amniotes
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
what makes amniotes different
amniotic egg
dont need water to reproduce
coverings on skin
amniotic egg
4 extraembryonic membranes, outer shell develops in moms uterus, eggs muct be layed on land
4 extraembryonic membranes,
yolk sac: provided nutrients
amnion fluid filled sac: cushions embryo
allantois: connects the end of gut tube, stores waste
chorion: aids in gas exchange
synapomorphies
keratinized skin
ankle bone (astrogaus)
more than 2 sacral bones
costal breathing
elongation of neck/trachea
keratinzied skin
thick, waterproof, non permeable
scales, hair, feathers formed by keratin and homologous to fish scales
costal breathing
intercostals opens ribs for inhalation, increases chest cavity
synapsids
extant mammals, mammal like reptiles
suaropsids
Lizards/snakes, turtles, crocs birds
distinction between synapsids and sauropsids
#of fenestration
anapsid: 0
synapsid: ONE on each side
diapsid: TWO on each side (living reptiles and sauropsids)
*turtles derived no fenestration
Locomotion
synapsid: quadrupedal, one lung can inflate at a time, legs under body, flex back up and down
suaropsid: bipedal, axial muscles not needed for locomotion,
lungs
amphibian: simple sac w/ septa to increase SA
synapsid: trachae→ primary bronchus, secondary bronchii, tertiarry bronchi, bronchioles→ aveoli (old and new air mixes)
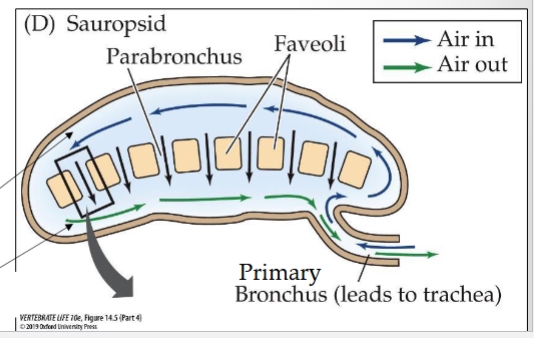
sauropsid: faveolar lung, faveoli in lung (cups/pockets), primary bronchi→ faveoli
parabronchial lung (crocs)
primary bronchus → dorsal secondary bronchus→ parabronchi → past faveoli
gas exchange in faveoli → into ventral seconday bronchus
hearts
evolved septum between ventricles, reduces mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
low blood pressure: to lungs to protect delicate lung tissue
high blood pressure: in systematic to get everywhere in the body
***** heart design in synapsids and suaropsids started different then derrived to be similar = analogous
skin
both have alpha keratin in epidermis
synapsids: smooth skin w/ hair from alpha keratin
suaropsids: beta keratin adding rigid , forms hard surface → birds beaks, claws, feathers
excretory system
fish ammonia in urine
synapsids: convert ammonia into urea, less toxic, conserves water, reabsorption happens in nephrons, urinary bladder only stores urine
suaropsids: converts citric acid, least toxic, conserves the most water but the most energetically costly, urinary bladder reabsorbs water
vision
rods: rod shaped, peripheral, night vision, sense movement
cones: cone shaped, see color
synapsids: generally poor vision, mostly rods, 2 types( green blue)
primates have 3 cones ( red, green, blue)
sauropsids: good color vison, primarily cones, 4 types( red,green,blue, UV) ( 4 cones ancestral trait)