enzymes
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:06 PM on 10/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1
New cards
catalyst
substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being changed in the process
2
New cards
enzyme
a biological catalyst, usually a protein
3
New cards
enzymology
the study of enzymes
4
New cards
substrate
substance acted upon by the enzyme
5
New cards
active site
region on the enzyme where the substrate binds and the chemical reaction occurs
6
New cards
allosteric site
site where a substance binds that alters the behavior of the enzyme
7
New cards
coenzyme
molecule that is independently synthesized and incorporated into the protein structure of the enzyme; provides opportunity for chemical reaction that may not be possible with the protein structure alone; commonly referred to as a cofactor when it contains a metal
8
New cards
inhibitor
substance that blocks activity of the enzyme
9
New cards
activator
a substance that enhances activity of the enzyme
10
New cards
higher
enzymes provide _______ reaction rates
11
New cards
conditions
enzymes cause milder reaction ___________
12
New cards
specificity
enzymes provide greater ___________
13
New cards
regulation
enzymes create a greater capacity for ________
14
New cards
transferases
catalyze transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
15
New cards
hydrolases
catalyze bond cleavage by the introduction of water
16
New cards
isomerases
catalyze reactions involving intramolecular rearrangements
17
New cards
different path
the first law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed; enzymes allow a reaction to take a _________
18
New cards
favorably
the second law of thermodynamics states that reactions trend toward greater entropy; enzyme structure orients reactants __________ using one or more active sites
19
New cards
transition state theory
A+B 🡪 Xǂ 🡪 P + Q
20
New cards
transition state
short-lived, high-energy state which represents both the reactants and the products; Exists at the top of the curve representing the free energy barrier or activation energy.
21
New cards
barrier of activation
barrier which must be overcome in order for a reaction to go to completion, also termed the energy of activation
22
New cards
Arrhenius equation
reaction is path independent; energy of activation involves contributions from both entropy and enthalpy
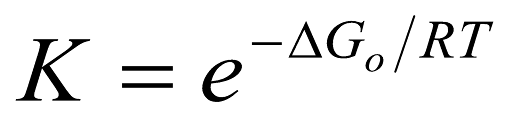
23
New cards
catalysts
all __________ function by decreasing the energy of activation required for the reaction
24
New cards
decreasing
all catalysts function by _________ the energy of activation
25
New cards
effective concentration
proximity and orientation effects increase the ______________, reducing the amount of entropy decrease required (lowers activation nrg)
26
New cards
active site specificity, substrate channels
proximity and orientation effects are accomplished by ________________ and _____________
27
New cards
active site specificity
enzyme selectively binds the substrate; functional groups are oriented such that only the substrate binds favorably
28
New cards
substrate channel
protein shape orients and directs the substrate to the active site region
29
New cards
acid-base catalysis
proton donors and acceptors in an active site catalyze the reaction
30
New cards
pH
acid-base catalysis reactions alter in activity as _______ changes
31
New cards
first order
reaction whose rate depends on the first power of the reactant concentration
32
New cards
k[A]
rate =
33
New cards
half life
the time required for something to fall to half its initial value
34
New cards
-k1 t
[A] / [A0] = e^______