Substance Abuse Disorders: Alcohol
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Misuse
Use of a medication or substance that was not prescribed to the individual or use “only for the feeling or experience it caused”
Abuse
Similar to misuse, but with the characteristic that the substance is used for nontherapeutic purposes to obtain psychotropic effect
Addiction
A chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use despite adverse consequences
Dependence
Physical → use of a substance that is associated with withdrawal symptoms or a withdrawal syndrome when there is a rapid reduction in exposure or exposure to an antagonist
Psychological → non-physiological attachment to a substance due to impaired control or compulsion and associated with behaviors to attain the substance
Tolerance
the need to increase the dose to obtain desired effects
Withdrawal
Signs or symptoms due to the decline in blood concentration of a drug substance or due to the administration of an antagonist
Craving
A very strong desire for a psychoactive substance of for the intoxicating effects of that substance
Intoxication
Changes in physiological functioning, psychological functioning, mood states, or cognitive processes, or all of these, as a consequence of excessive consumption of a drug; usually disruptive
disease, treatment, chronic, structural, loss, exposure, external
Addiction: Choice or Disease?
-Concept that addiction is a ________ is supported by its manifestations, course and response to ________ which is comparable with other ____ medical illnesses
-Addiction causes predictable and persistent ________ and functional changes in the brain
-Volume ____ of brain tissue has been found in individuals with substance use disorders
-Only a minority of people who try drugs / alcohol become addicted
-Rationale for those who consider addiction to be a choice → disease expression in substance use disorders requires ________ to a drug
-Challenges to this ideology → other psychiatric disorders also need ________ triggers
history, depression, antisocial
Risk Factors: Biologic
-Genetics → family _______
-Gender
-Mood disorder → major ___________, bipolar disorder
-Personality disorder → _________ or borderline
childhood, refusal, poverty, teens, mental, parental, good
Risk Factors: Environmental
-Risk Factors
Aggressive behavior in ___________
Lack of parental supervision
Low peer _______ skills
Drug experimentation
Availability of drugs at school
Community _______
_____ and people with mental disorders are at increased risk of drug use and addiction
-Protective Factors
Self-efficacy (belief in self-control)
________ monitoring and support
Positive relationships
______ grades
School anti-drug policies
Neighborhood resources
early, increased, experiment, peer, injected
Other Risk Factors
-_____ use
-Increased risk during times of transition → loss of loved ones, going to college, moving
-Adolescence → __________ tendency to experiment with drugs/alcohol. More vulnerable to ____ pressure
-Drugs that are _________/smoked associated with increased addiction potential
relapsing, alcohol, negative, binge, withdrawal, craving
Cycle of Addiction
-Chronic, __________ disorder associated with compulsive _________ drinking/drug use, the loss of control over intake, and the emergence of a ________ emotional state when alcohol/drug is no longer present
-Stages of the Addiction Cycle
(1) _____/Intoxication Stage → reward, incentive salience, and pathological habits
(2) Negative Affect / __________ Stage → reward deficits, stressful surfeit
(3) Preoccupation / Anticipation Stage → _______, impulsivity, executive function
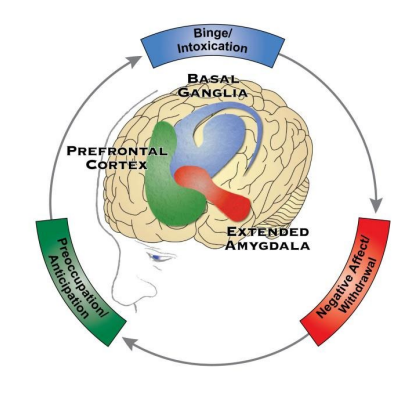
mild, dependence, remission
Severity and Specifiers: DSM-V
-Substance Use Disorder Classification → ____, moderate, severe
-Physical ___________ and withdrawal symptoms are key hallmark symptoms
-Specifiers → in early ________, in sustained remission, on maintenance therapy, and in a controlled environment
0.08, 5, 4, 14, 7
Alcohol Intake
-Binge Drinking → pattern of drinking alcohol that brings BAC to _.__% or higher
In the typical adult, that is _ or more drinks for males in ~2 hours and _ or more drinks in females
-Heavy Alcohol Use
Men → > 4 drinks/day or > __ drinks/week
Women → > 3 drinks/day or >_ drinks/week
increases, late, conduct, HTN
Alcohol Use Disorder
-Prevalence __________ in middle age, but the age of onset is most commonly in the ____ teens to early-mid 20’s
-Earlier onset noted in patients with ________ disorders and earlier age of intoxication
-Variable course → often perceived as an intractable condition, not commonly the cause
-Increased risk → ___, GI bleed, sleep disorders, MDD, hemorrhagic stroke, cirrhosis, HIV acquisition, and many cancers
stress, male, higher, Asian, decreased
Alcohol Use Disorder: Risk Factors
-Environmental → external ____, which is trauma in childhood, many significant stressors throughout life
-Genetic → ____ gender, Native American/White ethnicity, rate of condition is 3-4x ______ in close relatives of individuals with AUD
-Decreased risk → ______ ethnicity due to polymorphisms of genes for alcohol-metabolizing enzymes alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase. This affects their response to alcohol and is associated with _________ risk for alcohol use disorder
alcohol, 12, larger, desire, craving, tolerance, withdrawal
Alcohol Use Disorder: DSM V Criteria
-A problematic pattern of _______ use leading to clinically significant impairment or distress, as manifested by at least 2+ of the following, occurring within a __-month period:
(1) Alcohol is often taken in ______ amounts or over a longer period than was intended
(2) There is a persistent ______ or unsuccessful efforts to cut down or control alcohol use
(3) A great deal of time is pent in activities necessary to obtain alcohol, use alcohol, or recover from its effects
(4) _______, or a strong desire to urge or to use alcohol
(5) Recurrent alcohol use resulting in a failure to fulfill major obligations at work, school, or home
(6) Continued alcohol use despite having persistent or recurrent social or interpersonal problems caused or exacerbated by the effects of alcohol
(7) Important social, occupational, or recreational activities are given up or reduced because of alcohol use
(8) Recurrent alcohol use in situations in which it is physically hazardous
(9) Alcohol use is continued despite having a persistent or recurrent physical or psychological problem that is likely to have been caused or exacerbated by alcohol
(10) __________
(11) ___________
intoxicated, depression, coma
Alcohol Intoxication
-Large majority of people who use alcohol have been __________ to some degree
-Occurs as episodes lasting minutes to hours
-Common for patients to require care in the ED
-Overdose Symptoms → respiratory __________, stupor, seizure, shock, ____, and death
recent, behavioral, slurred, nystagmus, coma
Alcohol Intoxication: DSM V
-______ ingestion of alcohol
-Clinically significant problematic __________ or psychological changes that developed during, or shortly after, alcohol ingestion
-One or more of the following symptoms developing during, or shortly after, alcohol use:
_______ speech, incoordination, unsteady gait, ________, impairment in attention or memory, and stupor or ____
mild, delirium, DT
Alcohol Withdrawal: Background
-Acute withdrawal syndrome is often unexpected
-Symptoms are usually _____
-Common among medical and surgical inpatients and in ED
-Suspect alcohol withdrawal in unexplained ________
-If identified early, __ mortality rate < 5%
cessation, after, tremor, anxiety
Alcohol Withdrawal: DSM V
-_________ of (or reduction in) alcohol use that has been heavy and prolonged
-Two or more of the following, developing within several hours to a few days _____ the cessation of/reduction in alcohol use:
(1) Autonomic hyperactivity
(2) Increased hand ______
(3) N/V
(4) Transient visual, tactile, or auditory hallucinations or illusions
(5) Psychomotor agitation
(6) _______
(7) Generalized tonic-clonic seizures
6-36, tremor, nausea, 6-96, hypertension
Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome: Mild and Severe
-Mild Withdrawal → begins within _-__ hours after last drink
Symptoms include ______, anxiety, minor agitation, diaphoresis, palpitations, headache, tachycardia, ______/vomiting, and insomnia
Symptoms usually pass by 24-48 hours
-Severe Withdrawal → occurs _-__ hours after last drink
Usually preceded by prolonged heavy alcohol use
Symptoms include disorientation, agitation, diaphoresis, whole body tremor, N/V, _____________, and hallucinations
6-48, withdrawal, tonic-clonic, focal, severe, 48-96, hallucinations, death
Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome: Seizures
-Withdrawal Seizures
_-__ hours after last drink
More prevalent in patients with history of __________ syndromes
Generalized _____-______ seizures that are brief and resolve spontaneously
Can recur in untreated patients
Consider other etiology if seizures are _____, prolonged or recurrent, associated with trauma/fever, onset > 48 hours after the last drink
-Delirium Tremens (DTs)
The most ______ form of alcohol withdrawal
Acute organic psychosis (typically __-__ hours)
Symptoms → ___________, disorientation, tachycardia, hypertension, hyperthermia, agitation, and diaphoresis
Complications → dehydration, electrolyte disturbances, arrhythmias, seizures, CV collapse, and _____
12-24, resolve, visual, aware, not
Alcoholic (Organic) Hallucinosis
-Hallucinations that develop within __-__ hours of abstinence
-Typically _______ within 24-48 hours
-Hallucinations are usually ______; patients are _____ they are hallucinating
-___ associated with global clouding of the sensorium
-Vital signs are usually normal
thiamine, ataxia, nystagmus, amnesia
Chronic Alcohol Syndromes
-Wernicke Encephalopathy
Acute neuropsychiatric emergency due to _______ deficiency
Triad = mental status changes, _______, and ocular motor dysfunction (_______, lateral rectus palsy)
+/- peripheral neuropathy
Treatment is IV thiamine
-Korsakoff Syndrome
Late manifestation of Wernicke encephalopathy
Anterograde and retrograde ________
+ confabulations
Patients rarely recover
preventable, increased, single-item, 14, 7, all, known
Screening
-Unhealthy alcohol (and drug) use is among the most common causes of ________ death
Unhealthy = _________ likelihood of health consequence
-Many screening tools available to detect unhealthy alcohol use
Recommendation is to utilize ______-____ screening
-At Risk Use
Men > __ drinks/week on average
Women > _ drinks/week on average
-USPSTF recommends ___ adults be screened to identify unhealthy alcohol use
Patients with unhealthy use are to receive a “brief counseling intervention”
-Screening is insufficient for someone already _____ to have unhealthy use
AUDIT-C, SASQ, CAGE
Screening Tools and Recommendations
-The NIAAA recommends use of one of the following brief screening tools: _____-_ or ____
-Do not use yes/no questions, leading questions, and ____ questionnaire
TWEAK
What is the screening test for risk of drinking during pregnancy?
negative, 1, 2, abstain, AUDIT
Management
-When patients screen ________, encourage patient to stay within healthy alcohol consumption guidelines
<_ drink/day in women, <_ drinks/day in men
Less is more
Be aware of other medical conditions that would warrant a patient to ______ from alcohol entirely
-When patients screen positive, you need to get more information
Recommendation is to obtain an _____ questionnaire

AST, ALT, GGT, abstinence, health, Naltrexone
Primary Care Setting: Diagnostic Evaluation and Management
-Diagnostic Evaluation
Blood alcohol concentration (BAC)
Liver enzymes → ___, ___, albumin, bilirubin
CBC
___
Urine drug screen
-Management
Early recognition with a goal towards ___________
Preventative ______ and harm reduction measures
Psychosocial intervention
Pharmacologic therapy → Disulfiram, _________, Acamprosate
observation, chemistry, aggressive, Thiamine, coma
Alcohol Intoxication: Emergent Evaluation and Management
-Mild, isolated intoxication
Blood alcohol concentration
__________
-Moderate Intoxication
BAC and observation
________ studies
Glucose monitoring
Electrolyte monitoring
-Severe Intoxication
Moderate management
_________ supportive care
Monitor respiratory status → Intubation
_______ IV
Admission → ____, significant complications of intoxication, poison control center consult
80, hemoglobin, >, seizure, CIWA
Alcohol Withdrawal: Emergent Evaluation
-BAC
Legal limit is __ mg/dL
100-150 can cause ataxia, dysarthria, nausea, vomiting
300+ can be lethal
-Liver enzymes → AST, ALT, albumin, bilirubin
-CBC → _____________
-GGT, UDS, complete metabolic panel, amylase, lipase
-EKG
Pts _ 50 years
Cardiac history
-CT head
________ or altered mental status (if not typical for patient)
Rule out contributing/alternative pathology
-_____-Ar
15, thiamine, 10, librium, >, admission, Benzodiazepines, Propofol
Alcohol Withdrawal: Management
-CIWA scores < __
All patients get daily multivitamin with _______ + folate
Provide explicit plans for follow-up care prior to discharge
-Very mild withdrawal; CIWA-Ar < __
Gabapentin (DOC) or Carbamazepine
-Mild withdrawal; CIWA-Ar 10-15
Chlordiazepoxide (______) is the DOC, Diazepam is the alternative
-Severe withdrawal; CIWA-Ar > 15, requires ___________
Supportive care → IV fluids, thiamine, magnesium multivitamins
______________ → first line therapy for all alcohol withdrawal syndromes
If those fail, try Phenobarbital
If that fails, the patient needs to get sedated with ________ and intubated