structure and functions (movement of substances)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
define diffusion + its concentration gradient direction
the net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration
(down the concentration gradient)
diffusion is a _____ process. no ____ needed
diffusion is a PASSIVE process. no ENERGY needed
what is the end result of diffusion (e.g. left for a long time)
even concentration throughout space
define osmosis, include moves across a ____
the net movement of free water particles from a hypotonic to hypertonic solution, across a partially permeable membrane.
define hypo/hypertonic
hypo - lower solute concentration (than)
hyper - higher solute concentration (than)
draw osmosis diagram
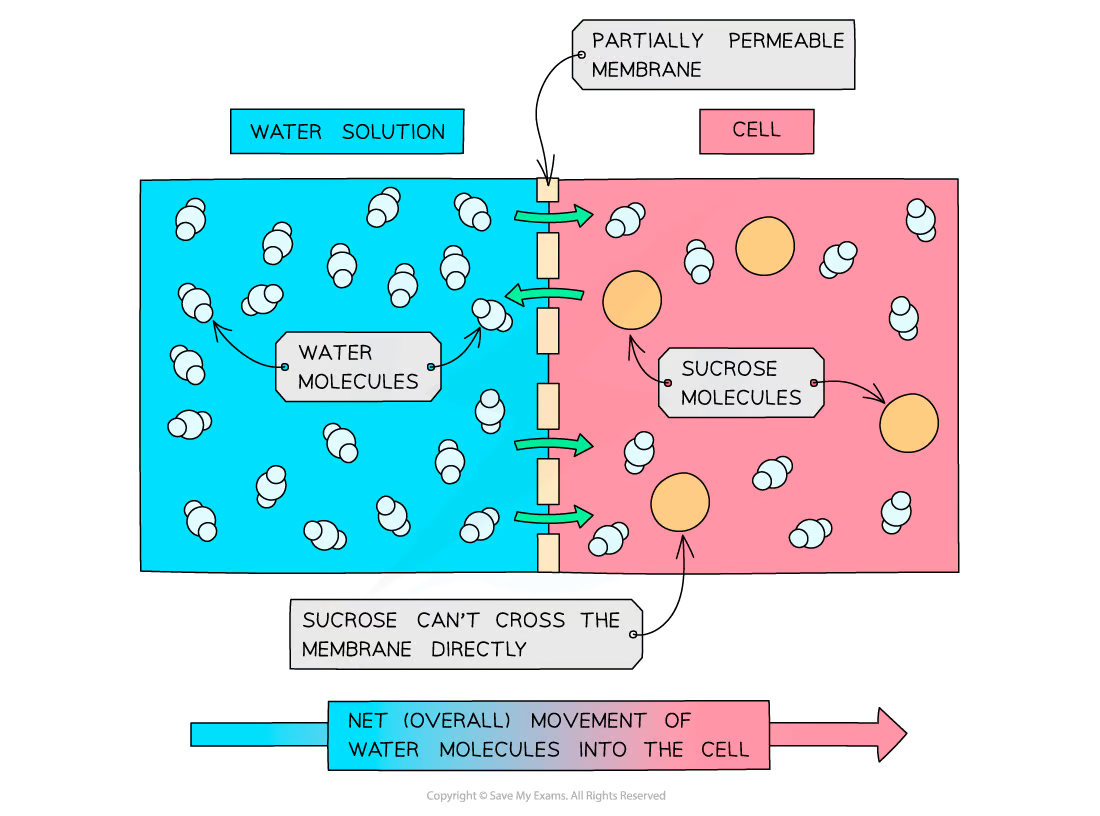
osmosis is also/a type of _______ because water moves ______ concentration gradient
osmosis is also DIFFUSION because water moves DOWN the concentration gradient
why can the results of osmosis be so severe in animals cels
the lack of a cell wall to support the cell means results can be severe
animal cell in concentrated solution:
cell is hypotonic to concentrated solution
osmosis: water moves hypo to hyper
water exits the cell
cell shrinks/shrivels
cell is CRENATED, this is CRENATION
animal cell in dilute solution:
cell is hypertonic to dilute solution
osmosis: water moves hypo TO hyper
water enters cell
cell swells/bursts
cell is LYSED, this is LYSIS
lysis etymology lol
luo in greek! luein to loosen, untie
cell bursts forth
plant cell protected from _______ by ________
plant cell protected from BURTSTING by CELL WALL
plant cell in concentrated solution (6)
- prev time forgot physical(?) state of cell after effect
plant cell is hypotonic to concentrated solution
osmosis: water moves from hypo to hyper
water exits cell vacuole
cell membrane pulls away from cell wall
cell retains its shape but isn’t stiff
cell is PLASMOLYSED, this is PLASMOLYSIS
etymology of plasmolysis
plasmo - (basically cell membrane, mould)
lysis - loosening, releasing
loosening of the cell membrane
plant cell in dilute solution
-last time forgot what happens after water movement, specifically to do with c__w__ (two stages)
cell is hypertonic to dilute solution
osmosis: water moves hypo TO hyper
water enters cell/vacuole
vacuole presses against cell wall (TURGOR PRESSURE)
cell can’t swell anymore
becomes TURGID
what is turgor pressure
force within the cell, by vacuole i think, that pushes the cell membrane against the cell wall
write table of concentrated/dilute VS plant/animal
concentrated | dilute | |
|---|---|---|
animal | crenation (shrivels) | lysis (swells/bursts) |
plant | plasmolysis (not stiff, cell membrane pulled away) | turgid (swelled, stiff) |
define active transport
last time - forgot through where it happens
the movement of particles through a cell membrane from an area of low concentration to high concentration
active transport goes ________ the concentration gradient
active transport goes AGAINST the concentration gradient
active transport needs ______ and involves _____ c______ m________ in the cell membrane
active transport needs ENERGY and involves PROTEIN CARRIER MOLECULES in the cell membrane
4 factors affecting diffusion + explanation
diffusion distance - shorter distance - faster diffusion
concentration gradient - greater the difference in concentration - faster diffusion
surface area - larger SA - more space for diffusion - faster
temperature → more KE - particles move faster - diffuse faster
explain a Sa:V ratio, e.g. big cube/small cube
a large surface area for a small volume
e.g. big cube has small Sa:V ratio
small cube has large Sa:V ratio
beetroot temperature diffusion experiment CORMMS
think what is necessary to mention in c
C - change temperature of beetroot water environment (20/40/60/80 )
O- same age, health, type of beetroot
R - repeat x3, avgs, anomalies
M - observe colour change of liquid, when whole test tube is purple
M - over 10 mins
S - same volume of water, dimensions of beetroot cube
potato diffusion concentration experiment CORMMS
C - change concentration of solution (sucrose at 0-1mol/dm3)
O - same age, species, health of potato
R - repeat x3, avgs, anomalies
M - measure change in mass of potato cylinders before/after being in the solution
M - for 4 hours
S - same volume of solution, dimensions of potato, dry every potato cylinder before weighing
how to calculate percentage change
final - initial / initial (x100%)
potato in distilled water result
potato is hypertonic to distilled water, hypo to hyper
via osmosis water moves into potato cells
increased mass
increased tugor pressure - potato is hard
potato in concentrated solution result
potato is hypotonic to concentrated solution, hypo to hyper
via osmosis water exits potato cells
most decreased mass
potato is floppy
why is the potato floppy in concentrated solution result
little tugor pressure, cells may be plasmolysis
how to tell which concentration the potato is (think ___tonic)
in isotonic solution (equal solution concentrations) - no net movement, no mass change