Non-Protein Nitrogen Compounds (NPN)
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
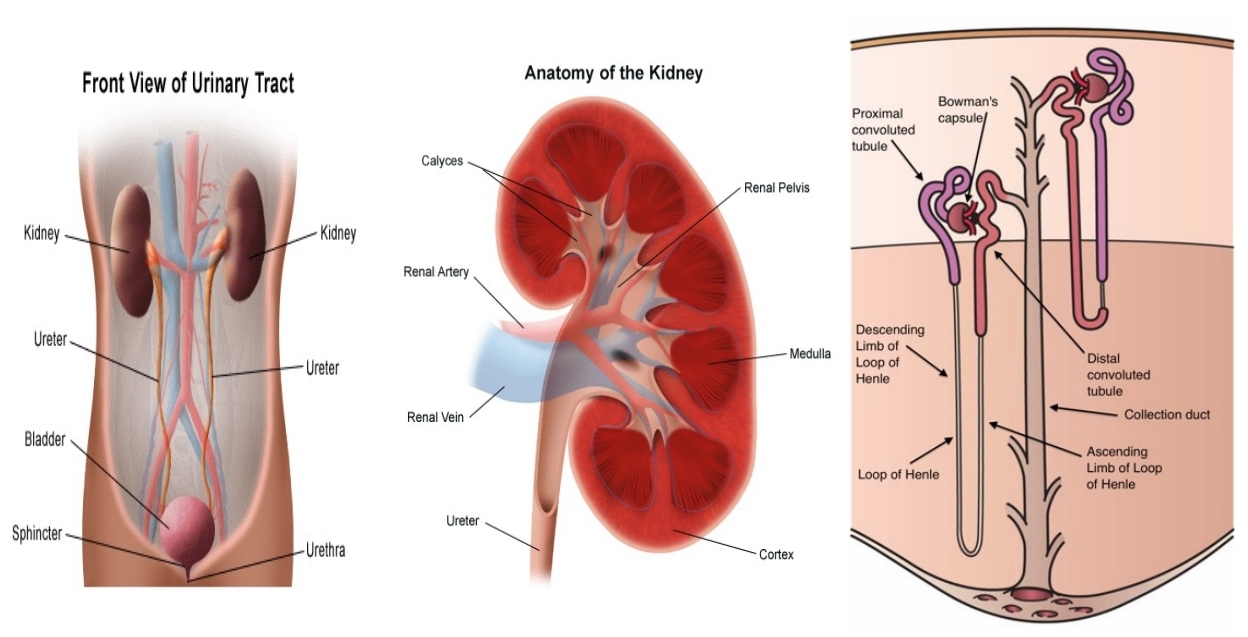
Paired, bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally on either side of the spinal column
Kidneys
Two regions of the kidneys
cortex (outer)
medulla (inner)
Functional unit of the kidney
Nephron
5 Basic Parts of Nephron
glomerulus
proximal convulated tubule
loop of henle
distal convulated tubule
collecting duct
Proximal Convulated Tubule (PCT) is the site of reabsorption for:
sodium
chloride
bicarbonate and other ions
glucose
amino acids and proteins
urea
uric acid
Anatomy of Kidney
Functions of the Kidneys
Elimination of Waste Products
Maintenance of Blood Volume
Maintenance of Acid-Base Balance
Endocrine Function > erythropoietin secretion
Renal Function Panel
Glucose
BUN
Creatinine
Sodium
Potassium
Chloride
Phosphorous
Calcium
Albumin
Carbon dioxide
Traditionally used to monitor renal function
Non-protein Nitrogen (NPN) Compounds
The term, Non-protein Nitrogen Compounds, originated when _
analytic methodology required removal of protein from sample before analysis
Concentration of nitrogen-containing compounds was quantified - by converting -
spectrophotometrically by converting nitrogen to ammonia
Non-Protein Nitrogen (NPN) Compounds
Subsequent reaction with - produced a yellow color
Nessler's reagent (K2[HgI4])
NPN fraction comprises about - compunds of clinical interest
15
Majority of these compunds arise from _
catabolism of proteins and nucleic acids
The test for NPNs (specifically - and -) is considered -
urea and creatinine
kidney function test (KFT)
Clinically Significant NPNs
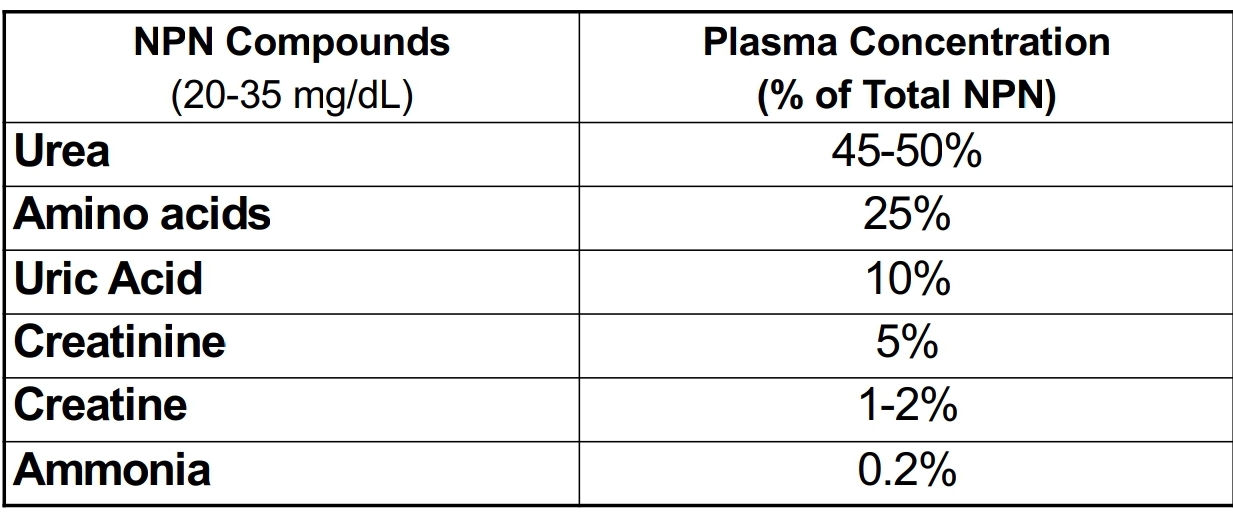
NPN compund present in highest concentration in blood
Urea
Urea is - formed in - from amino groups and free ammonia
major excretory product of protein metabolism
liver
first to elevate in kidney diseases
easily removed by dialysis
Urea
Urea - PHYSIOLOGY
- is released as a result or protein metabolism converted to - and excreted as a waste product
Nitrogen
Urea (80%)
Urea - PHYSIOLOGY
After synthesis in liver (through the - cycle), urea is carried in blood to the kidney and filtered out
Krebs-Henseleit Cycle
Urea - PHYSIOLOGY
Most urea in glomerular filtrate is excreted in - but some is reabsorbed in -
urine (90%)
renal tubules (10%)
Urea - CLINICAL APPLICATION
Evaluates renal function
Assess hydration status
Determines nitrogen balance
Aid in diagnosis of renal disease
Verify adequacy of dialysis
Urea - Methods of Measurement
Enzymatic > urease
electrode
isotope-dilution mass spectrometry > reference method
Urea - SPECIMEN REQUIREMENTS & INTERFERING SUBSTANCES
may be measured in -
in plasma > avoid -
susceptible to -
may be measured in plasma, serum, urine
in plasma > avoid ammonium ions and high citrate and fluoride
susceptible to bacterial decomposition > analyze quickly or refrigerate if urine
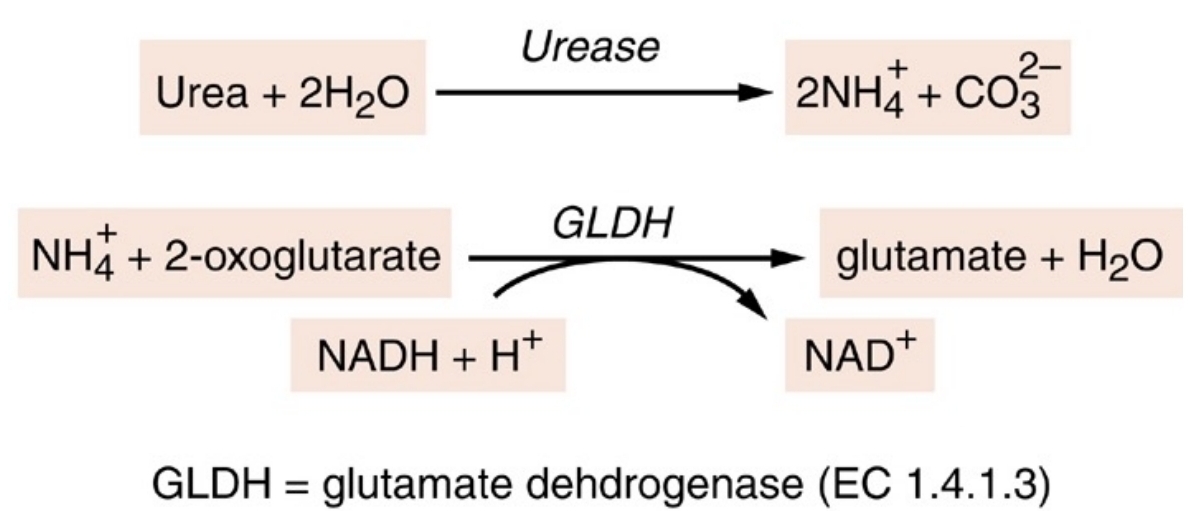
Enzymatic Methods for Urea use similar first step:
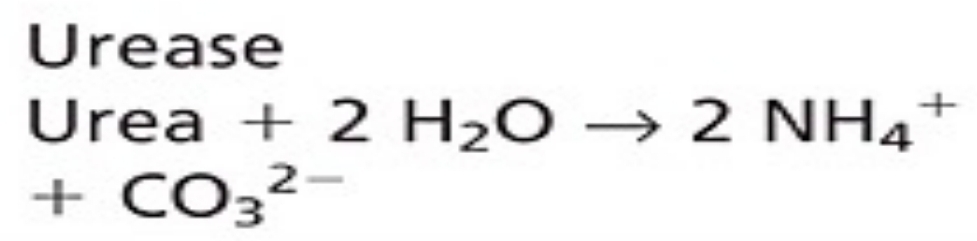
Enzymatic methods for urea
GLDH coupled enzymatic
Indicator dye
Conductimetric
Other Methods
Isotope dilution mass spectrometry
used on many automated instruments
best as kinetic measurement
GLDH coupled enzymatic
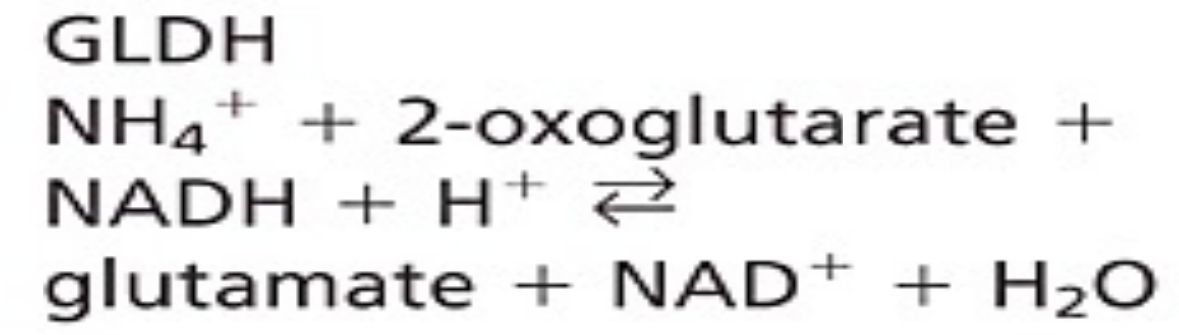
used in automated systems, multilayer film reagents, and dry reagent strips
Indicator dye

specific and rapid
conversion of unionized urea to NH4+ and CO3 2- results in increased conductivity
Conductimetric
proposed reference method
detection of characteristic fragments following ionization, quantificationm using isotopically labeled compund
Isotope filution mass spectrometry
Indirect methods for measuring urea
measure the nitrogen content of urea in blood urea nitrogen or BUN
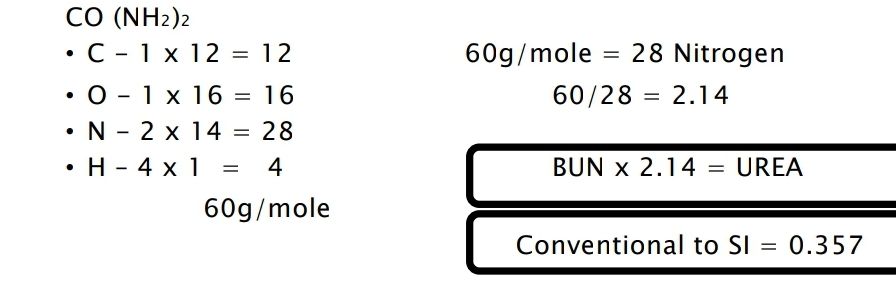
Enzymatic assay for urea
Normal value for Urea Nitrogen in Adults
In PLASMA/SERUM
6 to 20 mg/dL (2.1 to 7.1 mmol/L)
In URINE
24-hour sample
12 to 20 g/day (0.43 to 0.71 mol urea/day
Urea - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
elevated concentration of urea in blood
azotemia
Urea - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Very high plasma urea concentration with renal failure > acideia and electrolyte imbalance
Uremia
Urea - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
reduced renal blood flow caused by:
high protein diet
congestive heart failure (CHF)
shock
hemorrhage
increased catabolism
corticosteroid therapy
Prerenal azotemia
Urea - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
decreased renal function caused by:
renal failure
glomerulonephritis
Urea - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
obstruction of urine flow caused by:
renal calculi
tumors of bladder and prostate
severe infection
Postrenal azotemia
Urea - DISEASE CORRELATIONS
The following increases urea levels
Chronic renal disease
Stress
Burns
High protein diet
Dehydration
Urea - DISEASE CORRELATION
The following decreases urea levels:
poor nutrition
high fluid intake / excessive IV fluids
pregnancy
severe liver diseases
effects of some hormones
severe vomiting or diarrhea
Differentiation of the cause of abnormal urea concentration:
Urea Nitrogen / Creatinine ration
Norma Urea Nitrogen / Creatinine ratio
10:1 to 20:1
Urea Nitrogen / Creatinine ratio in Prerenal Azotemia
high urea
normal creatinine
HIGH UREA NITROGEN/CREATININE RATION
Urea Nitrogen / Creatinine ratio in Postrenal Azotemia
high urea
high creatinine
HIGH UREA NITROGEN / CREATININE RATIO
There will be LOW UREA NITROGEn / CREATININE RATIO in:
Decreased urea production
low protein intake
acute tubular necrossi
severe liver disease
product of catabolism or purine nucleic acids
Uric acid
Uric Acid
most is reabsorbed in - and reused
proximal convulated tubules (98% to 100%)
Uric Acid
at pH of - , more than -% of uric acid in body exists as -
pH of 7.4
95%
monosodium urate
Uric Acid
relatively insoluble in -
in high concentrations, can be deposited in -
relatively insoluble in plasma
in high concentrations, can be deposited in joints and tissues > painful inflammation
Uric Acid - Physiology
- are converted to uric acid in -
Uric acid is transprted in plasma from - to - and filtered by glomerulus
purine
liver to kidney
Uric Acid - Physiology
-% is eliminated by -, remainder passes into - and is degraded by bacterial enzymes
70%
renal excretion
GI tract
Uric Acid - CLINICAL APPLICATION
Assessment of inherited disorders of purine metabolism
Confirmation of diagnosis and monitoring of treatment of gout
Assistance in diagnosis of renal calculi
Prevention of uric acid nephropathy in chemotheraphy
Detection of kidney dysfunction
Uric Acid - Methods of Measurement
Caraway method
Uricase method
Coupled enzyme methods
Isotope dilution mass spectrometry (proposed)
Uric Acid - SPECIMEN REQUIREMENTS and INTERFERING SUBSTANCES
measured in -
remove - from cells quickly to prevent -
Avoid gross -,-,-
Diet may affect concentration overall but - not necessary
measured in heparinized plasma, serum, or urine
remove serum from cells quickly to prevent dilution by intracellular contents
Avoid gross lipemia, bilirubinemia, hemolysis
Diet may affect concentration overall but fasting not necessary
Uric Acid - CHEMICAL METHODS
Nonspecific
Requires protein removal
Phosphotungstic acid

Uric Acid - ENZYMATIC METHODS
Spectrophotometric
Coupled enzymatic (I)
Coupled enzymatic (II)
Uric Acid - ENZYMATIC METHODS
have similar first step:
very specific
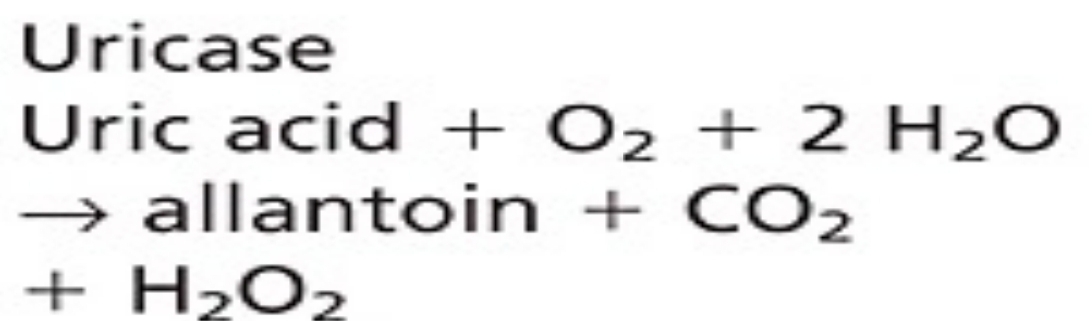
Uric Acid - Enzymatic Methods
decrease in absorbance at 293 nm measured
hemoglobin and xanthin interfere
Spectrophotometric
Uric Acid - Enzymatic Methods
commonly automated method
negative bias with reducing agents
Coupled Enzymatic (I)
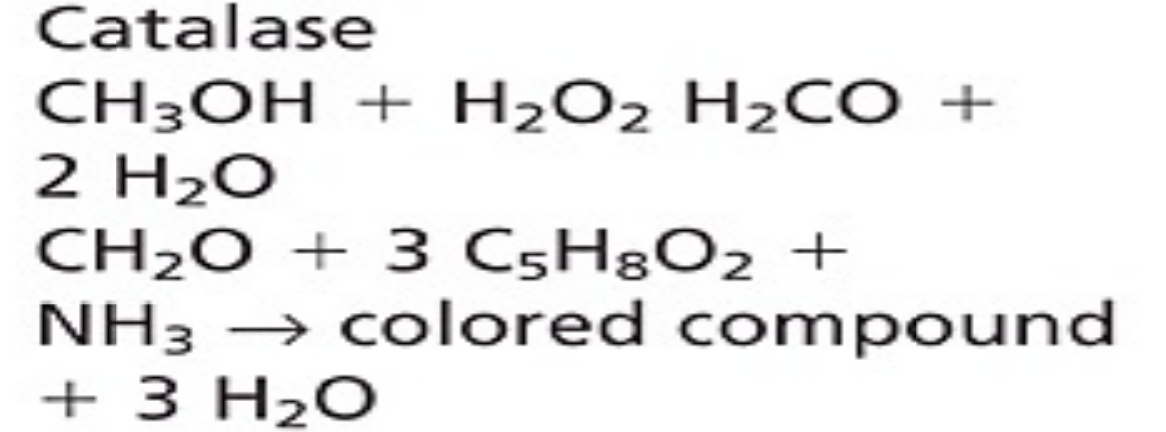
Uric Acid - Enzymatic Methods
readili automated
reducing agents interfere
Coupled enzymatic (II)

Uric Acid - OTHER METHODS
proposed reference method
detection of characteristic fragments following ionization
quantification using isotopically labeled compound
- Isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS)
Uric Acid - NORMAL VALUE
ADULT
plasma/serum
→MALE = 3.5 to 7.2 mg/dL
→FEMALE = 2.6 to 6.0 mg/dL
CHILD
plasma/serum
→ 2.0 to 5.5 mg/dL
Uric Acid - Pathophysiology
elevated levels of uric acid
hyperuricemia
Uric Acid - Pathophysiology
Hyperuricemia is found in:
inherited disorders of purine metabolism
Glucose-6-phosphate deficiency
Fructose intolerance > Fructose-1-phosphate aldolase deficiency
Gout
Treatment of myeloproliferative disorders with cytotoxic drugs
Chronic renal disease
Toxemia of pregnancy
Lactic acidosis
Drugs and poisons
Purine-rich diest
Increased tissue catabolism or starvation
Uric Acid - Pathophysiology
decreased levels of uric acid
hypouricemia
Uric Acid - Pathophysiology
Hypouricemia is found in:
Liver disease
Defective tubular resorption > Fanconi syndrome
Chemotherapy > azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine
Overtreatment with allopurinol
Uric Acid - Disease Correlations
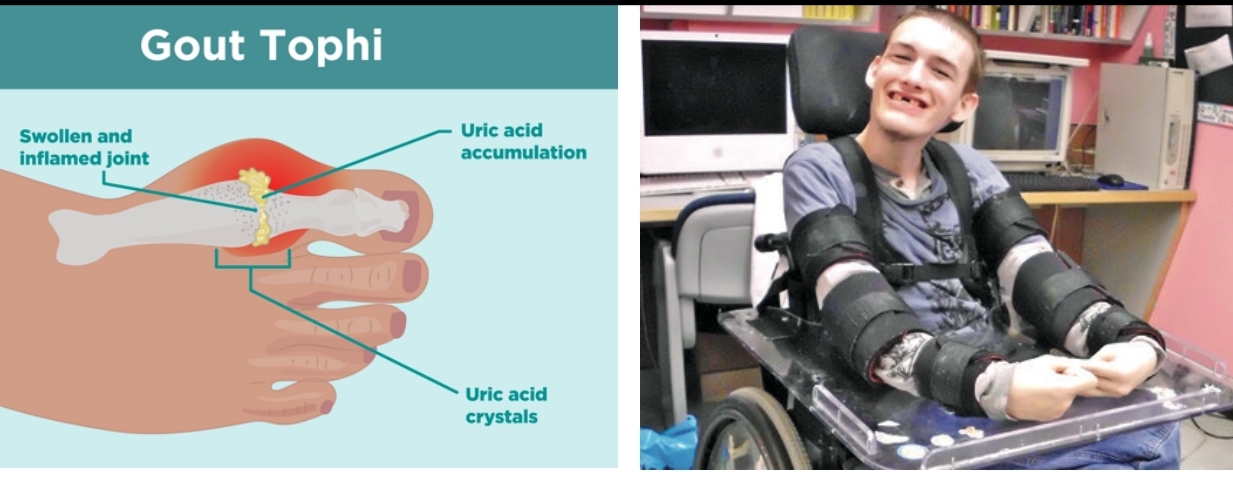
Gout
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome
Uric Acid - Disease Correlations
degenerative disorder
commonly found in males where there is deposition of uric acid crystals in joints or TOPHI
Gout
Uric Acid - Disease Correlations
in-born errors of metabolism
deficiency of hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT) > important in biosynthesis of purines
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome
Uric Acid - Disease Correlations
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome
Clue:
Orange sand in diapers
Uric Acid - Disease Correlations
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome
Complication:
can lead to mental retardation
Major end-product of metabolism
best index of kidney function
Creatinine / Creatine
Creatinine is formed from - and - in muscle and is excreted into plasma at rate related to -
creatine and creatine phosphate
muscle mass
Plasma creatinine is inversely related to - and is commonly used to assess -
glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
renal filtration function
Creatinine / Creatine - PHYSIOLOGY
Creatine is synthesized mainly in - from -,-, and -
liver
arginine, glycine, methionine
Creatinine / Creatine - PHYSIOLOGY
It is then transported to other tissues and converted to - which serves as high-energy source
creatine phosphate
Creatinine / Creatine - PHYSIOLOGY
Creatine phosphate and creatine for creatinine which difuses into plasma and is excreted
- % excreted
maximum of -% reabsorbed
100% excreted
1% reabsorbed
Creatinine / Creatine - CLINICAL APPLICATION
determine sufficiency of kidney function and severity of kidney damage
monitor progression of kidney disease
Creatinine / Creatine - CLINICAL APPLICATION
measure of amount of creatinine eliminated from the blood by the kidneys
Creatinine Clearance
Creatinine / Creatine - CLINICAL APPLICATION
volume of plasma filtered by glomerulus per unit of time
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Creatinine / Creatine - CLINICAL APPLICATION
Abbreviated Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) equation include 4 variables:
serum creatinine concentration
age
gender
ethnicity
Creatinine - Methods of Measurement
Jaffe Reaction
Kinetic Jaffe Method
Coupled Enzymatic Methods
Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry
Creatinine - Methods of Measurement
time-consuming, not readily automated
Jaffe Reaction
Creatinine - Methods of Measurement
Jaffe Reaction
Creatinine reacts with - in alkaline solution to form -
picric acid
red-orange chromogen
Creatinine - Methods of Measurement
rapid
inexpensive
easy to perform
Kinetic Jaffe Method
Creatinine - Methods of Measurement
Kinetic Jaffe Method
Serum is mixed with - and - is measured
alkaline picrate
rate of change in absorbance
Creatinine - Methods of Measurement
improves specificity
Coupled enzymatic methods
Creatinine - Methods of Measurement
reference method
Isotope dilution mass spectrometry
Creatinine - CHEMICAL METHODS BASED ON JAFFE REACTION
Jaffe-Kinetic
Jaffe with adsorbent
Jaffe witount adsorbent

Creatinine - CHEMICAL METHODS BASED ON JAFFE REACTION
Jaffe reaction performed direactly on sample
Detection of color formation timed to avoid interference of noncreatinine chromogens
Jaffe-Kinetic
Creatinine - CHEMICAL METHODS BASED ON JAFFE REACTION
Jaffe-Kinetic
positive bias from:
alpha-ketoacids and cephalosporins
requires automated equipment for precision
Creatinine - CHEMICAL METHODS BASED ON JAFFE REACTION
Creatinine in protein-free filtrate adsorbed onto Fuller's earth (aluminum magnesium silicate)
Then, reacted with alkaline picrate to form colored complex
Jaffe with adsorbent
Creatinine - CHEMICAL METHODS BASED ON JAFFE REACTION
Jaffe with adsorbent
Adsorbent improves -
specificity
Creatinine - CHEMICAL METHODS BASED ON JAFFE REACTION
previously considered reference method
Jaffe with adsorbent
Creatinine - CHEMICAL METHODS BASED ON JAFFE REACTION
Creatinine in protein-free filtrate reacts with - to form colored complex
alkaline picrate
Creatinine - ENZYMATIC METHODS
requires large sample
not used widely
Creatininase-CK
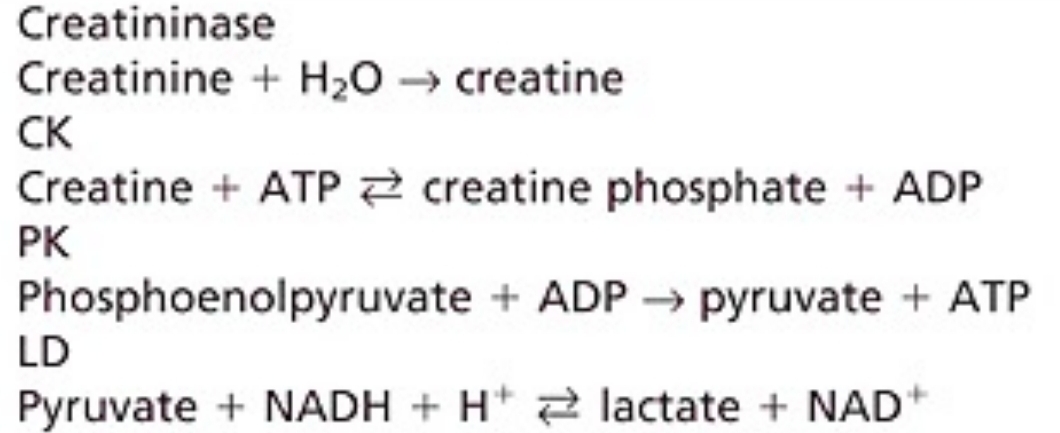
Creatinine - ENZYMATIC METHODS
adapted for use as dry slide method
potential to replace Jaffe
Creatininase-H2O2
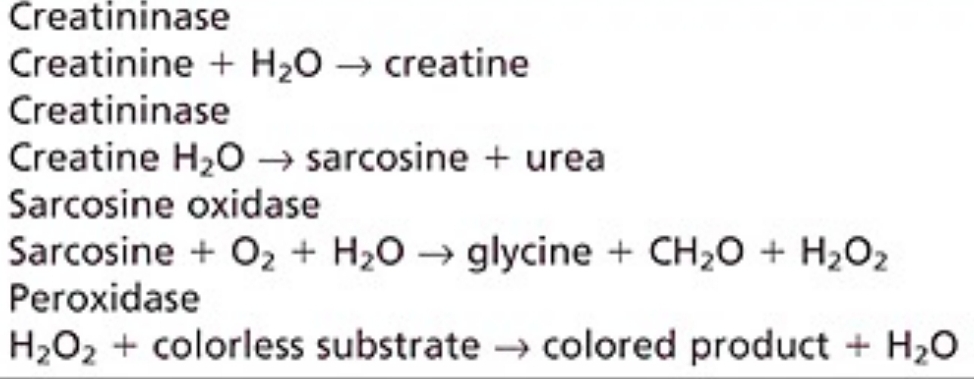
Creatinine - ENZYMATIC METHODS
No interference from -
Some positive bias due to -
acetoacetate or cephalosporins
lidocaine