Higher Physics - Light and Special Relativity
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What is the absolute refractive index?
The ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the medium.
What happens to the frequency of light when it enters a medium?
The frequency does not change.
How does the refractive index of a medium change with frequency?
The refractive index increases as the frequency of light increases.
What is the critical angle?
The angle of incidence that produces an angle of refraction of 90 degrees.
When does total internal reflection take place?
TIR occurs if the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle.
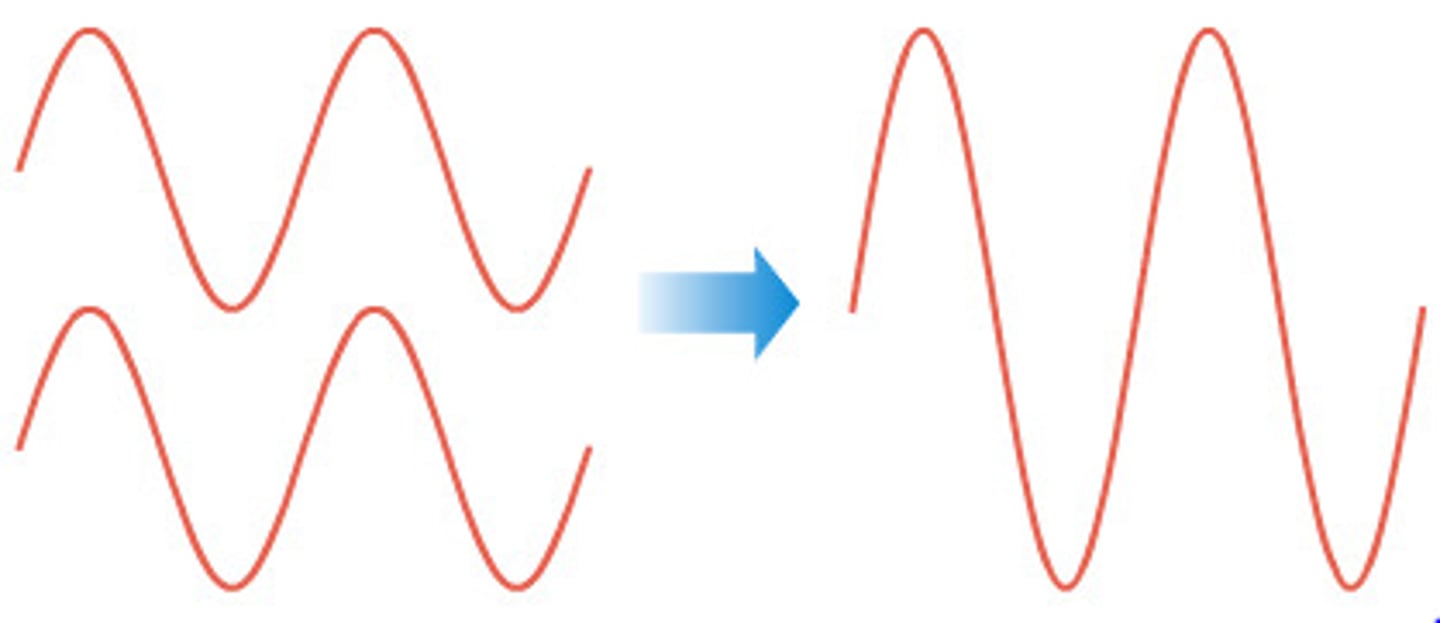
What is constructive interference?
Constructive interference occurs when two waves meet in phase.
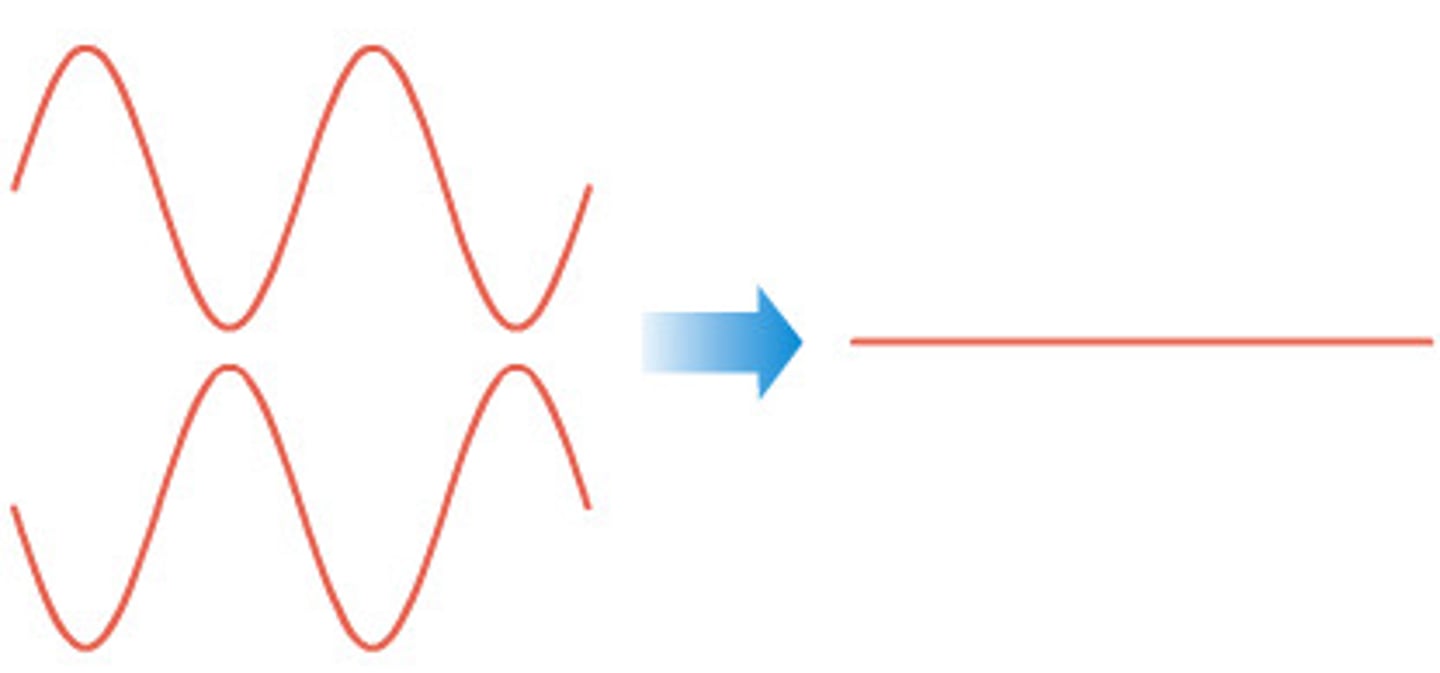
What is destructive interference?
Destructive interference occurs when two waves meet exactly out of phase.
What produces maxima in wave interference?
Maxima are produced when the path difference between waves is a whole number of wavelengths and the waves meet in phase.
What produces minima in wave interference?
Minima are produced when the path difference is equal to an odd number of half wavelengths and the waves meet out of phase.
What is the relationship between irradiance and distance from a point source?
Irradiance is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from a point source.
What is the Bohr model of the atom?
The Bohr model describes the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons occupying fixed, quantized energy levels.
What is the ground state of an electron?
The ground state is the lowest energy level of an electron in an atom.
What does ionization refer to in atomic physics?
Ionization refers to the process of removing an electron completely from an atom.
What is zero potential energy in the Bohr model?
Zero potential energy is defined as the energy of an electron when it is infinitely far from the nucleus.
What produces line emission spectra?
Line emission spectra are produced when electrons move into a lower energy state and emit a photon.
What is the relationship between photon frequency and energy transition?
The frequency of the photon emitted corresponds to the energy lost by the electron in the transition, given by E=hf.
What is photoelectric emission?
Photoelectric emission occurs when a photon of sufficient energy ejects electrons from the surface of materials.
What is the threshold frequency?
The threshold frequency is the minimum frequency of a photon required for photoemission.
What is the work function in photoelectric effect?
The work function is the minimum energy of a photon required to cause photoemission.
How is the kinetic energy of emitted electrons calculated?
Kinetic energy = Photon Energy - Work Function.
What effect does increasing irradiance have on photoemission?
Increasing the irradiance of light will increase the number of photons emitted per second, thus increasing the number of electrons emitted per second.
What are coherent waves?
Waves that have a constant phase relationship
What equation is used to find the path difference of a maxima?
P.D = m(lambda)
What equation is used to find the path difference of a minima?
P.D = m +1/2 (Lambda)
What is seen when white light is passes through a diffraction grating?
An interference pattern where the central maxima is white and a full colour spectrum is shown at each maxima.
What does the term the speed of light is absolute mean?
The speed of light is the same for all observers (in air 300,000,000m/s)
When does an observer measure dilated time (t')?
When the observe is in a different frame of reference to the event.
When does an observer measure true time (t)?
When the observer is in the same frame of reference as the event.
When does an observer measure contracted length (l')
When the observe is in a different frame of reference to the event.
When does an observer measure true length (l)
When the observer is in the same frame of reference as the event.
Define irradiance
Irradiance is the Power per unit Area (I=P/A)
What are Fraunhofer lines (the black lines in the spectrum of the sun) evidence for?
The composition of the suns outer atmosphere
What is the main evidence for light being a wave?
Interference
What is the main evidence for light being a particle?
Photoelectric Emission
What is wave-particle duality?
Wave-particle duality is the concept in quantum physics that light and matter exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties depending on how they are observed.