1 Cerebrum
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the difference between nuclei and ganglia?
Nuclei: groups of neurons within the CNS
Ganglia: groups of neurons outside of the CNS
What is the telencephalon?
Cerebral hemispheres and basal ganglia
What is the basal ganglia?
Group of nuclei deep within the cerebrum; participate in the control of movement.
What is the diencephalon?
Anything with the word thalamus in it
Difference between sulci and fissures?
Sulci refers to smaller grooves, and fissure refers to a deeper groove
Function of the telencephalon (cerebrum)?
Conscious thought processes and intellectual functions.
Memory storage and processing
Conscious and subconscious regulation of skeletal muscle contraction
Funciton of the metencephalon (cerebellum)?
Coordinates movements
Function of the mesencephalon (midbrain)?
Processing of visual and auditory data
Generation of reflexive motor responses.
Maintenance of consciousness
Function of the metencephalon (pons)?
Relays sensory information to cerebellum and thalamus
Subconscious somatic and visceral motor centers
Function of the medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)?
Relays sensory info to thalamus
ANS for visceral functions such as the heart and lungs
What structure is a dural fold of the dura mater, lies in the medial longitudinal fissure and separates the left and right hemispheres of the brain?
Falx cerebri
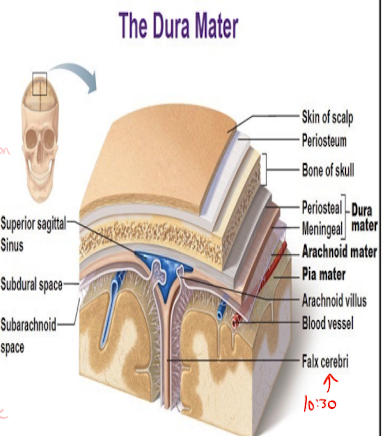
What structure sits between the occipital lobe and cerebellum, and protects the brain from rotatory/linear movement?
Tentorium cerebelli
The epidural space is between what structures?
Skull and dura mater
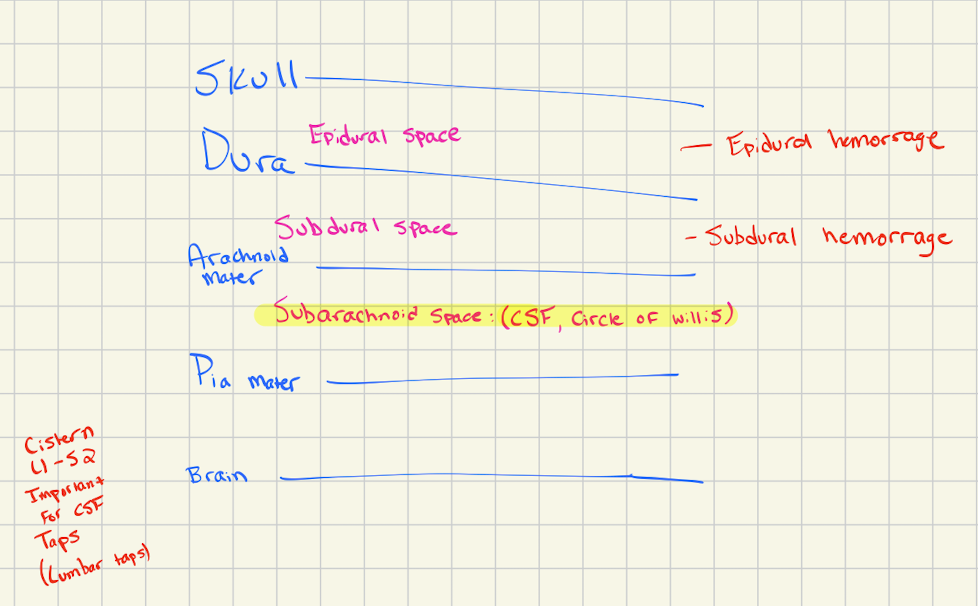
The subdural space is between what structures?
Dura mater and arachnoid mater
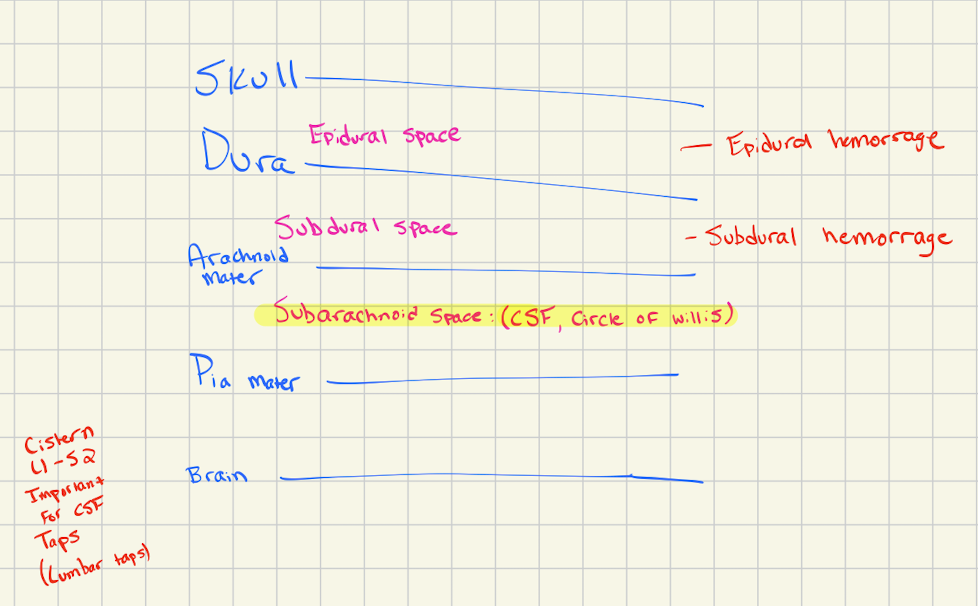
The subarachnoid space is between what structures?
Arachnoid mater and pia mater
What significant structures are in the subarachnoid space?
CSF and the circle of willis
What is the expansion of the subarachnoid space that is located between L1 and S2?
Lumbar cistern (important for lumbar taps)
What is the significance of CSF?
Provides nutrition
Protects brain and is a shock absorber
Blood brain barrier (prevents toxins from entering the brain and some medications)
Remove waste
Helps with diagnoses
What secretes CSF?
Choroid plexus
What structure divides the lateral ventricles?
Septum pellucidum which covers the medial half of each ventricle.
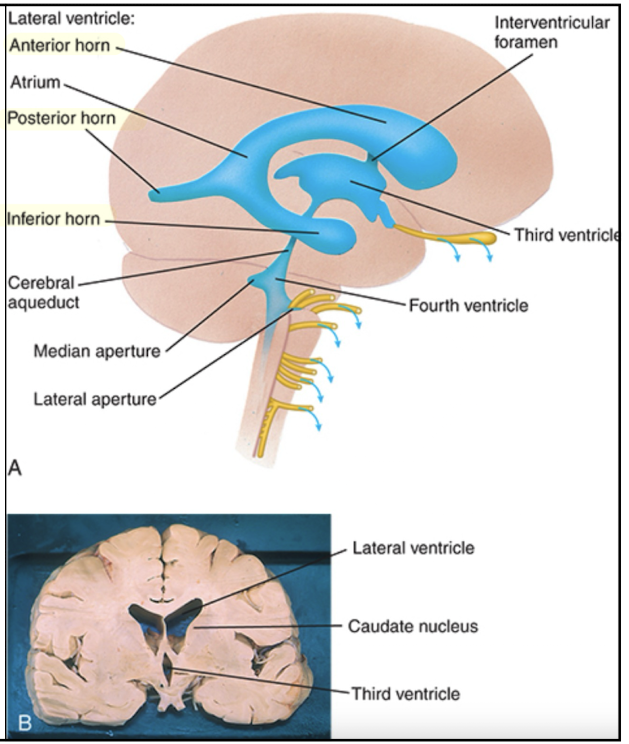
Each ventricle has 3 horns. List which lobe of the brain each horn projects into.
Anterior: projects into frontal lobe
Inferior: projects into temporal lobe
Posterior: projects into occipital lobe
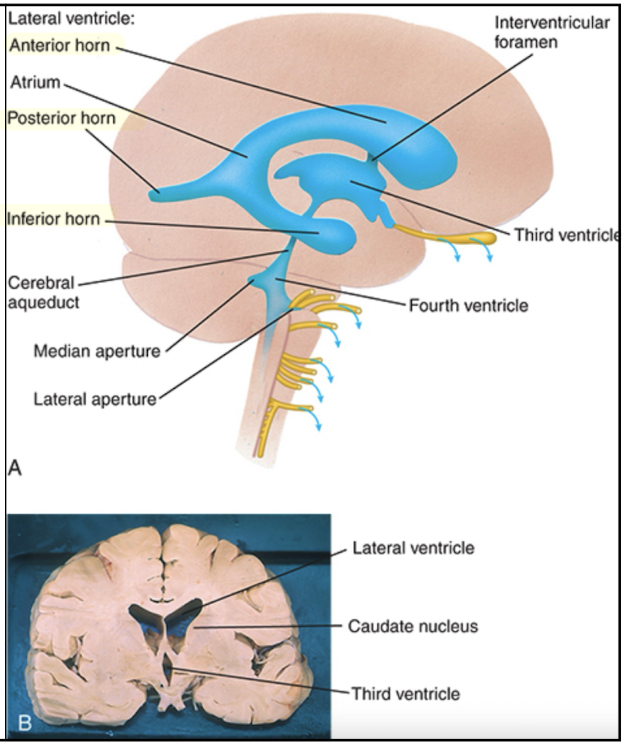
The 3rd ventricle is surrounded by what structure?
Diencephalon
Where is the 4th ventricle located?
Within the pons, rostral (anterior) medulla, and cerebellum
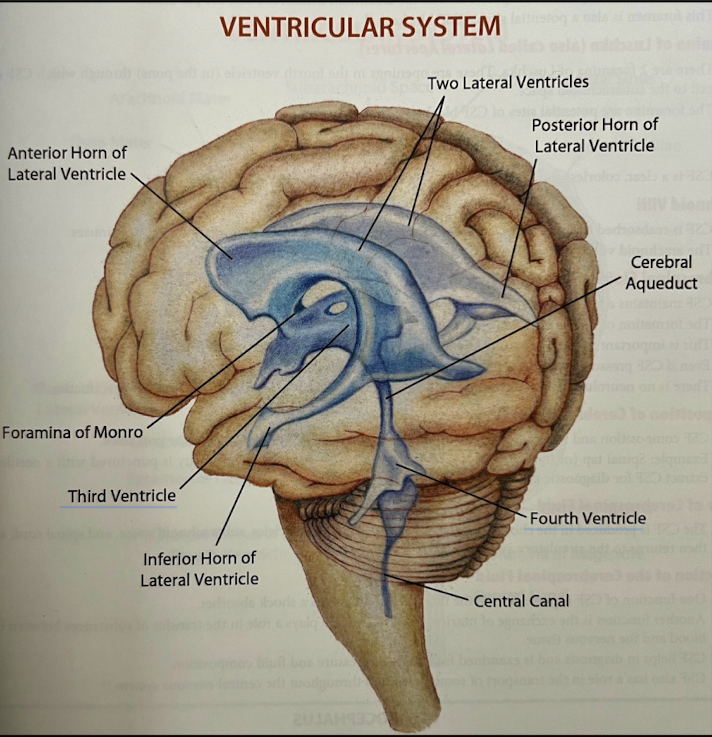
What structure connects the 3rd and 4th ventricles, and is a common site of blockage?
Cerebral aqueduct
What structure connects the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle?
Foramina monro
What is the structure that has 2 openings that goes into the 4th ventricle (in the pons) through which CSF exits to the subarachnoid space?
Foramina of Luscka
What structure is the opening in the 4th ventricle and opens to the subarachnoid space below the cerebellum, above the brain, and beneath the skull?
Foramen of Magendie
List the path of CSF and the structures if goes through.
Produced in the choroid plexus within the ventricle system
Lateral ventricles (L+R)
Foramina of Monro (interventricular foramina)
Third ventricle
Cerebral aqueduct (of Sylvius)
Fourth ventricle
Foramina of Luscka and Magendie
Subarachnoid space
Arachnoid villi
Venous drainage (cycle complete)
What are arachnoid villi?
Small protrusions on the arachnoid mater that helps reabsorb CSF to bring it back to the sinuses and back to the circulatory system
What is non-communicating hydrocephalus?
Blockage in the foramina or cerebral aqueduct (common blockage in the third ventricle)
What is communicating hydrocephalus?
From impaired reabsorption of CSF, NOT from a blockage.Subarachnoid space can be narrowed or blocked.
What is normal pressure hydrocephalus? What is the result of this?
Develops in older adults; spaces become enlarged without an accompanying increase in intracranial pressure.
Arachnoid cilli cannot reabsorb CSF. Can cause dementia, incontinence, gait abnormalities.