PSYC 304 midterm 1 BRAIN BASICS
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Describe how we have used, and continue to use, metaphors to descibe brain function. In what ways are these beneficial? In what ways are they limiting?
Galen: - humours, fluids govern diff aspects of our cognition and behaviour, animal spirits
L: reduces complex mental processes to the interaction of just four bodily fluids
Vesalius and Descartes: - hydraulics, body is a machine with fluids and pipes, driven by hydraulic pressure, soul tickles brain, soul->brain->mechanisms
L:
Galvani and du Bois-Reymond:
- brain as a battery, nerve signals are electrical impulses
L: don't look at the biochemical processes in the brain as well
- localization of function
- L: phrenology: shape of someone's head determines their characteristics which is a false theory
Schwann:
- cell theory: life is composed of cells, so study brain cells instead of as a whole
NOW: brain as a computer, or network of computers
Name two theories of neuron function. which one was shown to be predominantly correct?
Golgi vs Ramon y Cajal
Golgi: - brain is a mesh with all cells connected
Ryc: - cells have input and output, sense of directionality, not continuous bc they have a gap for chemical transmission
have a foundational understanding of basic brain facts. what aspect of human brain is most clearly, mechanistically related to our intelligence?
- size of brain does not equal to intelligence
- cells are not replaces
- neurons, glia, stem cells, blood vessels
- convoluted
- # of glia > # of neurons
intelligence = brain cell density = # of brain cells, sophistication of cellular connections
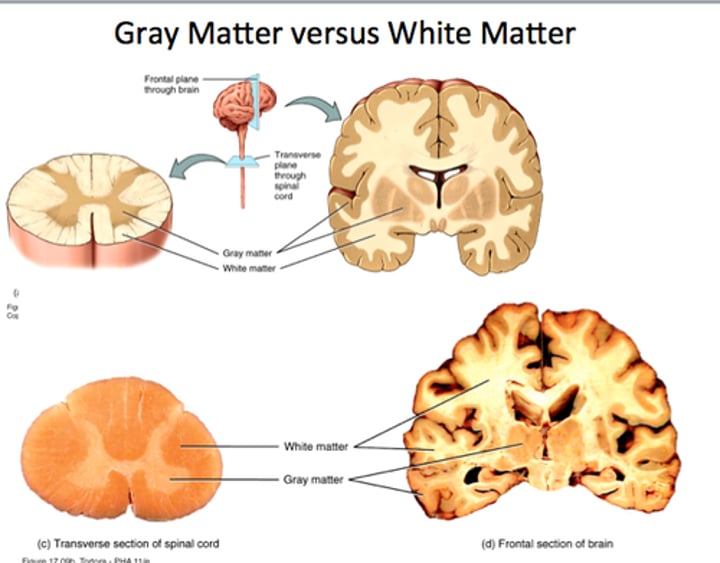
white vs gray matter
white matter : long-range myelinated axons, connections between neurons
grey matter: numerous cell bodies, unmyelinated axons
name and describe two general types of cells and describe some functional roles for each
neurons - communicate through axons, which generate action potential, which makes speed of communication very fast
glia - glue and support the system
name four types of glial cells and describe some functional roles for each
astrocytes:
- blood brain barrier - mediate nutritions into brain
- wrapped around synapse - maintain chemical environment
schwann cells:
- myelinate a single axon in PNS
oligodendrocyte:
- mylelinates several axons in CNS
microglia:
- covered in receptors
- swallows up bacteria in brain
explain what is meant by a tripartite synapse
conversation of 3 in the synapse:
- axon: releases neurotransmitters
- dendrite: has receptors
- astrocyte: has receptors and can release glia transmitters
Draw, label, and define the major features of a neuron AND TYPES
- single direction: dendrite => soma => axon => axon terminal
- input and output layer
- used for communication
types:
pyramidal - pyramid shaped and found in cortex
stellate - star-shaped and found under the cortex
purkinje - connected to thousands of neurons at once, found in the cerebellum
types 2:
projection neurons - long myelinated axons that go from one region in the brain to another, wire metaphor
interneurons: localized, unmyelinated, synchronize activity across many different neurons
describe the central dogma of molecular biology
DNA->mRNA>->protein
- protein is the basis of neuronal function
- transcription occurs when both activators are present and repressor is present
- expression of genes is determined by how tightly the histone is wrapped
name and describe the key function of some key cellular structures
RIBOSOMES:
- translate mrna to protein
- free ribosome = intracellular or free protein
ROUGH ER:
- protein is weaved into membrane
GOLGI APPARATUS:
- protein is packaged and sent to wherever needed
MITOCHONDRIA:
- oxygen + glucose = ATP
- makes energy for the cell
CELL MEMBRANE:
- phospholipid bilayer to keep things inside and outside cell
- you need membrane proteins to get across
cytoskeleton, axon, synapse and dendrites
cytoskeleton = internal structure of neuron, can grow or shrink
- main motive is to transport molecules
- kynesin and dyenin use atp to carry
synapse = site of neuronal communication = closer synapse is to an axon = stronger AP
- axosynaptic = axon ends on synapse and can modify the signal
dendrites = synapses are malleable = more malleability
identify three types of staining and the use for each
silver nitrate stain: tained only a subcomponent of cells, good for looking at structure of neuron
nissl stain - pigmented and binds to gray matter, looks at whole
fiber stain - white matter, staining insulating glia cells