Kinesiology Exam #3
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
175 Terms
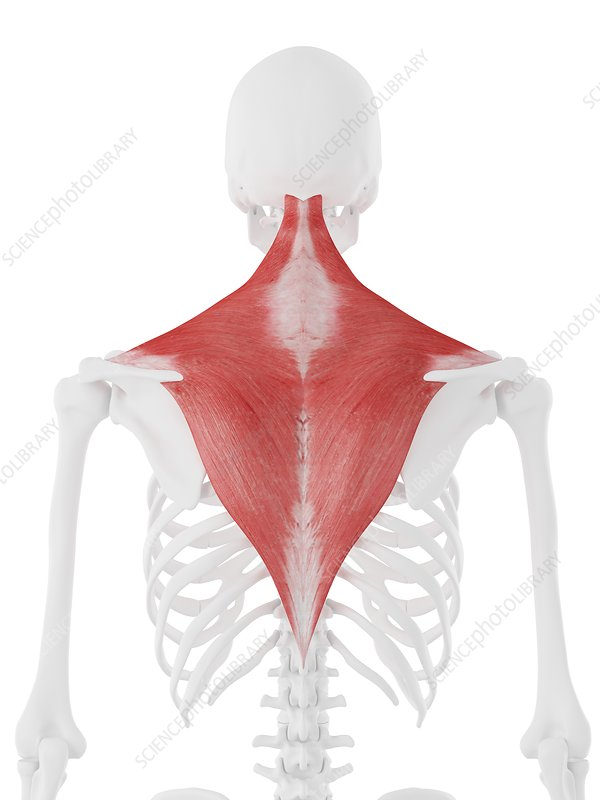
Trapezius
Trapezius Origin
Skull, nuchal ligament and spinous process of C7-T12
Trapezius insertion
clavicle, acromion, and scapula spine
Trapezius Actions
Abduction of upper limb at shoulder by rotating scapula, elevate scapula, middle fibers retract and lower fibers depress
Innervation of Trapezius
Accessory nerve
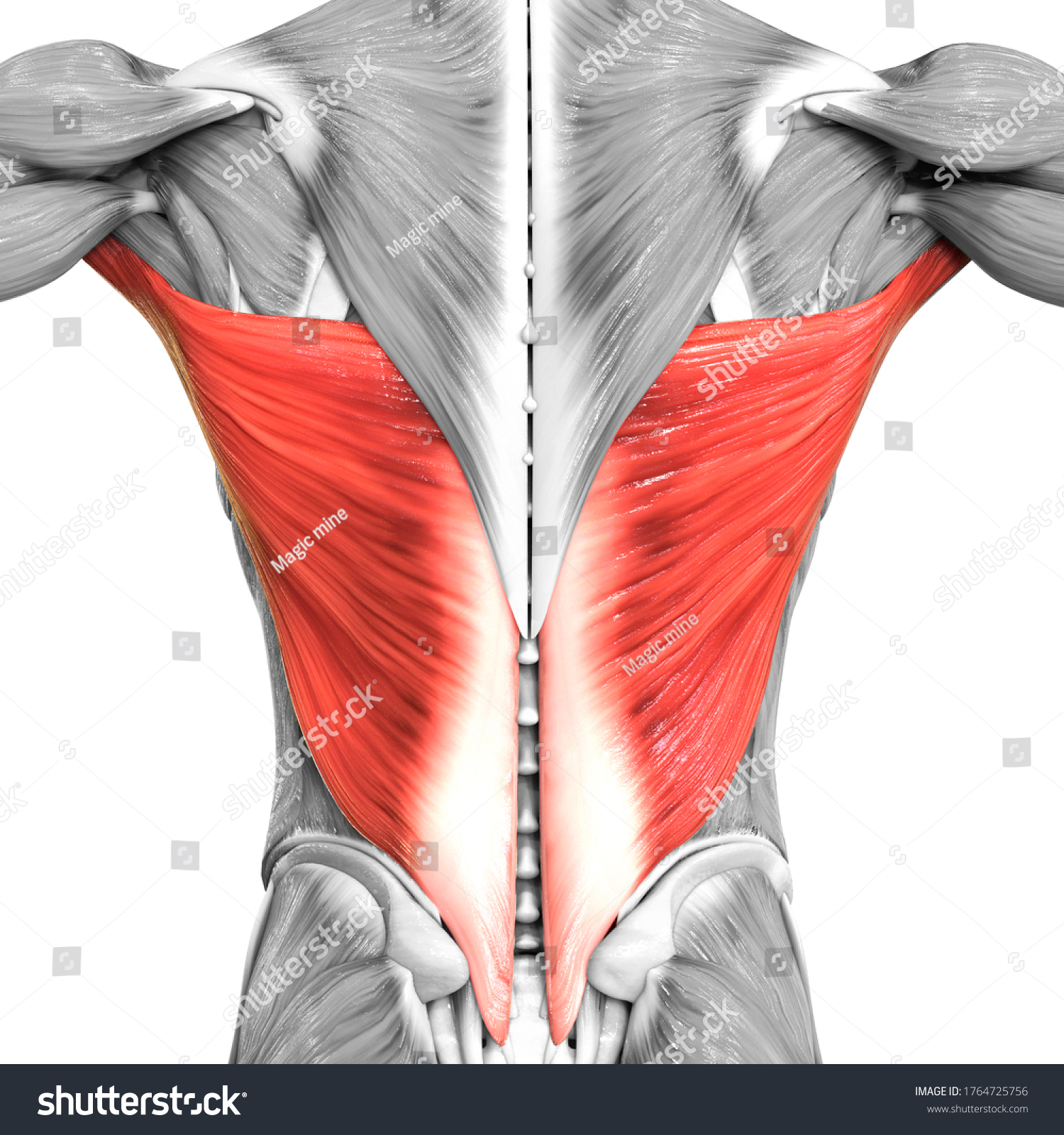
Latissimus dorsi
Latissimus dorsi origin
Spinous processes of T7-T12, illiac crest, thoracolumbar fascia, and inferior three ribs
Latissimus dorsi insertion
intertubercular sulcus of the humerus (also known as the bicipital groove)
Latissimus Dorsi action
Extension, adduction, and medial rotation of upper limb at the shoulder
Innervation of latissimus dorsi
Thoracodorsal nerve
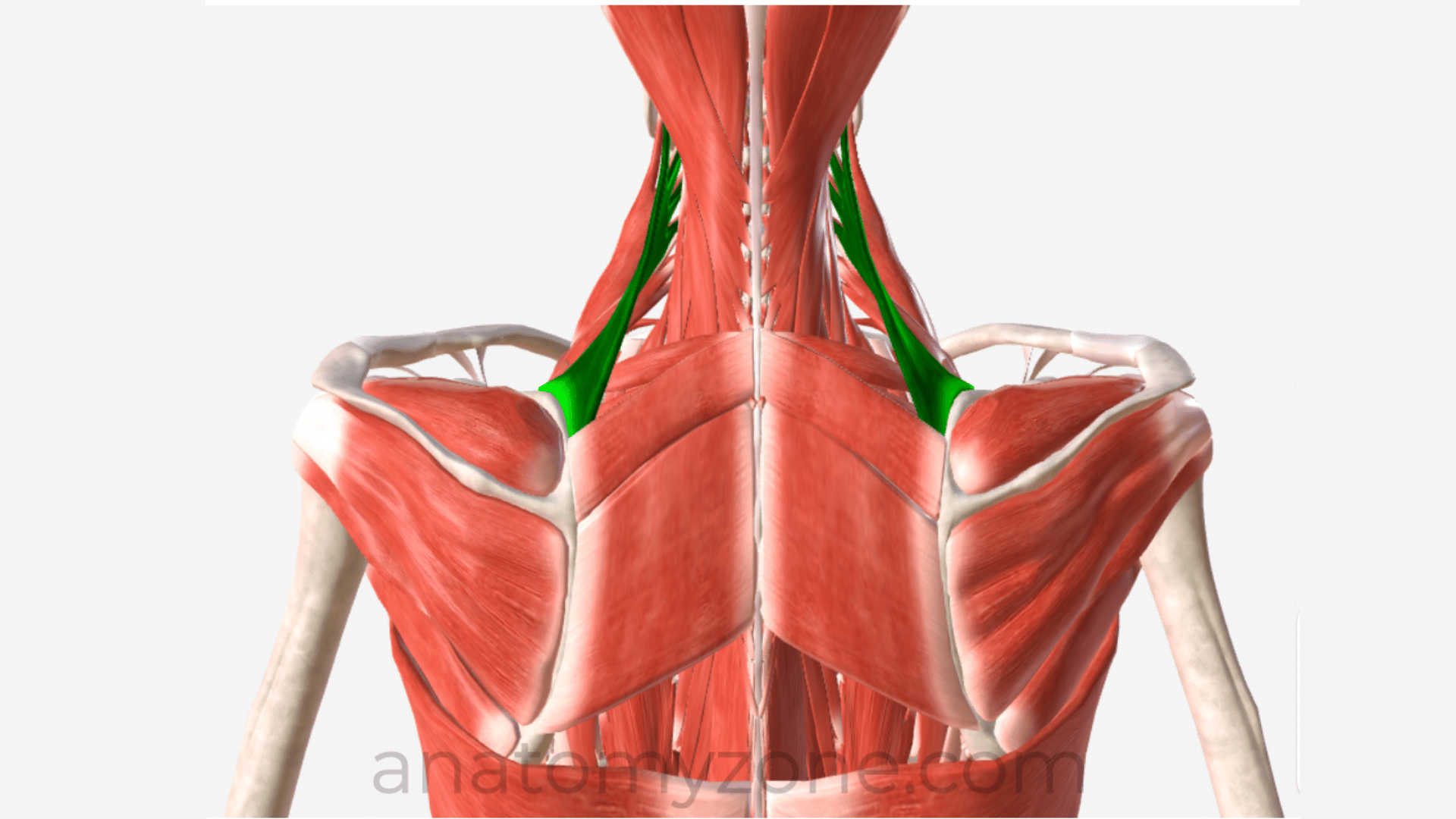
Levator scapulae
Levator scapulae origin
transverse processes of C1 -C4 vertebrae
Levator scapulae insertion
medial border of scapula
Levator scapulae actions
elevation of the scapula
Innervation of Levator Scapulae
Dorsal scapular nerve
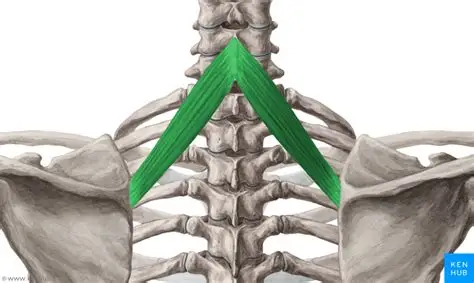
Rhomboid minor
Rhomboid minor origin
spinous processes of C7 -T1
Rhomboid minor insertion
medial border of scapula, at level of spine of scapula
Actions of Rhomboid minor
Retraction and rotation of scapula
Innervation of Rhomboid minor
Dorsal Scapular nerve
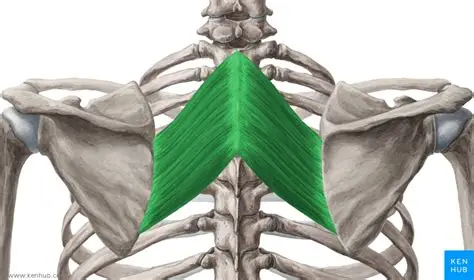
Rhomboid major
Rhomboid major origin
spinous processes of T2-T5
Rhomboid major insertion
medial border of scapula, between scapula spine and inferior angle
Actions of Rhomboid major
Retracts and rotates the scapula
Innervation of Rhomboid major
Dorsal scapular nerve
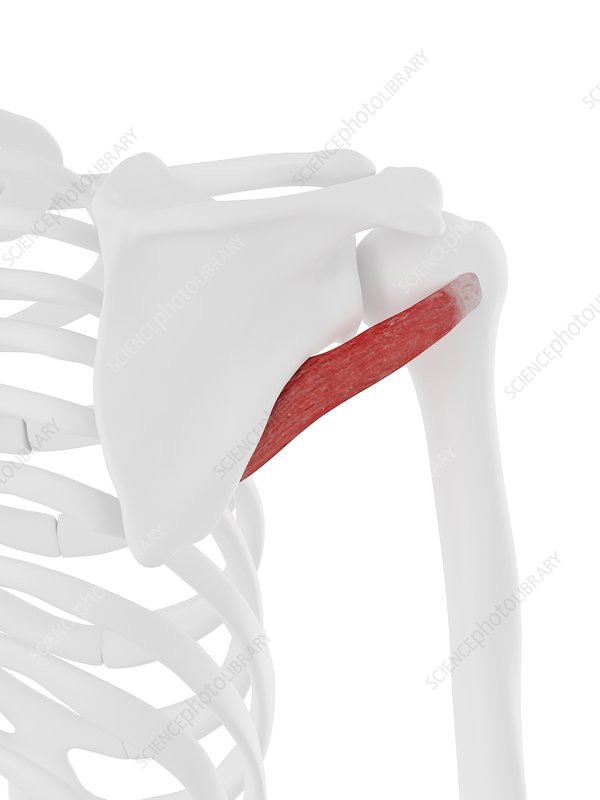
Teres minor origin
posterior surface of the scapula, adjacent to its lateral border
Teres minor insertion
greater tubercle of humerus
Actions of teres minor
Lateral rotation of arm
Innervation of teres minor
Axillary nerve
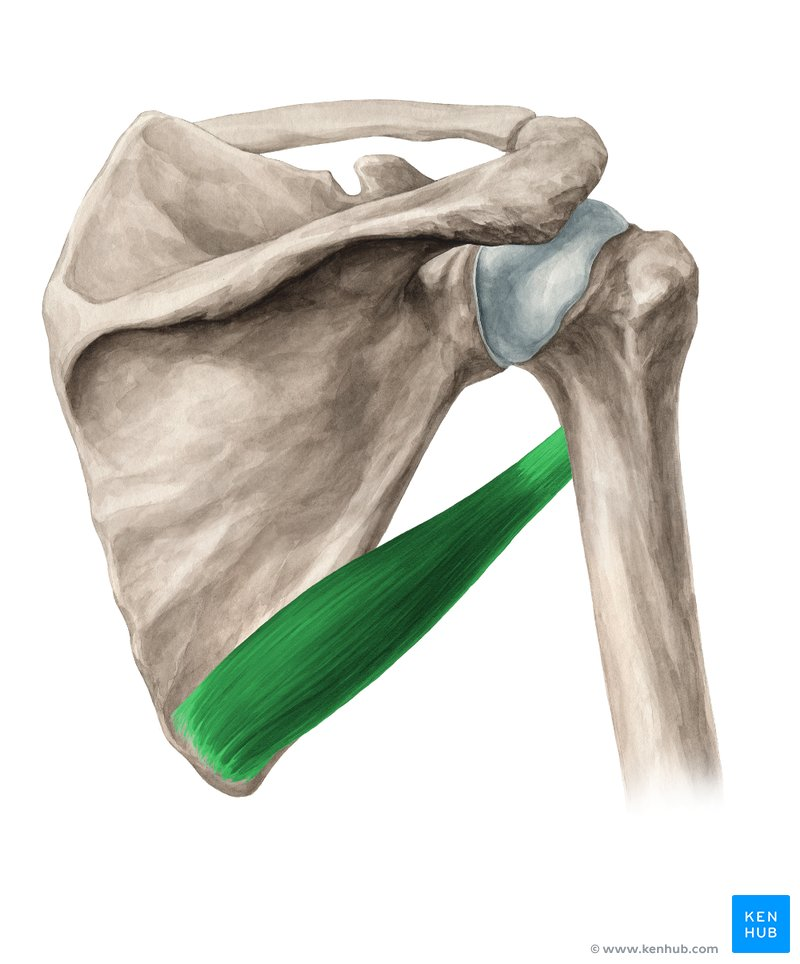
Teres major
Teres Major origin
posterior surface of the inferior angle of the scapula
Teres major insertion
medial lip of the intertubercular groove of the humerus (also known as bicipital groove)
Actions of the teres major
Adduction, extension and medial rotation
Innervation of teres major
lower subscapular nerve
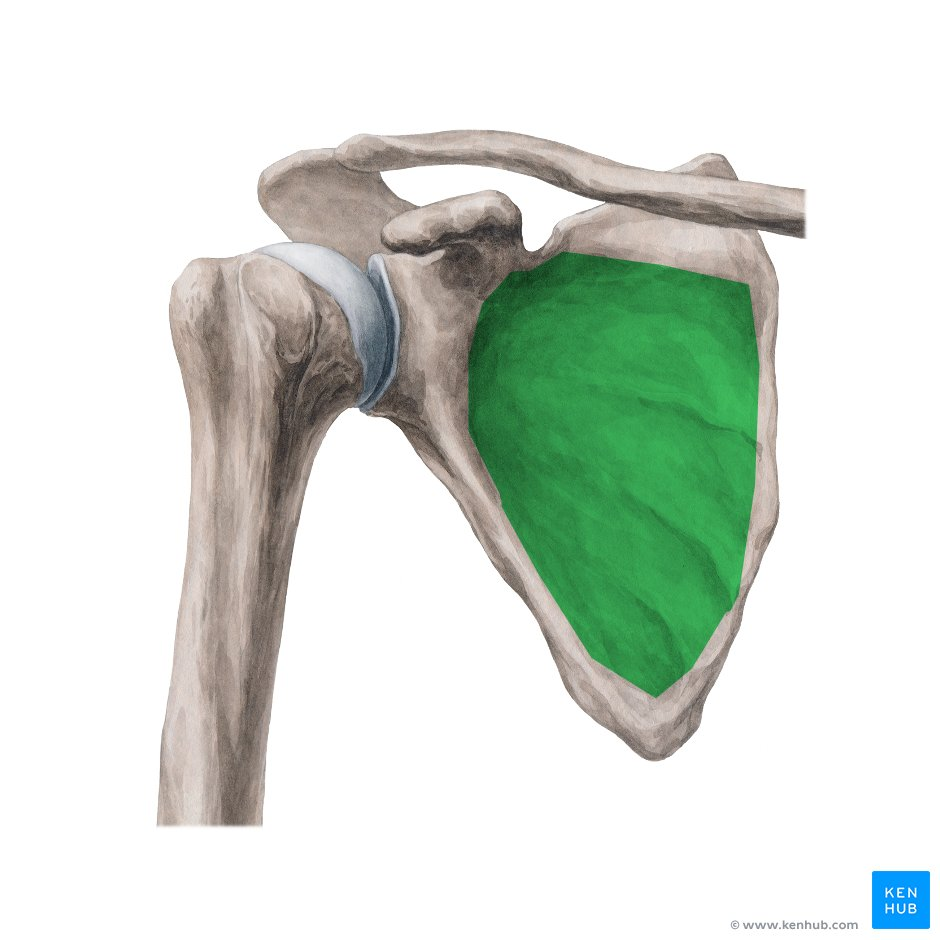
Subscapularis
Subscapularis origin
subscapular fossa (anterior surface of the scapula)
Subscapularis insertion
lesser tubercle of humerus
Actions of subscapularis
medial rotation of the arm
Innervation of the subscapularis
Upper and lower subscapular nerves
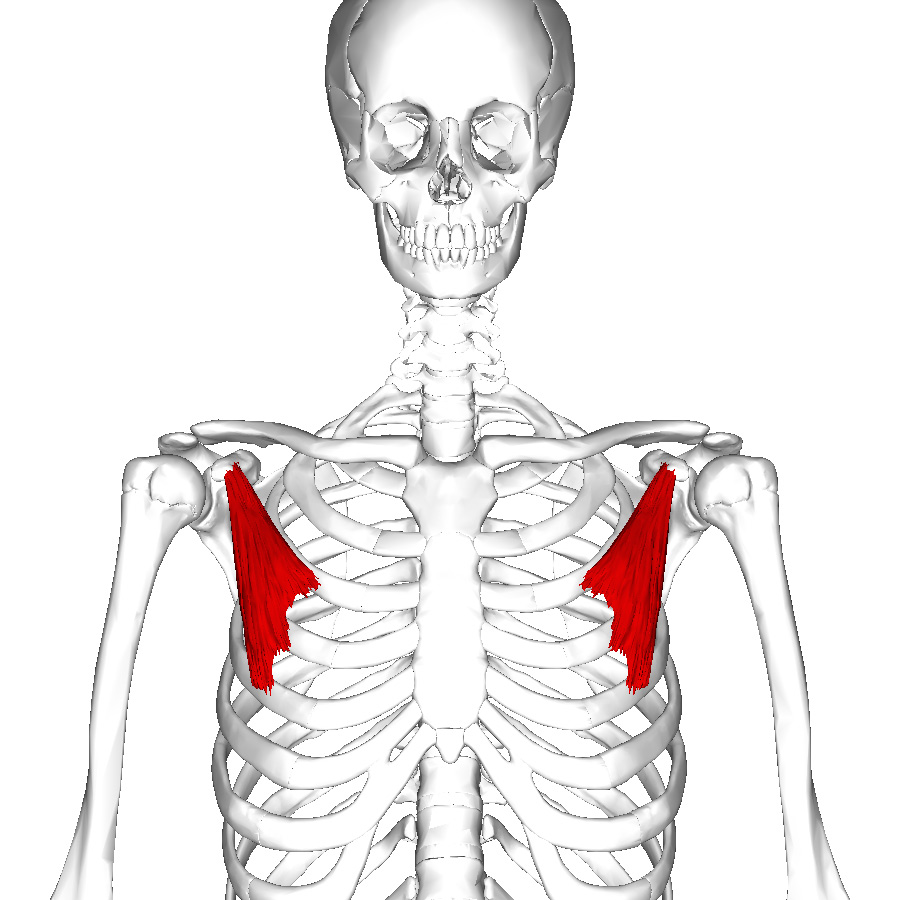
pectoralis minor
Pectoralsis minor origin
3rd -5 ribs
pectoralis minor insertion
coracoid process of scapula
pectoralis minor actions
stabilizes the scapula by drawing it anteroinferiorly against the thoracic wall
pectoralsis minor innervation
Medial pectoral nerve
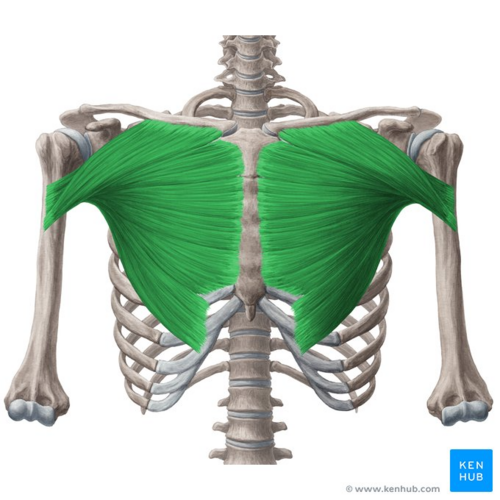
Pectoralis major
pectoralis major origin
clavicular head- originates from the anterior surface of the medial clavicle
sternocostal head- originates from the anterior surface of the sternum, the superior six costal cartilages and the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle
pectoralsis major insertion
intertubercular sulcus of the humerus (bicipital groove)
pectoralis major innervation
lateral and medial pectoral nerves
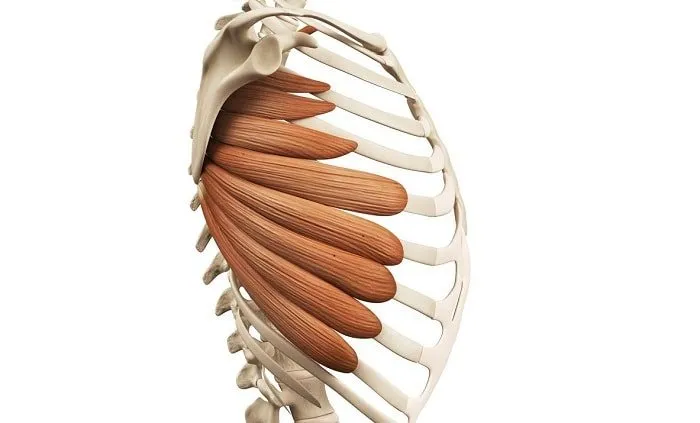
serratus anterior
serratus anterior origin
lateral aspects of ribs 1-8
serratus anterior insertion
costal (rib facing) surface of the medial border of the scapula
Serratus anterior actions
rotates scapula, allowing the arm to be raised over 90 degrees, also protracts the scapula, holding it against the ribcage
innervation of serratus anterior
long thoracic nerve
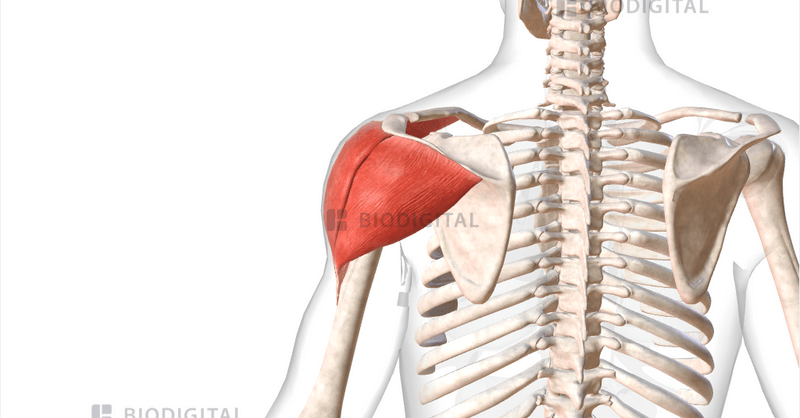
Deltoid
Deltoid origin
lateral third of the clavicle, the acromion of the spine of the scapula
Deltoid insertion
deltoid tuberosity on the lateral aspect of the humerus
Deltoid action
anterior fibers= flexion and medial rotation at the shoulder
posterior fibers- extension and lateral rotation at the shoulder
middle fibers- abduction at the shoulder - takes over from supraspinatus which abducts first 15 degrees.
Deltoid innervation
Axillary nerve
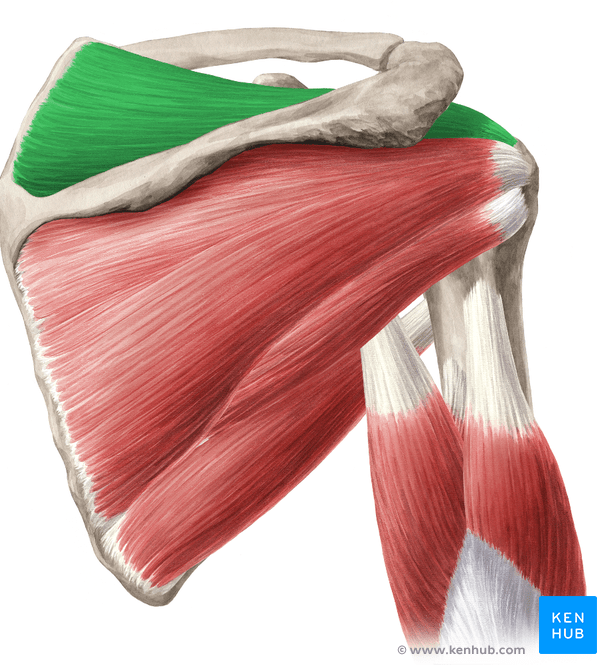
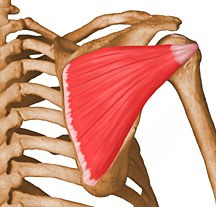
Supraspinatus
Supraspinatus origin
supraspinous fossa of the scapula
Supraspinatus insertion
greater tubercle of humerus
Supraspinatus actions
abduction of the upper limb at shoulder, performs first 15 degrees of abduction and assists deltoid until 90 degrees
Supraspinatus innervation
Suprascapular nerve
Infraspinatus
Infraspinatus origin
infraspinous fossa of the scapula
infraspinatus insertion
greater tubercle of the humerus
Infraspinatus actions
Lateral rotation of the upper limb at the shoulder
What three instances might the radius make contact with the humerus?
lateral force to the elbow
humerus load, like pushup
flexed elbow
what position is most likely to cause radial head fracture?
flexed elbow and supinated
A fall in this position on the arm?
What ligament runs from corocoid process to clavicle
coricoclavicular ligament
What ligament runs from the acromion to the clavicle?
Acromioclavicular ligament
What ligament runs from corocoid process to the acromion?
Coricoacromial ligament
What ligament runs from the base of the coracoid process to the humerus
coracohumeral ligament
What ligament wraps around the entire glenoid cavity and attaches to the humerus?
glenohumeral ligament
What ligaments make up the shoulder?
coricoclavicular ligament
Acromioclavicular ligament
Coricoacromial ligament
coracohumeral ligament
glenohumeral ligament
There is a ligament that goes from the clavicle to the humerus.
True
False
False
How many ligaments attach to coracoid process
3
Which ligament assists to support the ball and socket joint?
Glenohumeral ligament
How many degrees of freedom for Glenohumeral joint?
3
How many degrees of flexion in shoulder
180
How many degrees of extension for shoulder?
60
How many degrees of abduction for shoulder?
180
How many degrees of internal rotation of shoulder?
70
How many degrees of external rotation at the shoulder?
90
Where does upper extremities attach to the body?
sternoclavicular joint
Acromioclavicular joint characteristics
Wedge shaped articualar disc that typically wears away between our 20s and 40s
Acromion process characteristics
roof over the glenoid fossa and humeral head
Protects against trauma to the humeral head and superior dislocation
Common site for spurs, impingement, and pain with overhead activity
Characteristics of glenoid fossa
anteroposterior depth 2.5mm
superoinferior depth is 9mm
height of 35mm
width of 25
pear shaped
inverted comma
Humerus characteristics
2nd longest bone
head - 1.2 of a sphere, convex, part of glenohumeral joint
Greater tuberosity- supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor
Lesser tuberosity- subscap
Labrum
runs along outer edge of glenoid fossa, fibrocartilage, increases shoulder stability, doubles the depth of glenoid fossa, creates a seal for humeral head to attach onto
Bankart lesion
issue where part of glenohumeral ligament pulls on the inferior aspect of labrum and pulls lip of the labrum off
Subacromial bursa
reduces friction of the muscle on bone
ex: supraspinatus on acromion
Inferior part of capsule is saggy, why?
allows for flexion and abduction
In abduction, what is the roll and glide of shoulder?
Superior roll, inferior glide.
In flexion what is the roll and glide of the shoulder?
Anterior/superior roll, posterior/inferior glide.
in external rotation, what is the roll and the glide of the shoulder?
External rotation → Posterior roll, anterior glide
how many degrees of abduction does the scapula stay stationary for?
first 30 degrees
if the arm is abducted 30 degrees, how much is the inferior angle of the scapula rotated?
20 degrees laterally