Unit 5 - Bonding
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Octet Rule
The most stable atoms on the periodic table are the noble gases. They all (except He) have 8 valence electrons.
-"full octet" = 8 valance electrons
Other atoms will gain or lose electrons (and form ions) till their electron configuration is the same as a noble gas and they have 8 valence electron
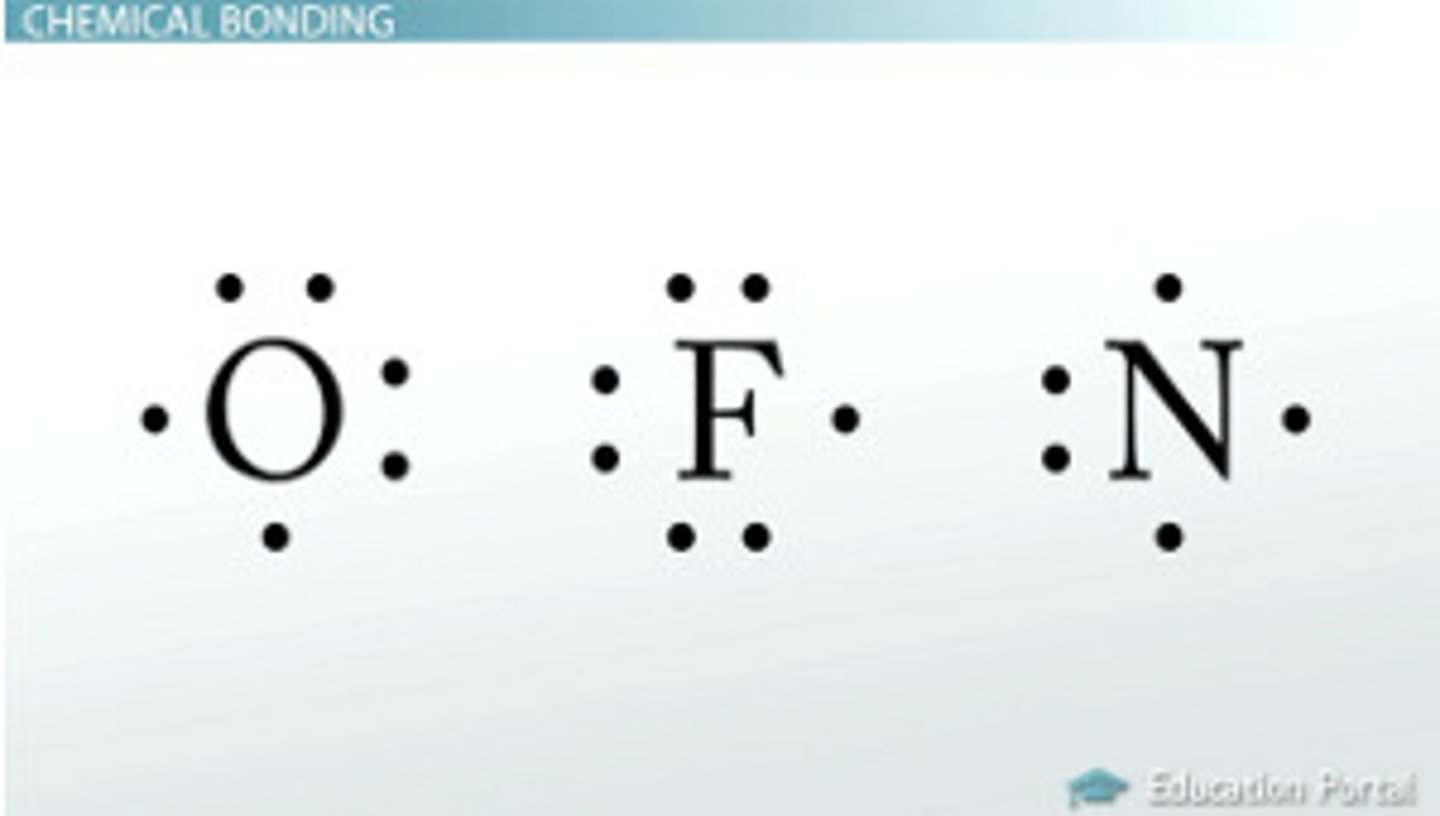
Lewis Dot Structure (including how to draw cations and anions)
Lewis Dot structures show the number of valence electrons that an atom has.
Atoms in the same group will have the same Lewis structure because they have the same number of valence electrons.
-Bond= line between the two, can be single bond, double bond, or triple bond
Anions: Lewis dot structure for anions show 8 Lewis dots (full valence shell) to show it gained electrons
Cations: Lewis structure for cations show no Lewis dots to show it lost electrons (next lowest energy level is full)
General Description (Ionic Bonding)
Ionic bonding occurs between a metal and a non metal. The non metal gains electrons to form an anion and the metal loses electrons to form a cation.
-the attraction between the positive and negative ions held them together is an ionic bond
-ELECTRONS ARE TRANSFERED
Rules for naming ionic compounds
-when naming ionic compounds the metal is always written first the name does not change
-the non metal is always written second and the ending is "ide" UNLESS ITS A POLYATOMIC
-Also make sure to include the roman numeral if its a transition metal!
Rule for how ions combine/Ionic bonding
-a metal combines with a nonmetal, can have more than one atom of the metal and the nonmetal
-metals lose electrons (+ charge) nonmetals gain electrons (- charge)
- the overall charge of the combined ions MUST BE ZERO
-include subscript to indicate if there is more than one atom of the metal or nonmetal
-MUST HAVE A METAL AND NONMETAL
Crisscross for writing ionic compound formulas
The charges of the ion become the subscript of the opposite ion
-charge of metal is a subscript of non metal
-charge of nonmetal is the subscript of the metal
Steps:
Write charges of each ion
Cross cross charge to subscript on opposite ion
Get rid of charges
Write chemical formula (simplify ratio if necessary)
Transition metal ionic compounds
Because they have multiple possible forms, transition metals have varying charges/oxidation states so it needs to be specified with a roman numeral which oxidation state is being used. This oxidation state that is notated is also used for the criss cross method.
Naming (transition metal ionic compounds)
-cation is always written first. The name does not change.
-if it is a transition metal then the name must be followed by the charge of the cation in Roman numerals
-may also see this with lead (Pb) and tin (Sn) even though they are not transition metals
-name of the anion is written second, ending in "ode"
Ex: copper (II) oxide or copper (II) oxide
Polyatomic ions and ionic compounds
The compound is the attraction between positively charged cation and negatively charged anion
-the cation or anion made of covalently bonded nonmetals
-the lost or gained electrons are spread evenly among covalently bonded ion
-ionic bonding with polyatomic contain both covalent and ionic bonding
-polyatomic is a covalent bonded thing that has its own charge
Polyatomic ions and ionic compounds - Naming
-name of the cation is written first followed by the anion
-Polyatomics: used the name directly from table E in reference packet
Formula is always cation then anion, use subscript to indicate there is more than one
-if there are multiple Polyatomic ions, put parentheses around them then put the subscript outside the parentheses
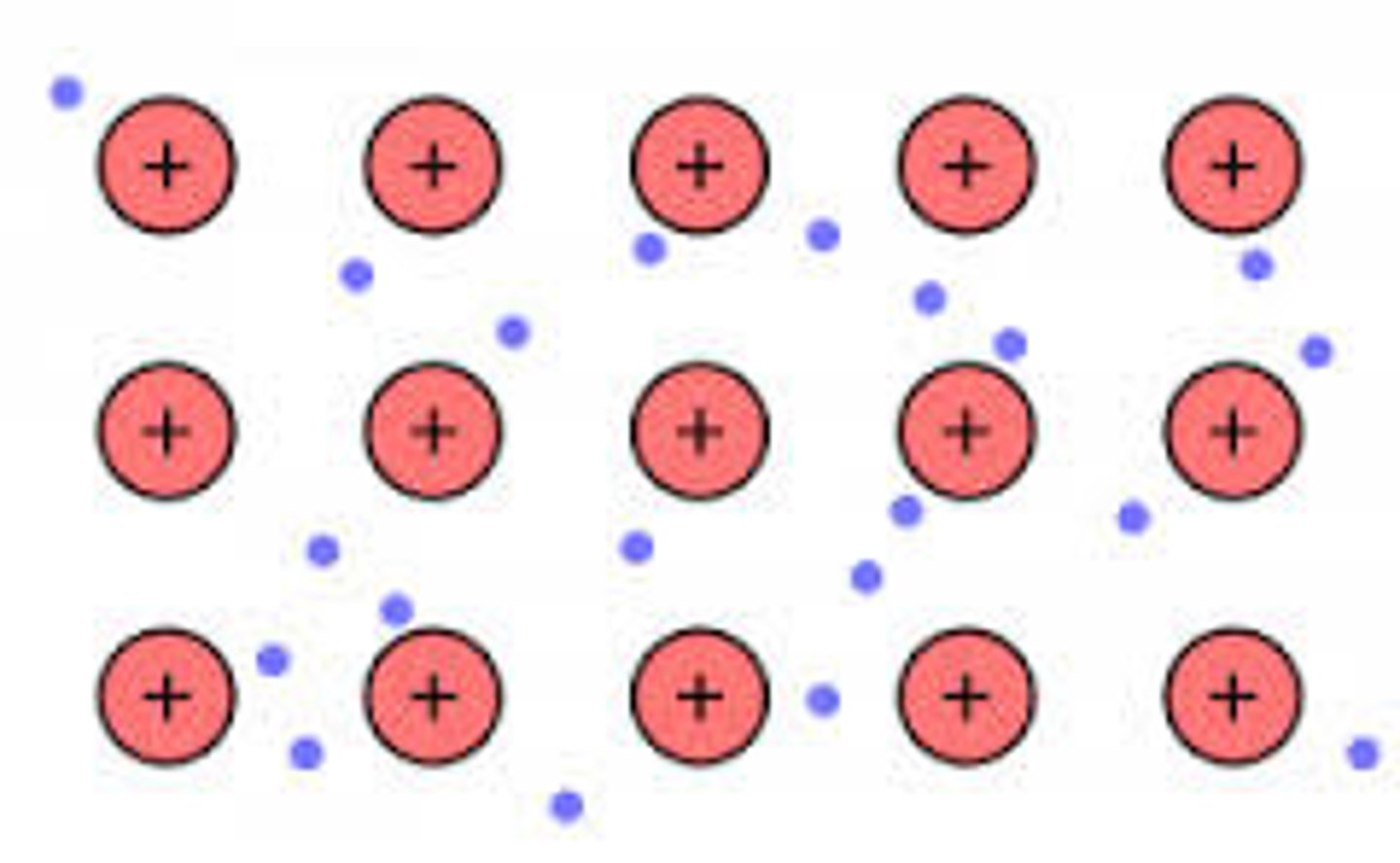
Metallic Bonding
Crystal lattice of positive metal ions surrounded by mobile delocalized valence electrons
-"sea of electrons"
-VERY CONDUCTIVE because of sea of electrons (theyre mobile)
Pure Metal
-contains only one type of metal atom (element)
-atoms are all the same size which allows them to easily slide and move past each other (malleable)
Substitution alloy
When two types of metal atoms of the same size are combined (no pattern)
-atoms are just "swapped out"
-ex: brass and steel
Interstitial Alloy
When two types of metal atoms of different sizes are combined.
Roman Numerals (1-8)
I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII
How to tell if something is Ionic Bonding
-one metal and one nonmetal
-together charges = 0
-one atom has a full shell
-high melting point
-conductive in aqueous solution