Series 7 Exam
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Short Straddle
Selling a call and a put with the same expiration and same strike price is a short straddle.
Credit Spread
A credit spread, regardless of whether it's a put or a call spread, will be profitable if the spread between the premiums narrows. Credit spreads are created when an investor sells the more expensive option and buys the less expensive option.
Debit Spread
Debit spreads will be profitable if the spread between the premiums widens.
Uncovered Straddle
The term "uncovered" refers to the sale (writing) of an option by itself (i.e., without an existing stock position). An uncovered straddle is the sale of a call and put with the same expiration and same strike price. Since an uncovered straddle includes an uncovered call the maximum potential loss is unlimited.
Covered Put
Selling a stock short and then writing a put is referred to as a covered put option. Although it's referred to as a "covered" position, it's important to recognize that the investor who creates the position is exposed to unlimited upside risk on the short stock position. As with any short stock position, the investor will generally make money if the underlying stock declines in value (i.e., the investor is bearish). If the stock declines and the put is exercised, the customer is obligated to buy shares at the put's strike price of $40. Since the stock was originally sold short at $40, there's no profit or loss when the short position is covered and closed ($40 short sale proceeds- $40 purchase from exercise of put). However, the sale of the put generated premium income of $5, which is the investor's profit.
Short Straddle and Combination
A short straddle is an option position that's created by selling a call and a put on the same underlying stock, with the same expiration date, and the same strike price. A short combination is similar; however, the call and put will have different strikes and/or different expirations. An investor who sells a straddle or a combination is hoping that the options will expire so she can keep the premiums received. This type of investor is neither bullish nor bearish, but is anticipating that the price of the underlying security (or index) will remain relatively stable or neutral.
An individual purchases 10 ABC June 90 calls at $4 and writes 10 ABC June 95 calls at $2. The individual's maximum loss is:
This is a debit spread because the premium on the long position ($4) is larger than the premium on the short position ($2). The maximum loss for the purchaser of any option, including the buyer of a spread (i.e., a debit spread), is the amount of the net debit (i.e., net premium). The spread's net debit is $2 ($4 - $2) and, since the individual's debit spread position involves 10 contracts, the maximum loss is $2,000 ($2 net debit x 100 shares per option x 10 options).
If an investor purchases a straddle, the maximum profit is:
A long straddle involves the purchase of both a call and put with the same expiration and strike price. Since buying a straddle involves purchasing a call, the maximum potential gain is unlimited. The maximum potential loss on a long straddle is the total premiums paid.
Class A shares of a mutual fund usually have front-end loads, thereby reducing the customer's investment in the mutual fund. Class C shares usually don't have front-end loads and are more suitable for this customer.
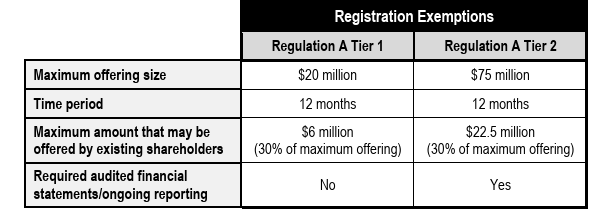
Regulation A
Tier 1 offerings are subject to both SEC and blue sky review. Continuing disclosure information must be filed.
Tier 2 offerings are subject to SEC review, but not blue sky review. Has stricter continuing disclosure information and filing requirements
Both the issues must file an offering statement with SEC and provide an offering circular to prospective investors.
Rather than a full registration, Reg A offering documentation can be prepared quickly and has lower legal and filing fees.
Regulation D
Under Regulation D, an issuer’s private placement of securities qualifies for an exemption provided the following conditions are met: The issuer must have reason to believe that the buyer is a sophisticated investor (i.e., one who is experienced enough to evaluate any risks involved) The buyer must have access to the same financial information that is normally be included in a prospectus. This information is provided in a document that’s referred to as a private placement memorandum. The issuer must be assured that the buyer doesn’t intend to make a quick sale of the securities. This is usually accomplished by means of an investment letter (also called the lock-up agreement). The securities are sold to no more than 35 non-accredited investors. Each non-accredited investor must appoint a purchaser representative who has knowledge and experience in financial and business matters to be capable of assisting in the evaluation of the risks and merits of the offering.
Reg 144
Regulates the sale of restricted and control securities. Restricted securities are unregistered and acquired through private placements, while control securities are registered and held by affiliated persons (e.g., insiders with over 10% ownership). Both types must be sold according to Rule 144.
Basic Requirements of Reg 144
Rule 144 has five basic requirements: 1. Current public information 2. Holding period 3. Notice of sale 4. Volume limitations 5. Manner of sale. Affiliates must meet all five, while non-affiliates only need to satisfy the first two. A non-affiliate cannot be an affiliate at the time of sale or in the prior three months.
Reg 144A
Reg 147 and 147A
If a company is conducting an offering and only selling its securities to the residents of the state in which it is doing business, the offering is exempt from SEC registration.
An issuer is considered to be “doing business” in a state as long as it meets just one of the following four new requirements: 1. At least 80% of consolidated revenue 2. At least 80% of its consolidated assets at the end of its most recent semi-annual fiscal period ; 3. At least 80% of the net proceeds are used in the state; or 4. A majority of the issuer’s employees are based in the state or territory (this fourth requirement was not included in the original Rule 147)
Resales to persons who reside outside of the state in which the offering is conducted are restricted for a period of six months from the date of the sale by the issuer to the purchaser (formerly nine months).
Reg 145
Reg S
Quiet Period for IPO and Follow On Offering
For a follow-on offering, if a firm is acting as the manager or co-manager of the offering, a research analyst of the brokerage firm must wait three calendar days following the offering before publishing research on the subject company. However, for firms that are syndicate members or a part of the selling group for the follow-on offering, there's no restriction on publishing research on the subject company. For an IPO, all firms that are involved in the IPO (i.e., manager, co-manager, syndicate members, and selling group members) are subject to a quiet period of 10 calendar days after the date of the offering before they may publish a research report or make a public appearance regarding the subject security.
Tax Treatment for OID and Market Discount
If a municipal bond is purchased at a discount in the secondary market and held to maturity, the increase in value will be a taxable and reported as ordinary income. On the other hand, if a municipal bond is purchased as an original issue discount (OID), the discounted price will be accreted each year to bring the basis up to par value at maturity. However, the accreted interest on a municipal OID is considered tax-free interest.
Maximum time allowed to appeal against decision of FINRA’s hearing panel
25 days to file appeal with the National Adjudicatory Council (NAC)
Under FINRA's Code of Arbitration, the statute of limitations on monetary disputes is:
6 years
Account Transfer Time
Within three business days following the validation, the carrying party (previous firm) must complete the transfer of the account to the receiving party (new firm).
Penny Stock
According to SEC rules, a penny stock is defined as an unlisted equity security that has a bid price below $5.00 per share. Exceptions to the penny stock definition are made for:
Exchange-traded equities (e.g., NYSE or Nasdaq) regardless of the price at which they're quoted
Investment company securities (e.g., mutual fund shares)
OCC-listed calls and puts
Securities with a market value of at least $5.00 per share.
CAT Clock Syncing Tolerance
To ensure that time stamps for reportable events are accurate, the Consolidated Audit Trail (CAT) system requires business clocks to be synchronized to within 50 milliseconds tolerance of the time maintained by the atomic clock of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
If an associated person of a broker-dealer violates FINRA rules, she may be subject to:
If FINRA member firms or any of their associated persons violate FINRA rules, they will be subject to the provisions of the Code of Procedure.
Form 4 and Form 3
A person must file Form 4 within 2 business days of the date on which an insider changes her ownership position i.e. buys or sells. A insider is defined as any director or officer of a corporation or any person with beneficial ownership of more than 10% of issuer’s equity securities.
Form 3 must be filed with the SEC within 10 days of the date on which a person becomes an insider.
Series K Preferred Stock
Series K preferred stock has no maturity date, they initially pay a fixed rate of dividend which then switches to a floating rate, the dividend is non-cumulative, does not carry voting rights and may be called i.e. bought back by the issuer. Series K will generally be called after the initial fixed period when interest rates rise. The issuer calls the shares to avoid paying a higher dividend.
Quotation Increments and Convention for various types of bonds
T-bills are quoted on a discounted yield basis, not as a percentage of their par value. The yield represents the percentage discount from the face value of the security. T-notes and T-bonds are quoted using a percentage of par and 1/32nd of 1% as the minimum price change. Corporate and municipal bonds use a percentage of par, but use 1/8th of 1% as the minimum price increment. The PSA model is used to estimate prepayment rates for mortgage-backed securities (MBS), such as CMOs and agency securities. The PSA model doesn't provide a price or value directly.
If a municipal dealer does not intend to buy or sell securities based on a given quote, it may identify the quote with
If a municipal securities dealer doesn't intend to buy or sell securities based on its quote, it may identify the quote with the terms subject, nominal, or workout. If any of these terms are used, the quote is not firm and is being given for informational purposes only.
To be considered a pattern day trader, a customer must execute how many day trades over a five-business-day period?
A pattern day trader is any customer who executes four or more day trades over a five-business-day period.
Consolidated Audit Trail
The Consolidated Audit Trail (CAT) System is a central repository that receives, consolidates, and retains the data over the lifecycle of trades and orders for all eligible securities, including listed equity securities and listed options.
Trade Reporting Facility (TRF)
The Trade Reporting Facility (TRF) is used for the reporting of trades involving listed securities that are executed over-the-counter.
Over-the-Counter Reporting Facility (ORF)
The Over-the-Counter Reporting Facility (ORF) is used for the reporting of transactions involving OTC securities that don't trade on Nasdaq or other exchange markets.
Trade Reporting and Compliance Engineer (TRACE)
The Trade Reporting and Compliance Engine (TRACE) is a system that provides greater transparency in the corporate bond market.
Real Time Transaction Reporting System
Broker-dealers are required to report transactions in municipal securities to the Real-Time Transaction Reporting System (RTRS), which is operated by the MSRB.
Electronic Municipal Market Access (EMMA)
The Electronic Municipal Market Access (EMMA) System provides primary market disclosure information related to municipal securities.
What's used to measure the prepayment rate for mortgage-backed securities?
The PSA Model estimates the prepayment rate for mortgage-backed securities as measured against a benchmark. If a CMO is assigned a PSA number that's equal to 100, the assumption is that the prepayment speed will remain stable. If the PSA number is greater than 100, the prepayment speed is expected to be faster than normal, while if it's less than 100, the prepayment speed is expected to be slower than normal. If interest rates decline, homeowners will refinance, thereby increasing prepayments (i.e., rising PSA). If interest rates increase, there will be a decline in the prepayment of mortgages and the PSA number will fall.
The responsibility for maintaining liquidity and promoting a fair and orderly market on the NYSE is given to:
On the floor of the NYSE, the designated market maker (DMM) is responsible for maintaining liquidity and promoting a fair and orderly market.
Equity Indexed Annuity
Equity-indexed annuities (EIAs) are a type of fixed annuity that provide a guaranteed minimum rate of return (unlike variable annuities), but may potentially provide a greater rate of return. An EIA's return is tied to the performance of a stock market index to which it's linked. As with standard annuities, they also provide tax-deferred growth. However, EIAs are not currently considered securities; instead, they're categorized as a life insurance product.
Cash Management Bills
Cash management bills (CMBs) are short-term Treasury securities and are structed like T-bills. However, T-bills are sold at a weekly auction, while CMBs are sold on an unscheduled basis. CMBs are typically sold when the government's cash reserve are low (e.g., during a pandemic). Unlike T-bills, T-notes, and T-bonds, CMBs have a large minimum investment which makes them more suitable for wealthy and institutional investors.
Record Retention Requirements for a broker-dealer
Final prospectus.
According to FINRA rules, all retail communications, research reports and correspondence ( including email and instant messages) that are used by a member firm must be kept on file for a minimum of three years.
SEC Registration Statements (i.e., Form S-1 or S-3), prospectuses, and other documents written by an issuer are not required to be kept on file by member firms.
Order Execution in Discretionary Accounts
RR must have a written POA
POA need not be updated periodically.
POA may be revoked by either death of the customer or in writing by the customer.
Each order in which the RR mentions exercises discretion must be marked discretionary
The RR should not enter orders that are excessive in size or frequency to earn commission.
The RR makes the investment decisions and does not need to receive the customer’s approval for each order being executed.
Direct Pay Build America Bond
It may be used to raise capital for the same purposes as regular tax-exempt municipal debt, except for refunding, working capital, and private activity bonds.
Escrowed to Maturity
Proceeds of a refunding issue deposited in an escrow account to enable payment of interest and principal of a maturing issue. The process is referred to as advance refunding. The new issue of the bond would be referred to as the refunding issue. The outstanding bond would be referred to as being prefunded.
Serial Bond vs Series Bond
Serial bonds mature sequentially over several years, whereas Series bonds are issued at different times but mature at the same time.
Certificate of Participation (COP)
COPs are lease financing agreements which are typically issued in the form of tax-exempt or municipal revenue bonds.
Planned Amortization Class (PAC) Tranches
The PAC is a type of CMO that is designed for more risk-averse investors and provides predetermined schedule of principal repayment, as long as mortgage prepayment speeds are within a certain range.
Temporary Hold
15 days + 10 days + 30 days
The Bond Buyer Municipal Bond Index
The Bond Buyer Municipal Bond Index represents the average of the prices of 40 long-term municipal bonds adjusted to a yield of 6%.
Consolidated Quotation System
The Consolidated Quotation System (CQS) provides subscribers with bid/asked quotations for securities listed on national exchanges, including quotes from OTC market makers in those securities (the third market).
In a customer's margin account, the interest charged on the debit balance is typically based on the:
Broker Call Rate