The Resonatory System and The Swallowing System
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anatomy and Physiology of Speech
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Aponeurosis
flat tendon
Levator veli palatini
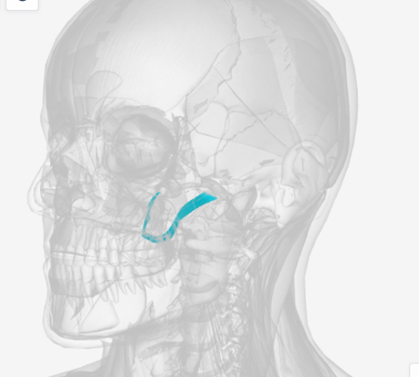
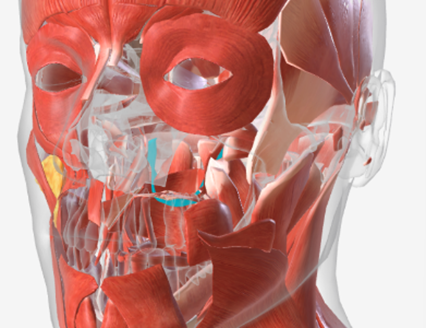
origin is on the petrous portion of the temporal bone, coursing down and forward to insert on the palatal aponeurosis of the soft palate; function elevates and retracts the posterior velum
Musculus uvulae
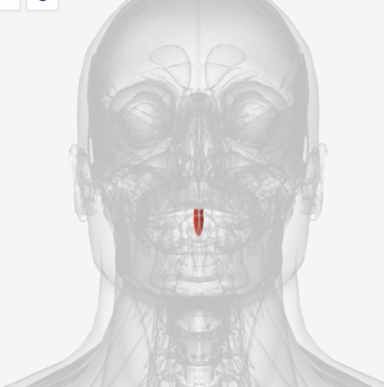
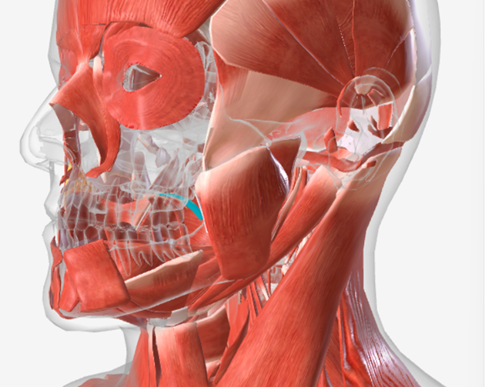
origin is on the posterior nasal spine of the palatine bones, coursing the length of the soft palate to insert on the mucous membrane that covers that velum; function is to shorten the soft palate
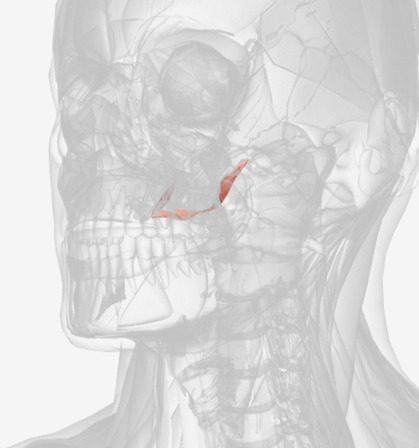
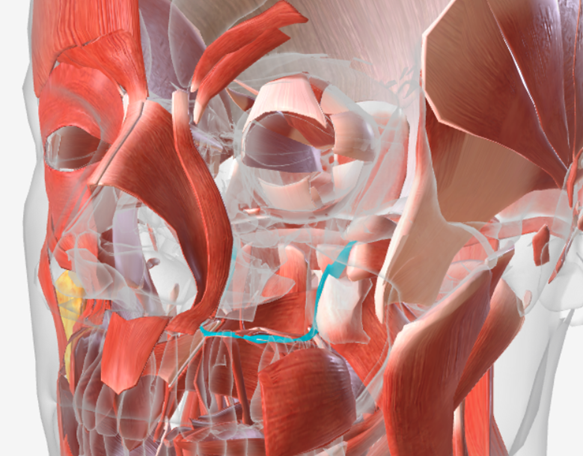
Tensor veli palatini
origin is on the sphenoid bone, coursing down to a tendon wrapping down around the pterygoid hamulus (of the sphenoid), then directed medially to the palatal aponeurosis; function is to dilate the Eustachian tube
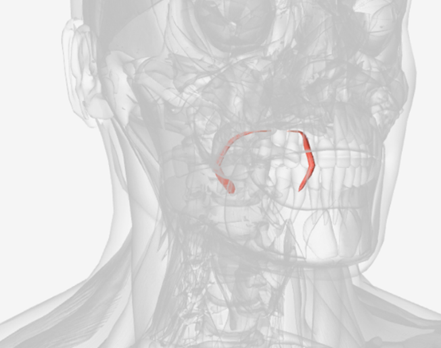
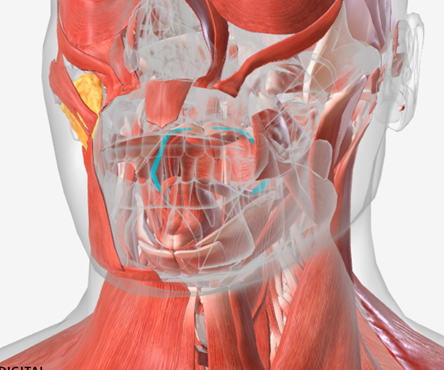
Palatoglossus
origin is the anterolateral palatal aponeurosis, coursing down to insert on the sides of the posterior tongue; function is to elevate the tongue or depress the soft palate; this is the muscle underlying the anterior faucial pillar
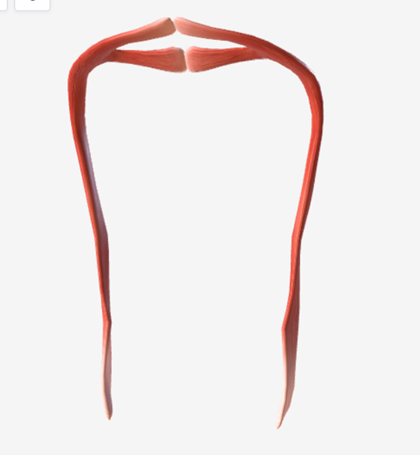
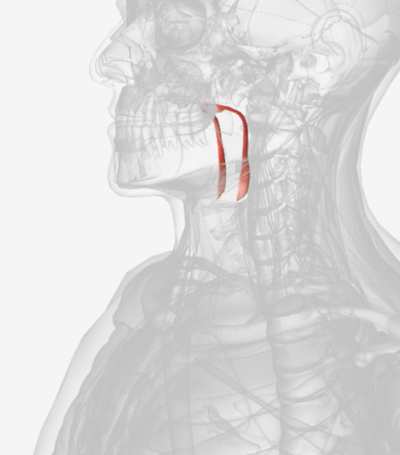
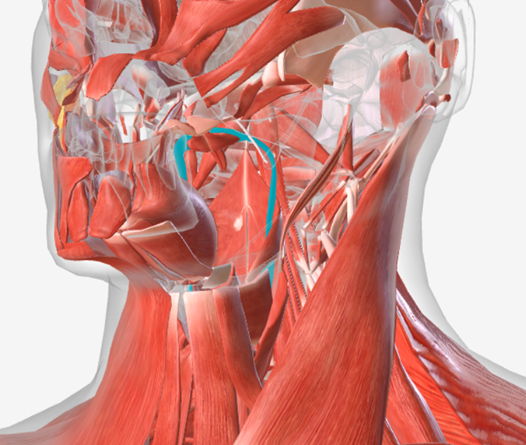
Palatopharyngeus
origin is the anterior hard palate and midline of the soft palate, coursing laterally and down to the posterior margin of the thyroid cartilage; function is to narrow the pharynx or lower the soft palate; this is the muscle underlying the posterior faucial pillar.
Raphe
a seam in an organ or tissue.
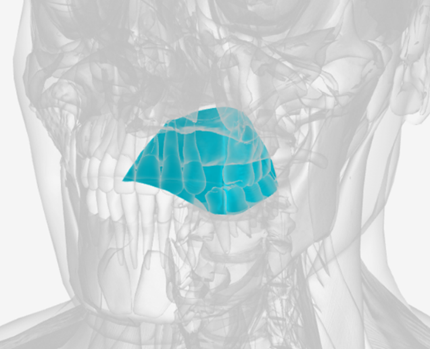
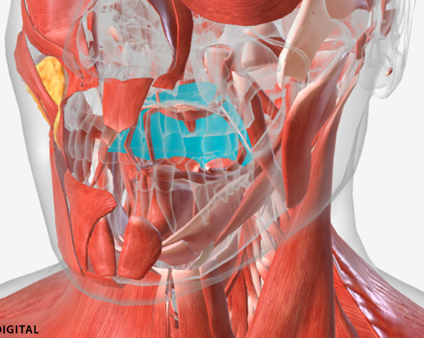
Superior pharyngeal constrictor
origin is on the pterygomandibular raphe, coursing posteriorly to insert on the median raphe of the pharyngeal aponeurosis function is to pull the pharyngeal wall forward to constrict the pharyngeal diameter
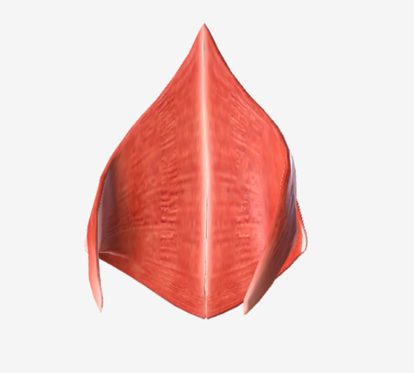
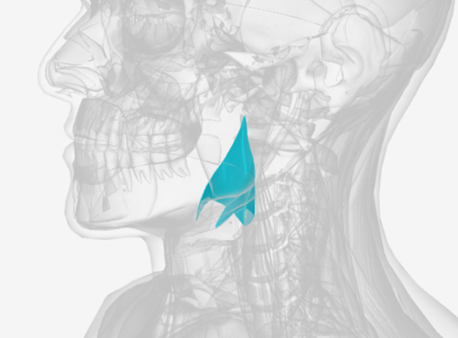
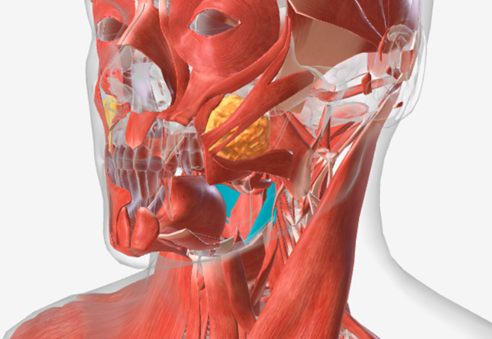
Middle pharyngeal constrictor
origin is on the horns of the hyoid and stylohyoid ligament, coursing up and back to the median pharyngeal raphe; function is to narrow the diameter of the pharynx
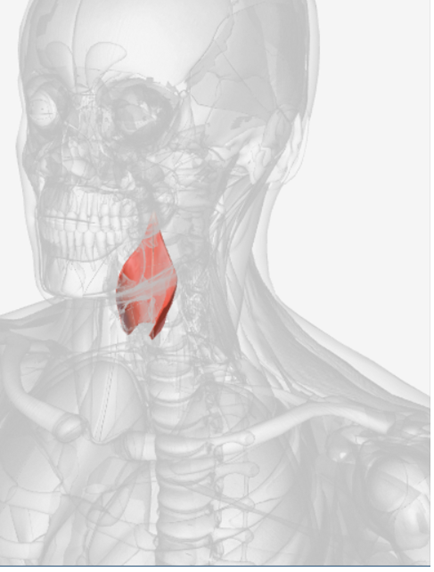
Inferior pharyngeal constrictor
origin is the oblique line of the thyroid laminae, coursing up and back to insert on the median pharyngeal raphe; function is to reduce the diameter of the lower pharynx
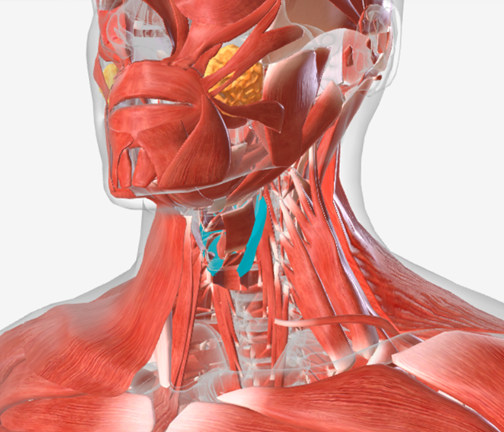
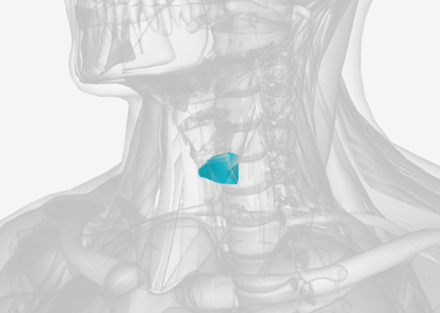
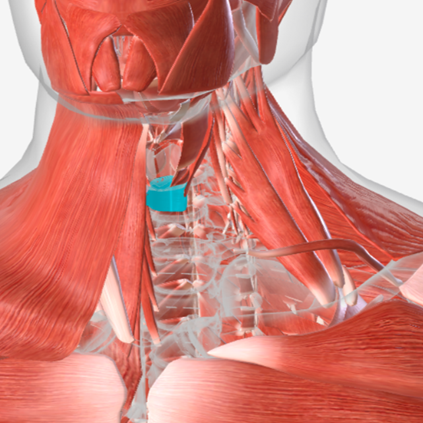
Cricopharyngeus
origin is the cricoid cartilage, coursing back to the orifice of the esophagus; function is to constrict the superior orifice of the esophagus; also referred to as the upper esophageal sphincter
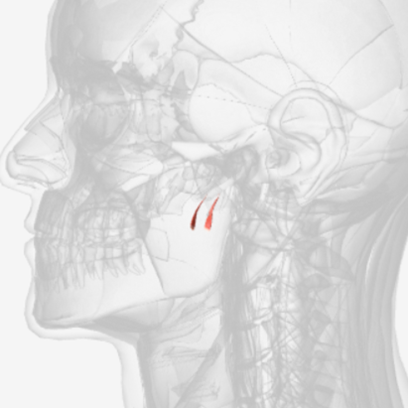
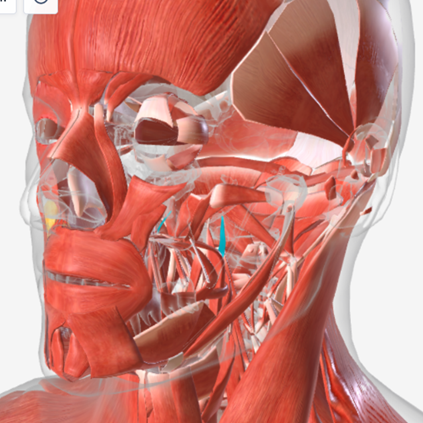
Salpingopharyngeus
origin is the lower margin of the auditory tube, coursing down to insert into the palatopharyngeus muscle; function is to elevate the lateral pharyngeal wall
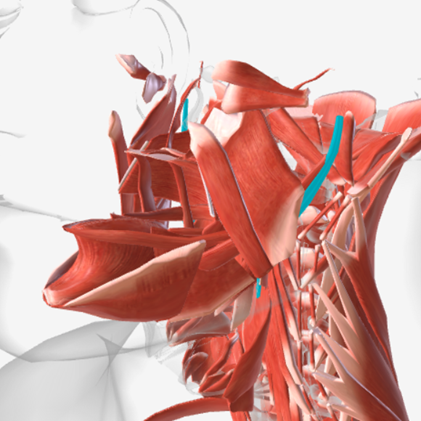
Stylopharyngeus
origin is the styloid process, coursing down to insert into the pharyngeal constrictors and the posterior thyroid cartilage; function is to elevate and open the pharynx
Mastication
the process of preparing food for swallowing.
Deglutition
the process of swallowing
Bolus
ball of food or liquid to be swallowed
Oral preparatory stage
food is prepared for swallowing; food is introduced to the mouth and held by occlusion of the lips, posterior elevation of the tongue, and depression of the soft palate to keep the food in the oral cavity. Through coordination of lingual, cheek, and mandibular muscles, the food is held on the molars and ground into a pulp while mixed with saliva. When sensory receptors detect the bolus is sufficiently broken down, the bolus is moved onto the dorsum of the tongue
Oral transport stage
the stage of swallow in which the bolus is transmitted to the pharynx. The anterior tongue is elevated to the hard palate and rolled back against the hard palate, pushing the bolus towards the faucial pillars. Presence of the bolus in the oropharynx is believed to be the strongest initiator of the reflex that is the pharyngeal stage
Pharyngeal stage
the stage of swallow in which the bolus moves from the oral cavity through the pharynx and to the entryway to the esophagus; it involves numerous protective responses including vocal fold adduction, hyolaryngeal elevation, epiglottic inversion, and velopharyngeal closure
Epiglottis inversion
movement of the epiglottis to cover the aditus (entryway to the larynx) during swallowing as part of the body's protection mechanism
Esophageal stage
the stage of swallow involving the peristaltic movement of food from the upper esophageal region to the stomach
Peristaltic
wavelike
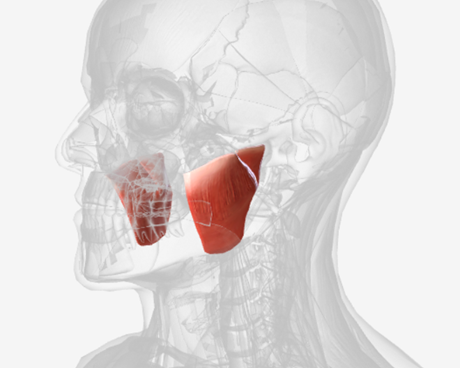
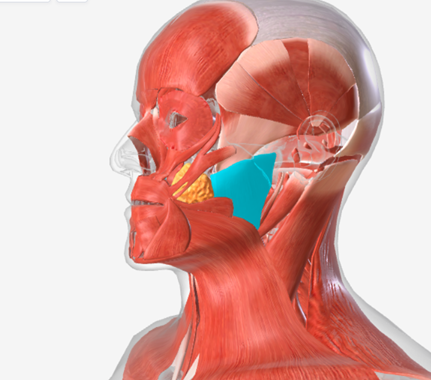
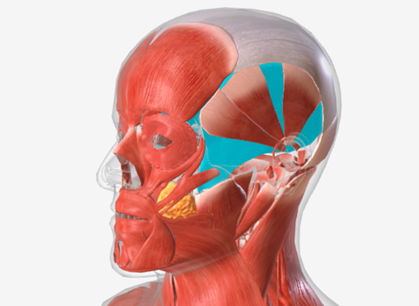
Masseter
origin is the zygomatic arch, coursing down to insert into the ramus of the mandible and the coronoid process, function is the elevate the mandible
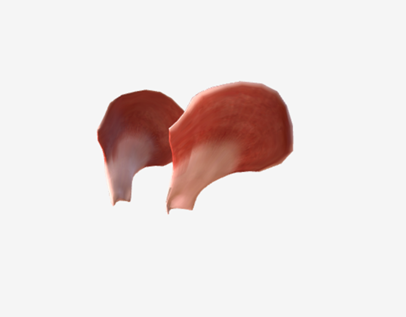
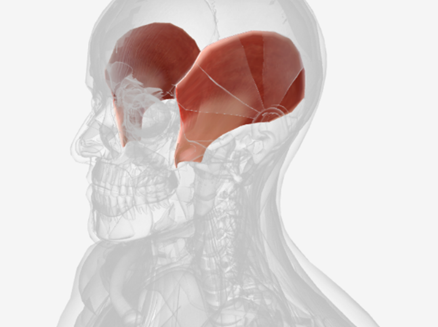
Temporalis
origin is the temporal and parietal bones of the cranium, coursing down and forward through the zygomatic arch, to insert on the coronoid process and the ramus of the mandible; function is to elevate the mandible and draw it back if protruded
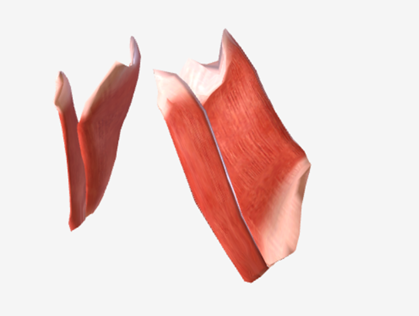
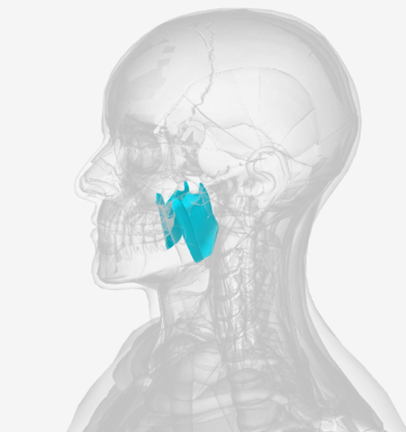
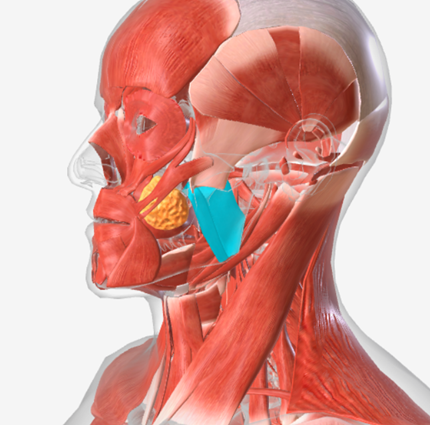
Medial pterygoid
origin is the medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone, coursing down and back to the mandibular ramus; function is to elevate the mandible
Lateral pterygoid
origin is the lateral pterygoid plate and the greater wing of the sphenoid, coursing back to the mandible; function is to protrude the mandible
Gustation
sense of taste
Olfaction
sense of smell
Tactile
sense of touch
Thermal
sense of temperature
Nociceptors
pain sensors
Salivation
production and release of saliva into the oral cavity
Sucking reflex
reflex involving tongue protrusion and retraction in preparation for receipt of liquid, simulated by contact to the upper lip
Rooting reflex
reflexive response of infant to tactile stimulation of the cheek or lips causing infants to turn toward the stimulus and open their mouth
Cough reflex
initiated by noxious stimulation of the pharynx, larynx, or bronchial passageway
Levator Veli Palatine
 |  |  |
Musculus Uvulae
 |  |  |
Tensor Veli Palatini
 |  |  |
Palatoglossus
 |  |  |
Palatopharyngeus

|  |  |
Superior Pharyngeal Constrictor
 |  |  |
Middle Pharyngeal Constrictor
 |  |  |
Inferior Pharyngeal Constrictor
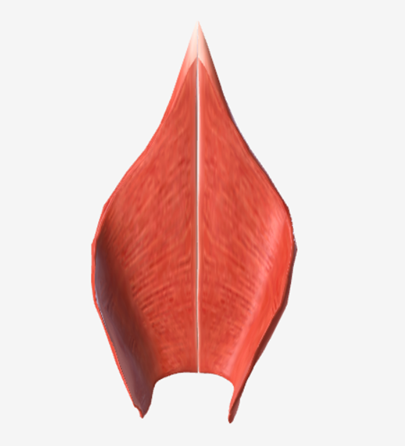 |  |  |
Cricopharyngeus
 |  |  |
Saplingopharyngeus
 |  |  |
Stylopharyngeus
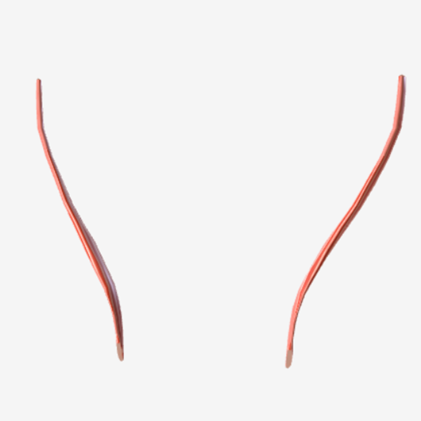 | 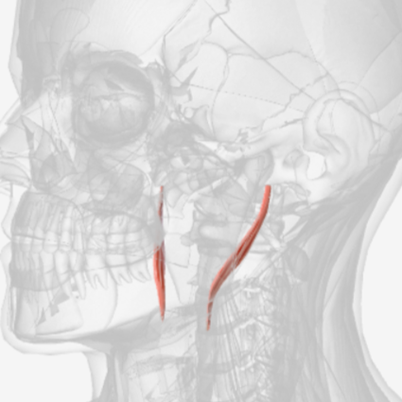 |  |
Masseter
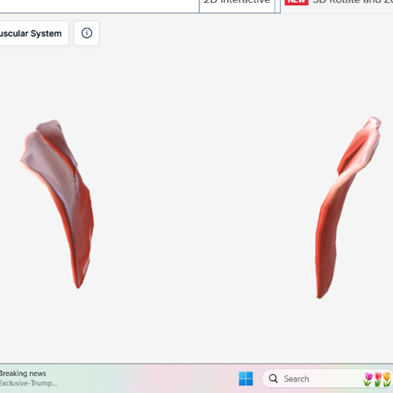 |  |  |
Temporalis
 |  |  |
Medial Pterygoid
 |  |  |
Lateral Pterygoid
 | 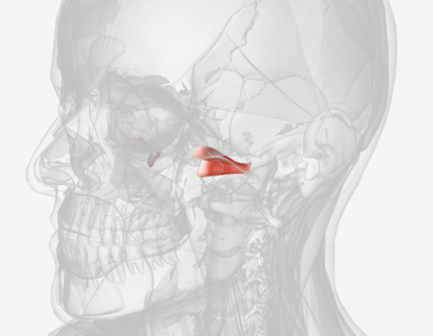 |  |
Superior pharyngeal constrictor
A

Stylopharyngeus
B

Salpingopharyngeus
C

Middle pharyngeal constrictor
D

Inferior pharyngeal constrictor
E

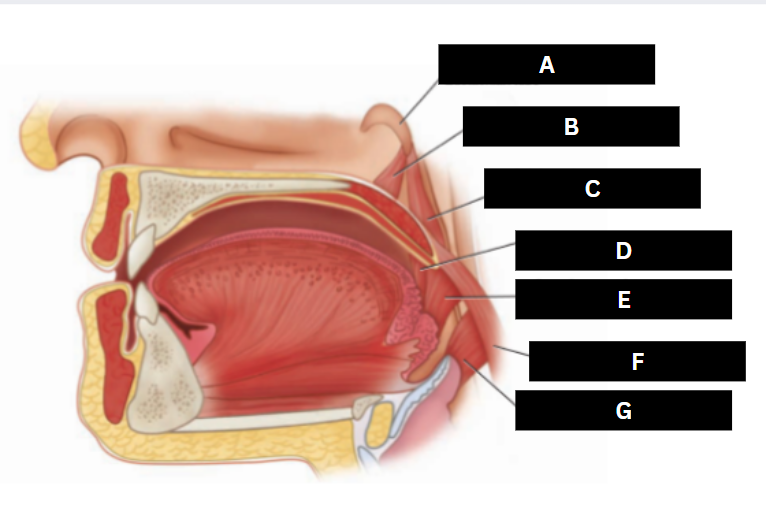
Palatine glands
A
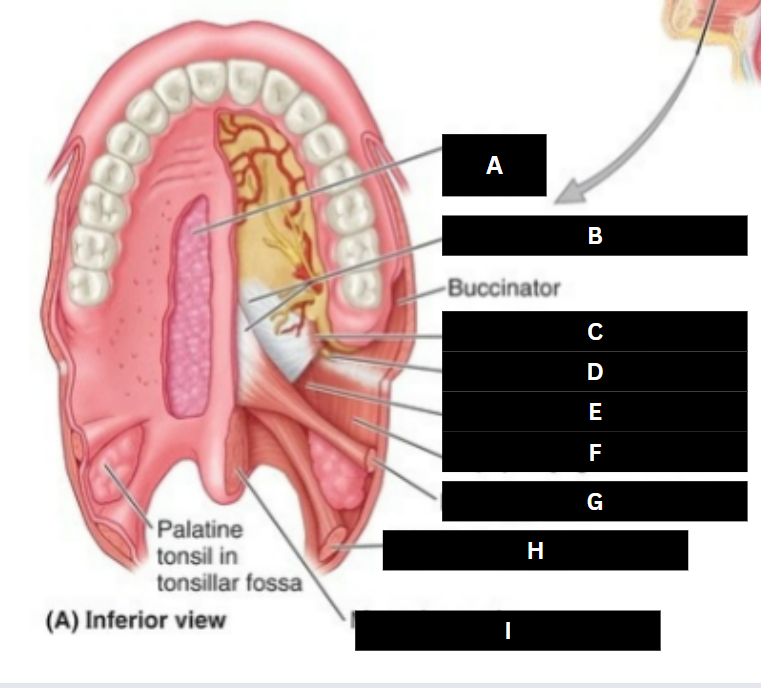
Palatine aponeurosis
B

Tensor veli palatini
C

Pterygoid hamulus
D

Levator veli palatini
E

Superior pharyngeal constrictor

F
Palatoglossus

G
Palatopharyngeus

H
Musculus uvulae

I
Superior pharyngeal constrictor
A
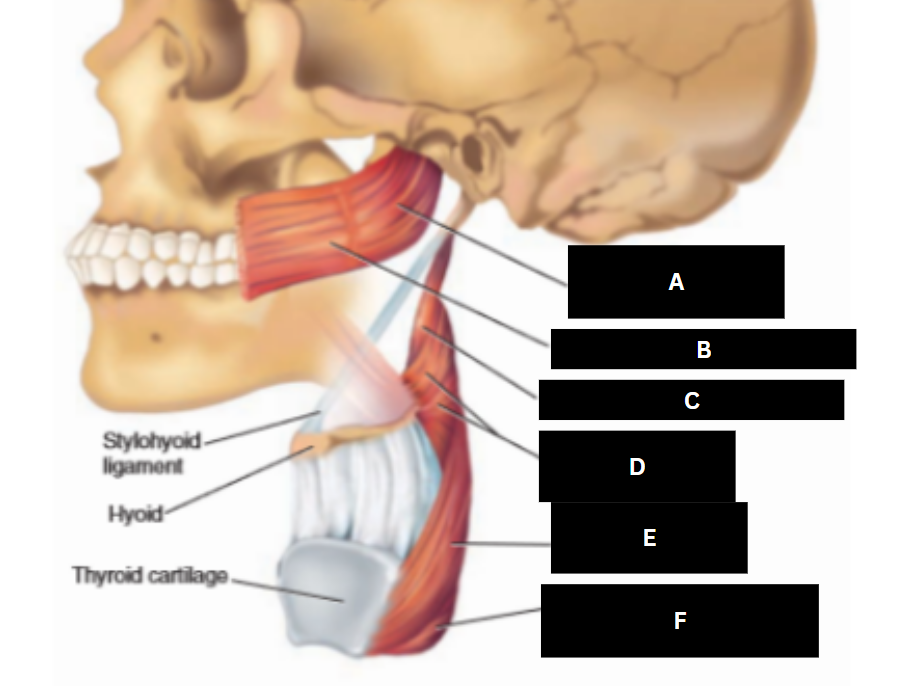
Buccinator
B
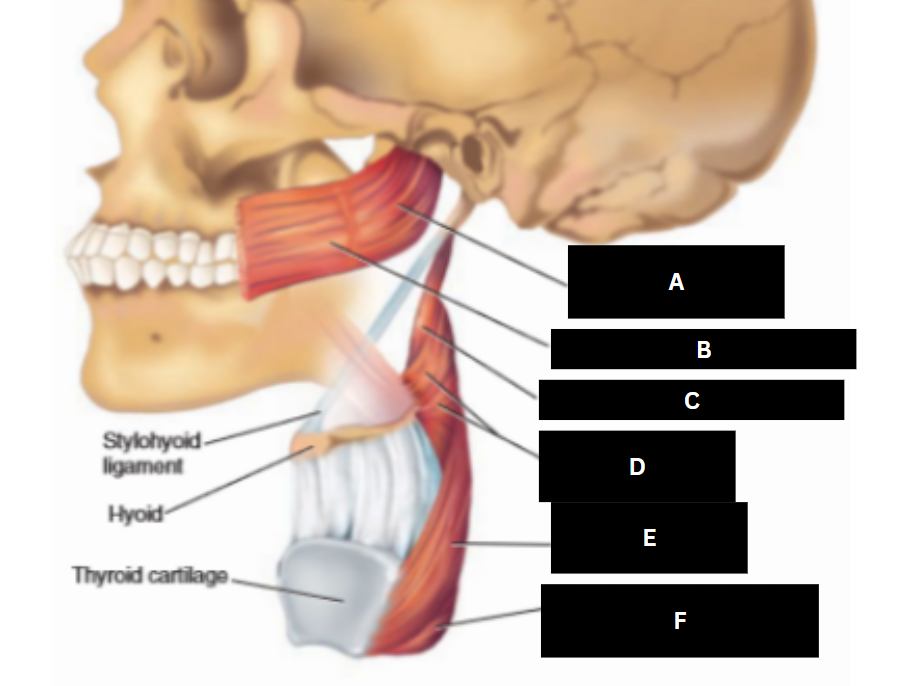
Stylopharyngeus
C
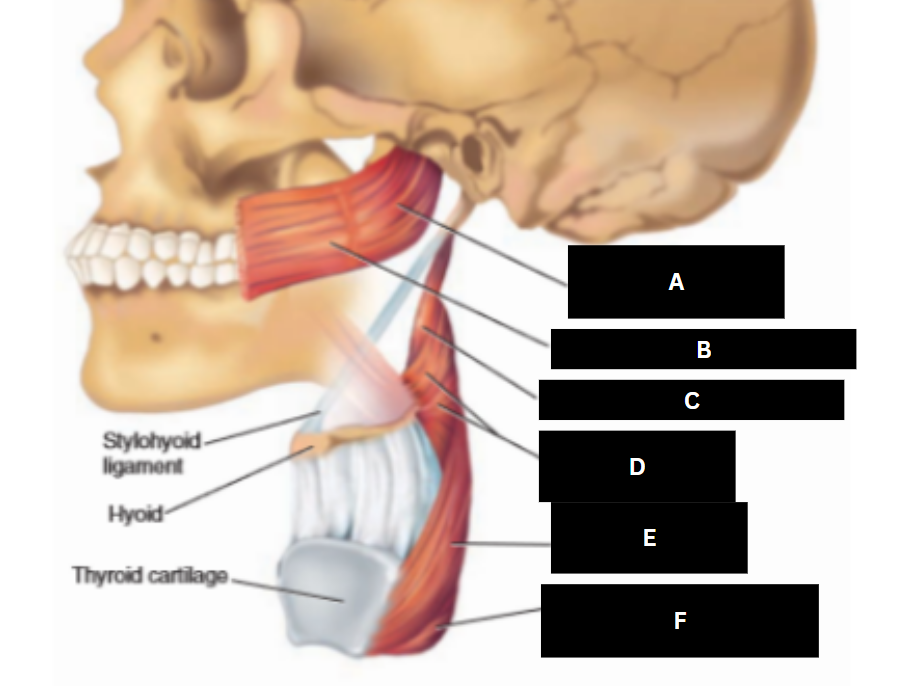
Middle pharyngeal constrictor
D
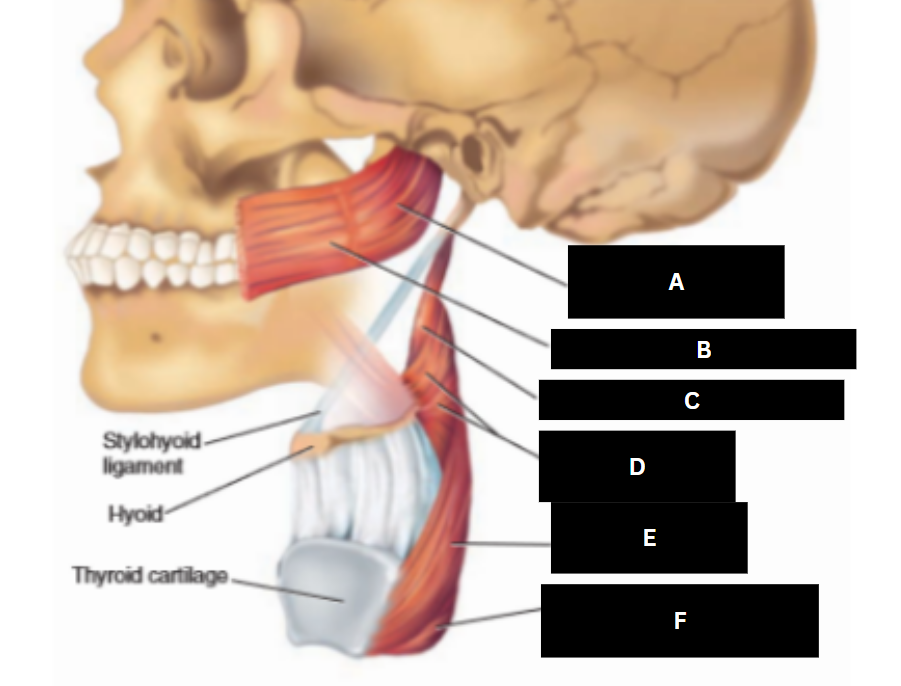
Inferior pharyngeal constrictor
E
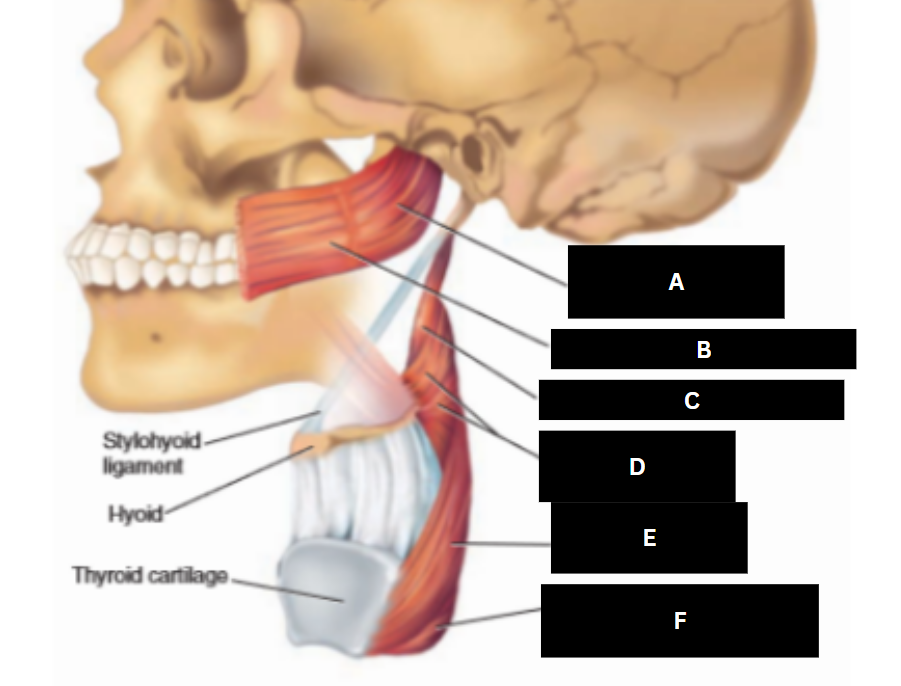
Cricopharyngeus
F
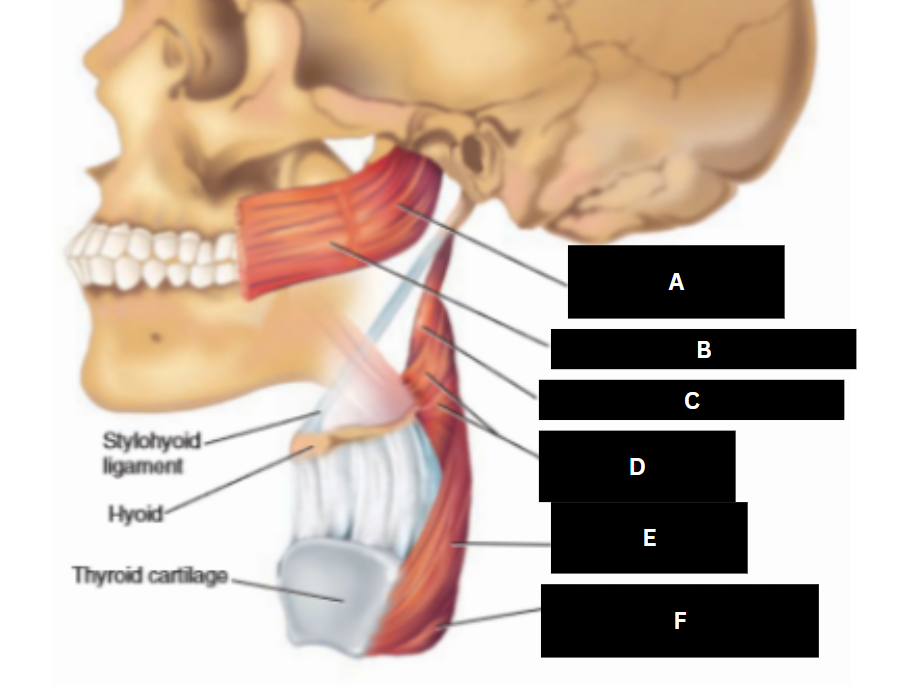
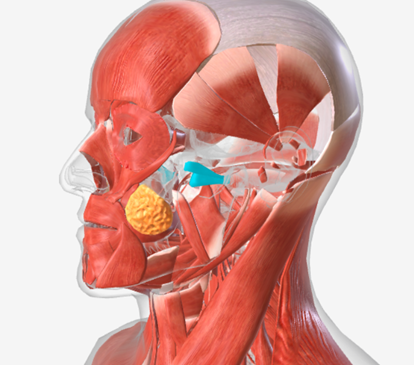
Eustachian tube
A
Levator veli palatini
B
Salpingopharyngeus
C
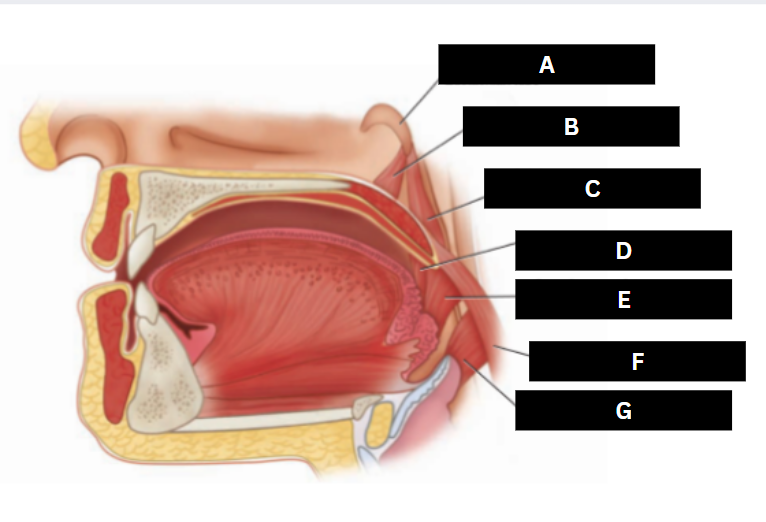
Palatoglossus
D
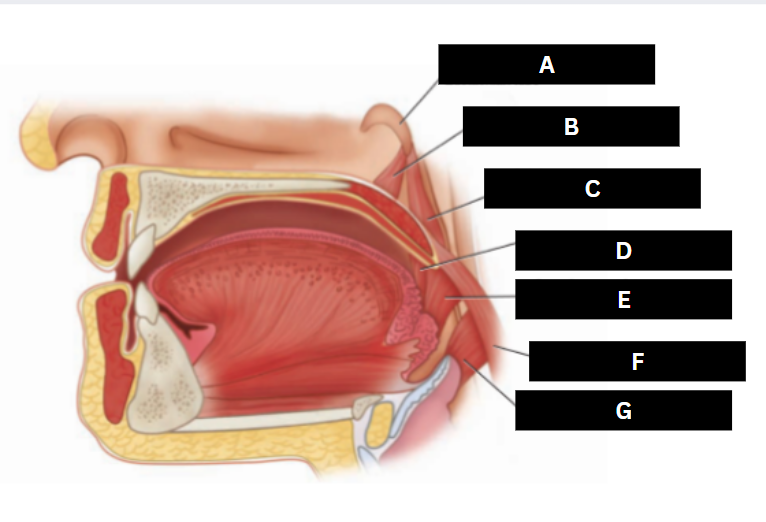
Superior pharyngeal constrictor
E
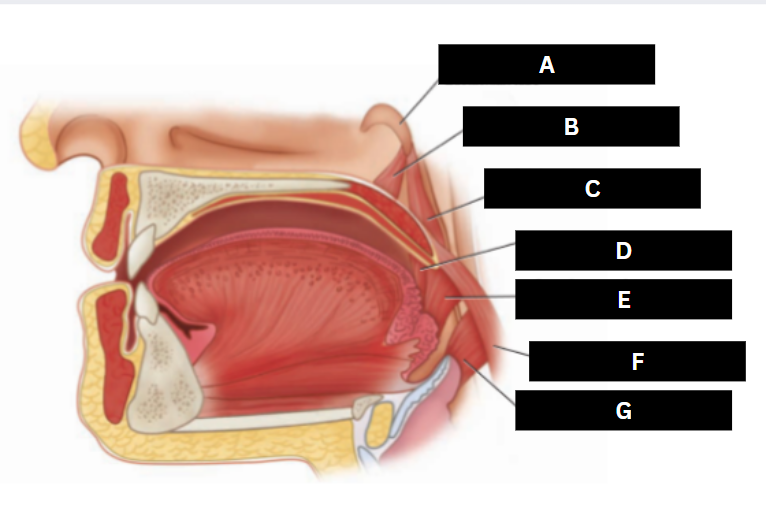
Palatopharyngeus
F
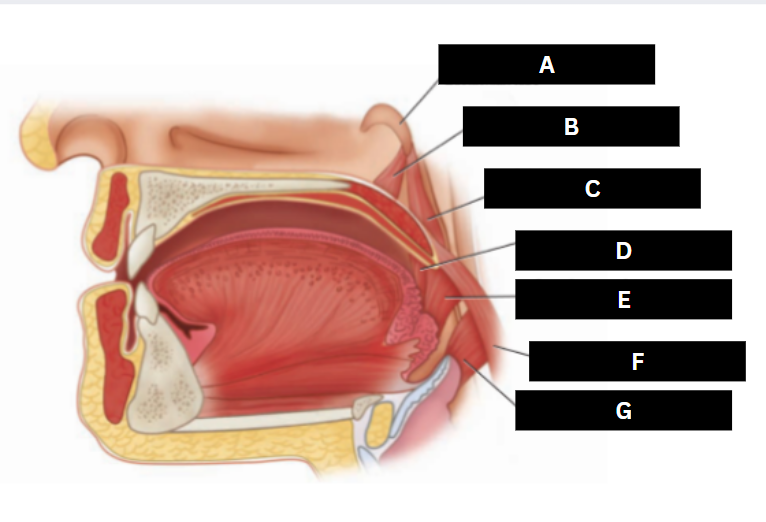
Middle pharyngeal constrictor
G
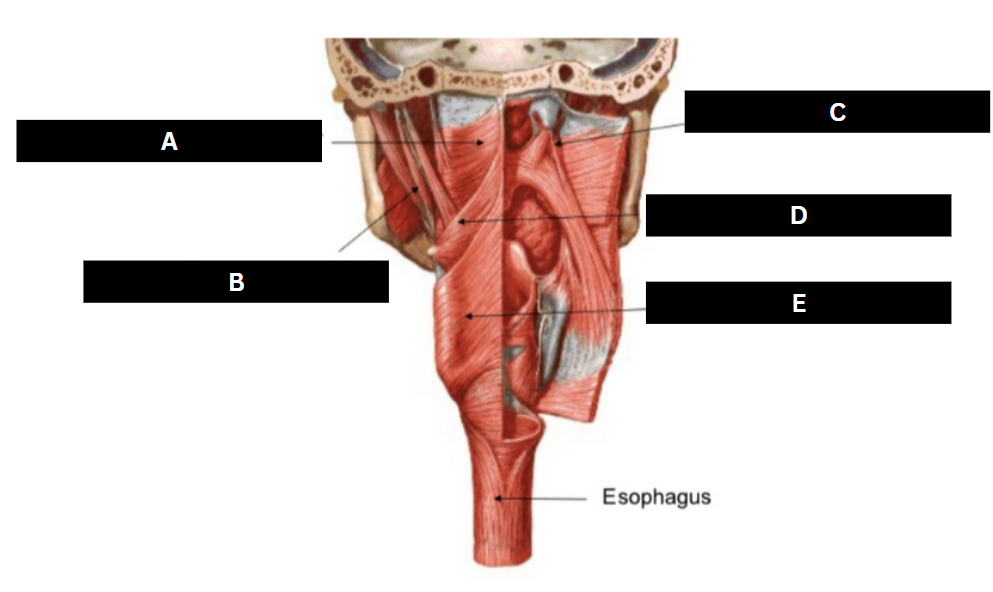
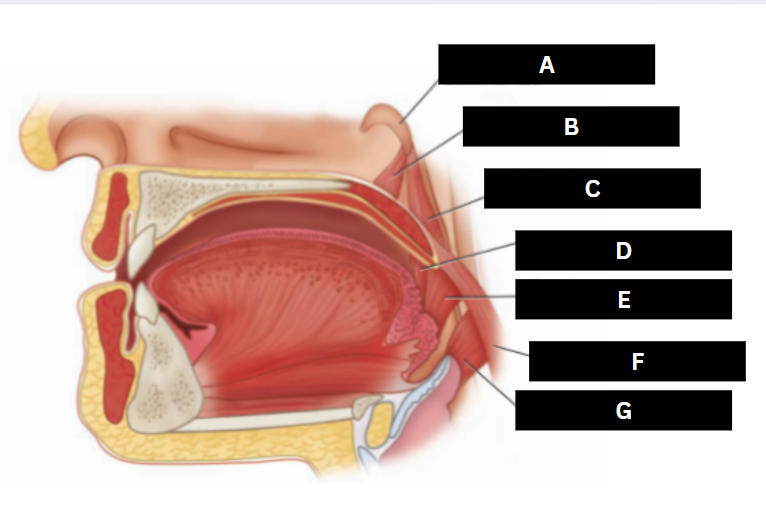
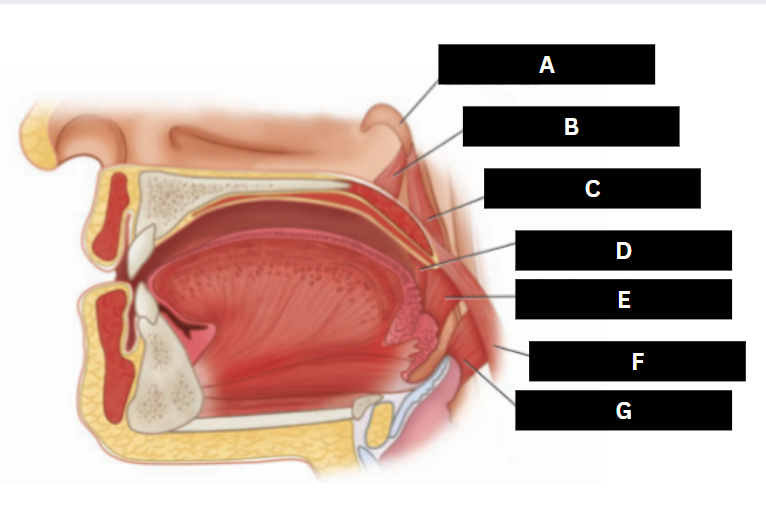
Stylopharyngeus
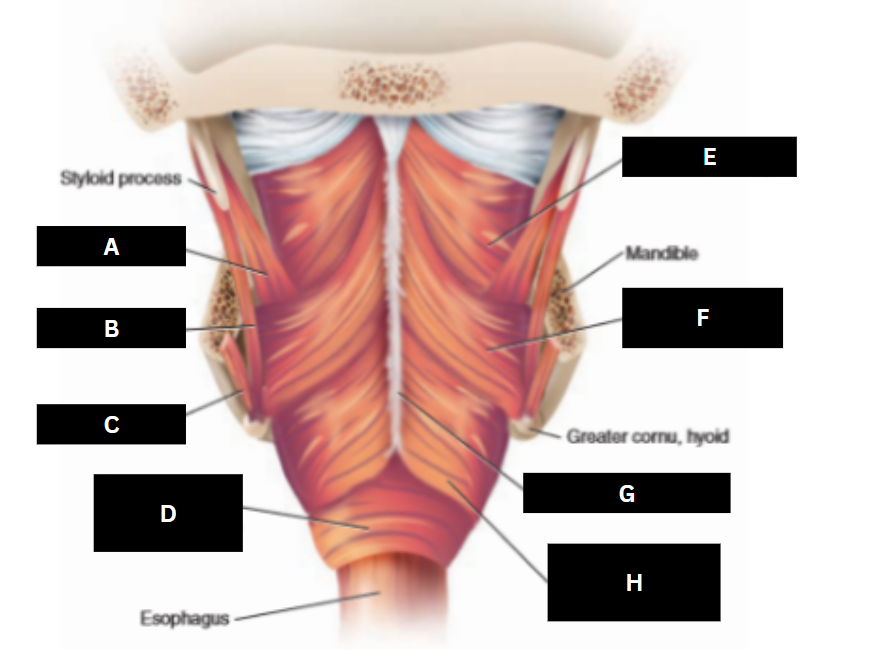
A
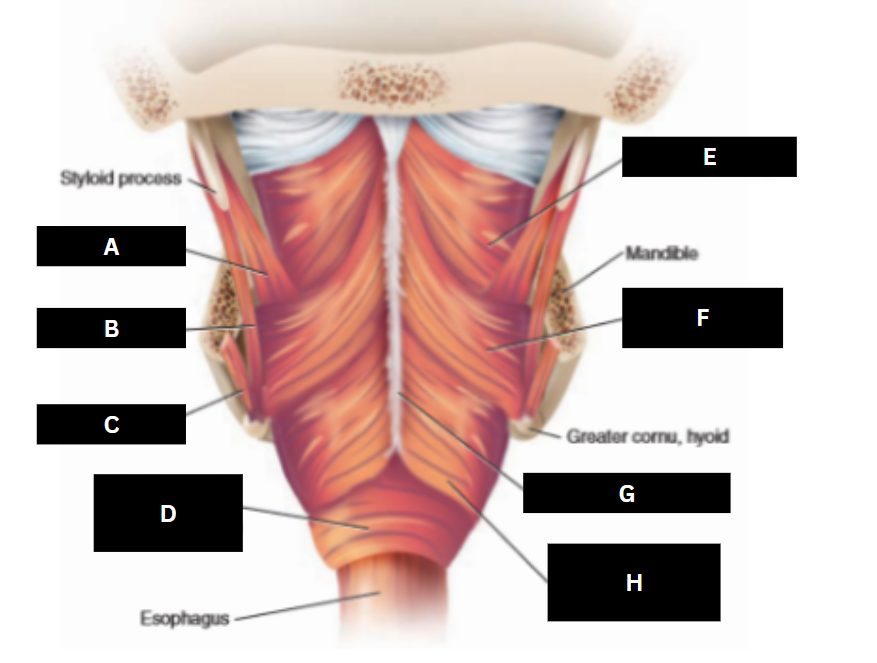
Styloglossus
B
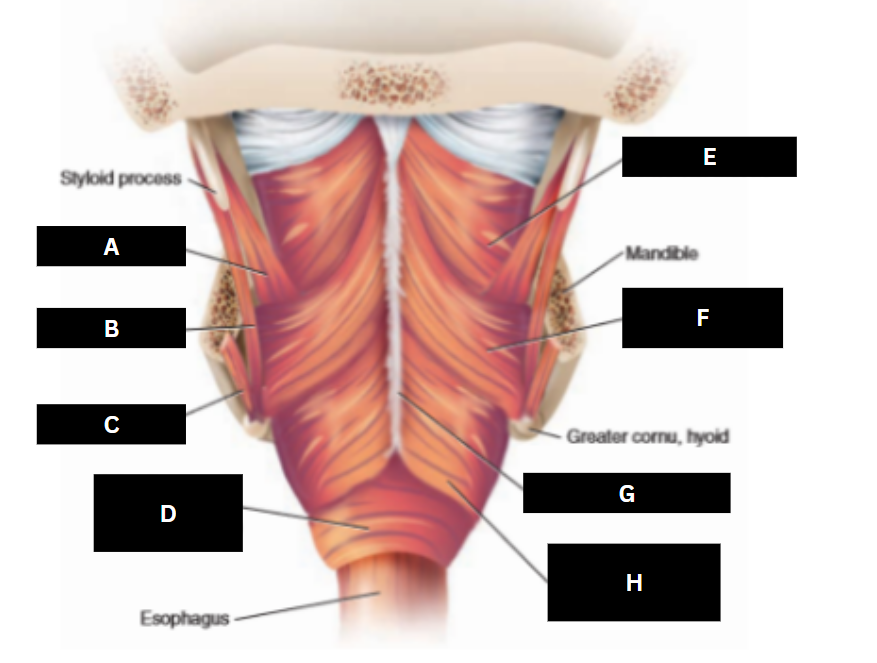
Stylohyoid
C
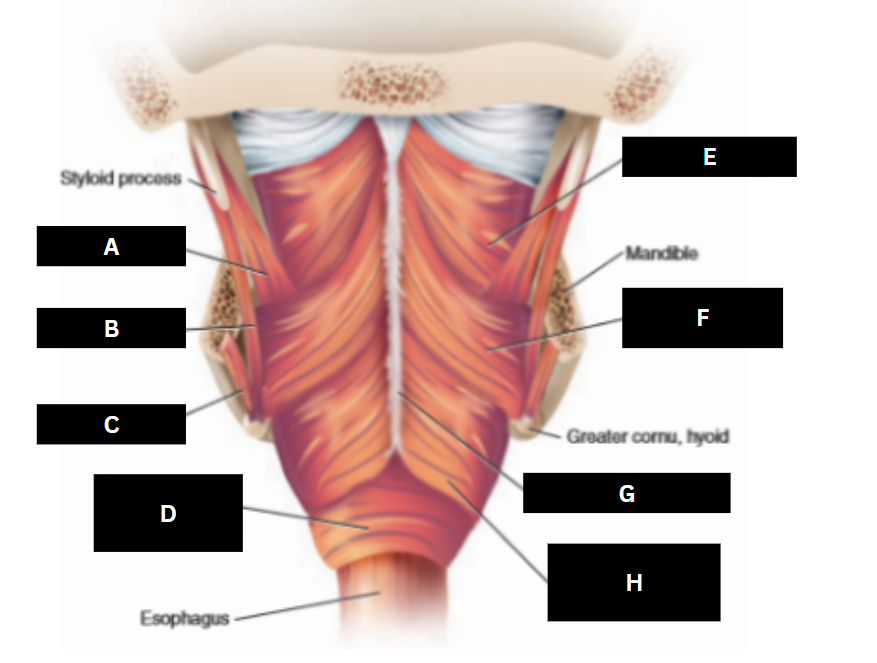
Cricopharyngeus
D
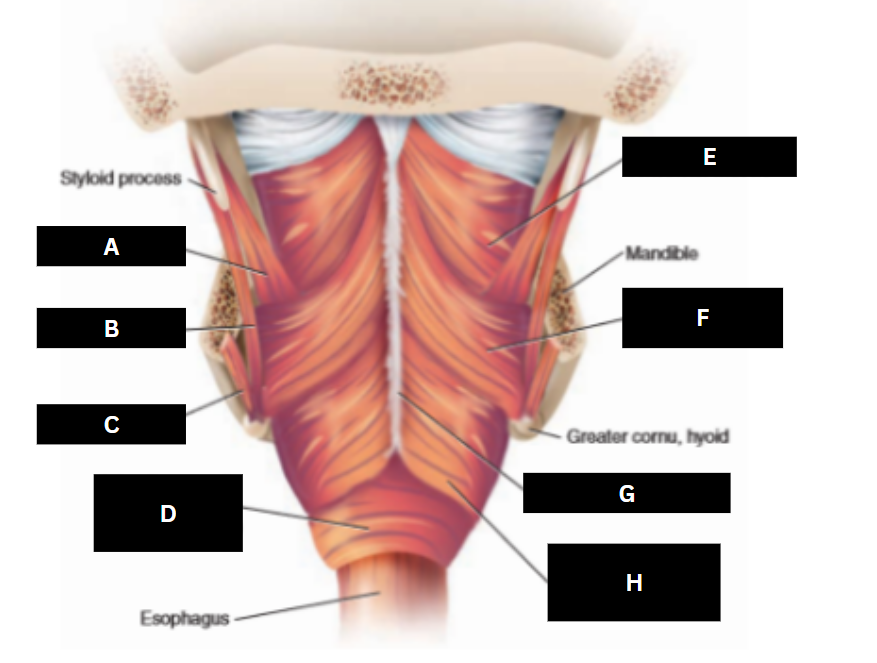
Superior pharyngeal constrictor
E
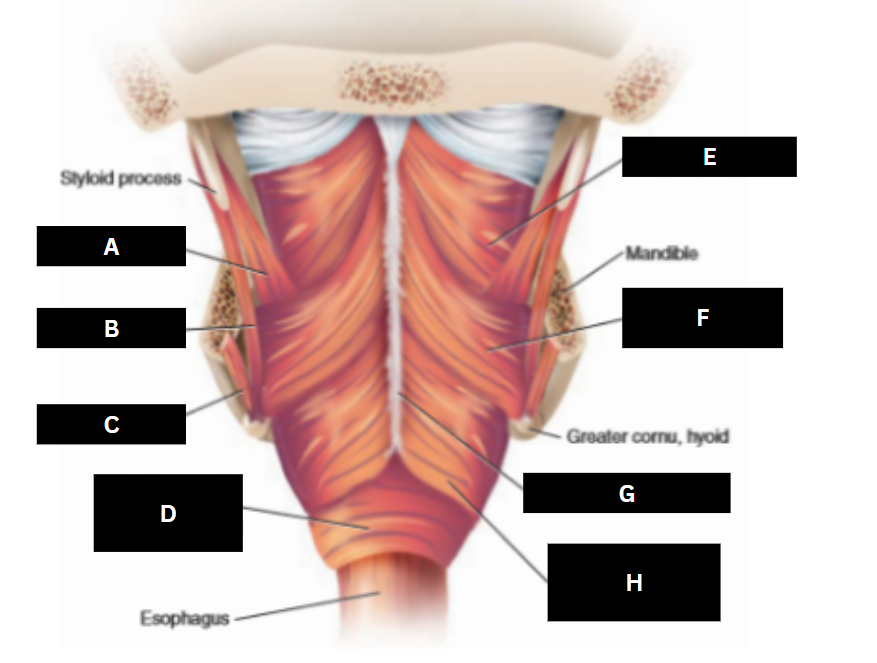
Middle pharyngeal constrictor
F
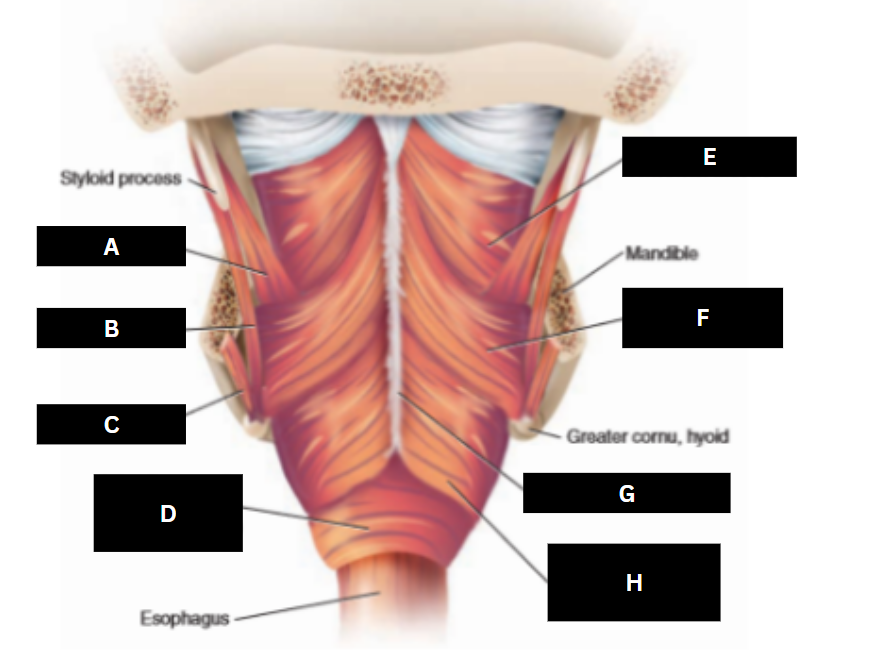
Pharyngeal raphe
G
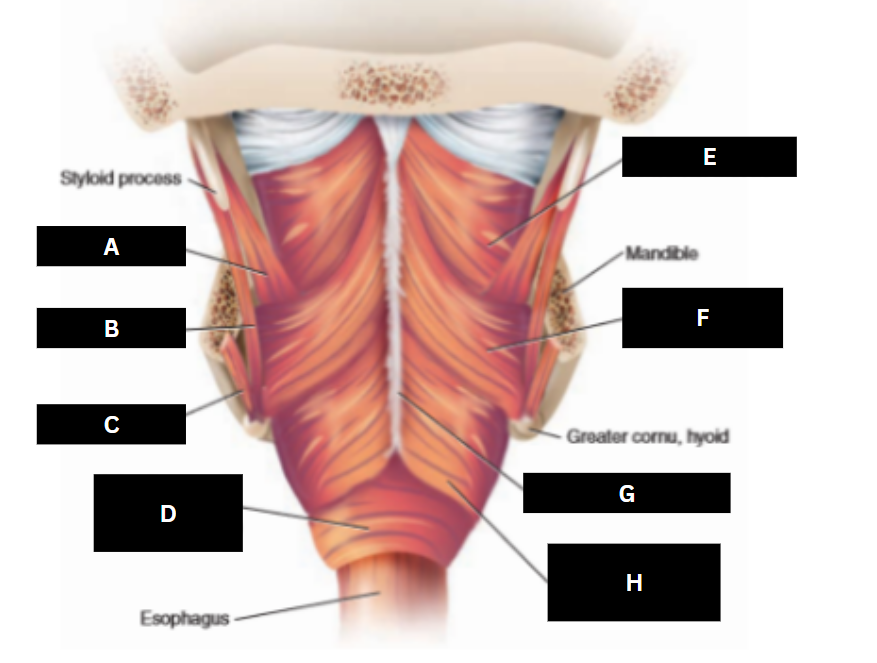
Inferior pharyngeal constrictor
H
Upper Esophageal Sphincter
Also know as the cricopharyngeus
cricopharyngeus
Also known as Upper Esophageal Sphincter
Oral Preparatory Stage
What stage? Food prepared for swallowing
Oral Preparatory Stage
What stage? Food kept in mouth by sealing of lips
Oral Preparatory Stage
What stage? Food ground up by lingual muscles and muscles of mastication
Oral Preparatory Stage
What stage? Food mixed with saliva to form a bolus in preparation for swallowing
Oral Preparatory Stage
What stage? Sensory receptors in the oral cavity continually monitor the bolus
Oral Transport Stage
What stage? Bolus pushed back toward the oropharynx by the tongue in a front to back squeezing action
Mandibular and tongue
What muscles are involved in the oral transport stage?
Pharyngeal Stage
What stage? Begins when bolus passes faucial pillars (initiating reflex) and involuntary muscle contractions
Pharyngeal Stage
What stage? A tight seal is formed to protect the airway (nasal and laryngeal)
Pharyngeal Stage
What stage? Bolus propelled through pharynx to relaxed upper esophageal sphincter which receives bolus and closes
Pharyngeal Stage
What stage? Food passes around epiglottis/aryepiglottic folds through the pyriform sinuses to the esophagus posterior to larynx/trachea
Pharyngeal Stage
What stage? Functional operations
Esophageal Stage
What stage? Swallowing involves peristaltic movement of the bolus through the esophagus