3.7 Alcohol and Drug Abuse: Wernicke Encephalopathy Insights
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
what type of drug is alcohol?
CNS depressant
ocular signs of intoxication with alcohol
horizontal gaze nystagmus
Cannabis type of drug
systemic signs of intoxication
psychoactive
decreased short term memory, impaired motor skills
Cannabis ocular signs of intoxication
- conjunctival injection
- reduced accommodative amplitude
- reduced IOP--typically 25%
Opiates type of drug (heroin, fentanyl, oxycodone)
systemic signs of intoxication are similar to ...
Ocular signs of intoxication?
- CNS depressant
- alcohol
- pupil constriction
Stimulants (cocaine, meth)
- systemic effects
- systemic signs of intoxication
- activate sympathetic NS
- tachycardia, high BP, perspiration/chills
Stimulants (cocaine, meth)
- ocular signs of intoxication
- pupil dilation
- slow pupillary reaction to light
Other CNS depressants (benzodiazapines, barbiturates)
- commonly used to ...
- systemic effects
- systemic signs of intoxication similar to ...
- ocular signs of intoxication
- counteract effects of stimulants
- slow brain activity
- alcohol
- horizontal gaze nystagmus
Cannabis/IOP lowering effect
- duration of effect?
- needs to be taken into account for patients with ...
- 2-4 hours (short)
- glaucoma
Nutritional optic neuropathy
- due to a nutritional deficiency in ...
- secondary to ..
- vitamin B complex (B12, B9-folic acid, B1-thiamine) or cooper
- long term alcohol abuse (2-20 yrs with >3 drinks per night)
- very poor nutrition
- malabsorption
Nutritional optic neuropathy -- characteristics
- bilateral, reduced VA
- very poor color vision
- temporal pallor ONH
- temporal RNFL wedge defect
- cecocentral/generalized VF defect
Nutritional optic neuropathy management
- extensive work up to rule out other causes
- vitamin supplementation
- addiction rehab
Alcohol abuse -- ocular manifestations
- nutritional optic neuropathy
- Wernicke encephalopathy
- dry eye
Wernicke Encephalopathy
- cause
- thiamine (b1) deficiency often due to alcohol abuse
Wernicke Encephalopathy triad of findings
- Encephalopathy (disorientation, inattentiveness, bad memory)
- Gait ataxia
- Ophthalmoplegia/nystagmus (horizontal gaze evoked nystagmus )
keep in mind this clinical triad may not be all present in up to 90% of patients
Wernicke encephalopathy should be considered in any patient who has ...
alcoholism and develops nystagmus
Wernicke Encephalopathy
- level of urgency?
- patient needs what?
- if left untreated ...
- emergency
- IV thiamine (B1)
- 20% untreated patients die
- surviving patients can develop Korsakoff syndrome (anterograde amnesia (can't form new memories) and retrograde amnesia (can't recall memories before event))
Alcohol and dry eyes explain how it happens?
- ethanol is secreted into tears after consuming alcohol -- causing hyperosmolarity and inflammation
- alcoholism increases risk for vit A deficiency (vit A deficiency caues xerophthalmia)
Protective effects of alcohol
- light moderate drinking (1 drink/night women, 2 drinks/night men) reduces risk of some forms of CV disease
Negative effects alcohol
- increases risk of many forms of cancer even in moderate use
- heavy use increases risk of many health problems
Talc retinopathy
- what is it?
- crystalline deposits in macular region
- due to talc fillers in drug being injected
- can occur after long term drug injection
- largely stable
Talc retinopathy
- significance
- management?
- typically minimal to no visual significance
- also seen in other parts of body
- rarely can cause retinal microvasculopathy
- monitor for signs of retinopathy
crystalline deposits in macular region -- Talc retinopathy
what is this and found in what thing?
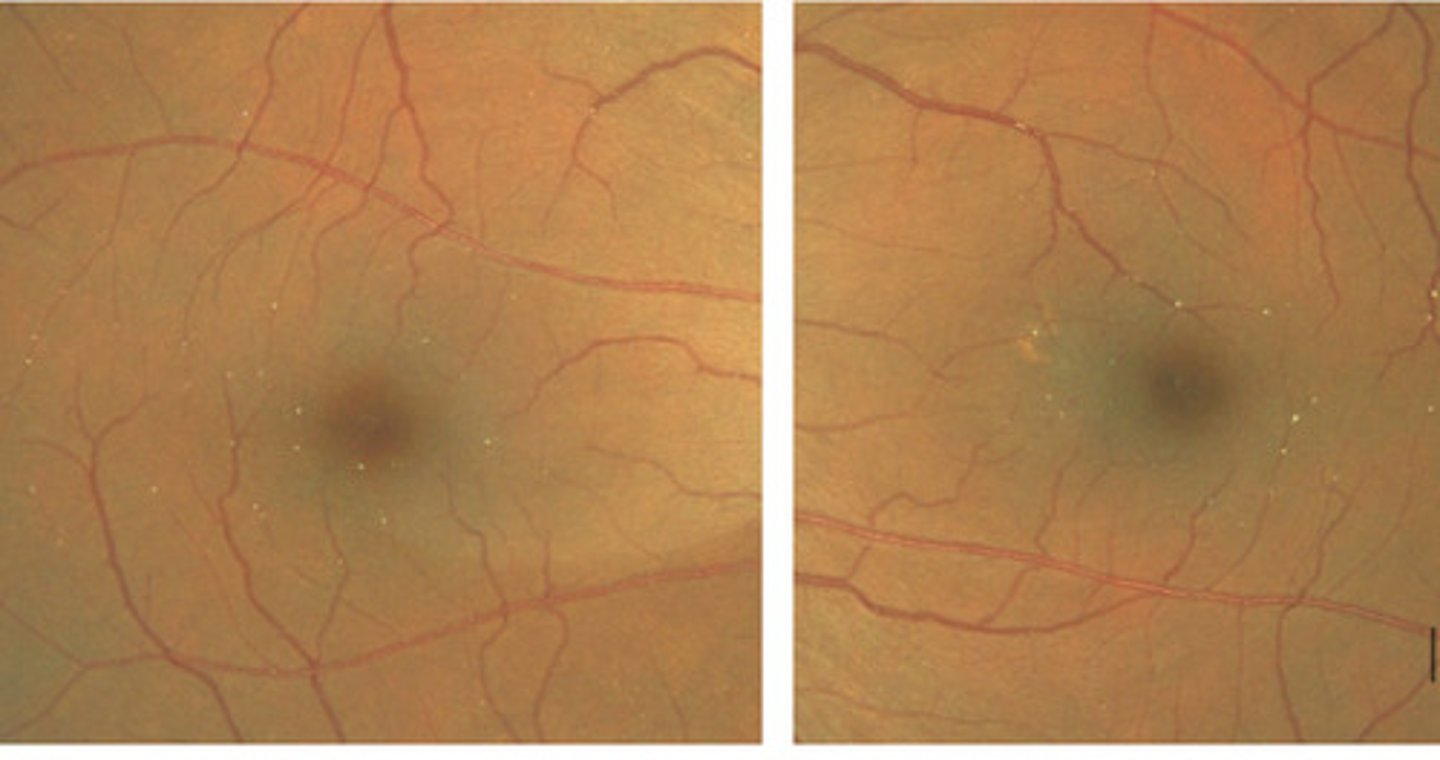
Why is talc retinopathy benign-- why doesn't it cause retinal vein occlusions?
- drugs are typically injected into vein in arm
- larger talc particles embolize in the lung
- the particles seen in retina are accumulations of very small particles that have been deposited on the side of vessel walls
Crack cornea
- what is this?
- reduced corneal sensitivity from chronic cocaine use
- can lead to neurotrophic keratitis
crack cornea -- from chronic cocaine use
what is this
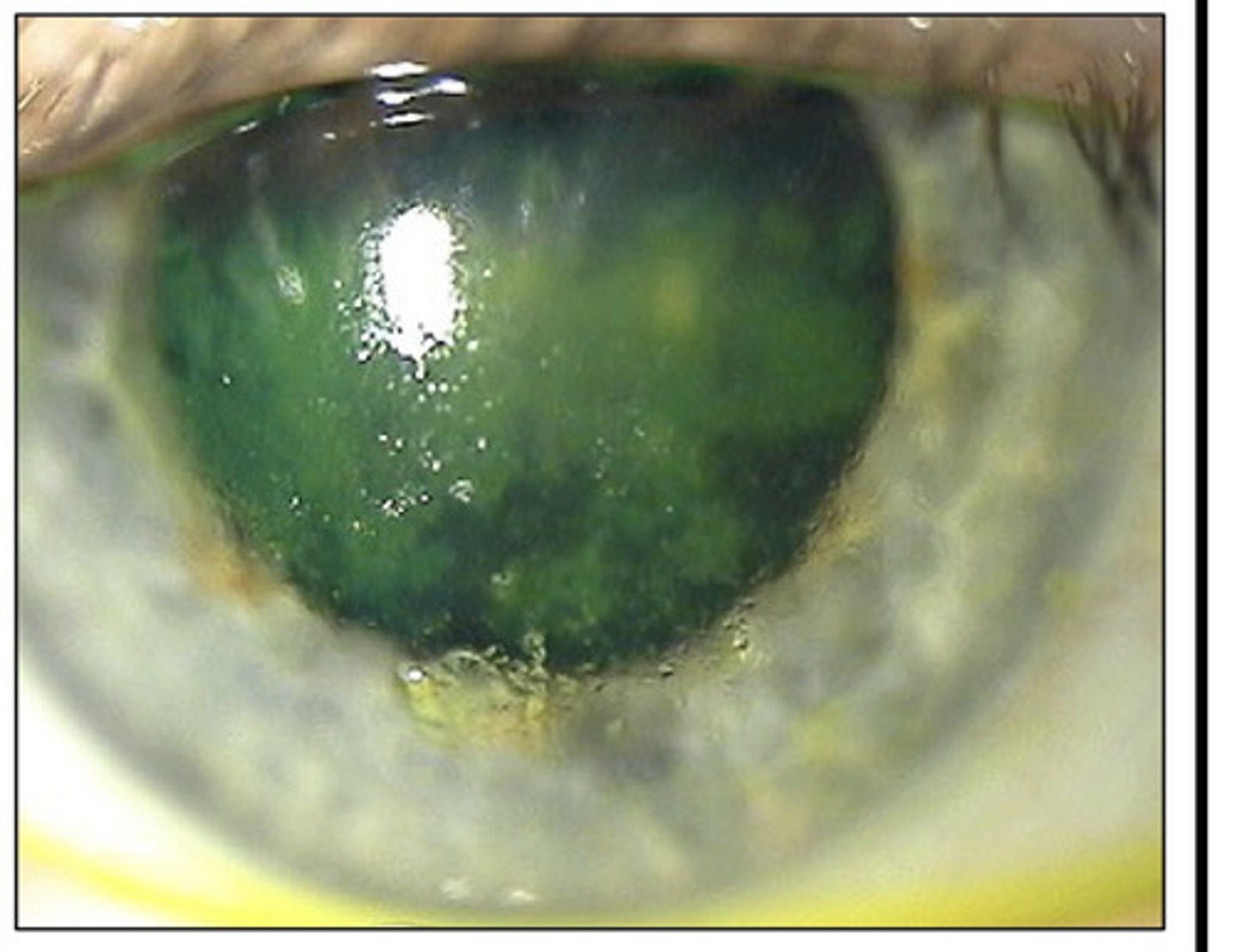
Why are stimulants uniquely risky?
- these drugs activate sympathetic nervous system
- they are pro-inflammatory so increased risk of vasculitis and atherosclerosis
- cocaine promotes thrombus formation
- ocular effects: INCREASED RISK OF ARTERIAL AND VENOUS OCCLUSIONS
Cigarette smoking ocular manifestations
- dry eye
- doubled risk of cataract formation
- 4x higher risk of AMD
- pts with Grave's/Hashimoto=increased risk of developing thyroid eye disease
- increased risk of developing uveitis
- increased risk of developing glaucoma