Neurons
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What are neurons?
Neurons make up 80% of the human nervous system.
Transmit signals electrically and chemically.
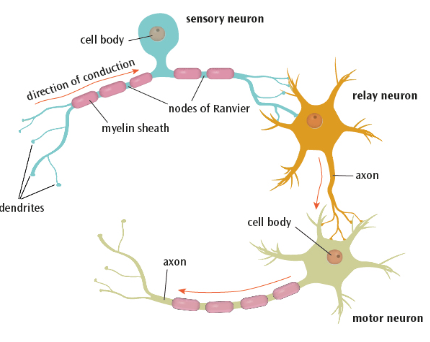
What are the 3 types of neurons?
Sensory
Relay
Motor
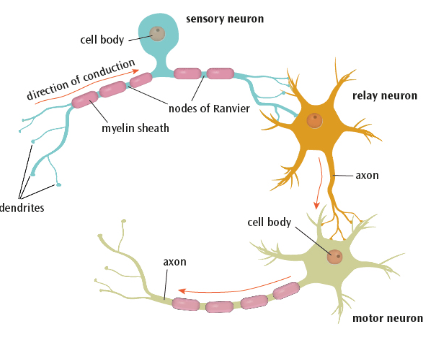
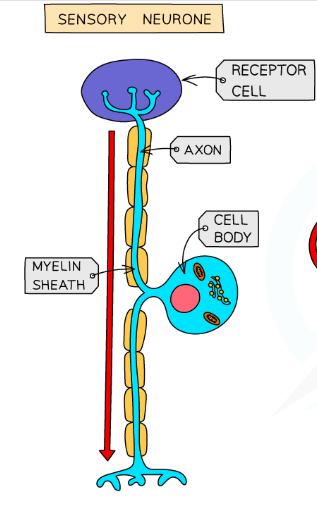
What are sensory neurons?
Carry messages from the PNS to the CNS
They have long dendrites and short axons
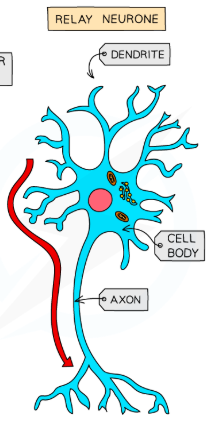
What are relay neurons?
Connect the sensory neurons to the motor or other relay neurons
They have short dendrites and short axons
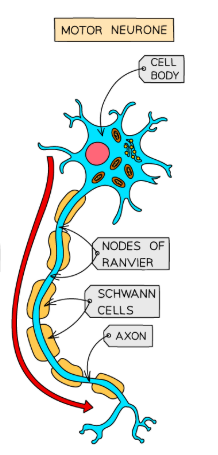
What are motor neurons?
Connect the CNS to effectors such as muscles and glands.
They have short dendrites and long axons
Control physical movements e.g. contraction of muscles
What is the structure of a neuron?
Neurons vary in size from less than a mm to up to a metre long but all share the same basic structure of a cell body and axon.
What is a neuron made up of?
Cell body and Axon
What is the cell body?
Includes a nucleus, which contains the genetic material of the cell.
Branchlike structures called dendrites protrude from the cell body. These carry nerve impulses from neighbouring neurons towards the cell body
What is the axon?
Carries the impulses away from the cell body down the length of the neuron.
Covered in a fatty layer of myelin sheath that protects the axon and speeds up electrical transmission of the impulse.
If the myelin sheath was continuous this would have the reverse effect and slow down the electrical impulse.
Thus, the myelin sheath is segmented by gaps called nodes of Ranvier which speed up the transmission of the impulse by forcing it to ‘jump’ across the gaps along the axon.
At the end of the axon are terminal buttons that communicate with the next neuron in the chain across a synapse.
Where are motor neurons located?
In the CNS
But they have long axons which form part of the PNS
Where are sensory neurons located?
In the PNS, in clusters known as ganglia
Where are relay neurons located?
Make up 97% of all neurons
Found in the brain and visual system
What is electrical transmission? (Firing of a neuron)
When a neuron is in a resting state, the inside of the cell is negatively charged.
When a neuron is activated by a stimulus, the inside of the cell becomes positively charged for a split second causing an action potential to occur.
This creates an electrical impulse that travels down the axon towards the end of the neuron.