Renewable sources of energy
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What are infinite energy sources
Energy sources that can last indefinitely without a reduction in their supply
Why are infinite energy technologies necessary
To provide energy for the current generation and future generations
What process produces the Sun’s energy
Nuclear fusion reactions
How much energy do the Sun’s nuclear fusion reactions release
About 3,800 million million million million units of energy
How much of the Sun’s energy output does Earth receive
1/200,000,000,000 of the Sun’s total energy output
How much of the solar energy reaching Earth could meet global human energy needs
Just 1% of the energy reaching Earth
What limitation prevents solar energy from being collected at all times
It cannot be collected at night
What factors cause sunlight to vary on Earth
Geographic location, time of year, time of day, and weather conditions
What technological improvement is needed to make solar energy more effective
More efficient harnessing techniques, particularly in battery storage
How do solar heat collectors work
Black tubing absorbs heat from the Sun, heating water moving through it
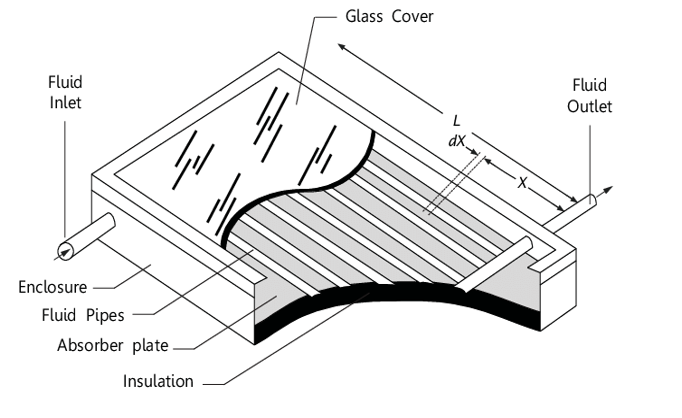
What is a common use of solar heat collectors
Warming swimming pool water
To what temperature can water be heated by flat plate collectors
Up to 100°C
Where are solar heat collectors commonly used
For hot water supply in homes, hospitals, industry, and agriculture
What happens when solar radiation is insufficient to maintain water temperature
Another energy supply (e.g., electricity) is used to maintain temperature
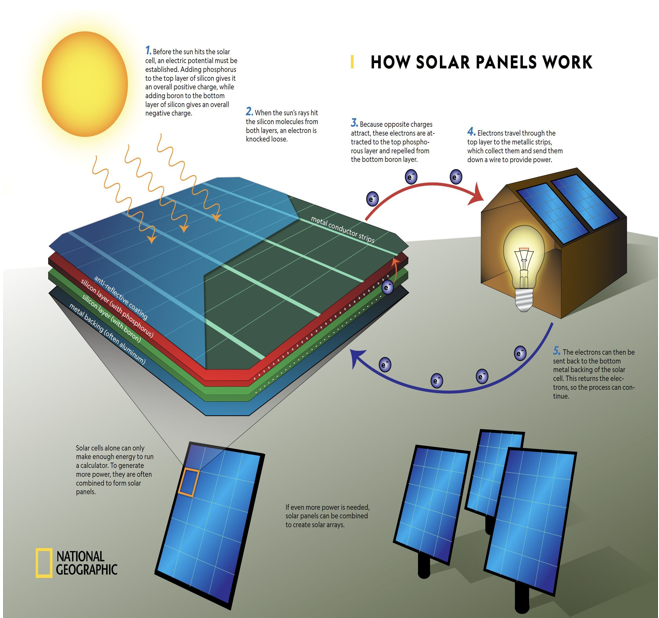
What do photovoltaic cells (PVs) do
Convert solar energy into electricity
What are photovoltaic cells primarily made of
Silicon, a semiconductor
What is a semiconductor
A material that will conduct electricity only under certain conditions
How are semiconductors made conductive in PV cells
By incorporating two types of impurities into silicon
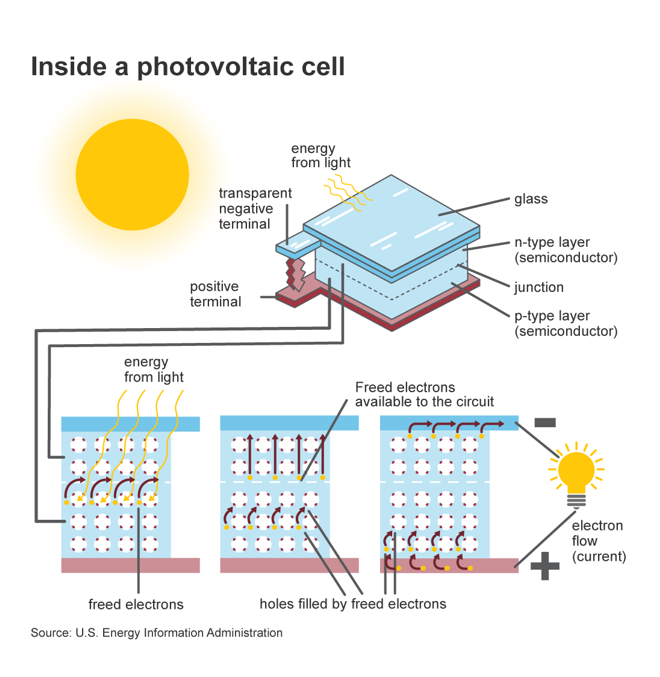
What impurity creates an n-type semiconductor in silicon
Arsenic or phosphorus, which provide extra electrons for conduction
Why are n-type semiconductors able to conduct electricity
They have free electrons available to participate in conduction
What impurity creates a p-type semiconductor in silicon
Boron or aluminium, which have a shortage of outer valence electrons
What happens when n-type and p-type silicon are in contact
A p-n junction is formed
What happens in a p-n junction in the dark (away from sunlight)
Excess electrons from the n-type silicon drift across to fill spaces in the p-type silicon
What charge does the n-type side of a p-n junction develop and why
Positive charge, because it loses electrons
What charge does the p-type side of a p-n junction develop and why
Negative charge, because it gains electrons
What does the charge separation across a p-n junction produce
An electric field across the junction
What happens when solar energy hits a photovoltaic cell
Energy excites electrons in the p-type silicon, moving them across the junction to the n-type silicon
How does a photovoltaic cell generate electricity for an external device
If a wire is connected across the junction, the moving electrons create an electric current that powers the device
How does the consumer cost of generating electricity from photovoltaic (PV) cells compare to power stations
It is quite high, but some costs are offset by reduced electricity bills
What is the cost trend for photovoltaic cells
Costs are falling, making them more viable for future generations
How are PV cells used in many Melbourne houses
Houses use PV cells while staying connected to the grid, exporting excess electricity and drawing from the grid at night or on cloudy days
What is a major environmental advantage of operating photovoltaic cells
They produce zero pollution while operating
What are two environmental concerns linked to photovoltaic cells
(1) Energy use and pollution during manufacturing
(2) Sand mining for silicon
What is the efficiency range of photovoltaic cells
15%–40%
How is wind created on Earth
Sunlight heats air unevenly; warm air rises, cooler air moves in to replace it, creating circulation
Give a local example of wind formation
Cool sea breezes moving over land as it heats up
Give a global example of wind formation
Hot air rises at the equator, and cooler air is drawn in from the poles
What factors influence global wind patterns
Earth’s rotation, ocean currents, and different land masses
How much potential energy could wind produce compared to humanity’s needs
Up to 10 times more energy than humanity uses per year
What are wind turbines used for
For mechanical tasks (e.g., wind pumps) and to generate electricity
What are the two main types of wind turbine designs
Vertical axis and horizontal axis
How do wind turbines generate power
Wind spins propeller blades, which drive a shaft connected to a mechanical device or electric generator
What conditions are required for efficient wind electricity generation
An unobstructed, steady flow of wind
Which country leads the way in electricity generated by wind
Denmark
What percentage of Denmark’s renewable and total electricity is from wind
About one-third of its renewable energy, and 4.9% of total electricity
How many wind turbines did Australia have in 2015, and where were most located
2,062 turbines in 76 locations; over half in South Australia, and 25 in Victoria
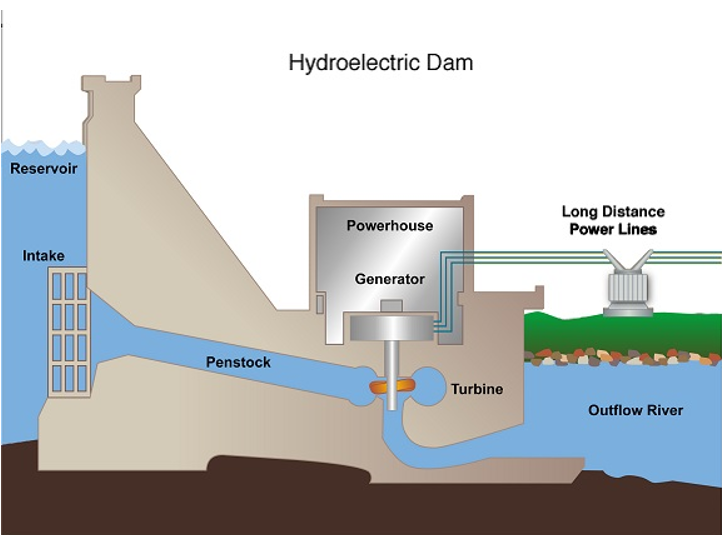
How is hydroelectric energy produced
Water stored in dams flows through a turbine, spinning a shaft connected to an electric generator
What factors affect electricity generation in hydroelectric systems
The volume of water flowing through the turbine and the vertical distance the water falls
How is energy converted in a hydroelectric dam
Gravitational potential energy of stored water → kinetic energy as it falls → electrical energy via the generator.
What is an operational advantage of hydroelectric power
It can be brought into operation quickly and easily, and can be turned up or down quickly
What is the efficiency rate of hydroelectric power
Approximately 70%
How much of the world’s electricity production comes from hydroelectric power
About 19%
What percentage of total global energy comes from hydroelectric power
About 10%
What is a major environmental advantage of hydroelectric power
It is clean and emits no particulate pollution
What is a social disadvantage of hydroelectric dams
Humans may be displaced when the initial dam is built, and large areas of occupied land are flooded
How do hydroelectric dams impact wildlife habitats
Storage, diversion, and release of water disrupt natural water flows, affecting aquatic and terrestrial habitats
How does diverting rivers and lakes for hydroelectric dams affect the environment
Water is often diverted from its natural course to maintain optimum levels for turbines, disrupting ecosystems
How does dam water release affect downstream aquatic species
Release water is usually cold and from the bottom of the dam, disrupting natural temperature and affecting species downstream
How is tidal energy similar to hydroelectric power
Both use moving water to spin turbines that generate electricity
How is electricity generated from tides
A dam wall is built across a bay or inlet; moving water passes through turbines to generate electricity
Can tidal energy use both incoming and outgoing tides
Yes, electricity can be generated from both incoming and outgoing water
What is required to generate large amounts of tidal power
Large volumes of water
What are the main disadvantages of tidal power
Few suitable sites, expensive to build, and massive disruption to aquatic ecosystems
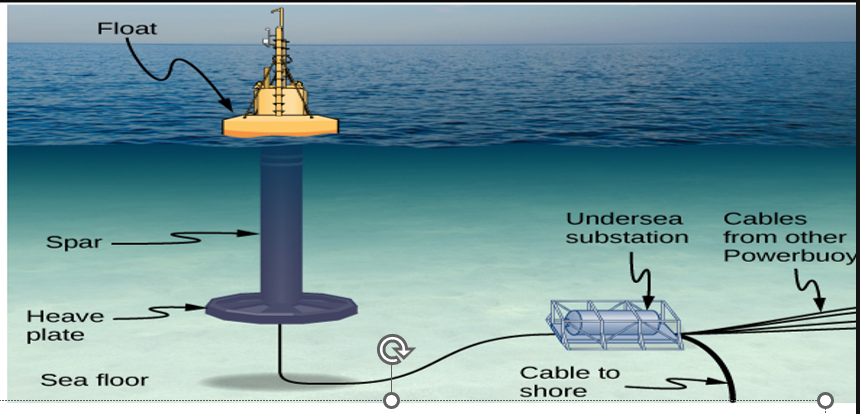
What factors determine the power a wave can produce
The wave height and period (time between successive wave fronts)
How do wave energy systems generate electricity
Using floats that move with the waves to compress air or lift fluid, driving generators
What are the main disadvantages of wave energy systems
They can be damaged by storms and corroded by salt water
Where does geothermal energy come from
High pressures and temperatures deep within the Earth
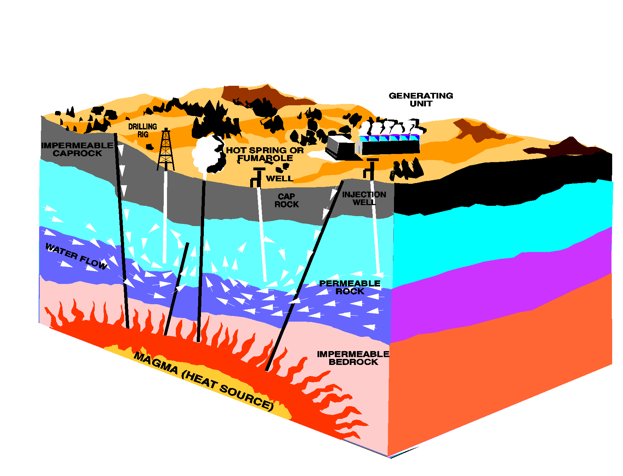
Why do some areas have high geothermal activity
The Earth's crust is thin, with cracks and faults allowing heat to approach the surface
How is geothermal energy extracted
Water seeps down cracks, is heated, and re-emerges as hot water or steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity
Can geothermal energy be used without water reaching the surface as steam
Yes, the heat can be extracted without steam emerging
Give an example of high geothermal energy use globally
In Iceland, 95% of buildings use geothermal energy
Give a local example of geothermal energy use in Australia
Portland, Victoria: heats public swimming pool complex and 14 buildings
Is geothermal energy considered renewable or non-renewable
Locally non-renewable (removal can deplete the source); globally renewable due to extensive availability
What are the environmental advantages of geothermal energy
Clean source of energy
What are the main environmental disadvantages of geothermal energy
Local depletion of resource, possibility of land subsidence, potential ecosystem damage
What is a limitation of geothermal energy in Australia
High-grade sources are rare and expensive to exploit
What is biomass energy
Energy derived from material produced by living things, such as plants and animals
Give examples of biomass materials
Waste from agriculture
Forestry products
Industrial human
Animal wastes
How can biomass be used directly
Wood can be burnt for heating
How can biomass be used to produce fuels
It can be converted into biofuels for transport or biogas for heating and electricity
Where does the energy in biomass originally come from
Solar energy, converted into biomass through photosynthesis
What is biogas and how is it produced
Gas produced from the breakdown of plant and animal waste in the absence of oxygen, usually containing ~60% methane
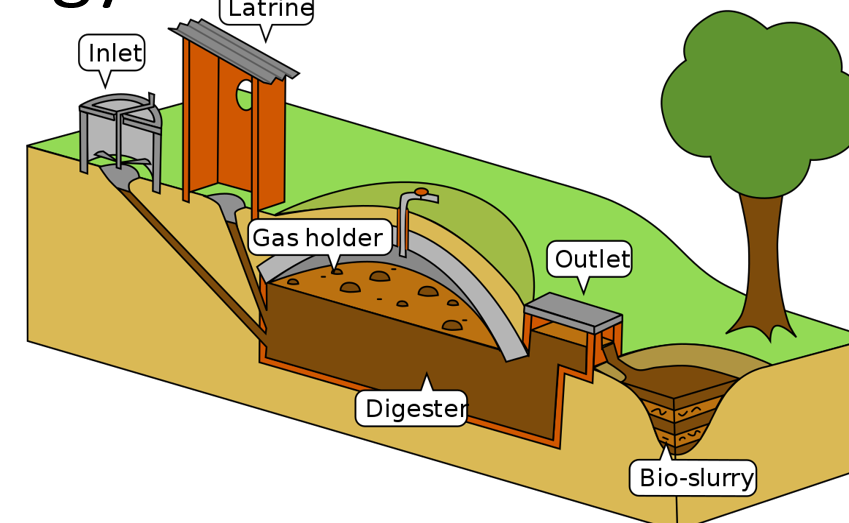
How can biogas be used
Burnt in power furnaces, heaters, engines, or used to generate electricity
Who relies on biomass for heating and cooking
About 30% of the world’s population, mainly in developing countries
What are the disadvantages of using wood for energy
Low efficiency; ~90% of heat lost in open fireplaces; smoke can cause air pollution; unsustainable use can lead to deforestation, soil erosion, and soil salting
What determines if biomass is renewable
The rate of deforestation—if used sustainably, it is renewable; otherwise, it is not
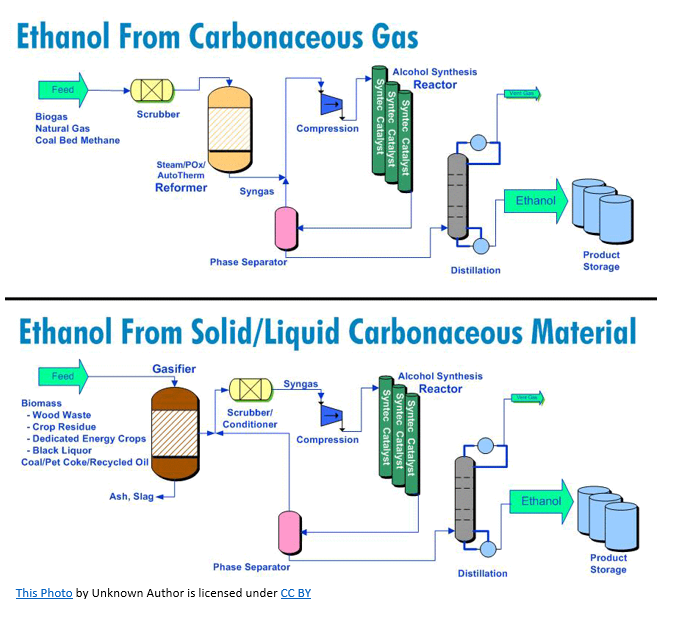
What is ethanol and how is it produced
A biofuel made from materials containing sugars, starch, or cellulose, produced via fermentation and distillation
How is ethanol used in transport
Blended with petrol to reduce petroleum use; in Australia, a 10% ethanol blend is available for most cars
What are the disadvantages of ethanol as a biofuel
Production can lead to photochemical smog, reduced tropospheric ozone, high costs, and competition with food production
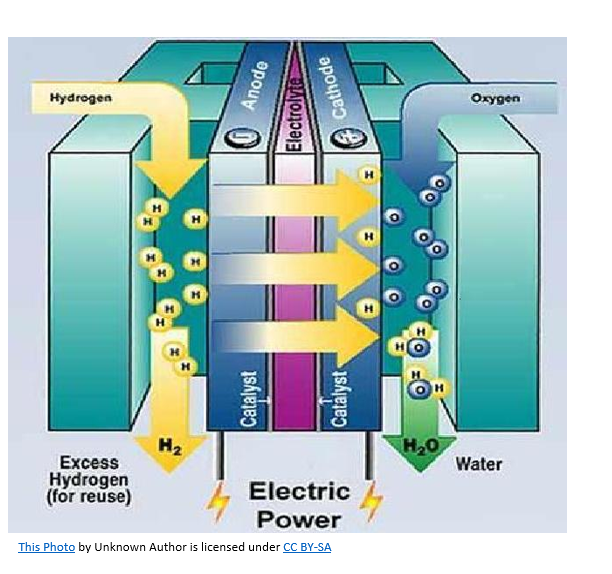
How abundant is hydrogen on Earth
It makes up 90% of Earth’s atoms and about 75% of its mass
How much hydrogen exists as gas in the atmosphere
Very little—only about one part per million. Most hydrogen is bound in water or carbon dioxide
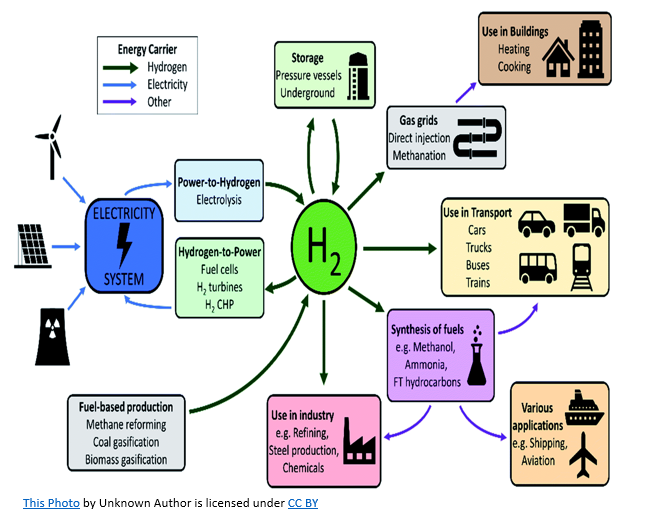
What type of reaction occurs when hydrogen combusts
An exothermic reaction, releasing heat energy
How does hydrogen compare to natural gas in density and energy content
Hydrogen gas is about 1/8 the density of natural gas and has about 3 times the energy content per unit mass
What is the byproduct of burning hydrogen in air
Water, which removes air pollution problems
How is hydrogen gas commonly produced
By electrolysis of water, which splits water into hydrogen and oxygen
What is a limitation of producing hydrogen via electrolysis using electricity from fossil fuels
It does not solve the environmental problems associated with fossil fuel use
Why is hydrogen energy currently expensive and challenging
Generating electricity for electrolysis via renewable sources (wind or solar) is costly, and fossil-fuel-derived electrolysis does not reduce environmental impacts