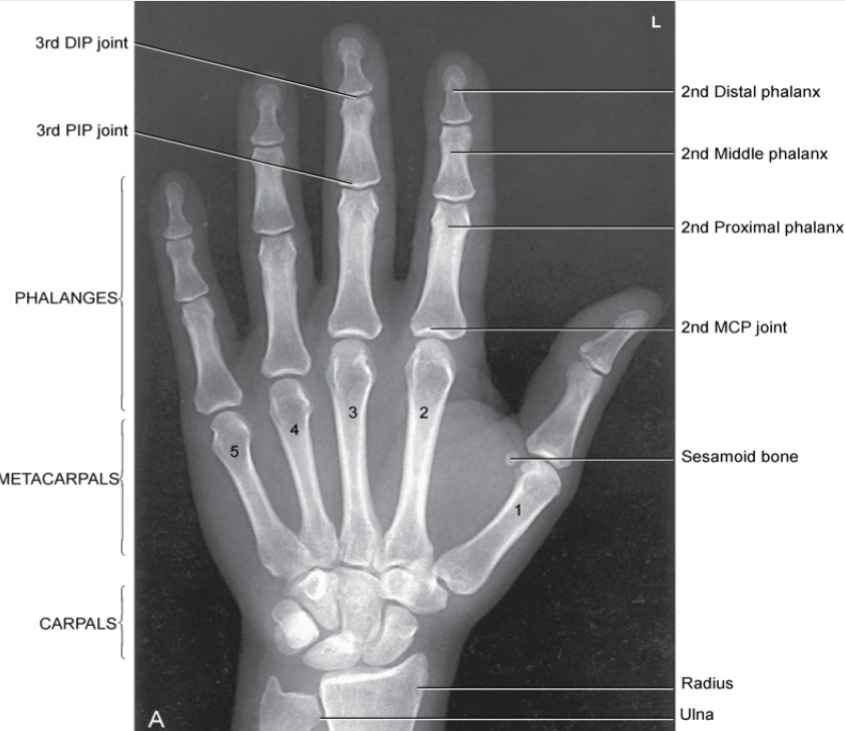
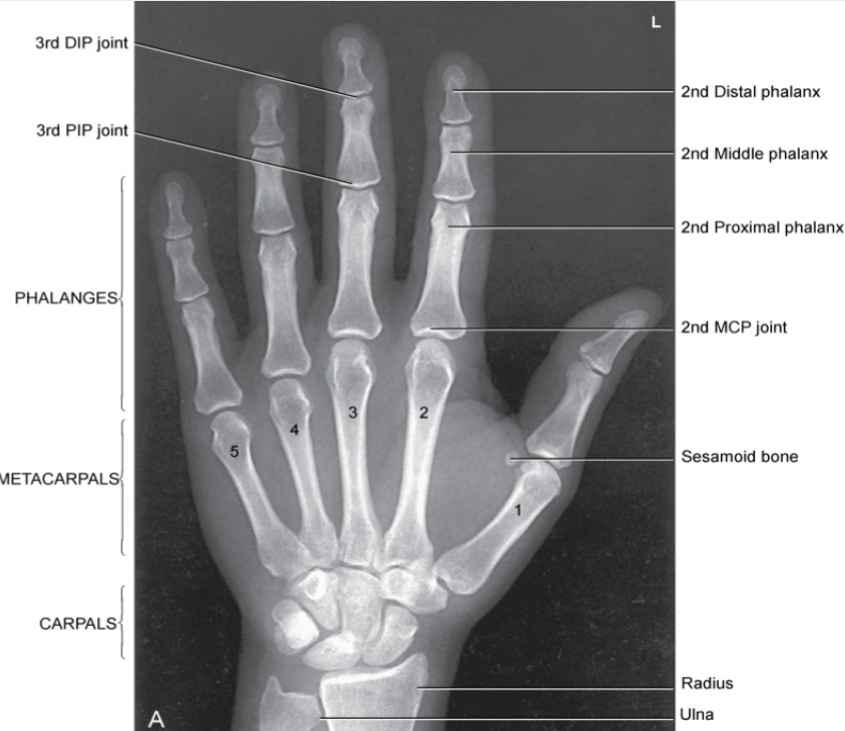
PA Projection of Hand Evaluation
-Proper collimation
-side markers laterally
-fingertips to distal ulna/radius
-No rotation: equal concavity of the metacarpal and phalangeal bodies on both sides
-fingernails middle
-equal distance between metacarpal heads
-open MCP and IP
-Trabecular detail and soft tissue
If the patient can’t put their palm flat on the IR, you can do a __ projection.
AP
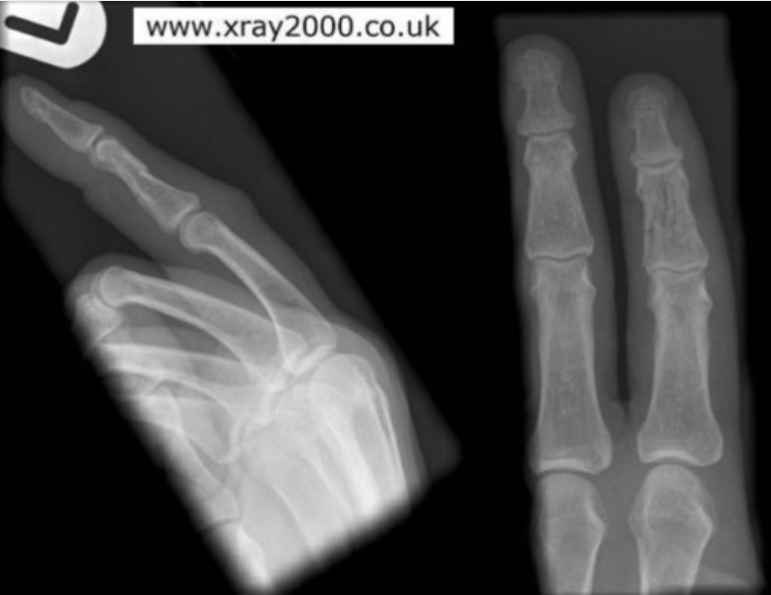
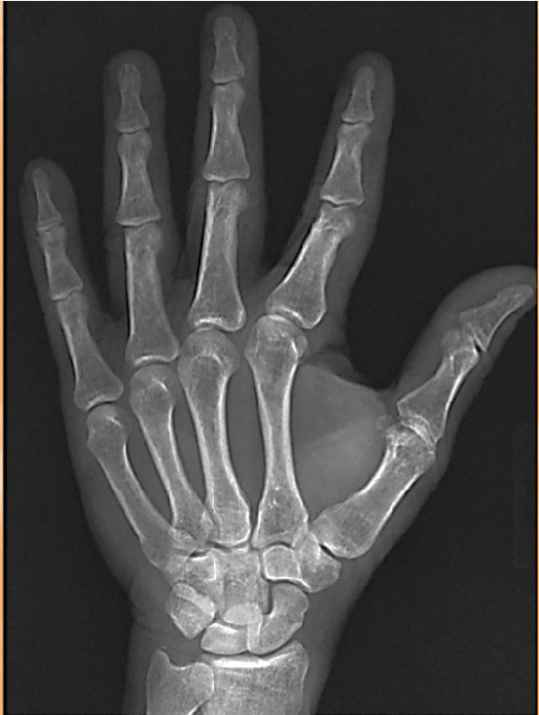
Why is this PA hand poorly positioned? Where is the fracture?
-hand was not flat
-the marker should be placed on the side of the thumb
fracture: on the head of the metacarpal of the 4th digit right hand
Is this PA- positioned correctly? If not, why not? and how do you fix it?
-not equidistant
-concavity, not symmetrical
Fix: retake image, open collimation, add a marker
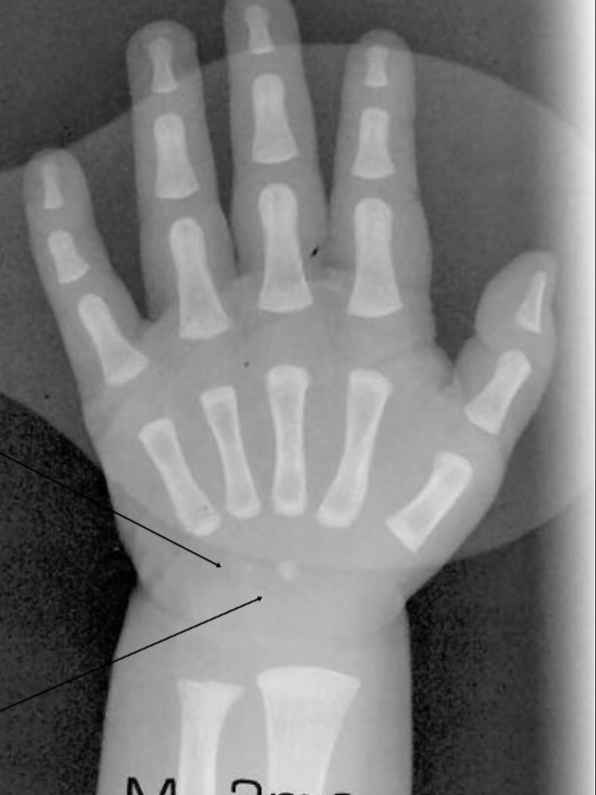
What carpal bones is the baby starting to develop?
hamate
capitate
PA oblique projection (hand)
Position:
pt. seated __, elbow flexed __
from prone, rotate laterally __
digit fully _______
Ctr. ____ jt. to midpt. of space
CR:
Position: lateral oblique
pt. seated 90, elbow flexed 90
from prone, rotate laterally 45
digit extended
Ctr. 3rd MCP jt. to midpt. of space
CR: perp. to 3rd MCP
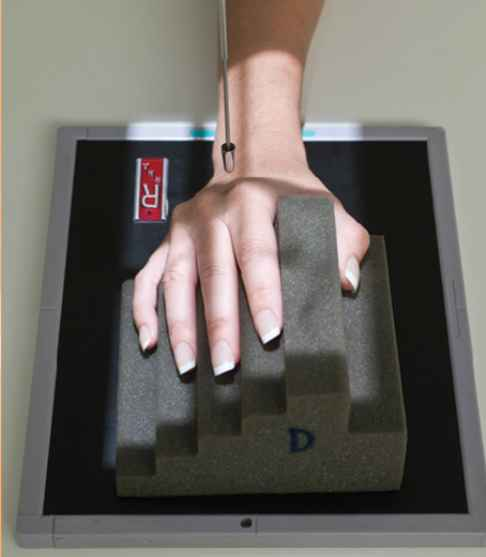

Evaluation Criteria for PA oblique hand
-proper collimation
-side marker
-fingertips to distal radius and ulna
-digits separated slightly with no overlap
-45 degree rotation
-decreasing amounts of separation between metacarpal bodies 2-5 with the second and third having greatest separation
-partial superimposition of 3-5 metacarpal bases and head
-open MCP jt.
-IP jt., when digits are positioned parallel to IR
-Bony trabecular detail and surrounding soft tissues
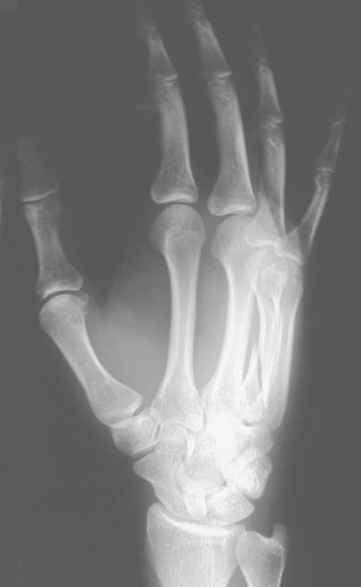
More superimposition =
more rotation (fix it by decreasing lateral rotation)
What is wrong with this image?
-over rotated
-digits not parallel
Lateromedial projection (hand)
Position:
pt. seated __, elbow flexed __
digit fully _______
Ctr. ____ jt. to midpt. of space
CR:
Position: “fan” lateral
pt. seated 90, elbow flexed 90
digit fully extended & separated
Ctr. 2nd MCP jt. to midpt. of space
CR: perp. to 2nd MCP jt.
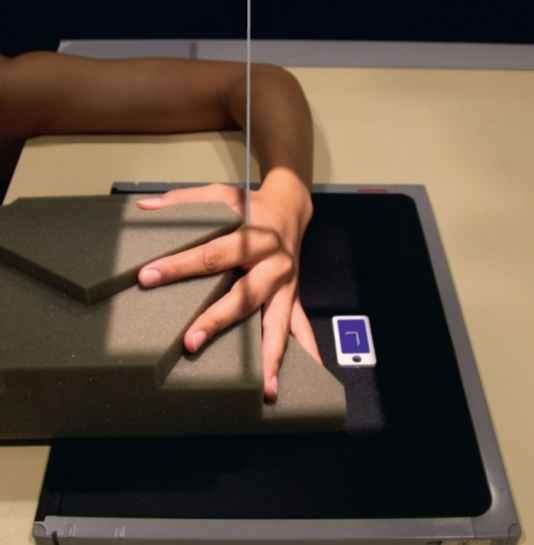

When do you use lateral extended on hand?
-to see foreign body entrance and exit (localizing)
-and metacarpal fx.
How would you fix this image?
-separate the fingers more
-don’t have 1st & 2nd digits touching
Lateromedial Projection (hand)
Position:
pt. seated __, elbow flexed __
digit fully _______
Ctr. ____ jt. to midpt. of space
CR:
Position: lateral in extension
pt. seated 90, elbow flexed 90
digit fully extended
Ctr. 2nd MCP jt. to midpt. of space
CR: perp. to 2nd MCP j.
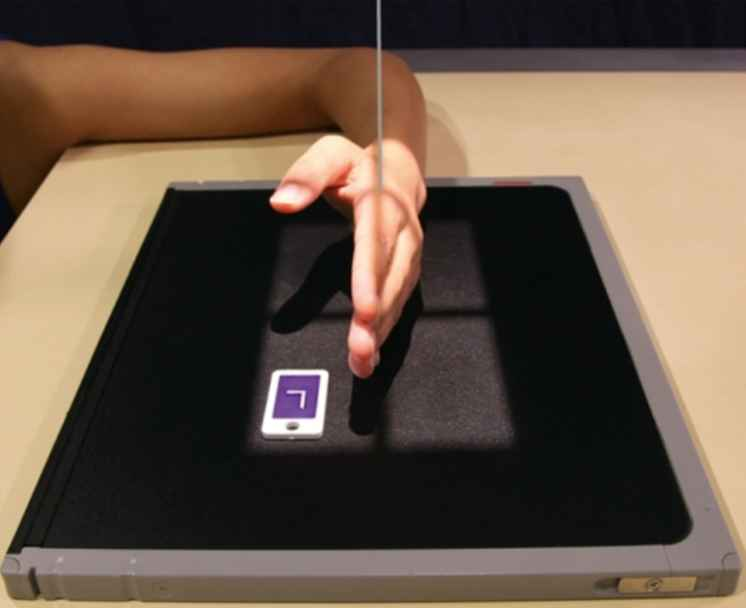

Evaluation criteria of Lateromedial Projection of hand
-Proper collimation
-side markers anteriorly
-fingertips too distal ends of the radius and ulna
-Extended digits
-Hand truly lateral: -superimposed phalanges, metacarpals, and radius and ulna
-thumb free of motion and superimposition
-bony trabecular detail and surrounding soft tissue
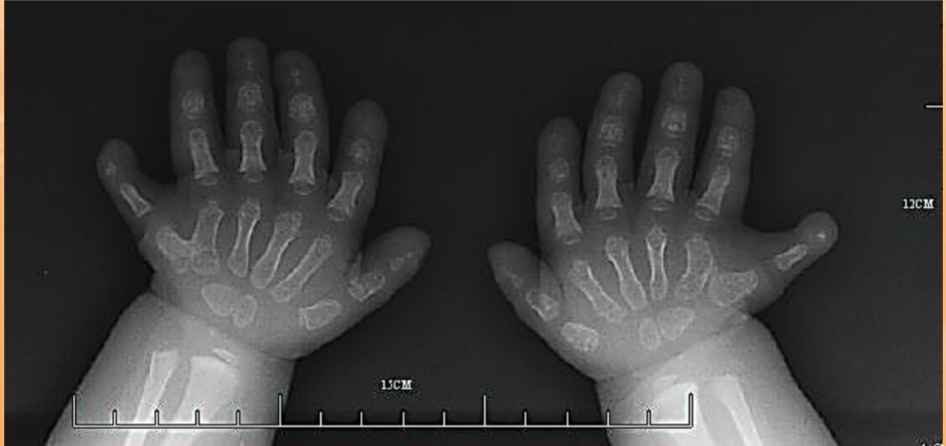
Congenital anomaly =
polydactylism
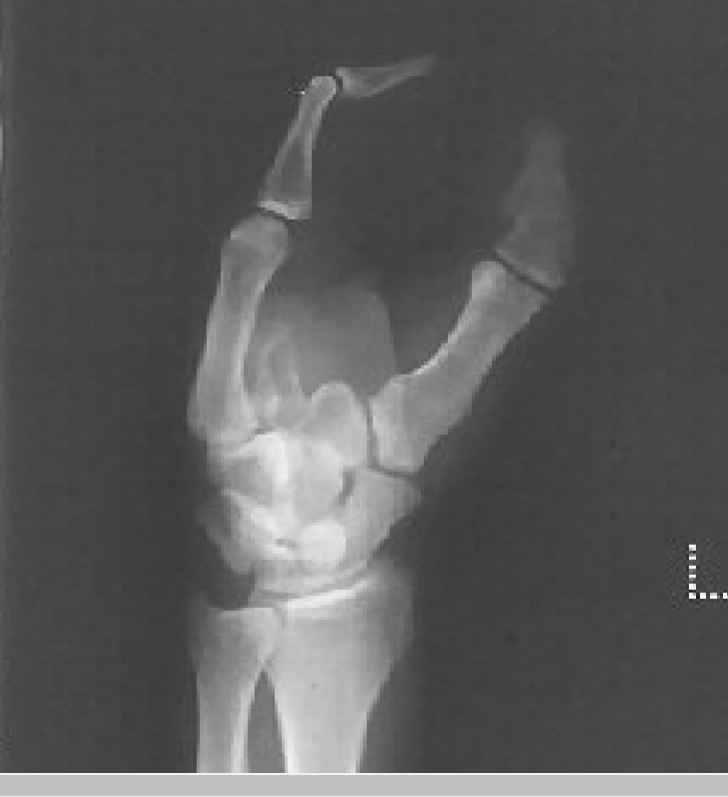
What syndrome is in this image?
“lobster claw” syndrome
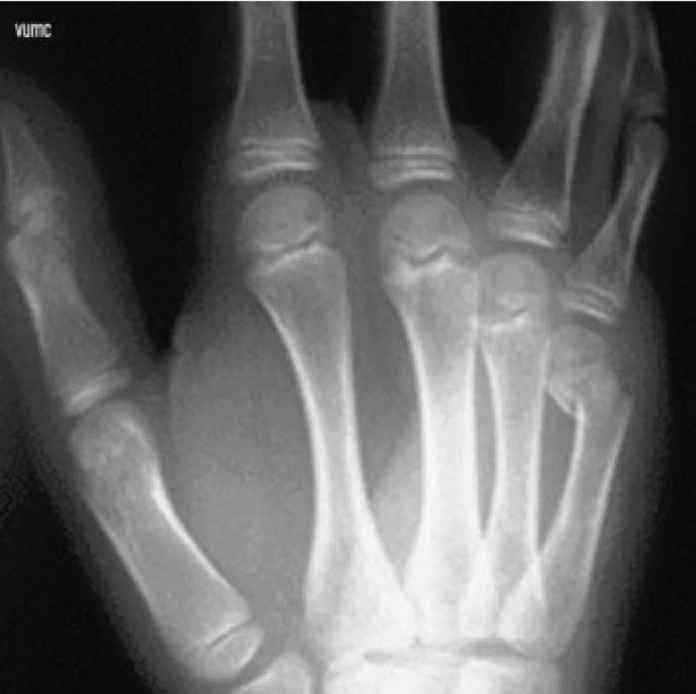
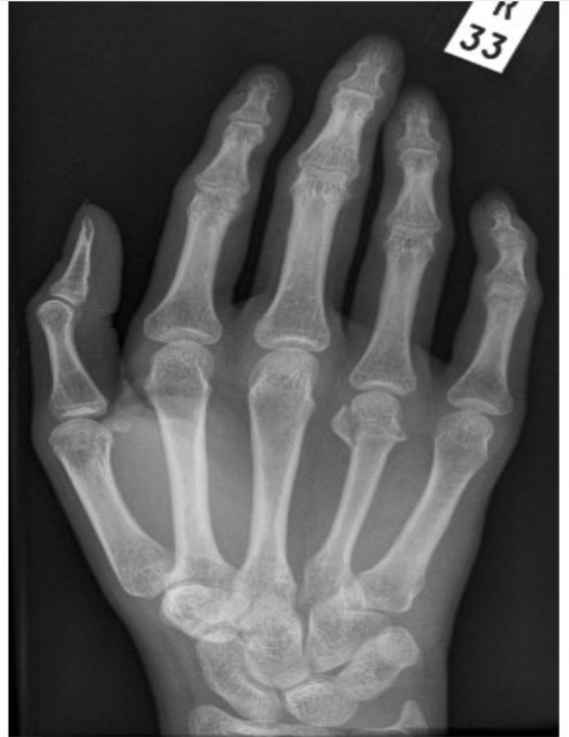
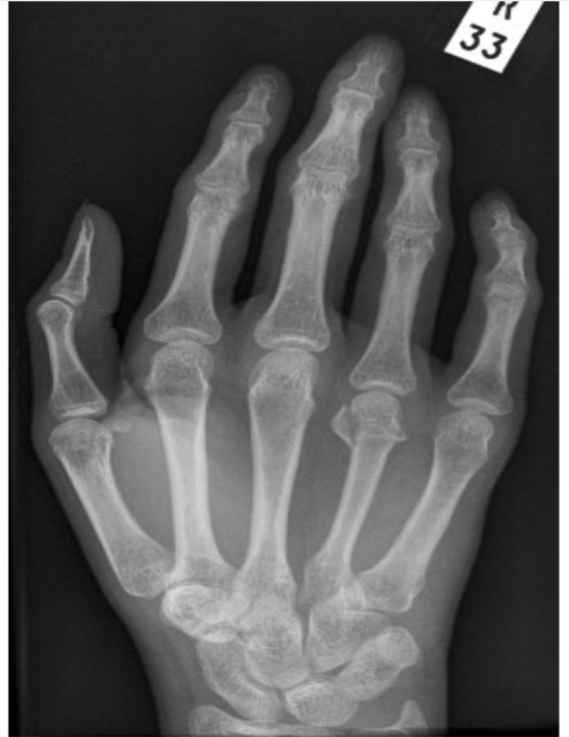
What fracture does this hand have? Is the patient young or old and how do you know?
Boxer’s fracture
-young because you can see the growth plates
Routine Wrist radiography
PA- prone
PA oblique - lateral rotation
Lateromedial -lateral
AP oblique - medial rotation
Optional Wrist Images (list 3)
prone in ulnar deviation
Stecher method
Gaynor Hart Method
PA projection (wrist)
Position:
pt. seated __, elbow flexed __
sight fist (carpals _____)
Ctr. to midpt. of space
CR:
Position: prone
pt. seated 90, elbow flexed 90
slight fist (carpals closer)
Ctr. wrist to midpt. of space
CR: perp. to midcarpal