AP Microeconomics Unit 2
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
1
New cards
Change in Demand
a shift of the demand curve, which changes the quantity demanded at any given price.
2
New cards
Change in Supply
a shift of the supply curve, which changes the quantity supplied at any given price.
3
New cards
Competitive Market
a market in which there are many buyers and sellers of the same good or service, none of whom can influence the price at which the good or service is sold.
4
New cards
Complements
two goods (often consumed together) for which a rise in the price of one of the goods leads to a decrease in the demand for the other good.
5
New cards
Consumer Surplus
the net gain received from purchasing a good or service; often used to refer to both individual and total
6
New cards
Consumption Bundles
Typical groups of goods and/or services purchased
7
New cards
Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand
(between two goods) measures the effect of the change in one good’s price on the quantity demanded of another good; is equal to the percent change in the quantity demanded of one good divided by the percent change in the other good’s price.
8
New cards
Deadweight Loss
the value of foregone mutually beneficial transactions; (from a tax) the decrease in total surplus resulting from the tax, minus the tax revenues generated.
9
New cards
Demand Curve
a graphical representation of the demand schedule; shows the relationship between quantity demanded and price.
10
New cards
Demand Schedule
table that shows how much of a good or service consumers will be willing and able to buy at different prices.
11
New cards
Determinants of Demand
Income of consumers, related goods or prices, expectations of future prices, number of consumers in the market, and tastes and preferences are all
12
New cards
Determinants of Supply
Cost of productive resources, opportunities for revenue from other goods/services, number of producers in the market, technology, expectations of future prices, subsidies, and taxes are all
13
New cards
Elastic Demand
when the price elasticity of demand is greater than 1
14
New cards
Elastic Supply
when the price elasticity of supply is greater than 1
15
New cards
Equilibrium Price and Quantity
The price (also known as market-clearing price) and quantity where quantity supplied and demanded are equal.
16
New cards
Factor/Resource Market
where resources, especially capital and labor, are bought and sold.
17
New cards
Income
money received, especially on a regular basis, for work or through investments
18
New cards
Income Effect
the change in the quantity of a good demanded that results from a change in the consumer’s purchasing power when the price of the good changes.
19
New cards
Income Elasticity
the percent change in the quantity of a good demanded when a consumer’s income changes divided by the percent change in the consumer’s income;
\
it measures how changes in income affect the demand for a good.
\
it measures how changes in income affect the demand for a good.
20
New cards
Inelastic Demand
When changes in price don’t heavily affect the quantity demanded
21
New cards
Inelastic Supply
When changes in price don’t heavily affect the quantity supplied
22
New cards
Inferior Good
when a rise in income decreases the demand for a good;
usually considered less desirable than more expensive alternatives.
usually considered less desirable than more expensive alternatives.
23
New cards
Input
a good or service that is used to produce another good or service.
24
New cards
Law of Demand
states that a higher price for a good or service, other things being equal, leads people to demand a smaller quantity of that good or service.
25
New cards
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
states that each successive unit of a good or service consumed adds less to total utility than does the previous unit.
26
New cards
Law of Supply
states that, other things being equal, the price and quantity supplied of a good are positively related.
27
New cards
Lump-Sum Tax
a tax of a fixed amount paid by all taxpayers, independent of the taxpayer’s income.
28
New cards
Market-Clearing Price
Alternative name for equilibrium price
29
New cards
Midpoint Formula
a technique for calculating the percent change by dividing the change in a variable by the average, or midpoint, of the initial and final values of that variable.
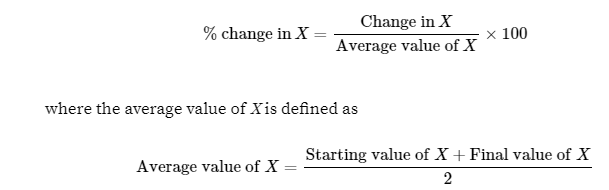
30
New cards
Normal Good
a type of good in which a rise in income increases the demand for it; most goods are these type of good
31
New cards
Perfectly Elastic
Elasticity where price change causes an infinite change in quantity (demanded or supplied) (horizontal line on graph)
32
New cards
Perfectly Inelastic
Elasticity where a price change causes zero change in quantity (demanded or supplied) (vertical line on graph)
33
New cards
Price Ceiling
a maximum price that sellers are allowed to charge for a good or service.
34
New cards
Price Controls
legal restrictions on how high or low a market price may go; typically take the form of either a price ceiling or a price floor.
35
New cards
Price Elasticity of Demand
the ratio of the percent change in the quantity demanded to the percent change in the price as we move along the demand curve (dropping the minus sign).
36
New cards
Price Floor
a minimum price that buyers are required to pay for a good or service.
37
New cards
Producer Surplus
refers to both individual and total surplus of sellers in a market
38
New cards
Product Market
where goods and services are bought and sold.
39
New cards
Profit
typically total revenue - total cost; difference between amount earned and amount spent in buying
40
New cards
Quantity Demanded
the actual amount of a good or service consumers are willing and able to buy at some specific price; shown as a single point in the demand schedule or along a demand curve.
41
New cards
Quantity Supplied
the actual amount of a good or service people are willing to sell at some specific price.
42
New cards
Quota
an upper limit on the quantity of some good that can be bought or sold; also known as a quantity control.
43
New cards
Revenue
the value of output sold, either marginal or total
44
New cards
Shortage
when the quantity of a good or service demanded exceeds the quantity supplied; occurs when the price is below its equilibrium level; also known as excess demand.
45
New cards
Subsidies
government payments to individuals and businesses: used to offset market failures and externalities to achieve greater economic efficiency.
46
New cards
Substitutes
two goods for which a rise in the price of one of the goods leads to an increase in the demand for the other good.
47
New cards
Substitution Effect
the change in the quantity of a good demanded as the consumer substitutes the good that has become relatively cheaper for the good that has become relatively more expensive.
48
New cards
Supply
the actual amount of a good or service people are willing to sell at various prices, rather than one specific price
49
New cards
Supply Curve
curve that shows the relationship between the quantity supplied and the price.
50
New cards
Supply Schedule
table that shows how much of a good or service producers would supply at different prices.
51
New cards
Surplus
when the quantity supplied of a good or service exceeds the quantity demanded; occurs when the price is above its equilibrium level; also known as excess supply.
52
New cards
Tariff
a tax on imports.
53
New cards
Tax Incidence
the distribution of the tax burden (tax burden is basically where money for paying a tax comes from.)
54
New cards
Total Surplus
the total net gain to consumers and producers from trading in a market; the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus.
55
New cards
Unit Elastic
Elasticty where price elasticity is equal to 1: the percent change in price equals the percent change in quantity
56
New cards
Utility
a measure of personal satisfaction.
57
New cards
World Price
The price of a good that prevails in the world market