IGCSE Edexcel Chemistry : 1 Principles of Chemistry
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Describe the arrangement of particles in a gas
1. the particles are not touching and are far apart from each other
2.no forces of attraction between particles
How do particles change from a solid to a gas ?
sublimation
heated
How do particles change from a gas to a solid?
deposition
cooled
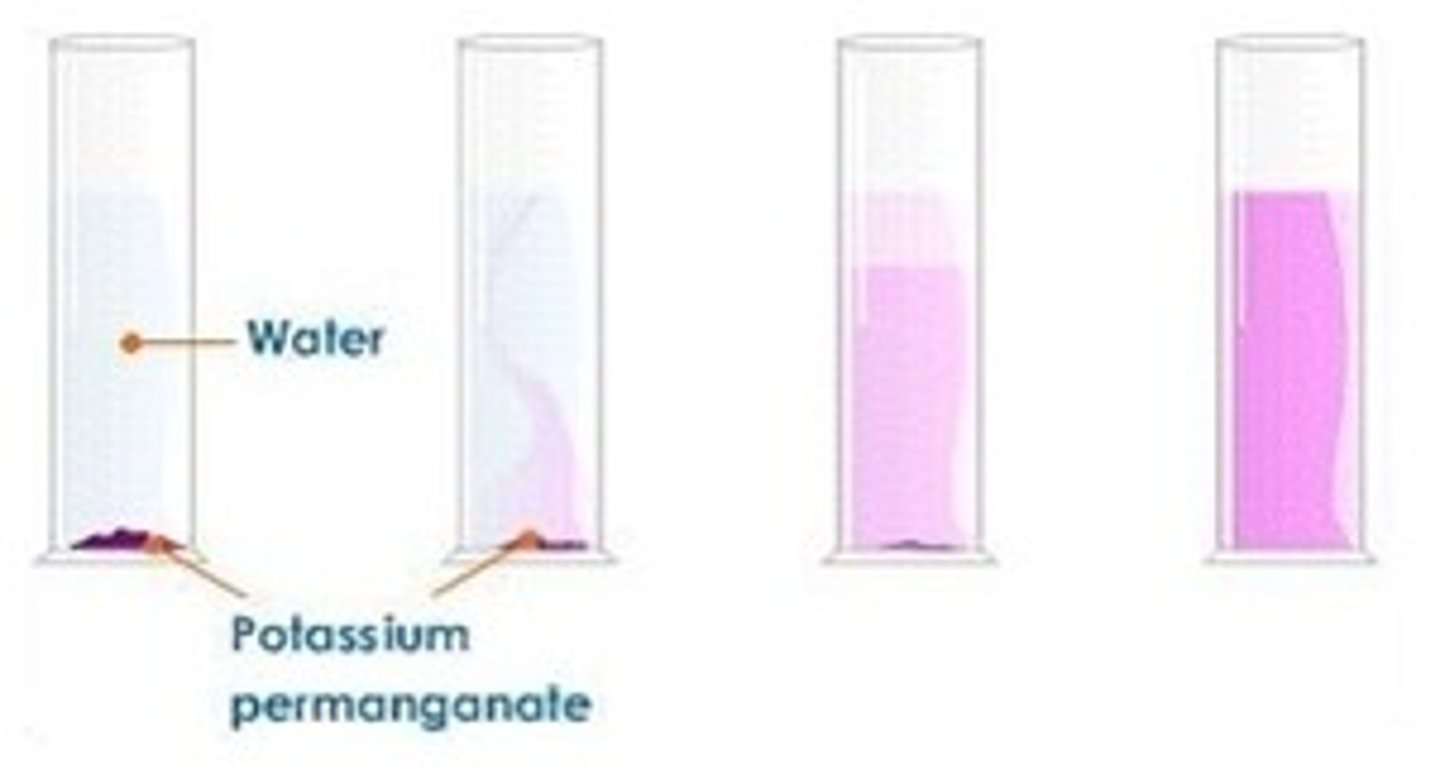
Practical: dilution of coloured solutions
when we add potassium manganate(VII) solution to a gas jar of water , the purple colour crystals) slowly diffuse across until the whole solution is the same colour
this is because the particles in a liquid move more slowly than the particles in a gas , also gas particles have more space to move into without colliding with other particles
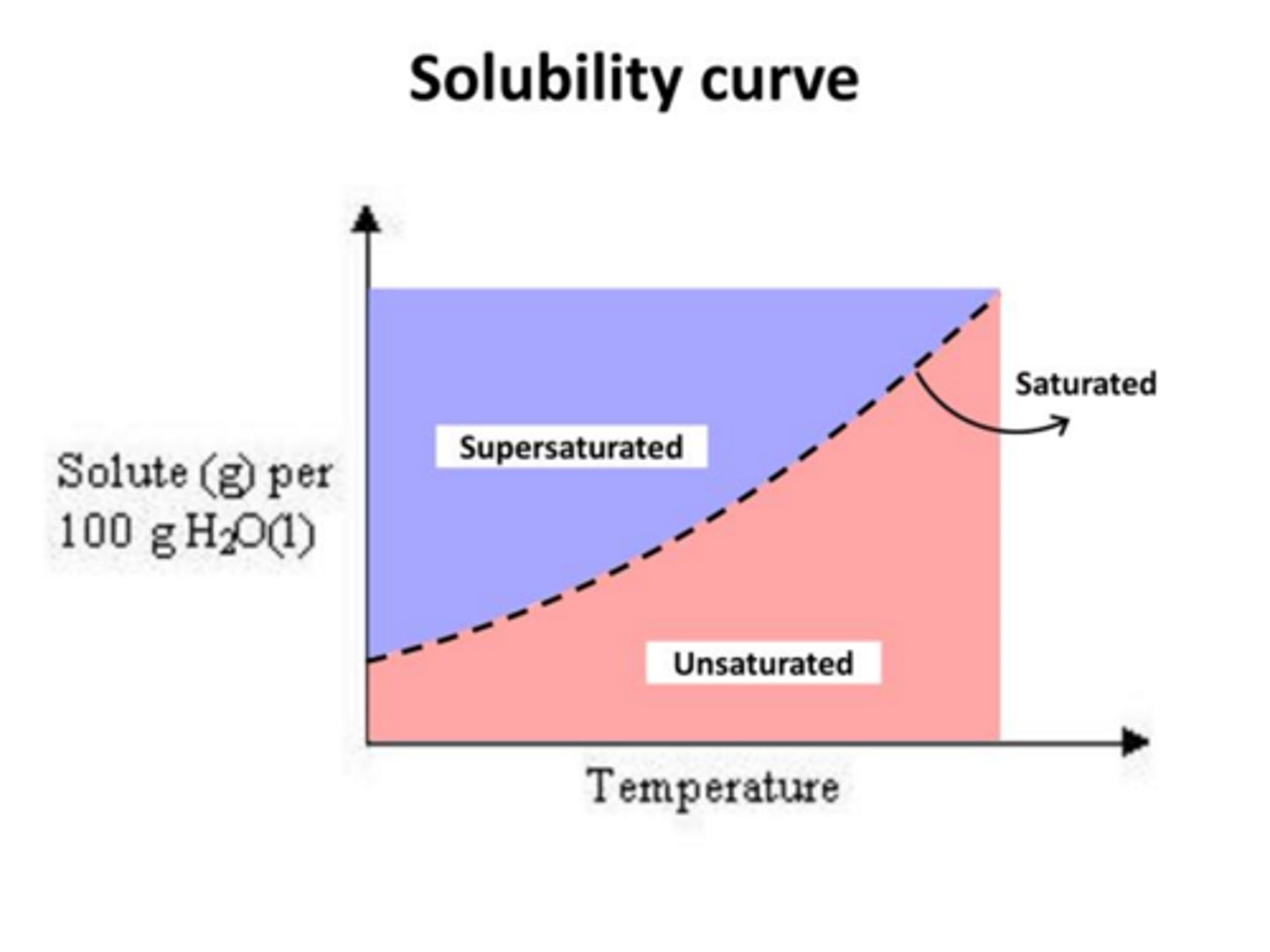
Define the term saturated solution
a solution which contains as much dissolved solid as possible at a particular temperature
Define the term element
substances that can't be split into anything simpler by chemical means
Define the term compound
two or more element chemically bonded together
Define the term mixture
Two or more different elements or compounds not chemically bonded together
If a substance is pure what does that tell us about its melting and boiling point
pure substances melt and boil at fixed temperatures
if there are impurities the melting point decreases and the boiling point increases
If a substance is a mixture what does that tell us about its melting and boiling point
it may melt or boil over a range of temperatures
Define the term particle
a small object. In chemistry , particle can be used to refer to atoms, molecules, ions or the subatomic particles , including protons, neutrons and electrons
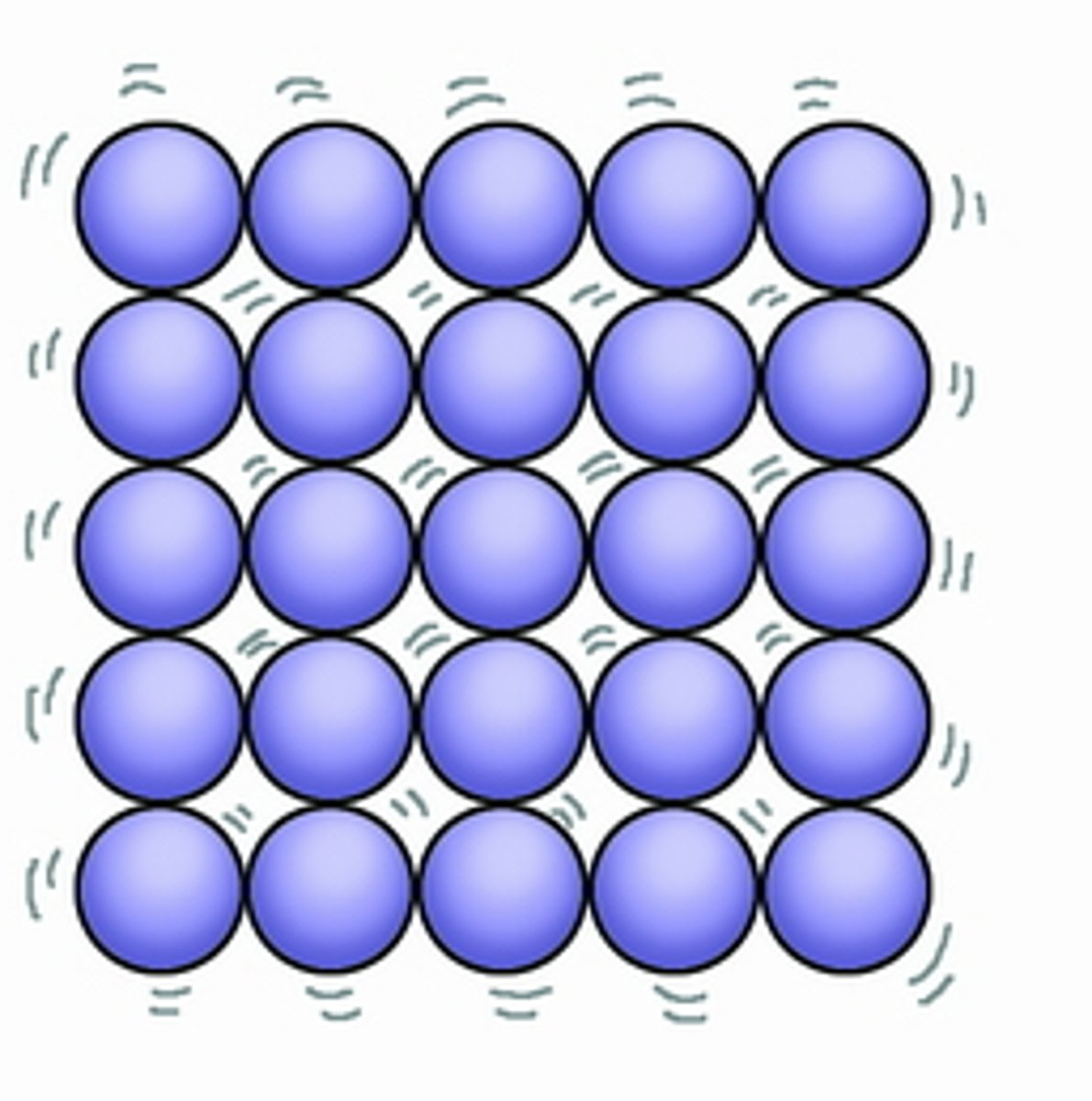
Describe the arrangement of particles in a solid
1. regularly arranged
2. packed closely together
3. strong forces of attraction between particles
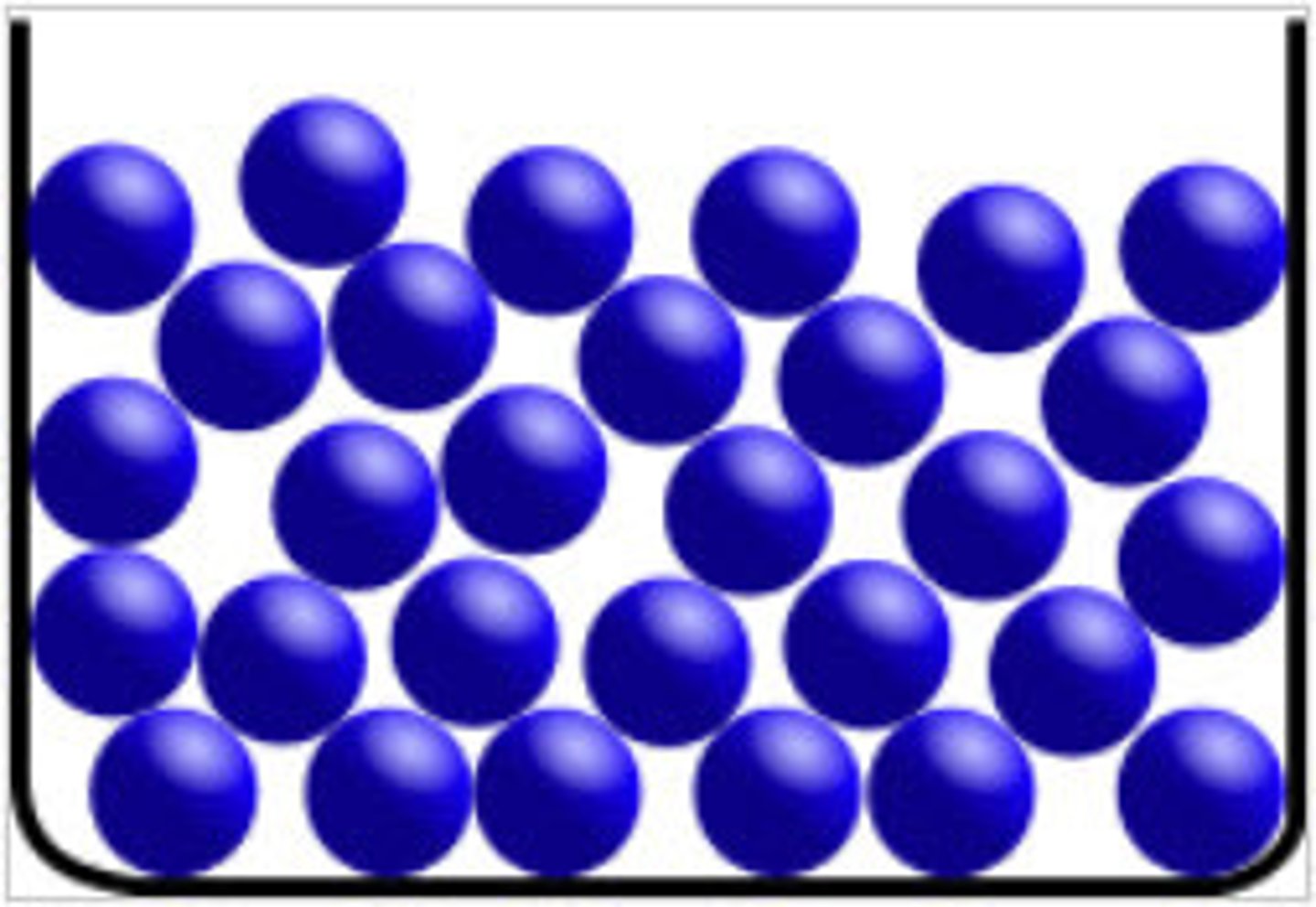
Describe the arrangement of particles in a liquid
1. particles are mostly touching
2. some gaps have appeared between particles
3. particles arranged randomly
4.weak forces of attraction between particles
Describe the movement of particles in a solid
vibrating about fixed positions
Describe the movement of particles in a liquid
the particles are moving around each other
Describe the movement of particles in a gas
the particles are moving quickly in all directions rapidly and randomly
Describe the energy of the particles in a solid
low kinetic energy
Describe the energy of the particles in a liquid
more kinetic energy than solid
Describe the energy of the particles in a gas
high kinetic energy
How do particles change from a solid to a liquid ?
melting
1. solid is heated so that the particles vibrate fast enough
2. so that the forces of attraction can't hold them together
3.and the particles can then move around each other
How do particles change from a liquid to a gas?
boiling and evaporation
Boiling:
1. liquid strongly heated
2. particles move fast enough to overcome all forces of attraction
Evaporation:
1. the speed of particles in a liquid vary
2. some very fast particles at the surface have enough energy to overcome forces of attraction and they break away to form a gas
How do particles change from a liquid to a solid?
freezing
1. liquid is cooled,
2. particles move slower ,
3. eventually forces of attraction can hold them into a fixed position
How do particles change from a gas to a liquid?
condensation
1. if a gas is cooled the particles move slowly enough
2. so that forces of attraction between them start to form
3. the particles get held together as a liquid
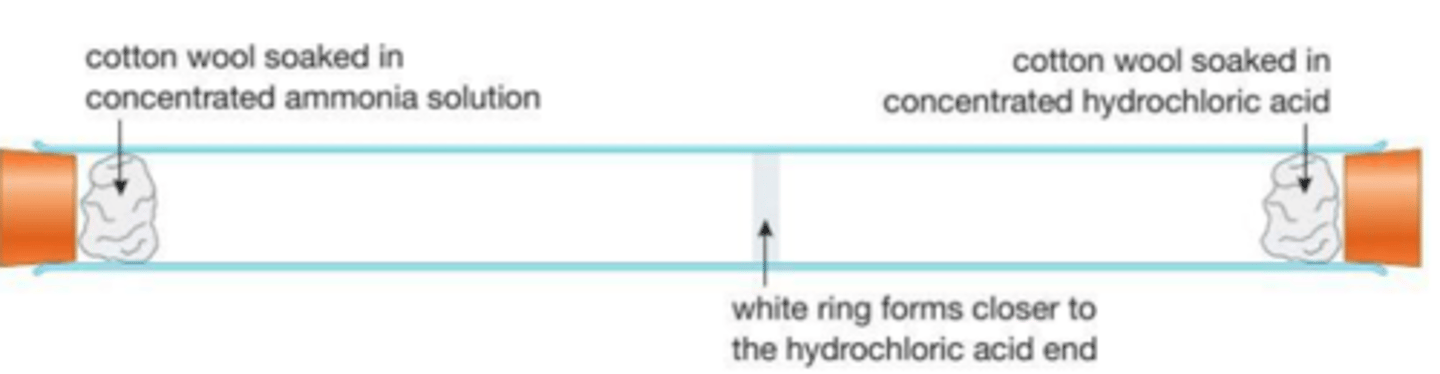
Practical: diffusion of gases
place two pieces of cotton wool soaked in ammonia and HCl at opposite ends
NH4Cl forms and a ring forms closer to the HCl as the ammonia is lighter and travels faster
Define the term solvent
the liquid that dissolves a solid
Define the term solute
the substance that gets dissolved in the liquid
Define the term solution
once the substance is dissolved the liquid formed is a solution
Define the term solubility (in the units g per 100g of solvent)
the mass of solute which must dissolve in 100g of solvent at that temperature to form a saturated solution
How do you interpret solubility curves
tells us how much solid dissolves in 100g solvent at each temperature
( solubility on y temp on x)
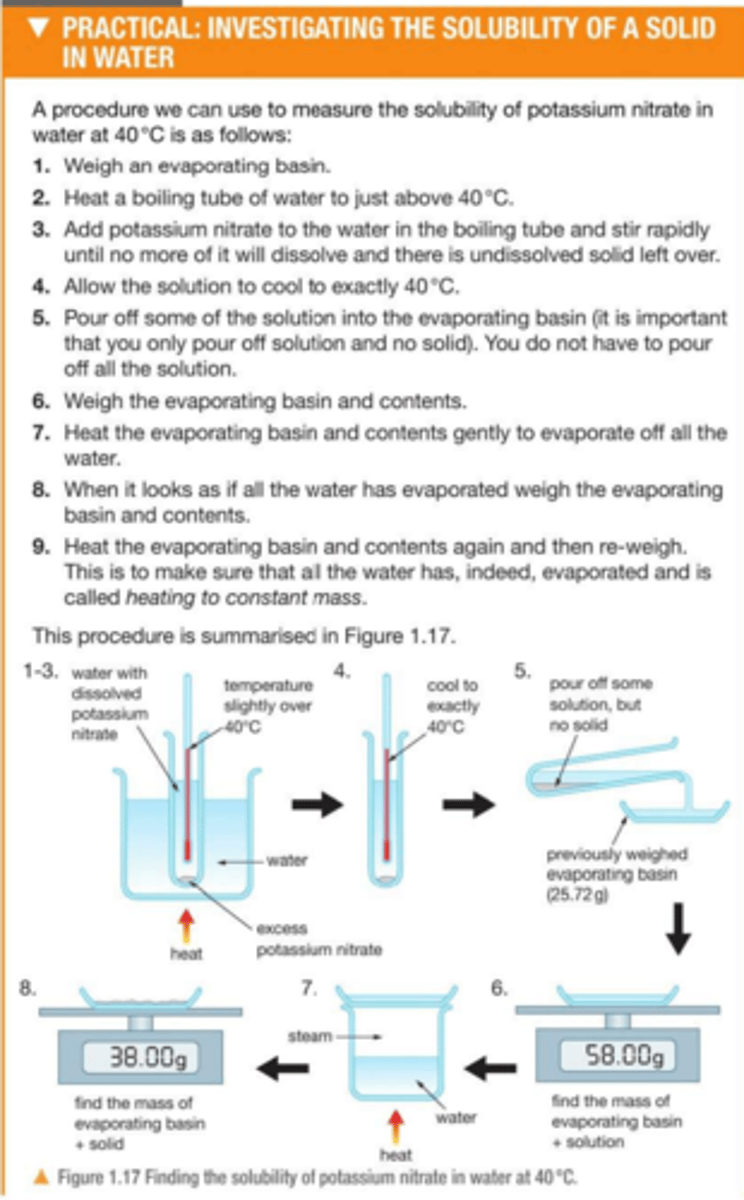
Practical: investigate the solubility of a solid in water at a specific temperature
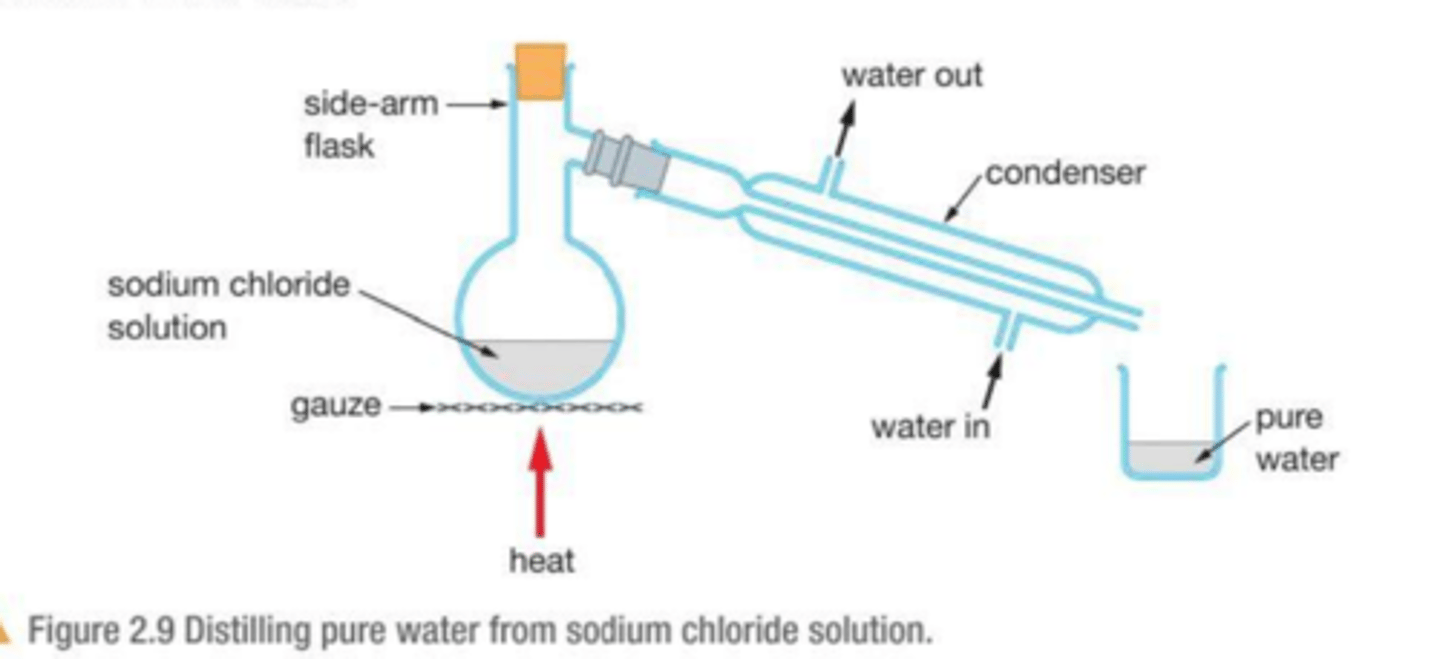
Describe the process of : simple distillation
simple distillation separates the components of a solution with a big difference in boiling points or when there is not a high purity requirement (e.g. salt from solution)
1. the mixture is heated and the component with the lower boiling point vaporises first
2. the vaporised component rises and passes into a condenser, the condenser is cooled causing the vapor to condense back into a liquid
3. the condensed liquid is collected in a separate container and the other liquid is left in the flask
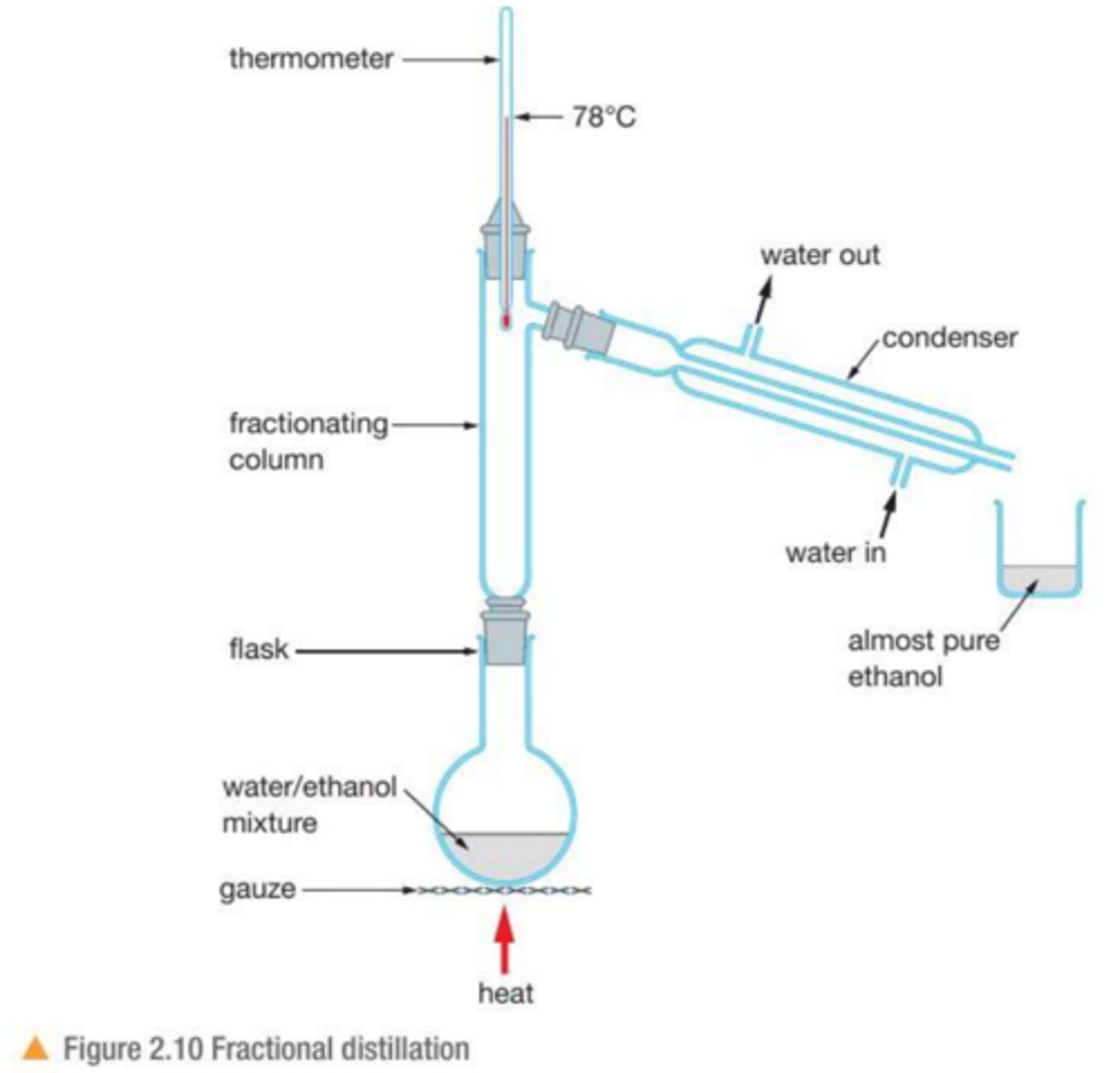
Describe the process of : fractional distillation
used to separate a mixture of liquids with similar boiling points or when there is a high purity requirements
1. solution is heated , water evaporates
2. the fractionating column allows for better separation
3. the solution condenses in the condenser and is collected in a beaker
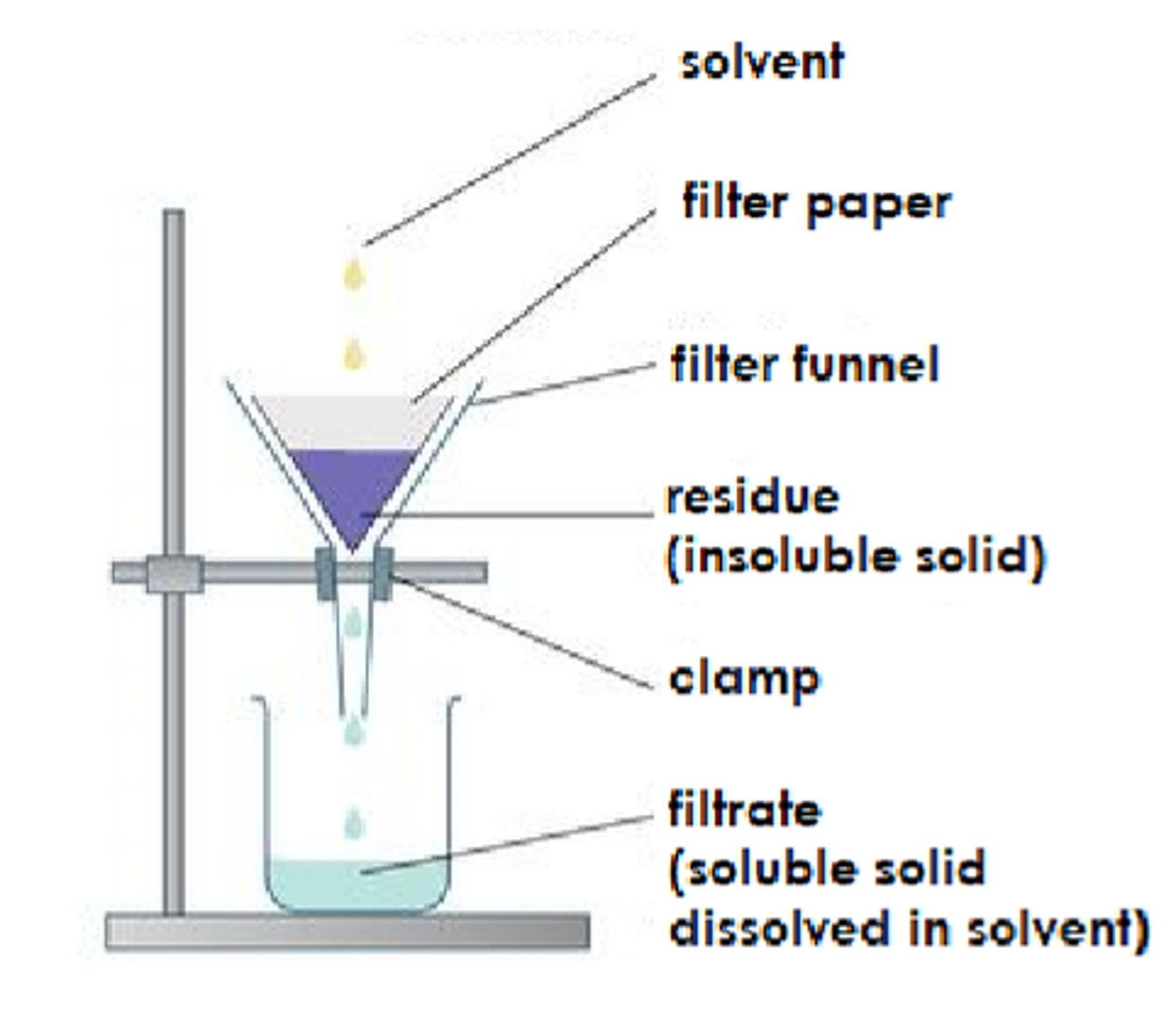
Describe the process of : filtration
to separate insoluble solids from a liquid or a solution
filtrate is trapped in the filter paper and the liquid collects in the beaker
Describe the process of : crystallisation
used to separate a solute from a solution
1. the solution is heated in an evaporating basin
2. until some of the water is evaporated and an almost saturated solution is formed
3. then dip a glass rod into solution and take it out to check if crystals form quickly
4. turn off Bunsen burner and let solution cool
5. the crystals can be removed by filtration
Describe the process of : paper chromatography
the base line must be drawn in pencil so the ink doesn't dissolve the spots into it
the solvent level must be below the base line so it doesn't dissolve the spots into it

What can we infer from a chromatogram?
the more soluble the dye is in the solvent the further it will move up the paper
each dye will be separated into smaller dyes , so we can see if dyes contain parts of each other
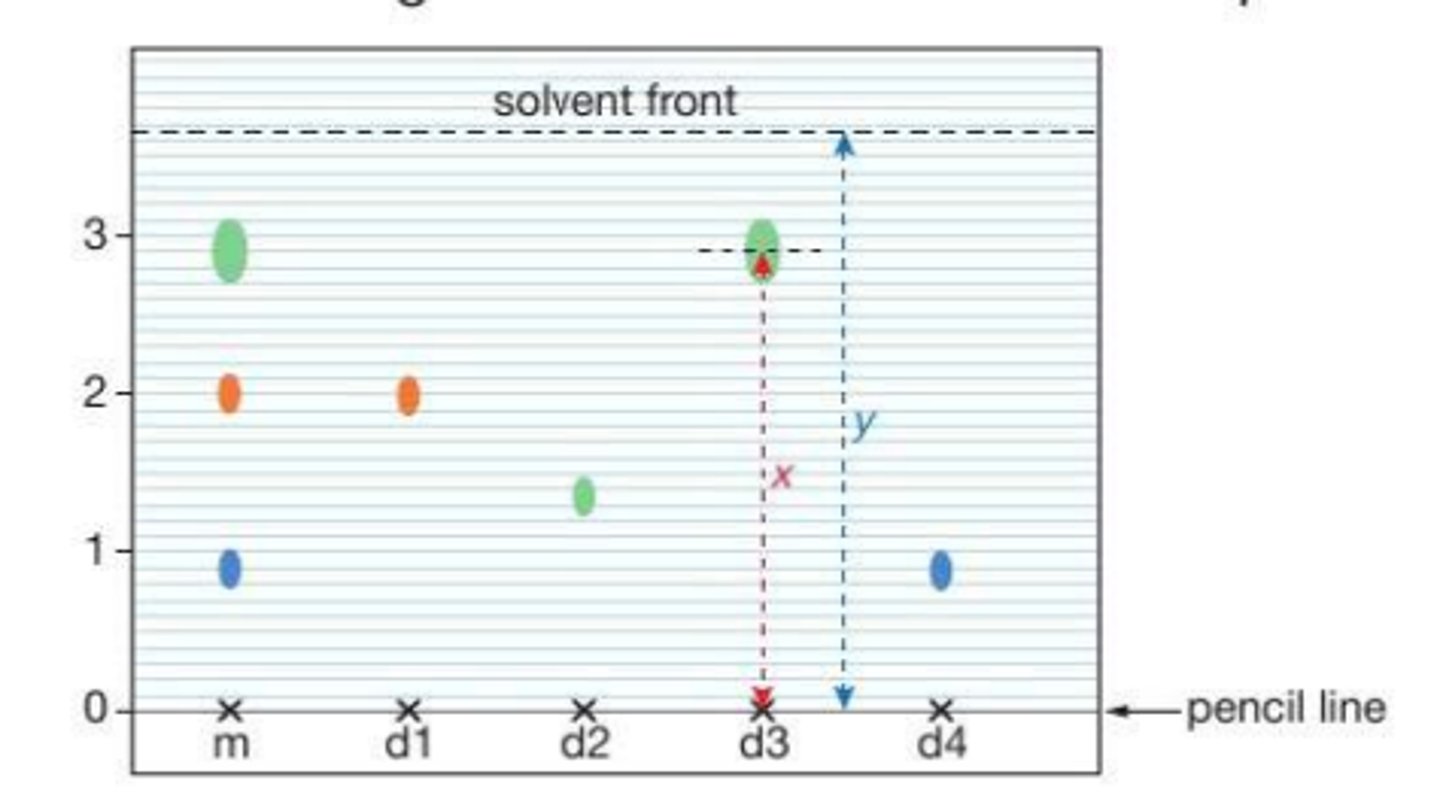
How do we calculate Rf values and what do they tell us ?
Rf= distance moved by spot (from pencil line)/ distance moved by the solvent front (from the pencil line)
they tell us how pure the compound is
Define the term atom
the smallest piece of an element that can still be recognised as that element
Define the term molecule
two or more atoms chemically bonded
Describe the structure of an atom
an atom consists of a central positively charged nucleus containing protons and neutrons
surrounded by negatively charged electrons
Describe the properties of a neutron
1. has a mass of 1
2. has a charge of 0
3. found in the nucleus
Describe the properties of a proton
1. has a mass of 1
2. has a charge of 1+
3. found in the nucleus
Describe the properties of a electron
1. has a mass of 1/1800
2. has a charge of 1-
3. found in the outer shells of the atom
Define the term atomic number
the number of protons in an atom's nucleus
Define the term mass number
also called nucleon number
number of protons + number of neutrons
Define the term isotope
isotopes are atoms of the same element which have the same atomic number but different mass number.
They have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
Define the term relative atomic mass (Ar)
the weighted average mass of the isotopes of an element, relative to 1/12th mass of a carbon 12 atom
How do you calculate the Ar from isotopic abundances
1. multiply the mass of each isotope by the percentage
2. add all these values up and divide that number by 100
3. the relative mass of the element will be a %
How are elements arranged in the periodic table
by increasing atomic number
How do you find the electronic configurations of elements in the periodic table ?
the group number tells you the number of electrons in the outer shells
the period number tells you the number of shells of the atom
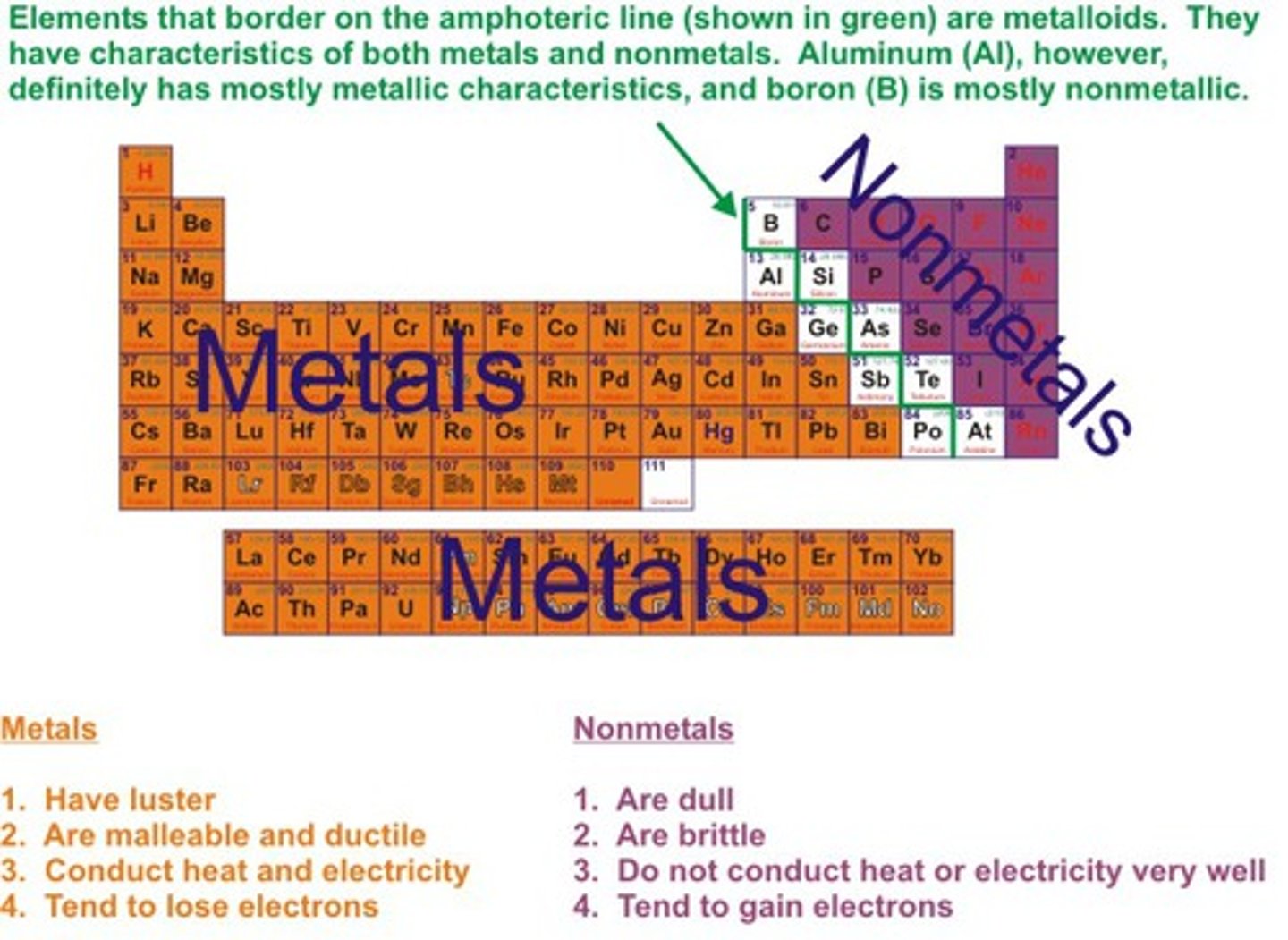
How do you classify elements as metals or non-metals?
metals are conductors of heat and electricity
non-metals are poor conductors of electricity
metals form positive ions
non-metals form negative ions
metallic oxides are alkaline and react with water to form hydroxide ions
non-metallic oxides are acidic and react with water to form hydrogen ions
Where on the periodic table are metals and non-metals ?
How does the electronic configuration of an element affect its position in the periodic table ?
the higher the number of electrons the lower down it goes (period number increases)
Why do elements in the same group in the periodic table have similar chemical properties
they have the same number of electrons in their outer shell
which determines how they react with other substances
Why do noble gases not readily react ?
they have a full outer shell and do not need to lose or gain electrons to complete their shells as they are stable and are chemically inert
How do you write a balanced equation ?
First write the skeleton equation.
Then use coefficients to balance the equation so that the number of each element balance each other out .
How do you calculate relative molecular mass from relative atomic mass
you add up the relative atomic mass of each element in the compound
What is a mole?
the unit of amount of a substance
How do you calculate moles of a substance , using Ar and Mr?
number of moles = mass / Mr
How do you calculate reacting masses using experimental data and equations?
1. use n= mass/mr
2. multiply n by the coefficient of the reacting amount
3. substitute into equation mass = n x Mr
How do you calculate percentage yield?
(actual yield/expected yield) x100%
How do you find the formulae of compounds, including metal oxides, water and salts, containing water of crystallisation ?
To find the mass of water there are a variety of calculations you may have to do
use n=mass/mr to find the number of moles of water
What does the term empirical formula mean
the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms present in a compound . It can be worked out from experimental data.
What does the term molecular formula mean ?
the actual number of each type of atom present in a molecule (covalent compound) or formula unit (ionic compound)
How do you carry out calculations for moles ,volume and concentration
number of moles = volume x concentration
to convert from centimetres to decimetres divide by 1000
How do you carry out calculations involving gas volume, molar volume of a gas ?
molar volume = 24 decimetres cubed
number of moles = volume of gas/molar volume
n = volume/24
(this is at room temperature and pressure)
practical: know how to determine the formula of a metal oxide by combustion (e.g. magnesium oxide)

practical: know how to determine the formula of a metal oxide by reduction (e.g. copper (II) oxide)

How are ions formed
ions are formed by atoms losing or gaining electrons
What are the charges of metals in group 1
1+
What are the charges of metals in group 2
2+
What are the charges of metals in group 3
3+
What are the charges of non-metals in group 5
3-
What are the charges of metals in group 6
2-
What are the charges of metals in group 7
1-
What is the charge of silver ions
1+
What is the charge of copper ions
2+
What is the charge of iron(II) ions
2+
What is the charge of iron(III) ions
3+
What is the charge of lead ions
2+
What is the charge of zinc ions
2+
What is the charge of hydrogen
1+
What is the charge of hydroxide
1-
What is the charge of ammonium
1+
What is the charge of carbonate
2-
What is the charge of nitrate
1-
What is the charge of sulfate
2-
How do you write formulae for compounds ?
you must balance the charges so they equal zero,
you do this by increasing the numbers of atoms of each element in the compound by adding a subscript number
How do you write formulae for compounds containing radicals
you draw brackets around radicals and treat the brackets like normal atoms
How do you draw dot an cross diagrams for the formation of ionic compounds ?
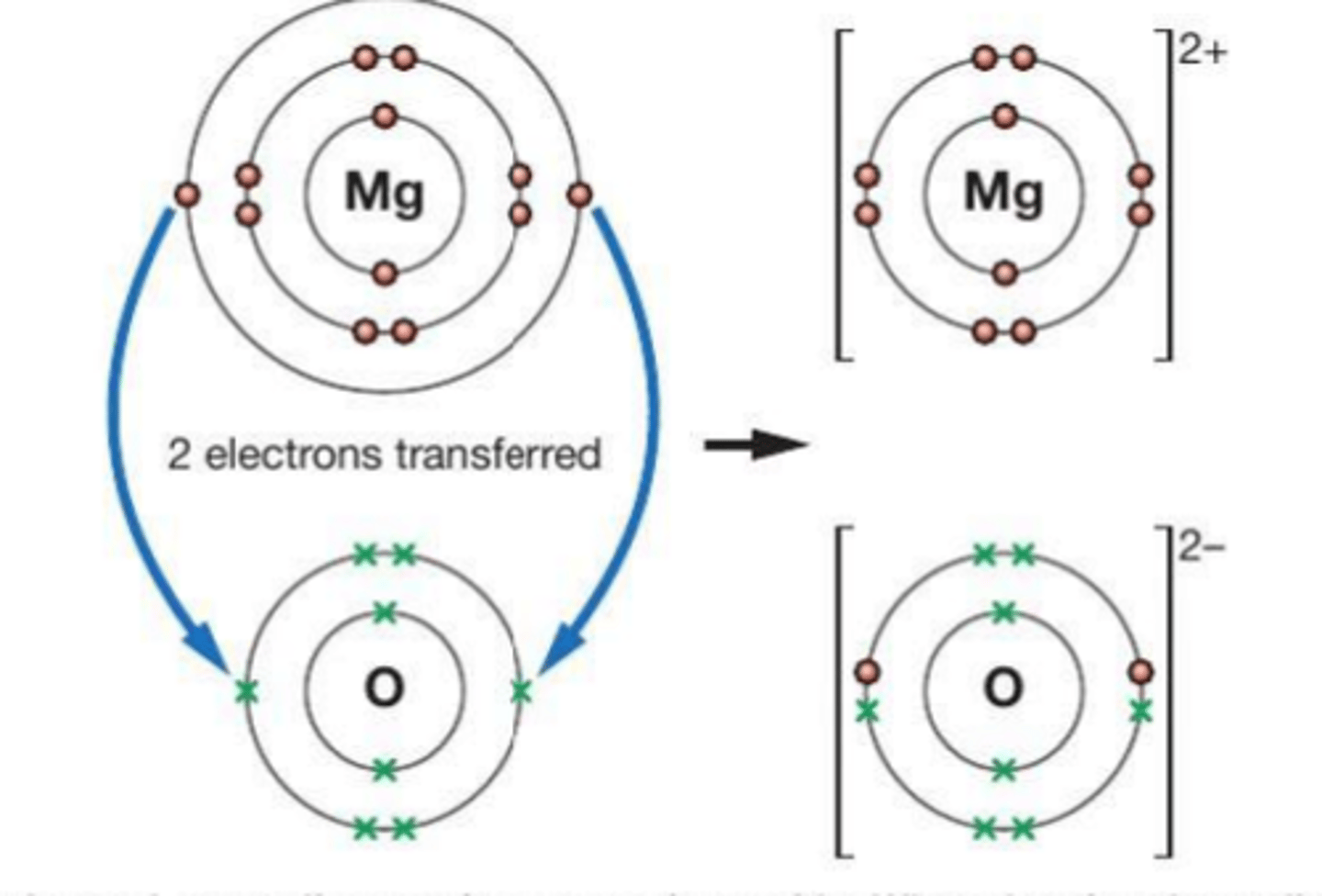
Define the term ionic bond
strong electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charges ions, formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another
(ionic compounds are usually metal)
Describe the melting and boiling point in ionic compounds and explain why it is high or low ?
1. ionic compounds have high melting pints and high boiling points
2. because there are strong electrostatic force of attraction holding the lattice together
3. a lot of energy has to be supplied to break the strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions in the giant lattice structure
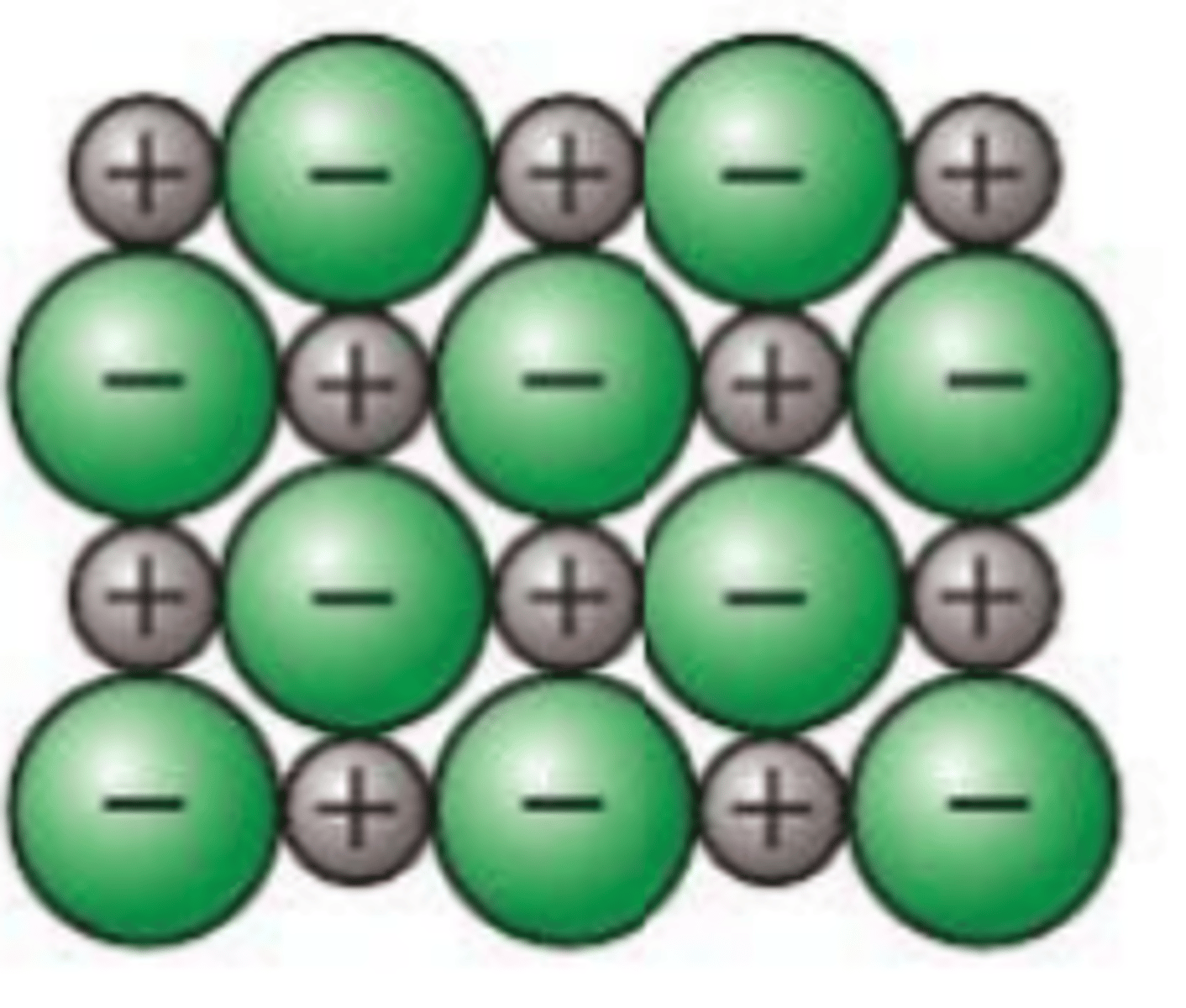
Do ionic compounds conduct electricity ?
1. ionic compounds don't conduct electricity when hey are solid
2. because the ions are fixed in position and are not free to move around
3. however when molten (melted) or dissolved in water
4. this is because the ions are free to move around and carry charge
Define the term covalent bond
strong electrostatic force of attraction between the nuclei of the atoms making up the bond and the shared pair of electrons
How do you draw dot and cross diagrams for covalent bonds ?
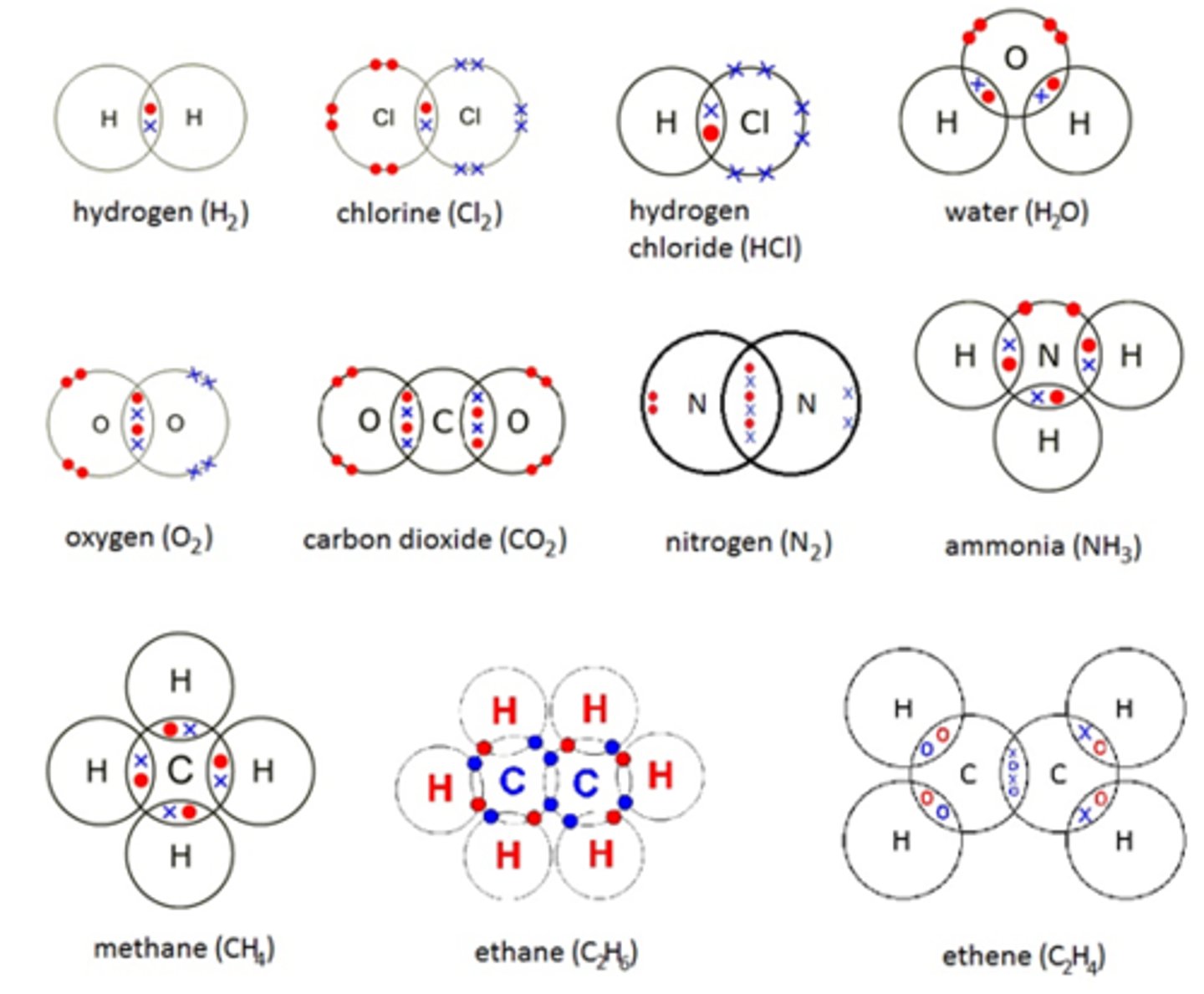
Which elements are diatomic?
hydrogen,
nitrogen,
oxygen,
fluorine,
chlorine,
bromine,
iodine
What is a simple molecular structure
1. molecules containing a fixed number of atoms joined together by strong covalent bonds
2. the covalent molecules are held together by intermolecular forces (forces of attraction between molecules)
3. these forces are weak
Describe the melting and boilng points for a simple molecular structure
substances with simple molecular structures tend to be gases or liquids or solids with low melting points and boiling point
this is because when we boil or melt a simple molecular structure we break the weak intermolecular forces of attraction
(covalent bonds are not broken)
Explain how the boiling and melting point of substances with simple molecular substances changes with increasing relative molecular mass
1. as the relative molecular mass increases, so does the melting and boiling point
2. this is because as the relative molecular mass increases the intermolecular forces of attraction become stronger
What are the physical properties of covalent compounds?
1. covalent compounds don't conduct electricity, this is because the molecules don't have an overall electric charge and electrons are held tightly in atoms or in covalent bonds and so are not able to move from molecule to molecule
2. covalent molecular substances tend to be insoluble in water
3. covalent molecules are often soluble in organic solvents