AP Psychology: Topic 5.1 - Introduction to Health Psychology, AP Psychology: Topic 5.2 - Positive Psychology , AP Psychology: Topic 5.3 - Explaining and Classifying Psychological Disorders, AP Psychology: Topic 5.4 - Selection of Categories of Psycho…
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
Health psychology
the study of how physical health
and wellness apply to behavior and mental processes
Stress
a state of tension caused by any thought or event that makes someone feel frustrated, angry, or nervous (can lead to disorders and disease)

Hypertension
a combination of high blood pressure and high psychological stress (also known as high blood pressure)
Immune suppression
when the immune system is unable to respond to infections and diseases as well as it normally would (can be caused by stress)

Stressors
specific events or chronic pressures that place demands on a person or threaten their well-being
Eustress
a positive (motivating) stress response that can be beneficial to a person's well-being
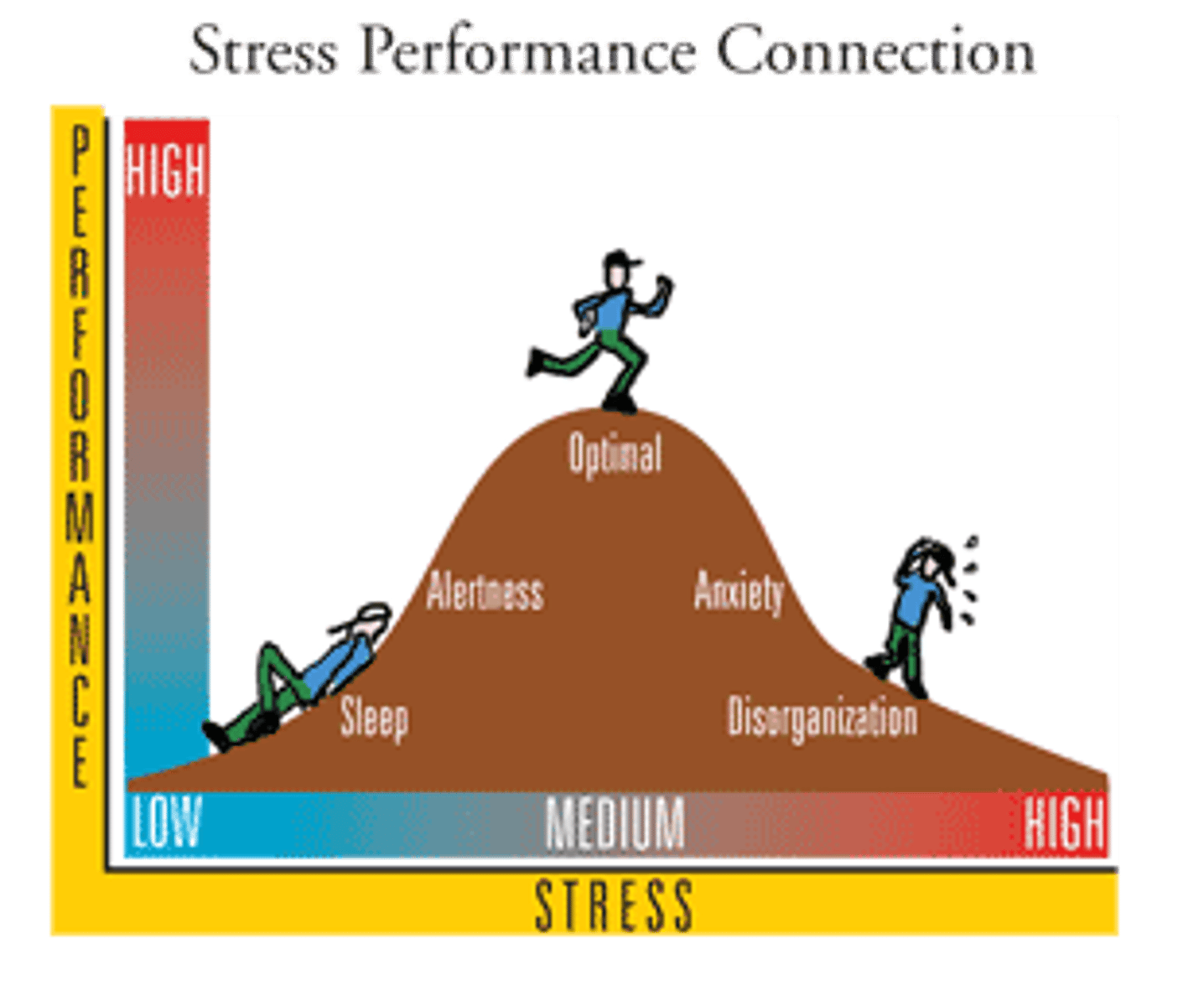
Distress
a negative (debilitating) type of stress that can cause unpleasant feelings, anxiety, and decreased performance

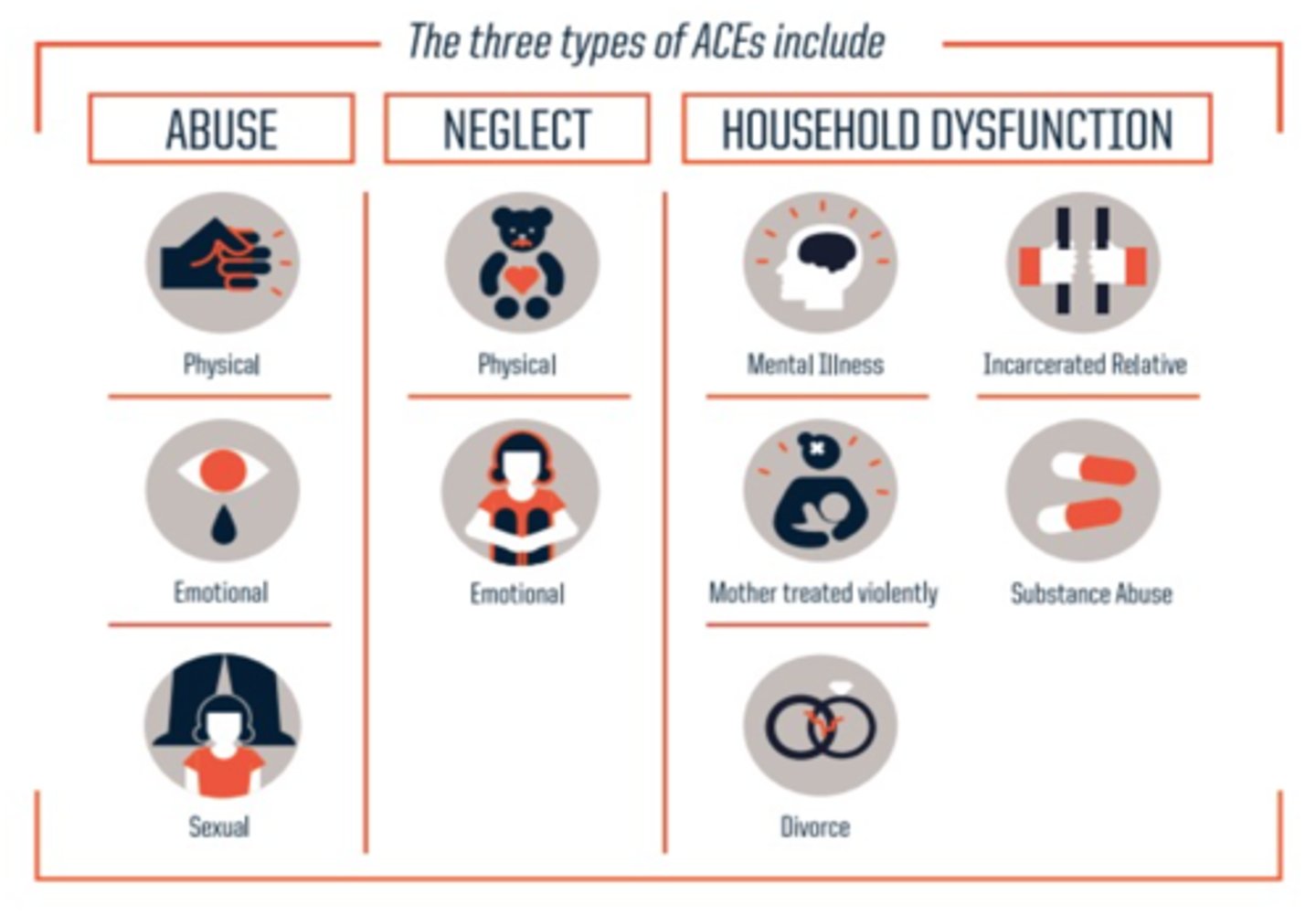
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs)
traumatic childhood experiences, such as abuse, neglect, violence exposure, or death of a parent, that are linked to mental and physical health problems later in life
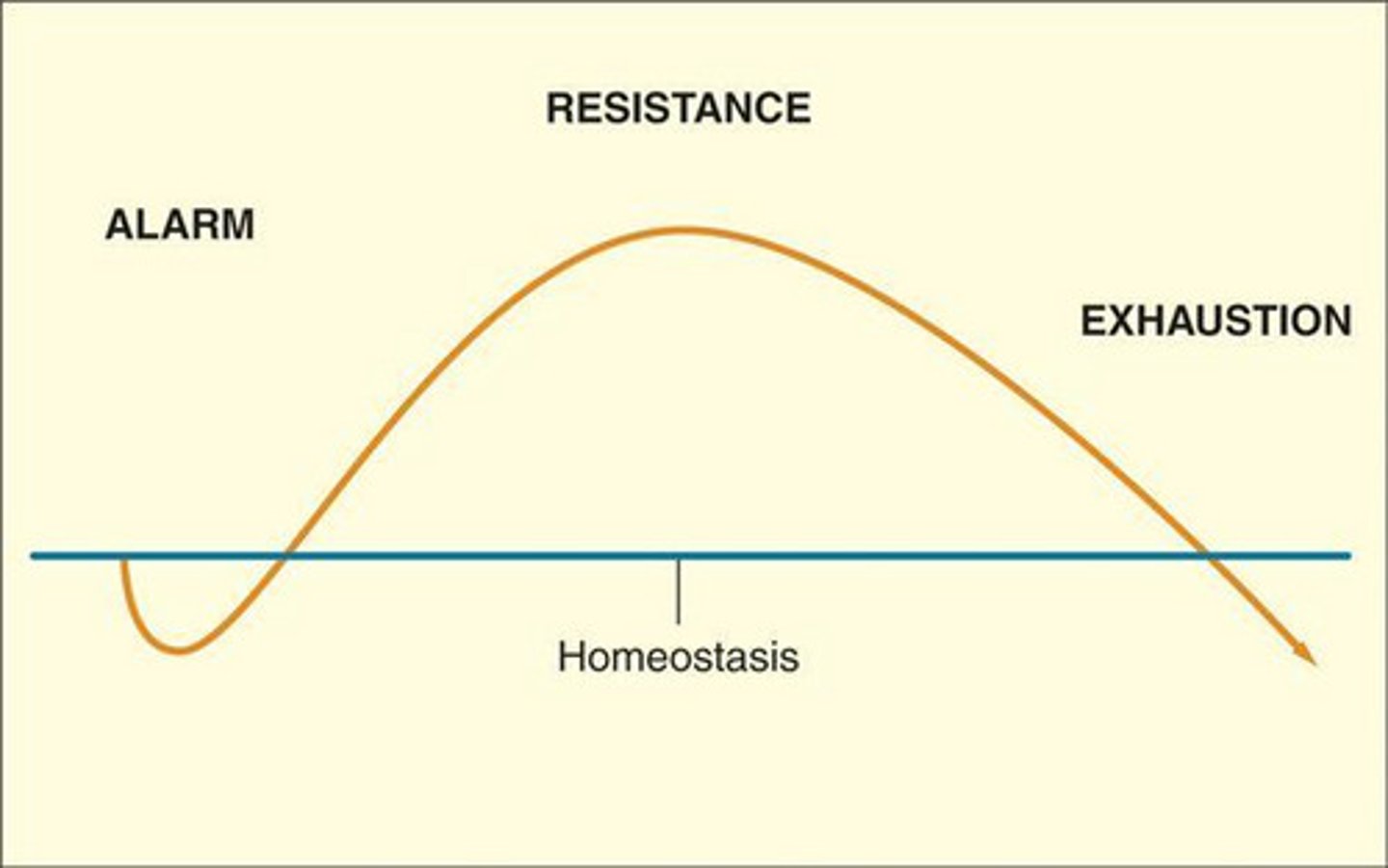
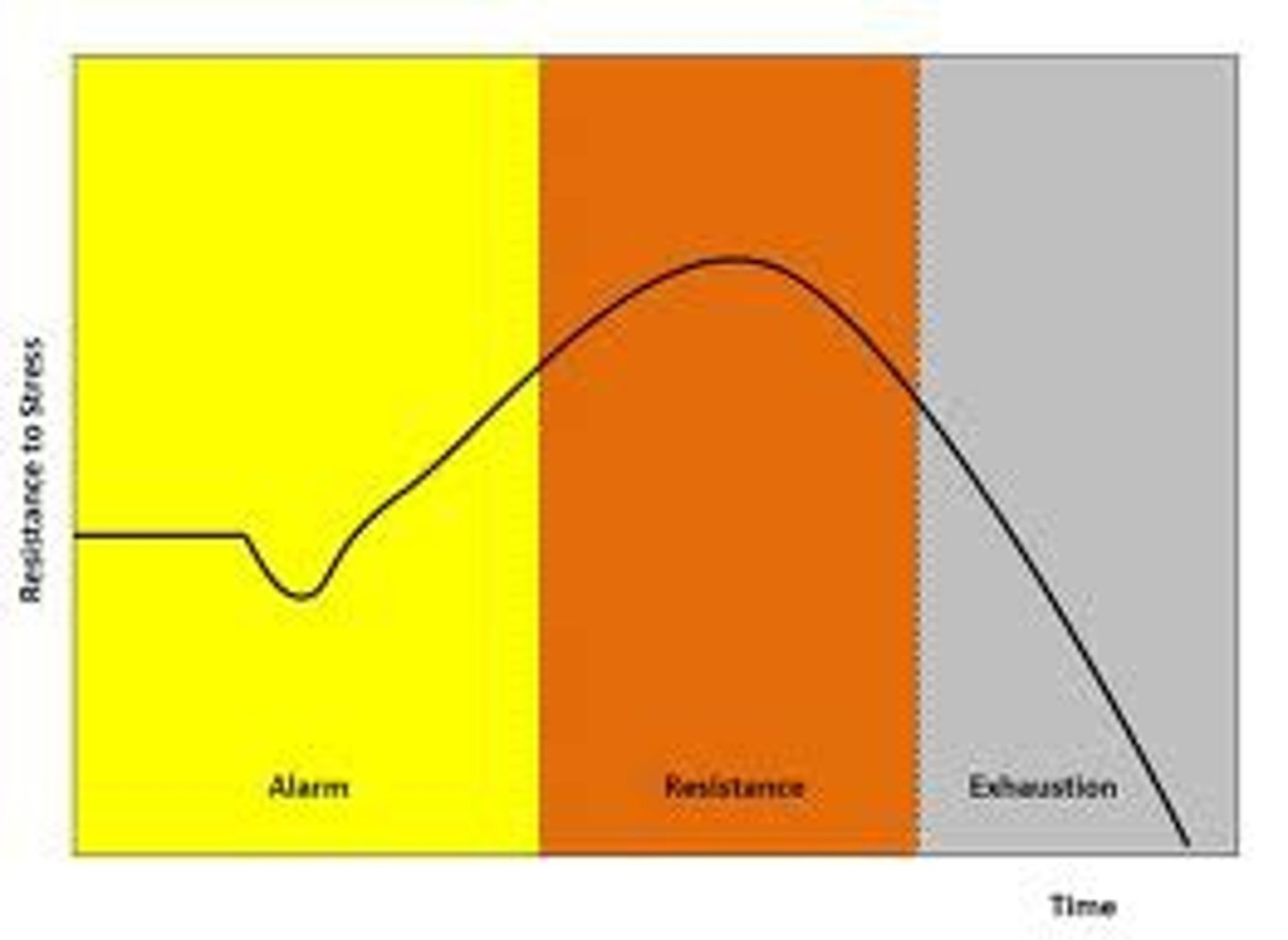
General adaptation syndrome (GAS)
describes a three-stage process the body goes through when exposed to any kind of stress, positive or negative
Alarm reaction phase
the first stage of GAS when the body reacts to a stressor with protective processes (fight-or-flight response)
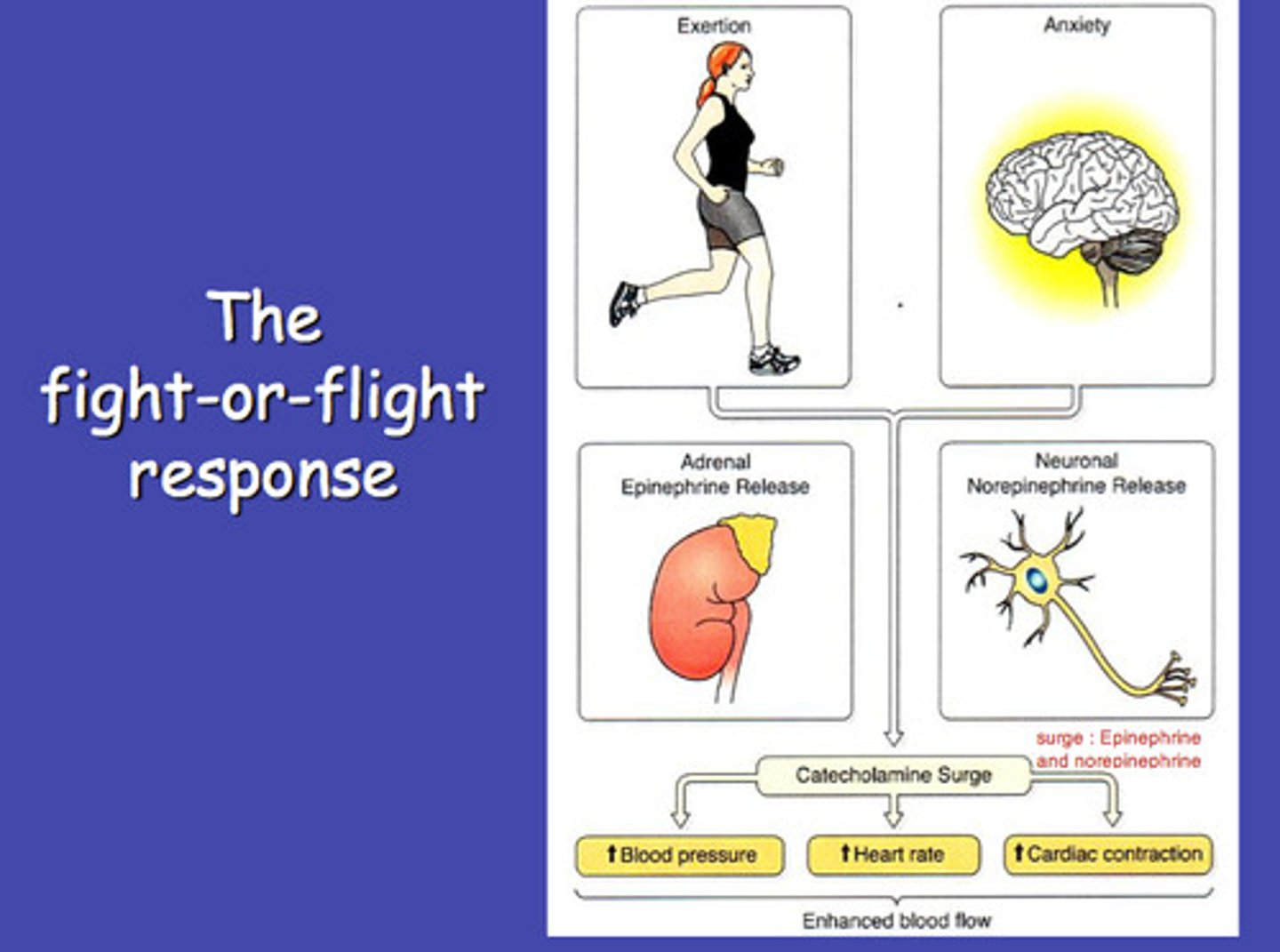
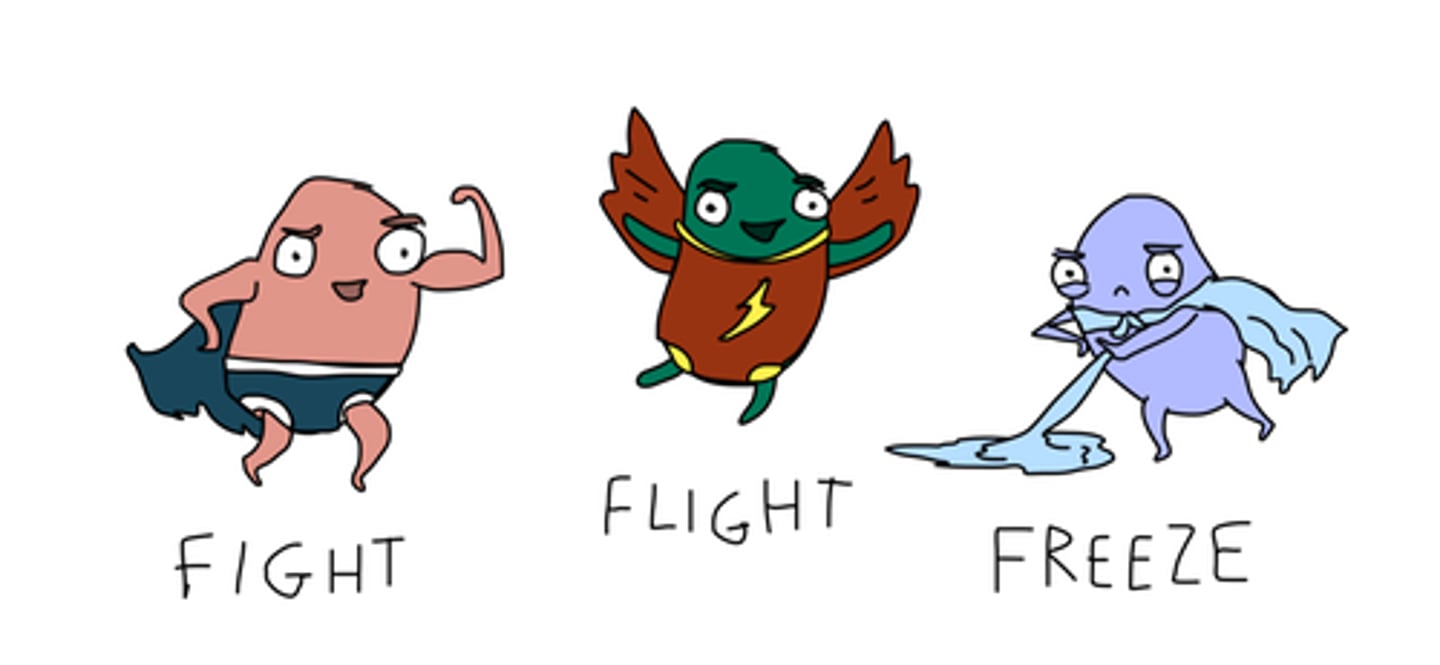
Flight-flight-freeze response
an involuntary, physical response to a sudden and immediate stressor that results in fight (facing a threat aggressively), flight (fleeing danger), or freeze (inability to move or act against a threat)

Resistance phase
the second stage of GAS when the body attempts to resist or adapt to the stressor through continued activation of physiological responses
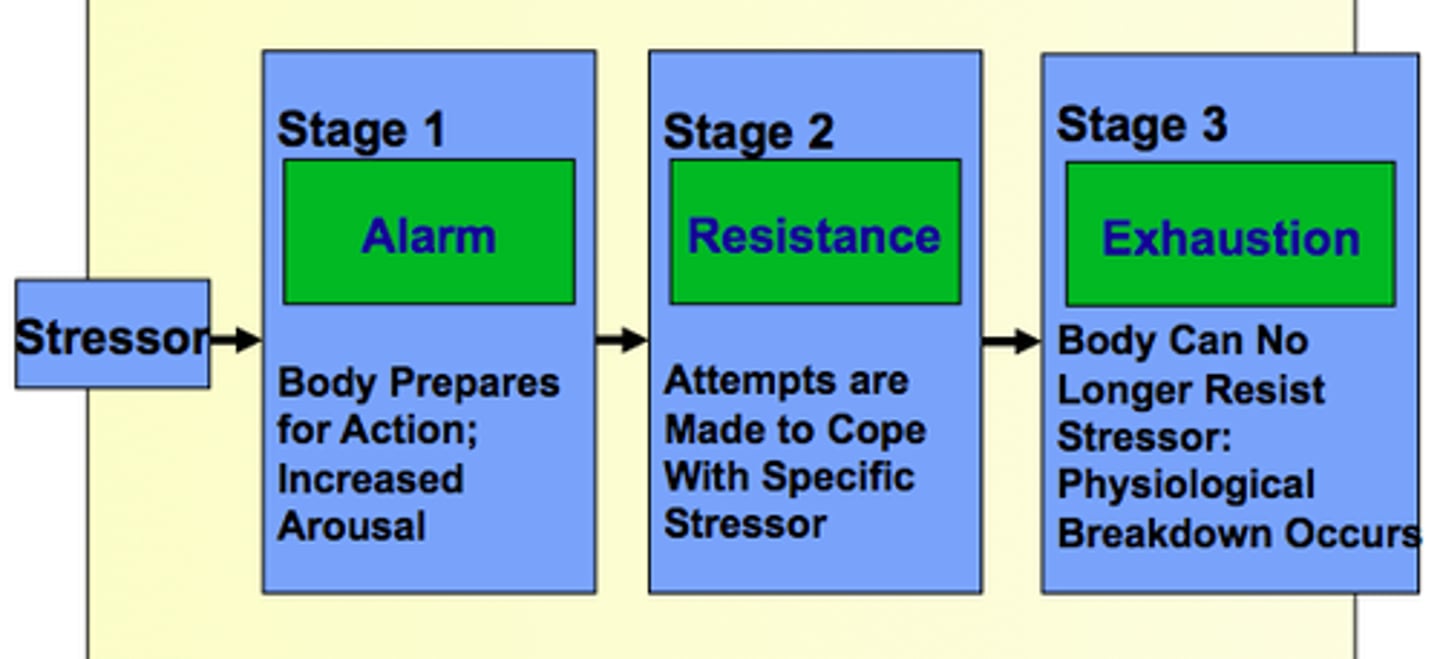
Exhaustion phase
the second stage of GAS when the body has depleted its resources and is unable to cope with stress (often results in fatigue, lethargy, irritability, decreased eating or sleeping, depression, anxiety)
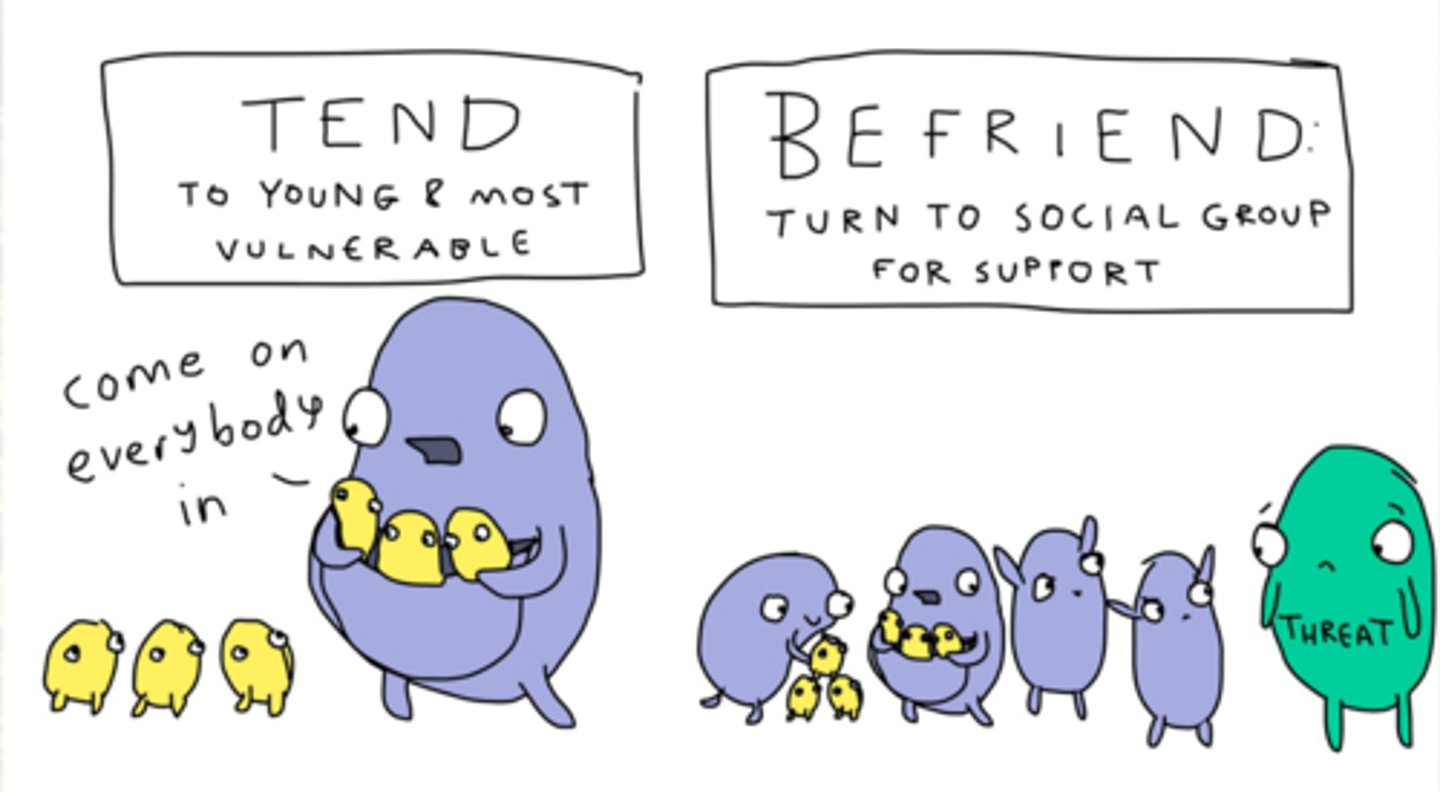
Tend-and-befriend theory
a theory that humans, especially females, cope with stressors by nurturing others and self (tending) and seeking social support (befriending)
Problem-focused coping
a technique that directly addresses a problem in order to eliminate or reduce its impact (actively working to change the situation that's causing stress)

Emotion-focused coping
a technique that manages negative emotions in response to a stressor, rather than trying to change the stressor itself (often used when the problem can't be changed or addressed)

Positive psychology
the study of human strengths and virtues which uses scientific principles to understand and improve human well-being

Well-being
a person's overall sense of happiness and satisfaction with their life, including how they feel and function in their personal and social lives

Resilience
the ability to adapt to challenging experiences, especially through behavioral, emotional, and mental flexibility as well as the ability to maintain well-being while facing adversity

Positive emotions
pleasant or desirable responses that range from interest and contentment to love and joy (indicating overall well-being and enhancing future growth and success)
Gratitude
a feeling of happiness and thankfulness in response to a gift, benefit, or fortunate happenstance

Positive subjective experiences
valued perceptions, emotions, and thoughts that are unique to each person such as gratitude, happiness, flow, contentment, and satisfaction

Subjective well-being
a person's evaluation of their overall happiness and life satisfaction

Signature strengths (virtues)
personality traits that are central to an individual and which produce positive outcomes for themselves and others

Positive objective experiences
observable aspects of well-being (e.g., happiness)

Happiness
a mental state of well-being characterized by positive feelings such as joy, contentment, fulfillment, and life satisfaction

Categories of virtues
the six classes of virtues (wisdom,
courage, humanity, justice, temperance, and transcendence) that are made up of 24 character strengths

Posttraumatic growth
the positive psychological change that some individuals experience after a life crisis or traumatic event

Dysfunction
a breakdown in a person's cognition, emotion, or behavior that indicates a significant issue with their psychological processes

Distress
a state of emotional suffering characterized by depression (e.g., loss of interest; unhappiness; desperateness) and anxiety (e.g., restlessness; feeling tense)

Deviation from the social norm
behavior significantly differing from societal expectations (cultures vary, so a universal set of social rules cannot be established)

Cultural/societal norms
shared beliefs, values, and behaviors that are expected of a society's members

Stigma
a negative social attitude towards a person's characteristic that is considered a physical, mental, or social deficiency
Racism
when a person or group is mistreated, disadvantaged, harassed, or degraded because of their ethnicity

Sexism
beliefs and behaviors that negatively evaluate people based on their gender, or that support unequal status between men and women

Ageism
prejudice, discrimination, or stereotyping of people based on their age

Discrimination
unjustifiable negative behavior toward a group and its members

Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)
a reference book that provides a standardized guide for diagnosing mental health disorders

International Classification of Mental Disorders (ICD)
a global system published by the World Health Organization for classifying mental and physical health conditions, including mental and behavioral disorders

Eclectic approach
an approach to psychotherapy that uses techniques from various forms of therapy that are tailored to a patient's needs

Behavioral perspective
proposes that the causes of mental disorders focus on maladaptive learned associations between or among responses to stimuli

Maladaptive learned associations
abnormal behaviors or cognitive processes that are a result of learning and go against social norms (e.g., post-traumatic stress disorder)

Psychodynamic perspective
proposes that the causes of mental disorders focus on unconscious thoughts and experiences, often developed during childhood
Humanistic perspective
proposes that the causes of mental disorders focus on a lack of social support and being unable to fulfill one's potential
Cognitive perspective
proposes that the causes of mental disorders focus on maladaptive thoughts, beliefs, attitudes, or emotions

Evolutionary perspective
proposes that the causes of mental disorders focus on behaviors and mental processes that reduce the likelihood of survival

Sociocultural perspective
proposes that the causes of mental disorders focus on maladaptive social and cultural relationships and dynamics

Biological perspective
proposes that the causes of mental disorders focus on physiological or genetic issues
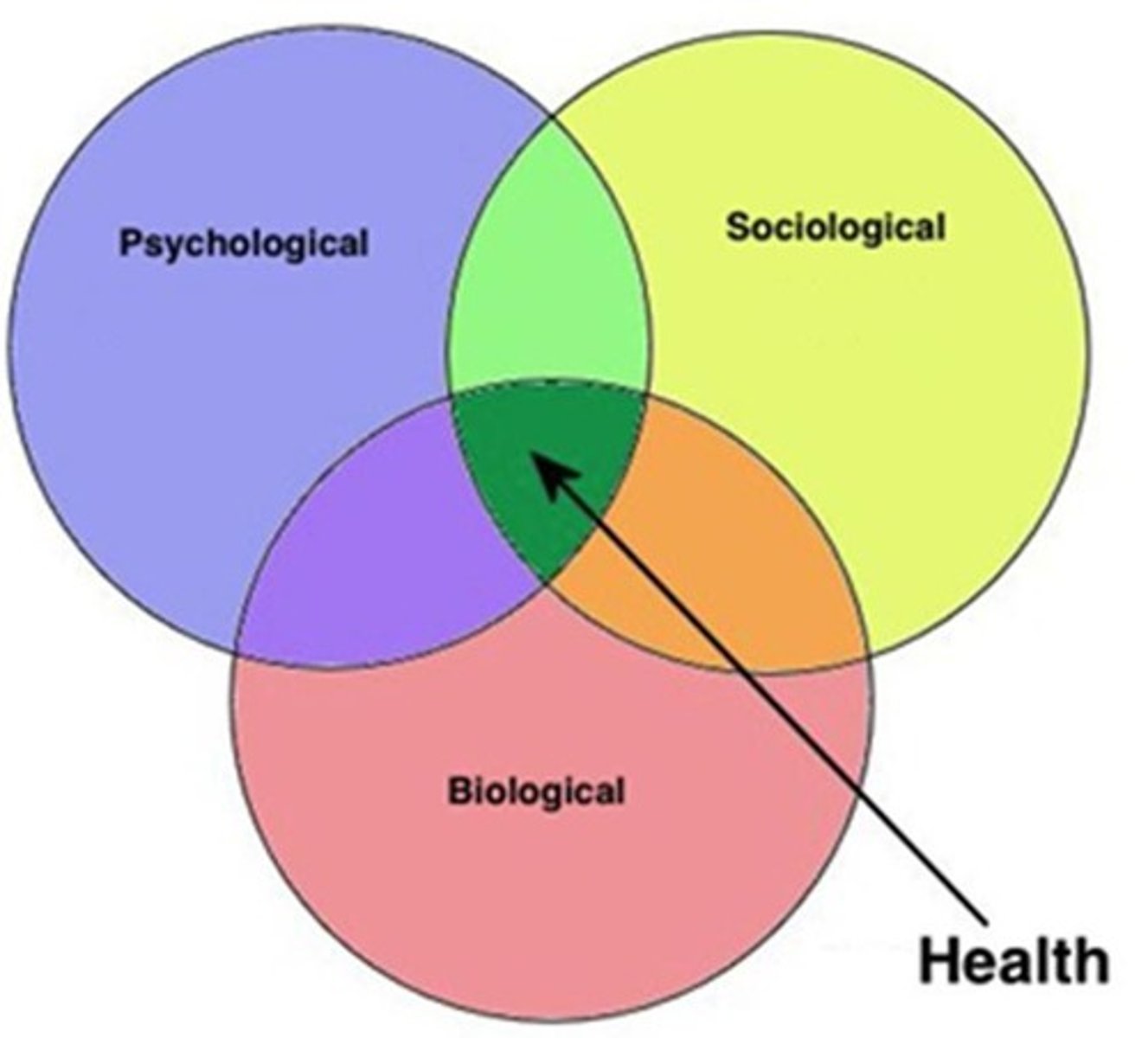
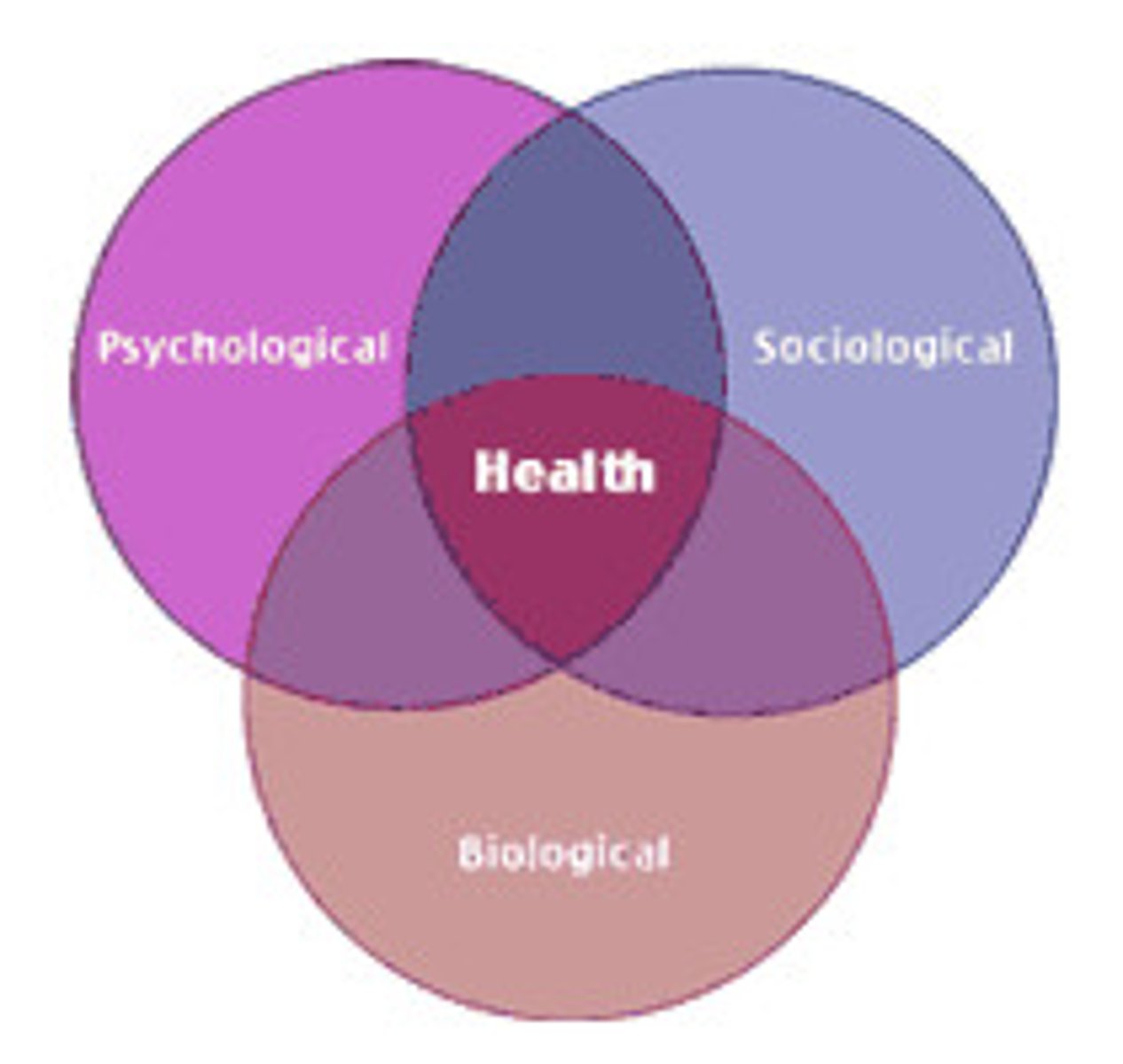
Biopsychosocial model
assumes that any psychological problem potentially involves a combination of biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors
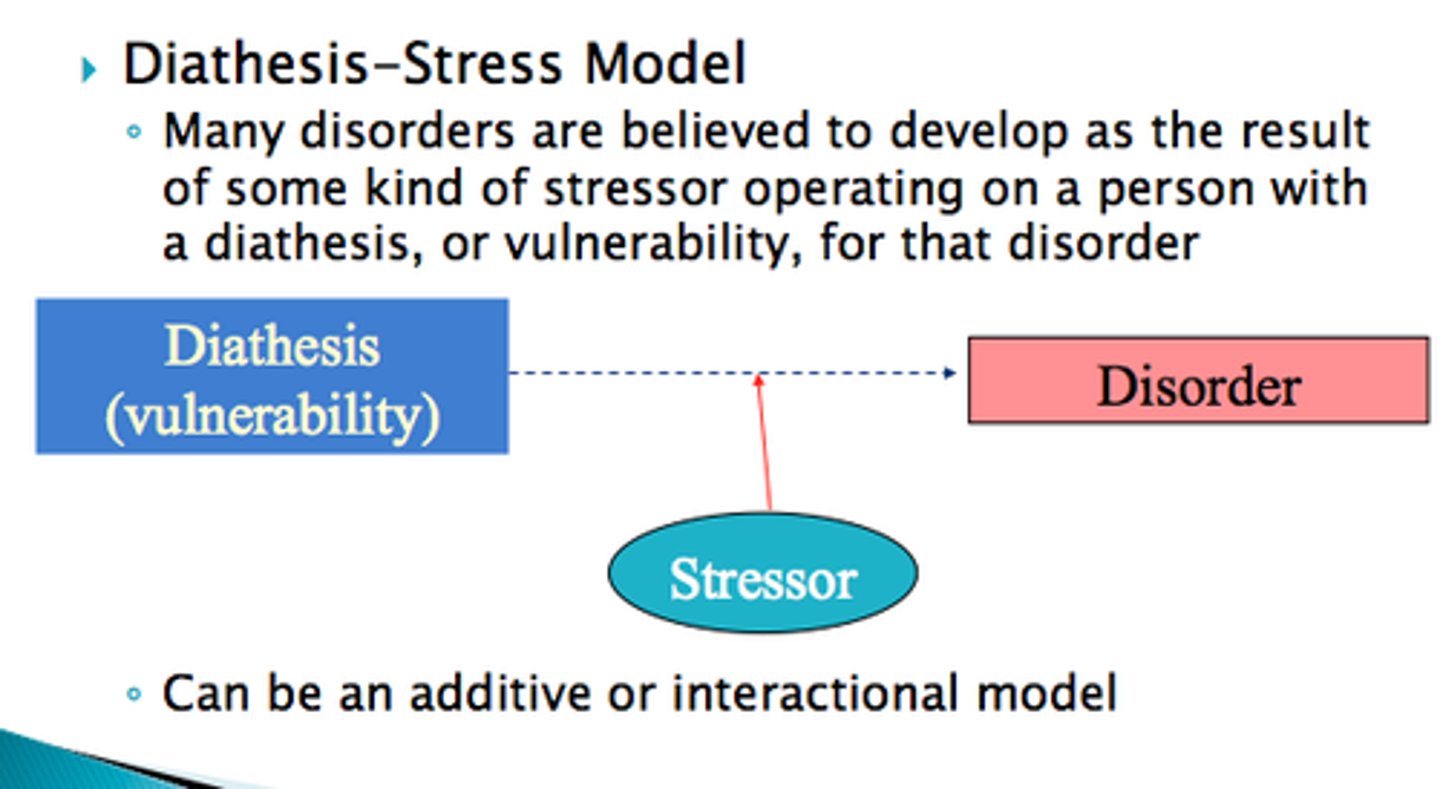
Diathesis-stress model
assumes that psychological disorders develop due to a genetic vulnerability (diathesis) in combination with stressful life experiences (stress)
Neurodevelopmental disorders
a group of disorders with onset occurring during the developmental period with a focus on whether the person is exhibiting behaviors appropriate for their age or maturity range

Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
a neurodevelopmental disorder that makes it difficult for people to focus and control their actions

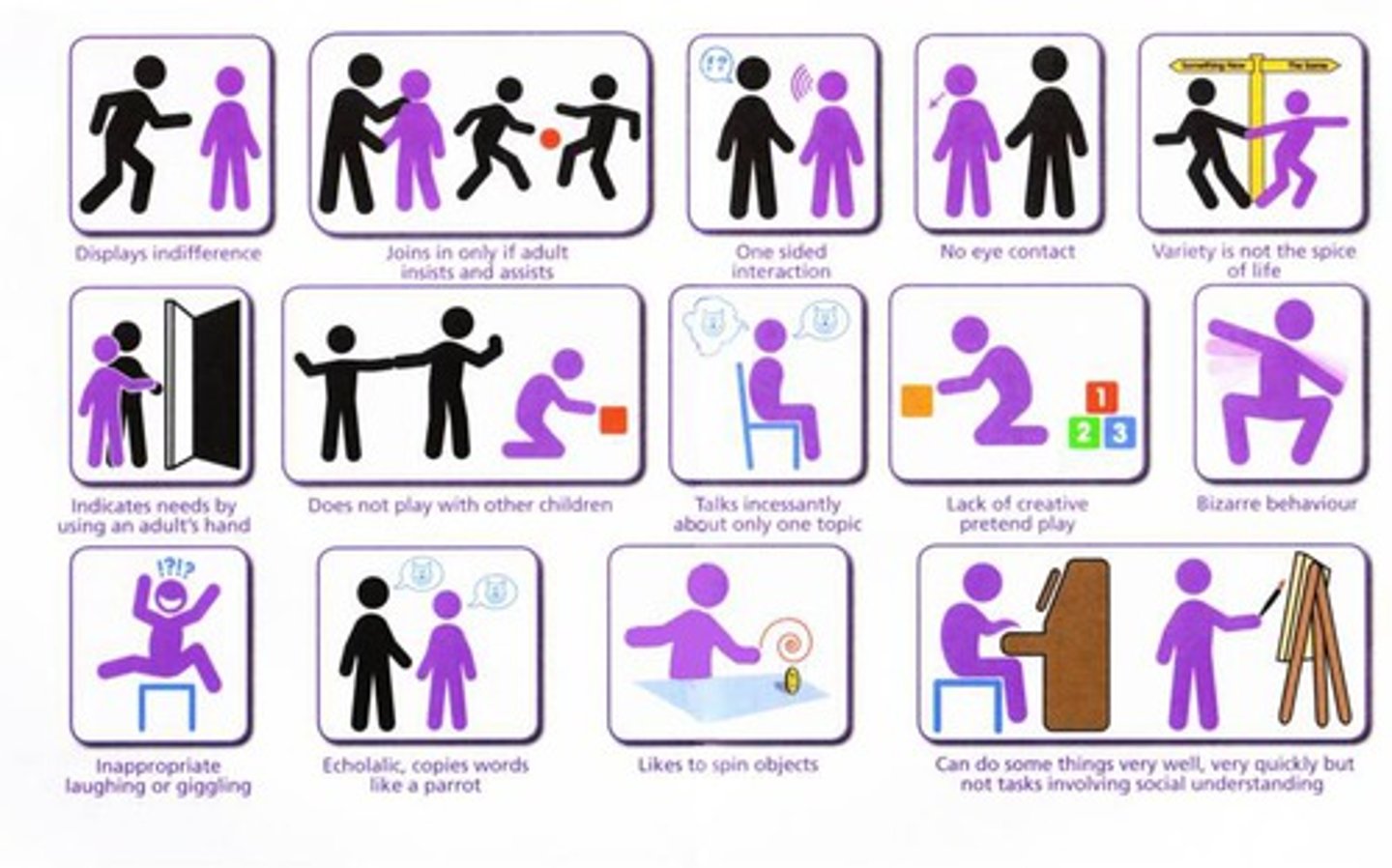
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by difficulties with social communication and interaction along with restricted and repetitive patterns in behaviors, interests, and activities
Schizophrenic Spectrum Disorders
a serious mental illness characterized by incoherent or illogical thoughts, bizarre behavior and speech, and delusions or hallucinations, such as hearing voices

Delusions
a positive symptom on the schizophrenic spectrum involving false beliefs (may include delusions of persecution or grandeur)

Delusions of persecution
a positive symptom on the schizophrenic spectrum involving a person believing they are being harmed or mistreated by others

Delusions of grandeur
a positive symptom on the schizophrenic spectrum in which a person falsely believes they are more important or powerful than they actually are

Hallucinations
a positive symptom on the schizophrenic spectrum related to false perceptions (may involve one or more of the senses)

Disorganized thinking
a positive symptom on the schizophrenic spectrum characterized by incoherent and disjointed thought processes (e.g., rambling, illogical remarks, as well as difficulty understanding, remembering, or completing tasks)

Disorganized speech
a positive symptom on the schizophrenic spectrum characterized by incoherent speech

Word salad
a form of disorganized speech involving stringing together words in nonsensical ways

Disorganized motor behavior
a positive symptom on the schizophrenic spectrum characterized by unusual movements or behaviors that can range from childlike silliness to unpredictable agitation
Catatonia
a symptom of disorganized motor behavior that is a positive symptom of schizophrenia in which someone is awake but does not seem to respond to other people and their environment (may involve impaired communication, unusual movements, bizarre postures, limited reactivity)

Excited catatonia
a positive symptom of schizophrenia involving excessive movement, agitation, and unusual behavior
Catatonic stupor
a negative symptom of schizophrenia characterized as unresponsiveness (e.g., lack of movement, isolation, withdrawal, mutism, bizarre posture)

Flat affect
a negative symptom of schizophrenia characterized by a lack of emotional expression (e.g., no facial expression, no eye contact, monotone voice, no body language, apathy)
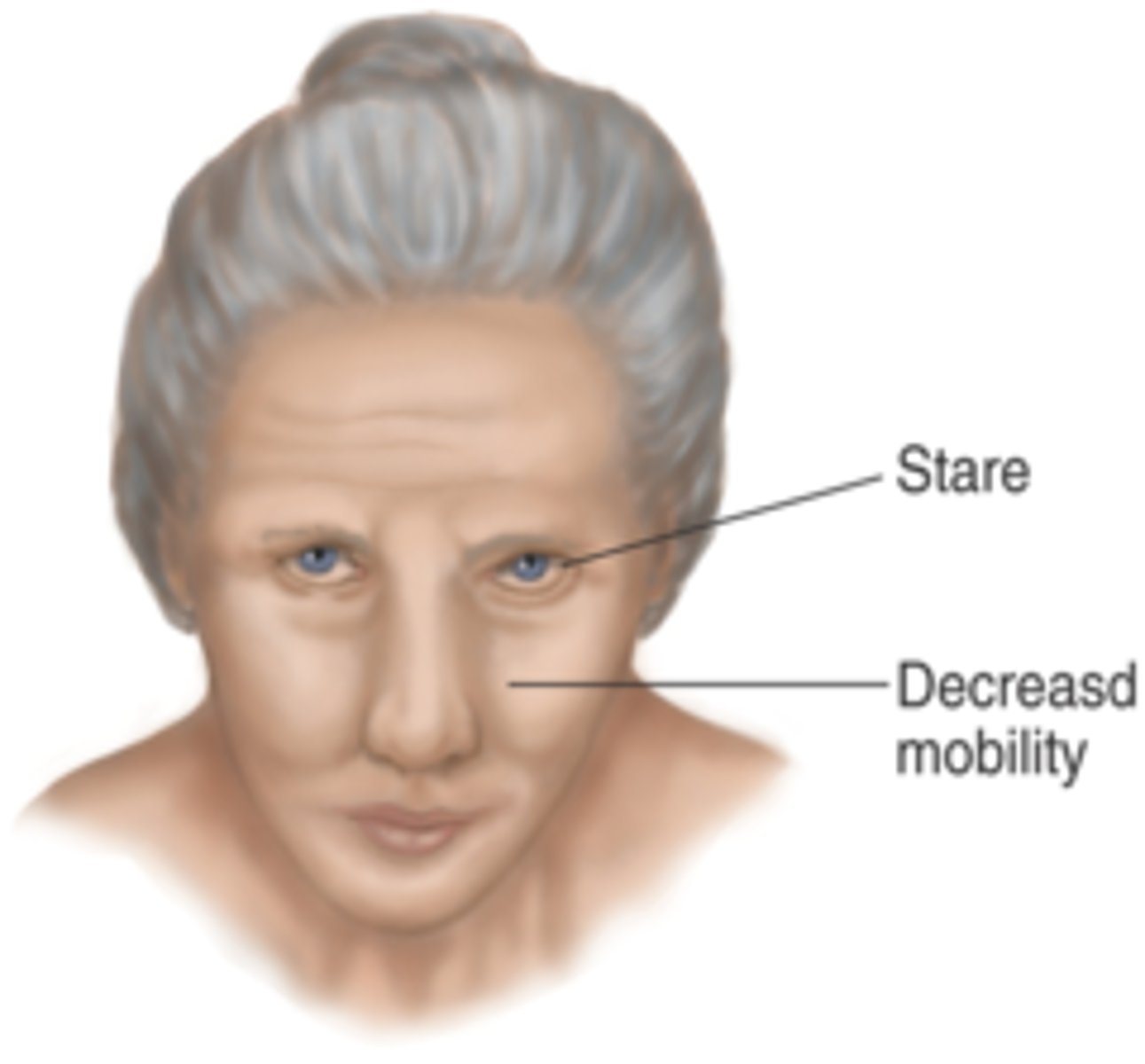
Negative symptoms
on the schizophrenic spectrum, these are symptoms that involve a decrease or absence of normal behaviors (e.g., the lack of movement or emotional expression)

Positive symptoms
the presence of psychotic behaviors on the schizophrenic spectrum such as hallucinations, delusions, inappropriate affect, and disorganized thinking/speech/behavior

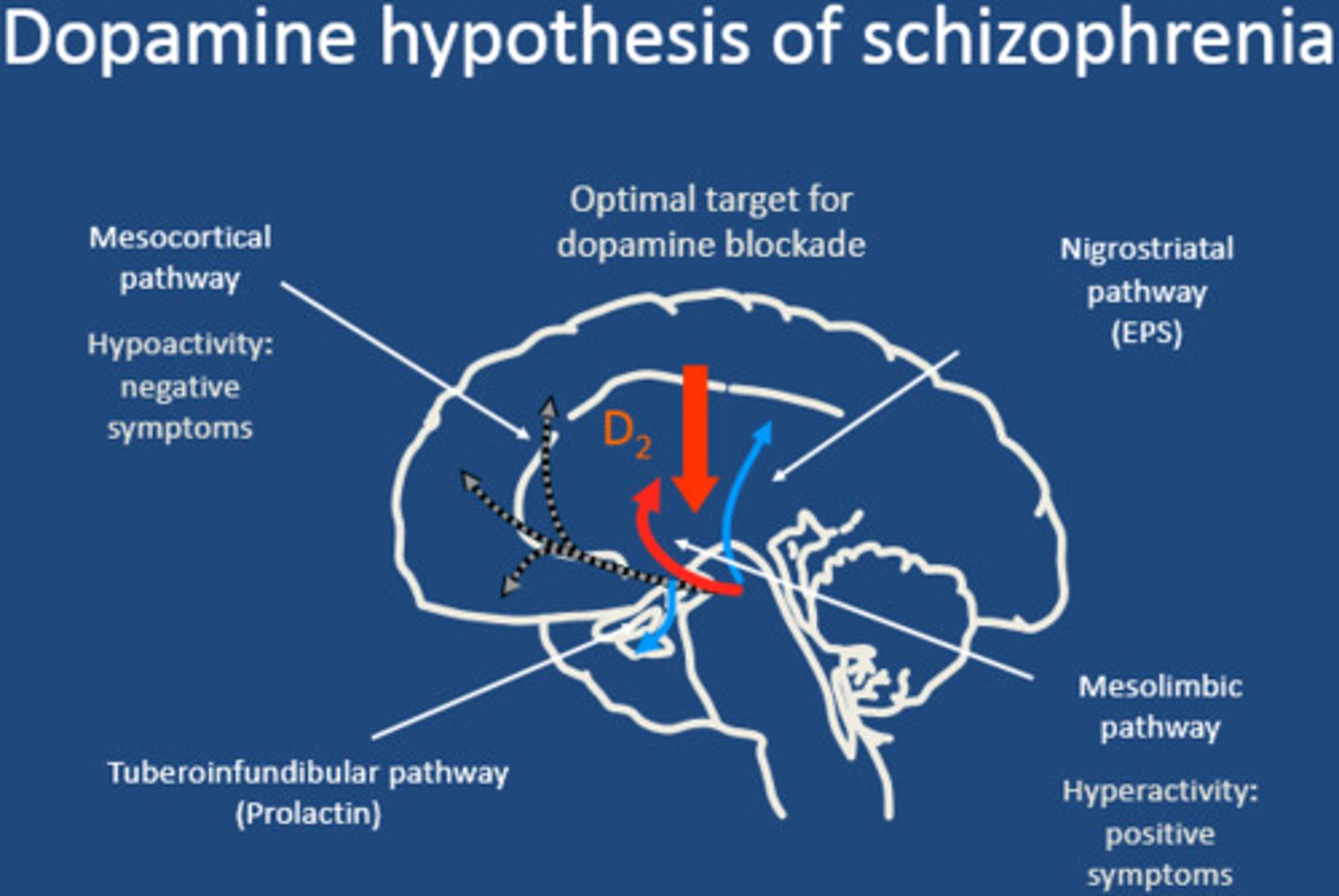
Dopamine hypothesis
a theory that schizophrenia is caused by imbalances with certain neurotransmitters which create an excess of dopamine in the brain
Depressive disorders
mental disorders characterized by the presence of sad, empty, or irritable mood along with physical and cognitive changes that affect a person's ability to function

Major Depressive Disorder
a condition that causes a persistent low mood, loss of interest in activities, and feelings of hopelessness and sadness

Persistent Depressive Disorder
a chronic low-level depression that is not as severe, but may last longer Major Depressive Disorder (also known as dysthymia)

Bipolar disorders
serious mental illnesses that causes extreme mood swings, often unpredictably

Depression
sadness or despair that lasts more than days and interferes with the activities of daily life

Cycling
an aspect of bipolar disorders where a person experiences four or more distinct mood swings within a year

Mania
an aspect of bipolar disorders characterized by abnormal arousal (e.g., high energy, impulsivity, euphoria, irritability)

Bipolar I Disorder
a type of bipolar disorder marked by full manic and major depressive episodes

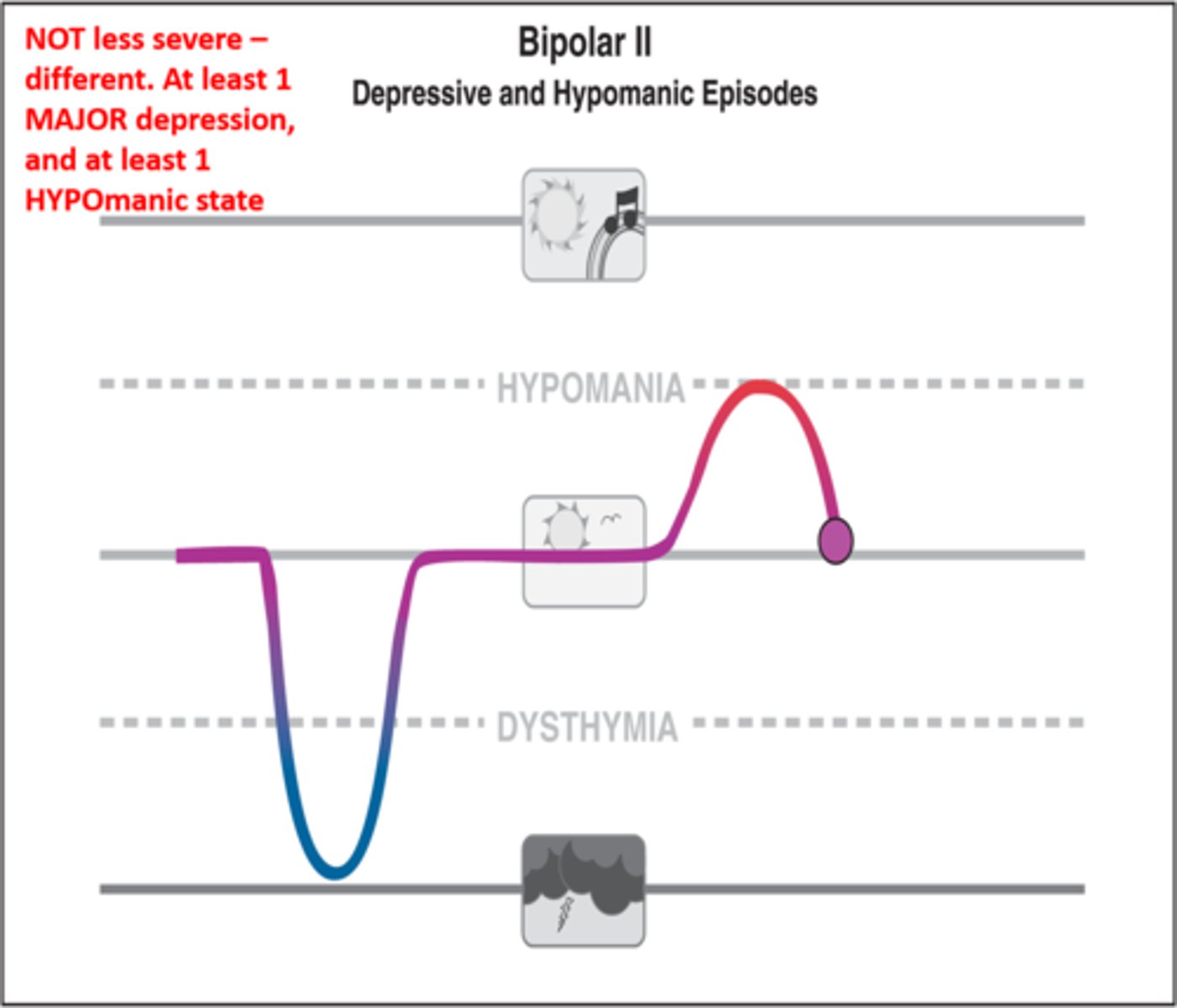
Bipolar II Disorder
a type of bipolar disorder marked by at least one mildly manic (hypomanic) episode and at least one major depressive episode
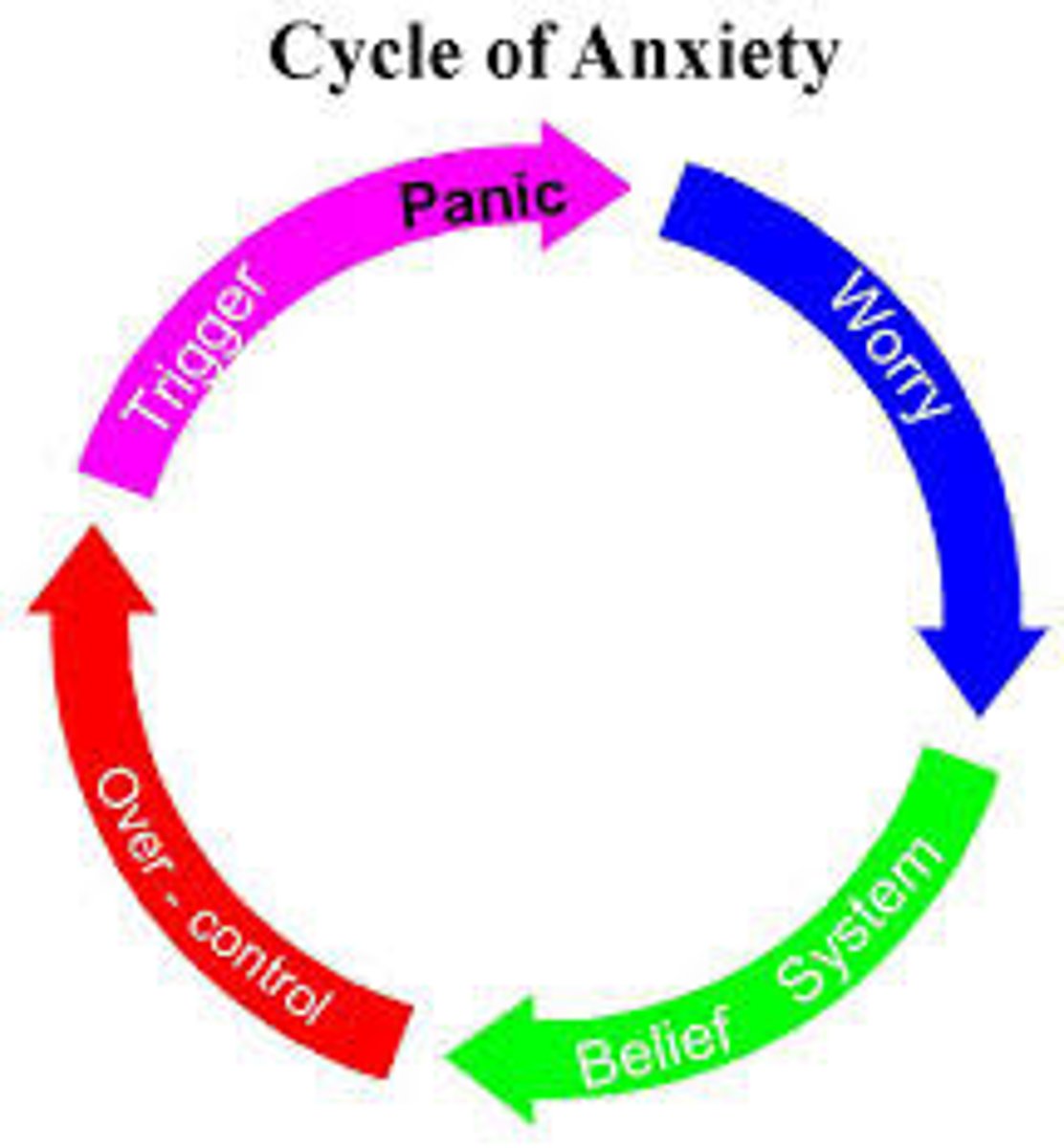
Anxiety disorders
mental health conditions characterized by excessive fear and/or anxiety with related disturbances to behavior
Specific phobia
an intense, irrational, and persistent fear of a particular object, situation, or activity that is much greater than the actual risk
Acrophobia
a specific phobia involving an irrational and excessive fear of heights

Arachnophobia
a specific phobia involving an irrational and excessive fear of spiders

Agoraphobia
an intense fear of specific social situations, including using public transportation, being in open spaces, being in enclosed spaces (e.g., shops, theaters, etc.), standing in line or being in a crowd, or being outside of the home alone

Panic disorder
an anxiety disorder characterized by repeated, unexpected panic attacks

Panic attack
unanticipated and overwhelming biological, cognitive, and
emotional experiences of anxiety

Ataque de nervios
a culture-bound anxiety disorder experienced mainly by people of
Caribbean or Iberian descent characterized by mental incapacitation fears, shakiness, chest tightness, palpitations, and a sense of inner heat

Social anxiety disorder
involves the intense fear of being judged or watched by others (may include agoraphobia)

Taijin kyofusho
a culture-bound anxiety disorder experienced mainly by Japanese people characterized by a fear that others are judging your body as undesirable, offensive, or unpleasing

Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
prolonged experiences of nonspecific
anxiety characterized by chronic excessive worry along with three or more of the following: restlessness, fatigue, concentration problems, irritability, muscle tension, and sleep disturbance

Obsessive-compulsive (and related) disorders
overlapping disorders involving unwanted thoughts along with behaviors that drive a person to do something over and over
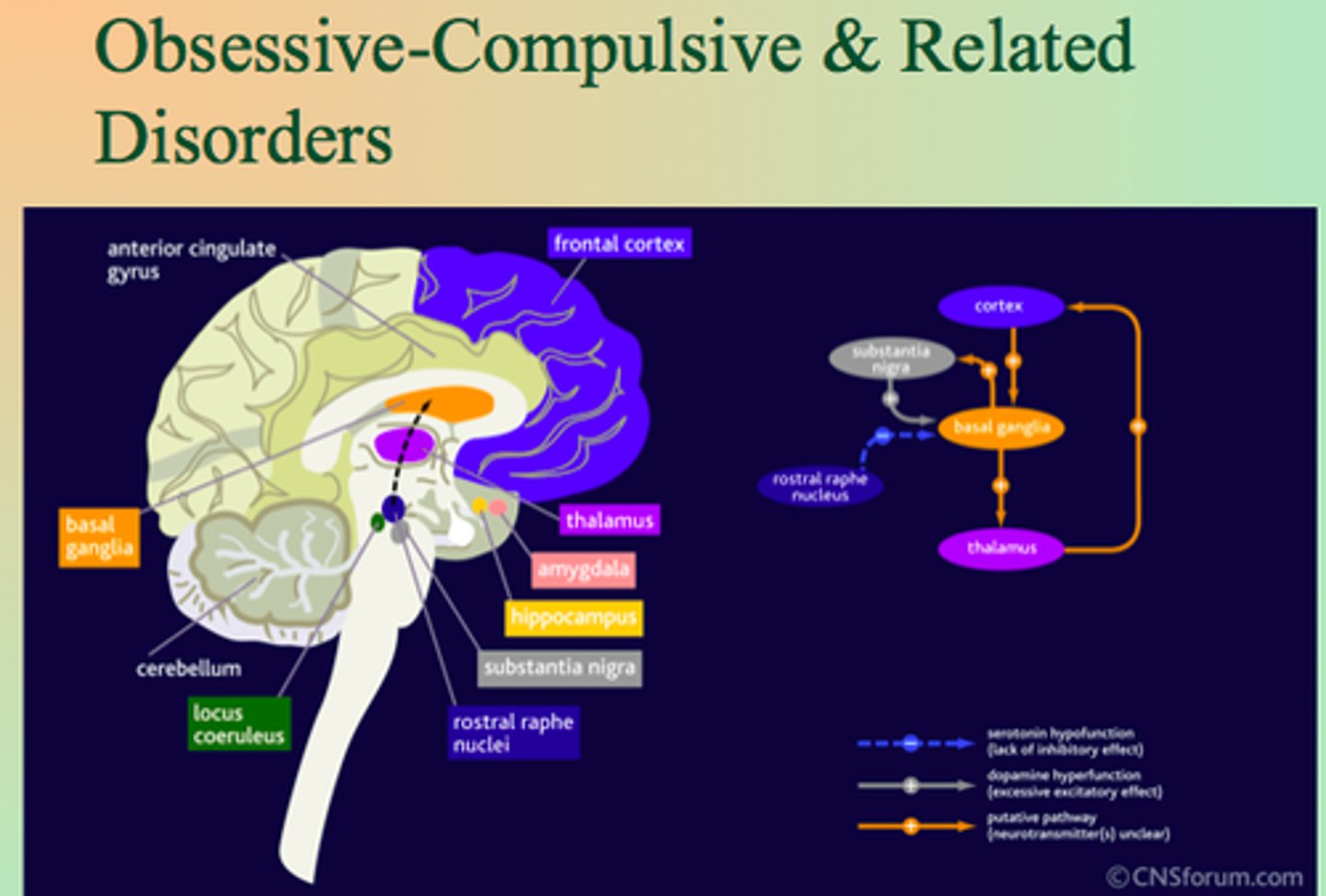
Obsessions
unwanted, intrusive, and distressing thoughts or urges that are difficult to control (e.g., excessive concern about germs)

Compulsions
repetitive actions or mental events that are performed to reduce distress or prevent a feared outcome (e.g., excessive hand washing)

Hoarding disorder
a persistent difficulty discarding possessions even if they have no clear value

Dissociative disorders
mental health conditions involving a loss of connection between a person's sense of self, memories, and identity (a person is "split off" or dissociated from their core sense of self)

Dissociation
when a person disconnects from their thoughts, feelings, memories, or sense of identity as a defense mechanism

Dissociative amnesia
a dissociative disorder characterized by memory gaps (often related to a traumatic or stressful event)

Fugue
a dissociative disorder characterized by sudden but temporary amnesia which may result in confusion about identity,
unexplained wandering, assuming a new identity

Dissociative identity disorder
a rare disorder in which a person seems to have two or more distinct (also known as multiple personality disorder)

Trauma and stressor-related disorders
various type of psychological
distress which can develop after a traumatic event or major life change

Hypervigilance
a symptom of trauma or stress characterized by being abnormally alert, especially to potential threats
