Body Fluids and Acid-Base Balance in Chemistry
Intracellular fluid
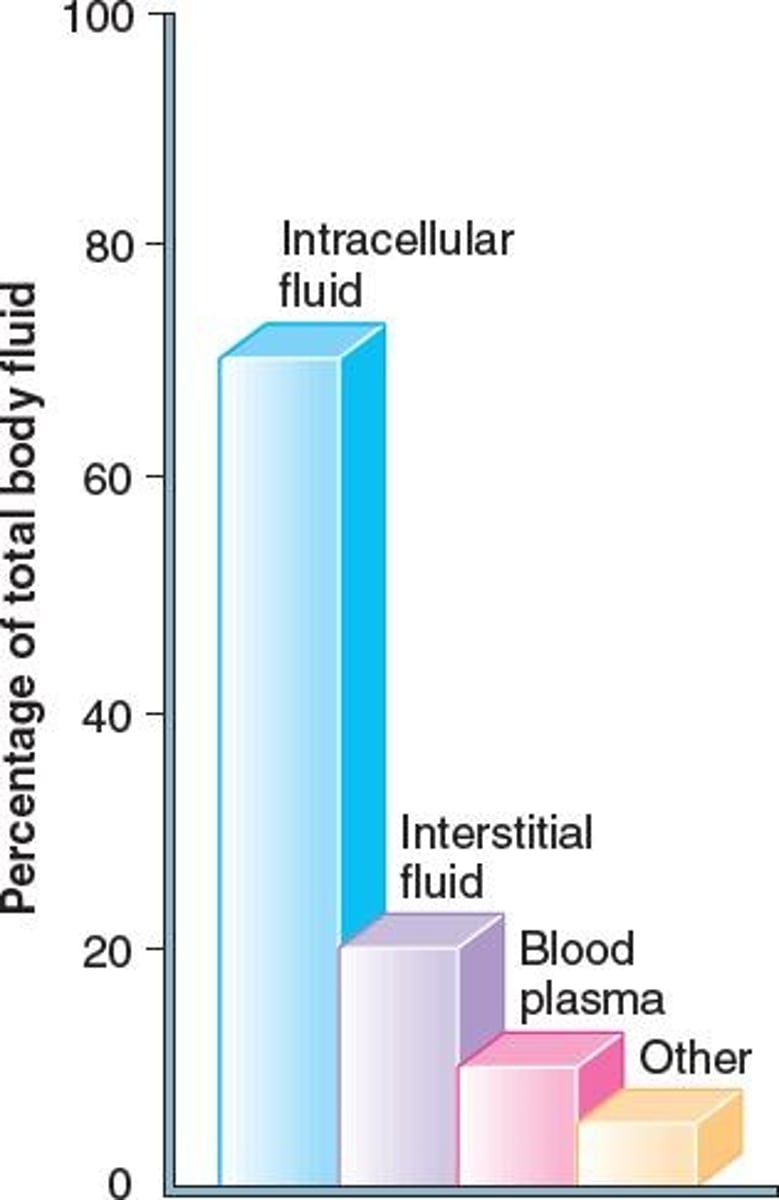
Fluid located inside cells, majority body fluid.
Extracellular fluid
Fluid located outside cells, transports substances.
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Intracellular fluid
Fluid located inside cells, majority body fluid.

Extracellular fluid
Fluid located outside cells, transports substances.
Interstitial fluid
Fluid between tissue cells, moves in lymph.
Plasma
Fluid component of blood, contains proteins.
Oxyhemoglobin
Oxygen-hemoglobin complex in red blood cells.
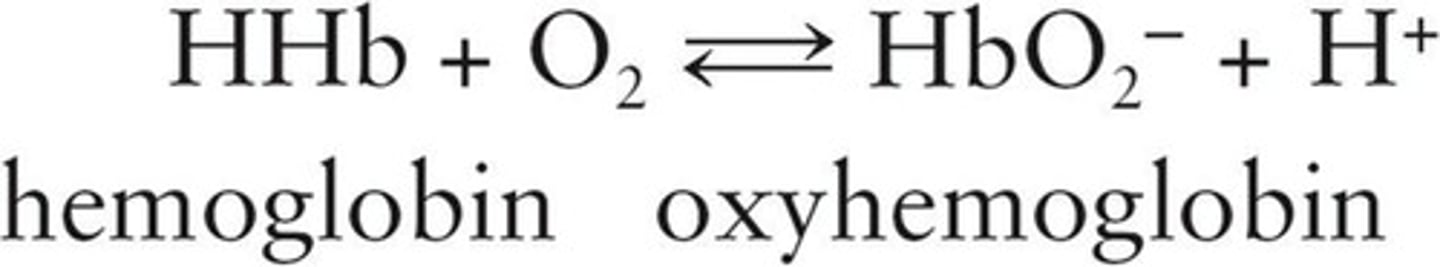
Deoxyhemoglobin
Nonoxygenated form of hemoglobin.
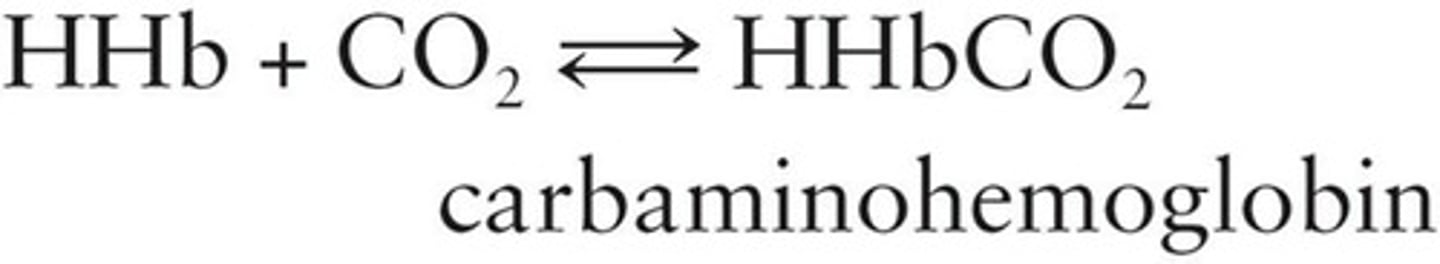
Carbaminohemoglobin
Hemoglobin combined with carbon dioxide.
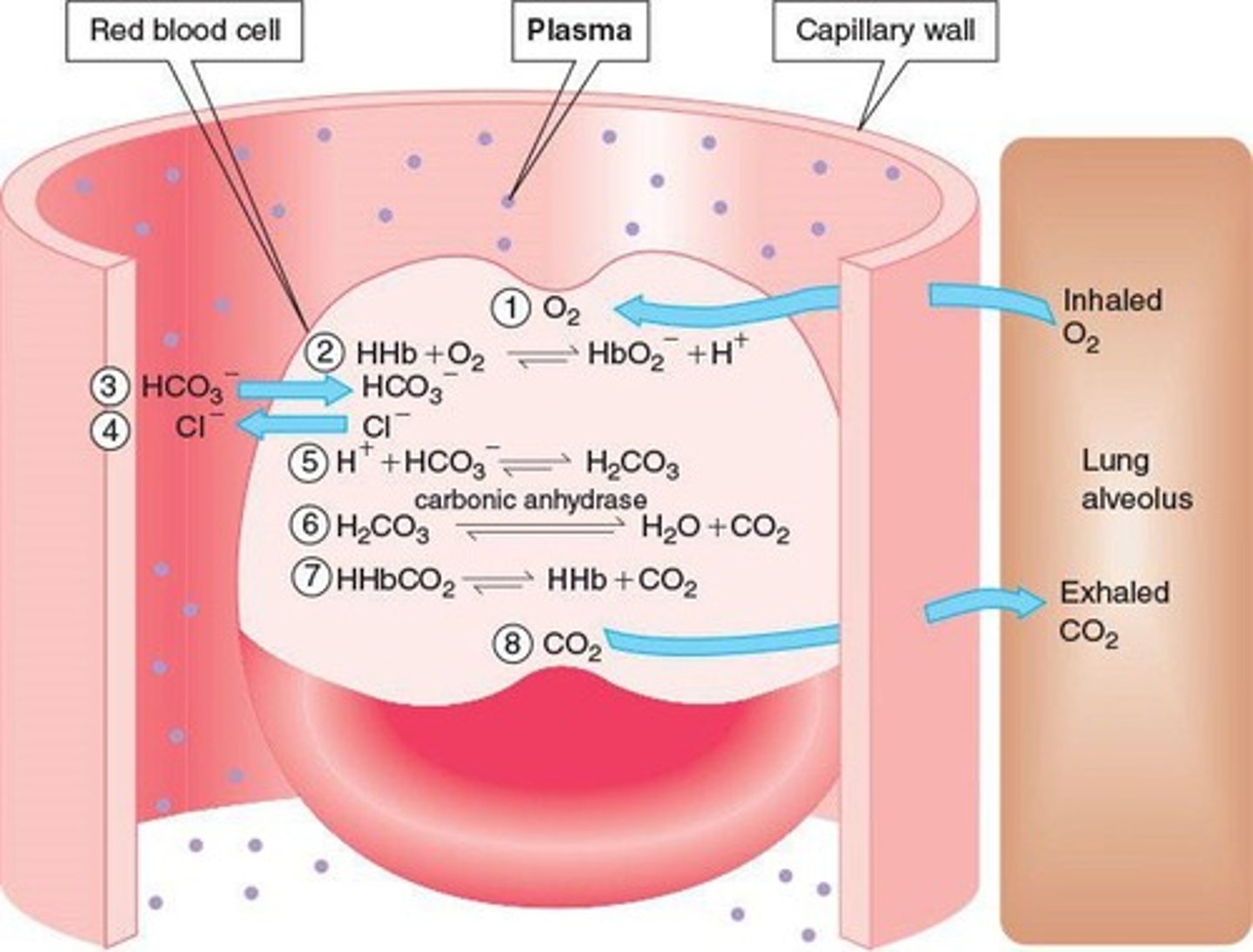
Chloride shift
Exchange of chloride ions for bicarbonate ions.
Acidosis
Condition of increased acidity in blood.
Alkalosis
Condition of increased alkalinity in blood.
Oxygen transport
Oxygen carried mainly by oxyhemoglobin.
Carbon dioxide transport
CO2 transported as bicarbonate ions primarily.
Normal urine constituents
Includes urea, creatinine, and uric acid.
Urine pH range
Healthy urine pH ranges from 4.5 to 8.0.
Fluid balance
Maintaining proper fluid and electrolyte levels.
Electrolyte balance
Maintaining ion concentrations in body fluids.
Hemoglobin concentration
Human blood contains 15 g hemoglobin per 100 mL.
Bicarbonate ions
Transport most CO2 from tissues to lungs.
Carbonic anhydrase
Enzyme that converts carbonic acid to CO2.
Diffusion
Movement of substances from high to low concentration.
Oxygen partial pressure
Higher in alveoli than in red blood cells.
Blood pressure
Creates pressure differences across capillary walls.
Osmotic pressure
Pressure due to protein concentration differences.
Urine composition
96% water, 4% dissolved waste products.
Respiratory control of pH
Regulates blood pH via CO2 levels.
Urinary control of pH
Regulates blood pH via excretion of H+.
Fluid compartments
Body fluids are compartmentalized into regions.
Chemical transport
Substances must enter bloodstream for transport.
Intracellular fluid
Fluid located inside cells, majority of body fluid.
Interstitial fluid
Fluid filling spaces between tissue cells.
Deoxyhemoglobin
Hemoglobin without bound oxygen.
Chloride shift
Movement of chloride ions to maintain balance.
Oxygen partial pressure
Pressure exerted by oxygen in a mixture.
Carbonic anhydrase
Enzyme that catalyzes carbonic acid formation.
Hemoglobin concentration
15 g hemoglobin per 100 mL blood.
Normal urine pH
Healthy urine pH ranges from 4.5 to 8.0.
Urine constituents
Includes urea, creatinine, and uric acid.
Fluid balance
Maintenance of proper fluid levels in body.
Electrolyte balance
Regulation of ions in body fluids.
Oxygen transport
Oxygen carried mainly by red blood cells.
Blood pressure
Pressure exerted by circulating blood on vessel walls.
Osmotic pressure
Pressure from solute concentration differences.
Chemical transport
Movement of substances through bloodstream.
Body fluid volume
Average adult body contains 42 L of fluids.
Fluid compartments
Divided into intracellular, interstitial, and plasma.
Respiratory control of pH
Regulation of blood pH via CO2 levels.
Urinary control of pH
Regulation of blood pH via kidney function.
Normal urine output
Average daily urine output is 1400 mL.
Protein content
Intracellular fluid has more protein than plasma.
Urine Composition
Used for diagnosing pathological conditions.
Paper Test Strip
Checks urine specimen for abnormal constituents.
Glucosuria
Presence of glucose in urine.
Diabetes Mellitus
Condition causing high glucose levels.
Proteinuria
Presence of protein in urine.
Ketonuria
Presence of ketone bodies in urine.
Hemoglobinuria
Presence of hemoglobin in urine.
Hematuria
Presence of red blood cells in urine.
Bile Pigments
Indicates liver dysfunction or bile duct blockage.
Fluid Balance
Maintained by equal fluid intake and output.
Thirst Mechanism
Stimulated by dehydration to regulate water intake.
Urine Output
Normal is approximately 1400 mL/day.
Vasopressin
Hormone regulating water reabsorption in kidneys.
Aldosterone
Stimulates sodium reabsorption and water retention.
Acid-Base Balance
Maintains blood pH between 7.35 and 7.45.
Alkalosis
Abnormally high blood pH.
Acidosis
Abnormally low blood pH.
Buffer Systems
Maintain constant blood pH through chemical reactions.
Bicarbonate Buffer
Regulates pH with bicarbonate and carbonic acid.
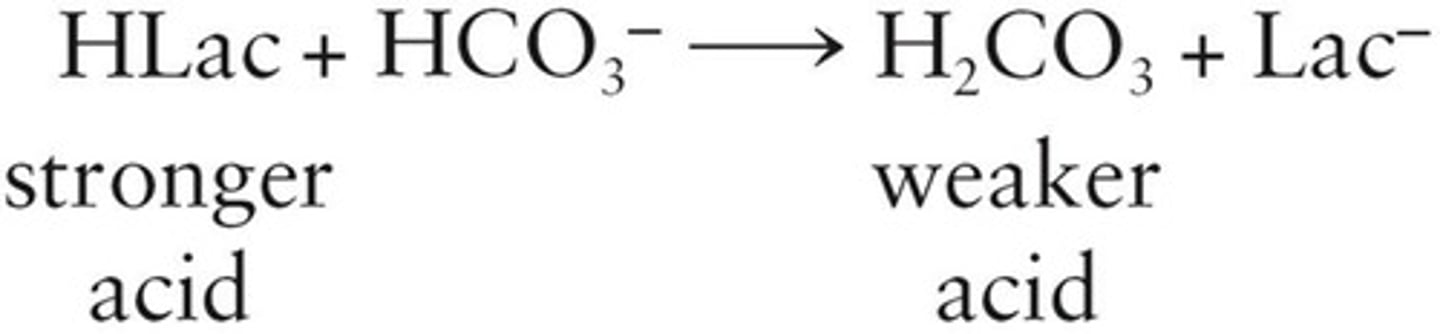
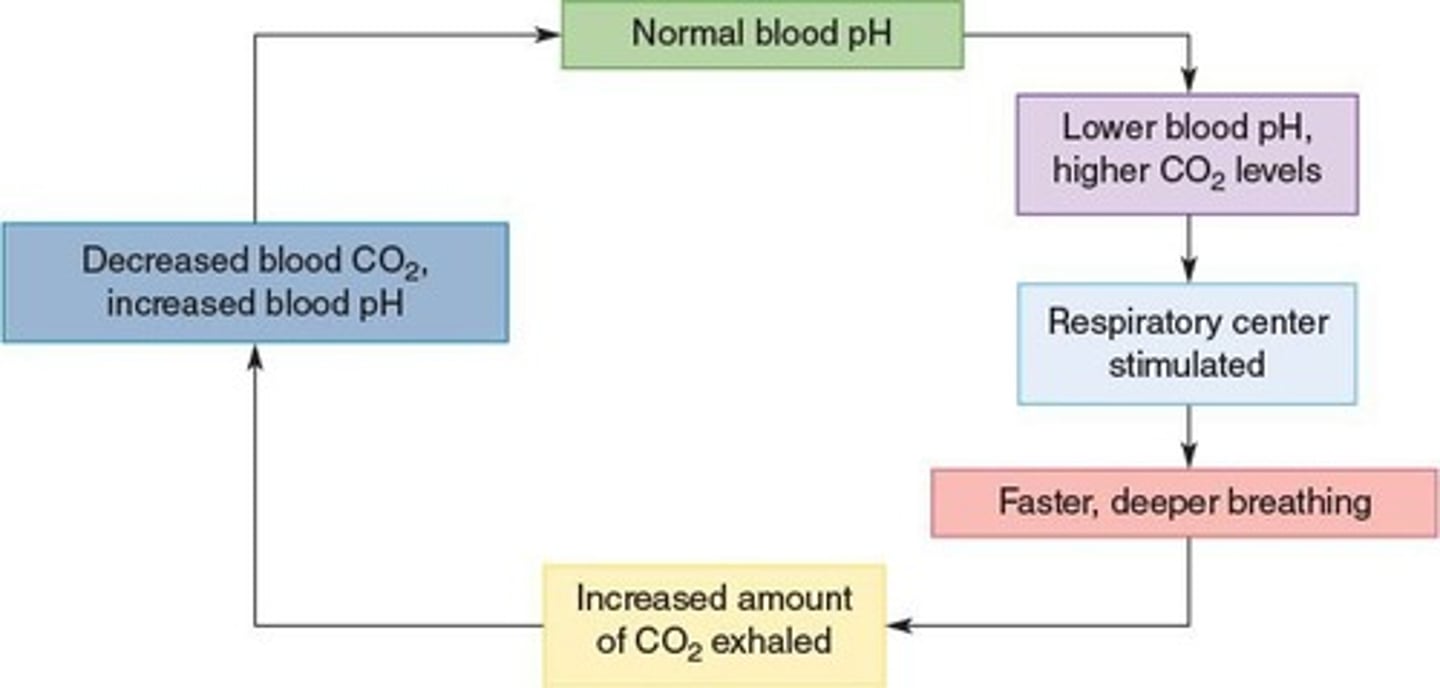
Respiratory Control
Regulates blood acidity by CO2 elimination.
Hyperventilation
Rapid breathing causing decreased CO2 levels.
Hypoventilation
Slow breathing causing increased CO2 levels.
Metabolic Acidosis
Caused by increased H+ levels in blood.
Metabolic Alkalosis
Caused by loss of acid or excess base.
Respiratory Acidosis
Result of hypoventilation decreasing blood pH.
Respiratory Alkalosis
Caused by hyperventilation increasing blood pH.
Treatment for Acidosis
May involve bicarbonate or hemodialysis.
Symptoms of Acidosis
Includes hyperventilation, headache, and disorientation.