Fruad Test 1
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Occupational fraud and abuse
Occupational fraud and abuse: the use of one’s occupation for personal enrichment through the deliberate misuse or misapplication of the employing organization’s resources
Fraud Examination vs Forensic Accounting
Fraud Examination vs Forensic Accounting
Forensic accounting is the use of accounting knowledge for courtroom purposes, therefore could include bankruptcy, divorce, etc
Fraud examinations are usually performed by accountants
Fraud Examination vs Auditing
timing
scope
objective
relationship
methodology
presumption
why conduct both
Fraud Examination vs Auditing
Issue:
Timing
Audit: Recurring
Examination: nonrecurring
Scope:
Audit: General
Examination: Specific
Objective:
Audit: opinion
Examination: addix blame
Relationship:
Audit: Non-adversarial
Examination: adversarial
Methodology:
Audit: audit techniques
Examination: fraud examination techniques
Presumption:
Audit: Professional Skepticism
Examination: Proof
Why conduct an audit? - It is a recurring requirement
Why conduct a fraud examination?
Based on predication: a total of circumstances exist that whenever a reasonable person thinks a fraud has, is, or will occur
Fraud examinations encompass more than just the review of financial data they include interviews, record searching, and forensic document examinations
Predication
Predication
Totality of circumstances that would lead a reasonable, professionally trained and prudent individual to believe fraud has occurred, is occurring and/or will occur
Fraud examinations must be based on predication
How to conduct a fraud examination:
How to conduct a fraud examination:
Documentary evidence
Interviewing witnesses
Writing investigative reports
Testifying in court
This is where the forensic accountancy scope must get into the courtroom
Analyze available data
Create a hypothesis
Test the hypothesis
Refine and amend the hypothesis
Elements of Fraud
Elements of Fraud
A material false statement
Knowledge that the statement was false when it was uttered
Reliance on the false statement by teh victim
Damages resulting from teh victim’s reliance on the false statement
Researchers on occupational fraud and abuse
Researchers on occupational fraud and abuse
Edward Sutherland claims that white collar crime isn’t a bad person who set out to commit a crime, it is learned and developed
Donald Cressey created the fraud triangle
Cressey’s hypothesis
Steve Albrecht- created the Fraud Scale
Richard Hollinger looks at data, the workplace
Fraud Triangle
Fraud Triangle
Opportunity: mitigated by internal controls
General information vs technical skill
General: doors are always unlocked, everyone has access to the system
Technical: I have this specific asset and expertise
Pressure: something unique to me, something I need that I have pressure because of
Cressey found that these are the nonshareable problems that fall into 6 categories
Violation of ascribed obligations - people in trustworth positions feel like they are being held to higher standards and when they cannot maintain that(ie they get in debt because of a drug addiction) they feel the need to steal to maintain self-image (embarrassed they are in debt due to drugs)
Problem resulting from personal failure - this is a result of pride and not wanting to let people know you made a bad decision (ran your business into the ground)
Business Reversals - your business is failing due to factors outside of your control(interest rates, a poor economy, etc)(status still plays a role even though it is outside of their control)
Physical Isolation - someone has nobody to ask for help and feels stuck
Status- gaining - desire for a better lifestyle
Employer- employee relations -an employee resents thier status
However, all situations deal in some way with status seeking or status maintaining
Rationalization: can be shared amongst everyone
You think this is essentially noncriminal
Somehow justified
Part of general irresponsibility (they are asking for it)
Hollinger says there is a relationship to workplace dissatisfaction
Fraud scale
Fraud scale
Situational pressures
Opportunity
Integrity
Stats
Stats
Hard to quantify, may be close to 5% of all transactions
Most theft is done by employees, then managers, then owners/execs
However, owners/execs steal much more than managers do than employees do
Guys do it twice as often and twice the amount of $
The most common department a person is in is teh accounting/finance department
Most of the time ha never gotten charged with a crime
Usually frauds are detected by tips(external fraud only detects 3% of fraud)
Ussullay its an employee however and owenr/executive steals more
Usually male and men steal more
Usually in accounting
Teh hughet loss is by mangement/upper management
Most have never been charged
Usually detected by tips
Occupational fruad and abuse
Fraud Theroy Aproach
Fraud Theroy Aproach
Analayzed available data
Jeff skilling announced resignation
Create a hypotheses
WSJ says something seems shady
Test the hypothesis
Interview Jeff Skilling
Refine and amend the hypothesis
Jeff Skilling says the stock price impacted this decision so we go back to the related party section from teh 10Q adn then the 10K- they then relized that these arrangements have been around for awhile
Then we go public, and a whistleblower comes forward
Whistleblower confirms inappropriate structure and suggests broader significant concerns
who is responaible for the Fs
Company management is responsible for the financial statements
The company’s board of directors and senior management set the code of conduct
The CEO and CFO sit on both the board of directors and are responsible for the financial statements
who are teh users of fs
Users of fs
Transaction activity is captured in the accounting system, which then flows to fs and is communicated to users who make decisions on investments, loan terms, etc.
The decision aspect is where damages incur
Who commits FS fraud?
Who commits FS fraud?
Senior management
Mid and lower-level employees can do it, but are less incentivized
Organized criminals
Why do people commit fs fraud?
Why do people commit fs fraud?
To conceal true business performance
To preserve personal status/control
To maintain personal income/wealth
Overstate performance
To meet or exceed the earnings or revenue growth expectations of stock market analysts
To show a pattern of growth to support a planned securities offering or sale of the business
To comply with loans covenants or meet a lenders criteria for granting or extending loanfcitlites
To meet goals from parent companies
Satisfying analyst expectations
To meet personal performance criteria
To trigger performance related compensation or earn payouts
To support the stock price in an acquisition or merger
Understand performance
To take all possible write-offs in one “big bath” now so future earnings will be consistently higher
Have one giant impairment loss, rather than taking some in following periods
To defer surplus earnings to teh next accounting period
To reduce expencations
To preserve a trend of consisten growth avoiding volatile results
To come out on top in a divorce settlement
Missed one
How do people commit FS fraud
How do people commit FS fraud
Playing the accounting system - least egregious
Arguing LT assets have longer lives than they do, aggressive with BDE
There is a level of judgement you are taking advantage of
Beating the accounting system
False and fictitious information into the accounting system
Documents are forged to support claimed numbers
Going outside the entire system
Produces what ever fs you want
Don’t record something or make false JE
You may just change the FS themselves or leave sometime out
Change numbers directly on FS
how does a change in stock price relate to fs fruad
Damages in financial statement fraud are not changes in stock price
That does not fully capture the extent of damages(IE loan approval, fincncail investment decisions, etc.)
Conceptual framework for financial reporting
measurement assumptions
measuremnt principles
contratins
qualative characteristics
Conceptual framework for financial reporting
Recognition and measurement assumptions:
Economic entity
Going concern
Monetary unit
Periodicity
Recognition and measurement principles
Historical cost
Revenue recognition
Matching
False disclosure
Recognition and measurement contraints
Cost-benefit
Materiality
Industry practice
Conservatism
Recognition adn measurement of qualitative characteristics
Revlaence and reliability
Compariablity adn consistency
SOX Goals and 7 new rules
Sarbanes-Oxley Act
SOX GOALS:
Establishing higher standards for corporate governance and accountability
Create an independent regulatory framework for the accounting profession
Enhancing teh quality and transparency of financial reports
Developing severe civil and criminal penalties for corporate wrongdoesrs
Establish new protections for whistleblowers
SOX rules: 7 new sox rules are covered in depth below
Management must report on IC
Increase disclosures in management’s discussion
Conditions for use of Non-GAAP measures
Certification of disclosure by CEO and CFO of companies' quarterly adn annual reports
Disclosures for ethics
New standards for attorneys
Standards for audit committees
Audio independence
Retention of record and workpaper
what did the estpblishmen to fthe PCAOB do
PCAOB was established
Purpose: to oversee the audit of public companies that are subject to the sercuriteis laws, and related matters, in order to protect the interests of investors and further the public interest in the preparation informative, accurate, and independent audit reports for companies, the securities of which are sold to, and held by and for public investors
What do they do?
The registered public accounting firms that audit publicly traded companies
Establishing or adopting auditing, quality control, ethics, independence and other standards for public companies
Inspecting registered public accounting firms
Investigate registered public accounting firms adn their employees, conducting disciplinary hearings nad imposing sanctions where jsutfiied
Peroform other dutires necessary to improve the quality of audit services
Enforce compliance with sarbanes oaxley the rules of the board, professional standards and securities law
Certification obligations of CEOs and CFOs
Certification obligations of CEOs and CFOs
Criminal certification: teh have ot say they did not
knowing violates teh certification requirements is up to $1 million and up to 10yrs in prision
willfully(worse) violate teh cerfiticaiton is up $5 million and up to 20 years in prision
Civil certification, they have to say
They have personally reviewed teh report
Based on the knowledge, the report does not contain a material weakness
Based on management knowledge, there are no issues with teh financial conditions and internal controls
The disclosure to teh auditor of any material weaknesses in teh controls and any fraud
General Standards for audit committee independence
Standards for audit committee independence
The audit committee has increased responsibilities
There needs to be a financial expert
Changed teh composition of the audit committee
Established a whistleblowing structure
Standards for auditor independence
Standards for auditor independence
Restrictions(not necessarily never allowed) on non-audit activity:
Bookkeeping services
Financial information system design and implementation
Appraisal or valuation services, fairness opinion or contribution in kind reports
Acutalal services
Internal audit outsource services
Management function or HR
Legal services and expert services unrelated to the audit
Any other service that the PCAOB prescribes
Mandatory audit partner rotation
Conflict of interest provisions
Improper influence on audits
Auditor reports to audit committees
All critical accounting policies and procedures use
Aletnerative GAAP method
Communication of any material weakness
Improper influence on audits
Enhanced fincncail disclosure requirements
Enhanced fincncail disclosure requirements
Off-balance sheet transactions
Pro forma financial information
Prohibitions on personal loans to executives
Restrictions on insider trading
Code of ethics for senior fincnical officers
Enhanced review of periodic filings
Real time disclosures
Protections for whistleblowers
Protections for whistleblowers
Civil liability whistleblower protection: creates civil liability for a company that retaliates against whistleblowers
Protects only employees of publicly traded companies
Employees must report the suspected misconduct to a federal regulatory or law enforcement agency
Employees are protected against retaliation for filing, testifying in, participating in, or otherwise assisting in a proceeding
Protected even if there was no fraud, as long as it was a reasonable thought
The employee will also get compensatory damages if there was fraud to make the employee whole
Criminal: makes it a creim eot knowingly retaliate
Information must be provided to law enforcement
Broader than civil liability protections cover all individuals regardless of where the work is
Enhanced penalties for white collar crime
Enhanced penalties for white collar crime
White collar crime:
Attempt and conspircay
Mail fraud and wire fraud
Securities fraud
Document destruction
Bankruptcy loopholes
Repercussions:
Freezing of assets
Disgorgement of bonuses
Fraud Risk
Why be concerned about fraud risk?
Fraud Risk: vulnerability of an organization to overcoming the interrelated elements that enable someone to commit fraud
Why be concerned about fraud risk?
Awareness of risk is key to establishing a mechanism to reduce risk
Internally or externally
No organizatino is immune
Factors that influence fraud risk:
Factors that influence fraud risk:
Nature of business
Operating environment
Effectiveness of internal controls
Ethics and values
Fraud risk assessment:
Fraud risk assessment: a process aimed at proactively identifying and addressing an organization’s vulnerabilities to internal and external fraud
To help an organization recognize what makes it most vulnerable so that it can take proactive measures to reduce its exposure
Why conduct a fraud risk assessment:
Why conduct a fraud risk assessment:
Improve communication adn awareness of fraud
Identify what activities are most vulnerable to fraud
Develop plans/techniques to mitigate and identify fraud risk
Comply with regulations and professional standards
PCAOB AS 5 effectively requires a fraud risk assessment with the assessment of internal controls
A good risk assessment:
A good risk assessment:
Collaborative effort of management and auditors
Independence and objectivity of the people leading and conducting the work
A good working knowledge of the business
Access to all levels of the organization
Engendered trust
A plan to keep it alive and relevant
Packaging it right: the deliverable - an audit gives an opinion and an audit committee deck - tailor the communication approach to the organization
One size does not fit all - adapt the framework to the business model and culture
Keeping it simple - focus on areas that are most at risk for fraud
Assembling the right team -
Accounting adn finance personnel
Personnel who have knowledge of day-to-day operations
General counsel, compliance functions, internal audit, external consultants
Determing the best techniques:
Interviews
Focus groups
Surveys
Anonymous feedback mechanisms
Educating the organization and openly promoting the process
Obtaining the sponsor’s agreement on work
Scope, methods, participants, form of output
Execution of fraud assessment: 7 steps
Execution: 7 steps
Identify potential inherent fraud risks
Fraud risk triangle
Risk of management’s override of controls
Population of fraud risks:
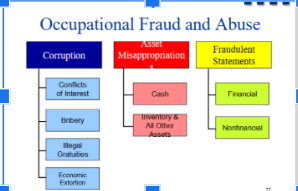
fraudulent financial reporting
Asset misappropriation
Collusion opportunities
Regulatory and reputation risk
Information technology
Assessing the likelihood of the occurrence of the identified fraud risk
Past instances
Industry
Support of management
Unexplained losses
Complexity of risk
Complaints from vendors/customers
Assessing the significance of fraud risks
Fiancncail statement and monetary significance
Financial condition of the organization
Value of the threatened assets
Signifcaince to the organization’s operations, brand value and reputation
Evaluating which periole and departments are most likely to commit fraud and identifying the methods that they are likely to use
Identifying and mapping existing preventative and effective controls
Evaluating whether the identified controls are operating effectively and efficiently
Review accounting policies and procedures
Interview management and employees
Observe control activities
Perform sample control testing
Review past reports
Identifying and evaluation the residual fraud risks resulting from ineffective or nonexistent controls
Addressing fraud risk
Addressing fraud risk
Establishing an acceptable level of risk
Responding to residual fraud risk
Avoid the risk
Transfer the risk
Mitigate the risk
Assume the risk
Report the results objectively
Keep it simple
Identify clear and measurable objectives
Relationship with the audit process
Relationship with the audit process
Auditors should validate that the organization is managing the moderate-to-high risks
Evaluate internal controls
Assess management override of internal controls
Deliver reports that incorporate the results of testing controls