Bio 120 cell membrane and transportation
1/31
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What is the plasma membrane?
It’s a boundary
It exhibits selective permeability
It’s different proteins + fluid matrix of lipid bilayer
What did Singer and Nicholson propose?
The membrane is a Fluid Mosaic Model:
Fluids:lipids and proteins
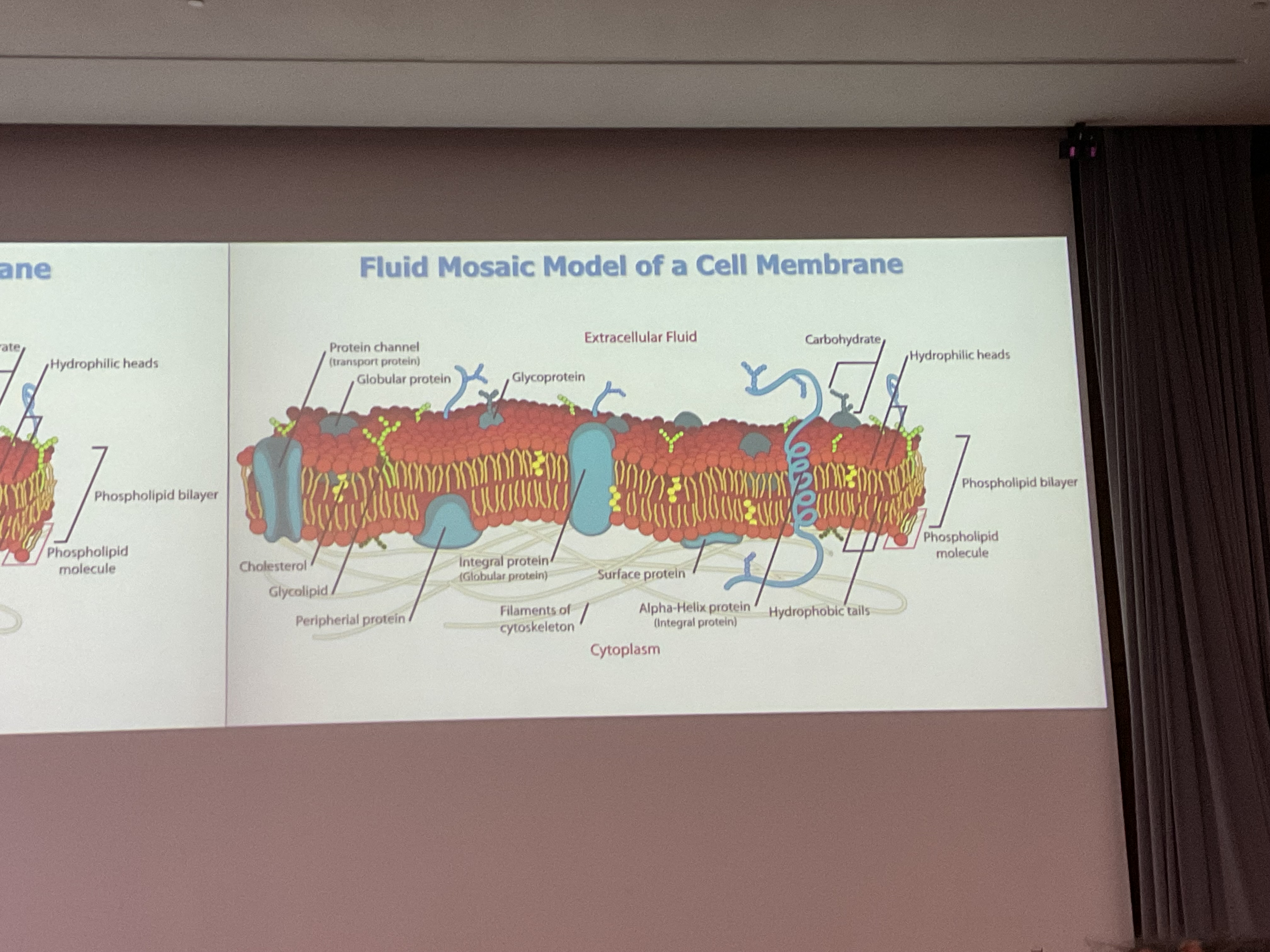
How do the phospholipids move
They move in the bilayer by drifting laterally
What is flippase
Phospholipid from outer leaflet to inner leaflet
What is Floppase?
From inner leaflet to outer leaflet of the plasma membrane
In what type of temperature do fluids work properly?
In hotter temperature. They become liquids
Unsaturated fatty acids in membrane are more or less fluid?
More fluid,easy to move
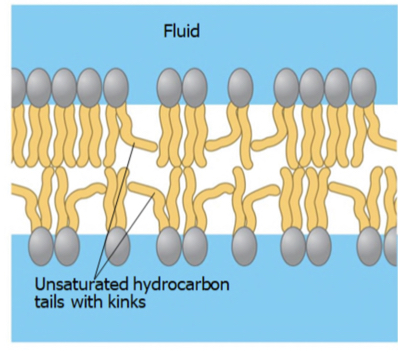
Saturated fatty acids are more or less fluid?
Less fluid , cuz more solid
What does the steroid cholesterol do?
(3 functions)
Essential for building the cellular membrane
Regulates the fluids in membrane
Maintain internal structure
What are the functions of proteins in the membrane?
(6 major fns)
Transport
Enzymatic activity
Signal ransduction
Cell-cell recognition
Intercellular joining
Attachment to cytoskeleton
What are the three types of transport across membrane?
Passive transport, active transport and Exocytosis Endocytodis
Describe passive transport
Diffusion of a substance across a membrane with no energy invested
Explain diffusion
The molecules spread evenly.
They move from a higher concentration to lower concentration
What is Osmosis?
Diffusion of water across the membrane.
From a lower concentration to higher concentration of solute.( goes towards more solute)
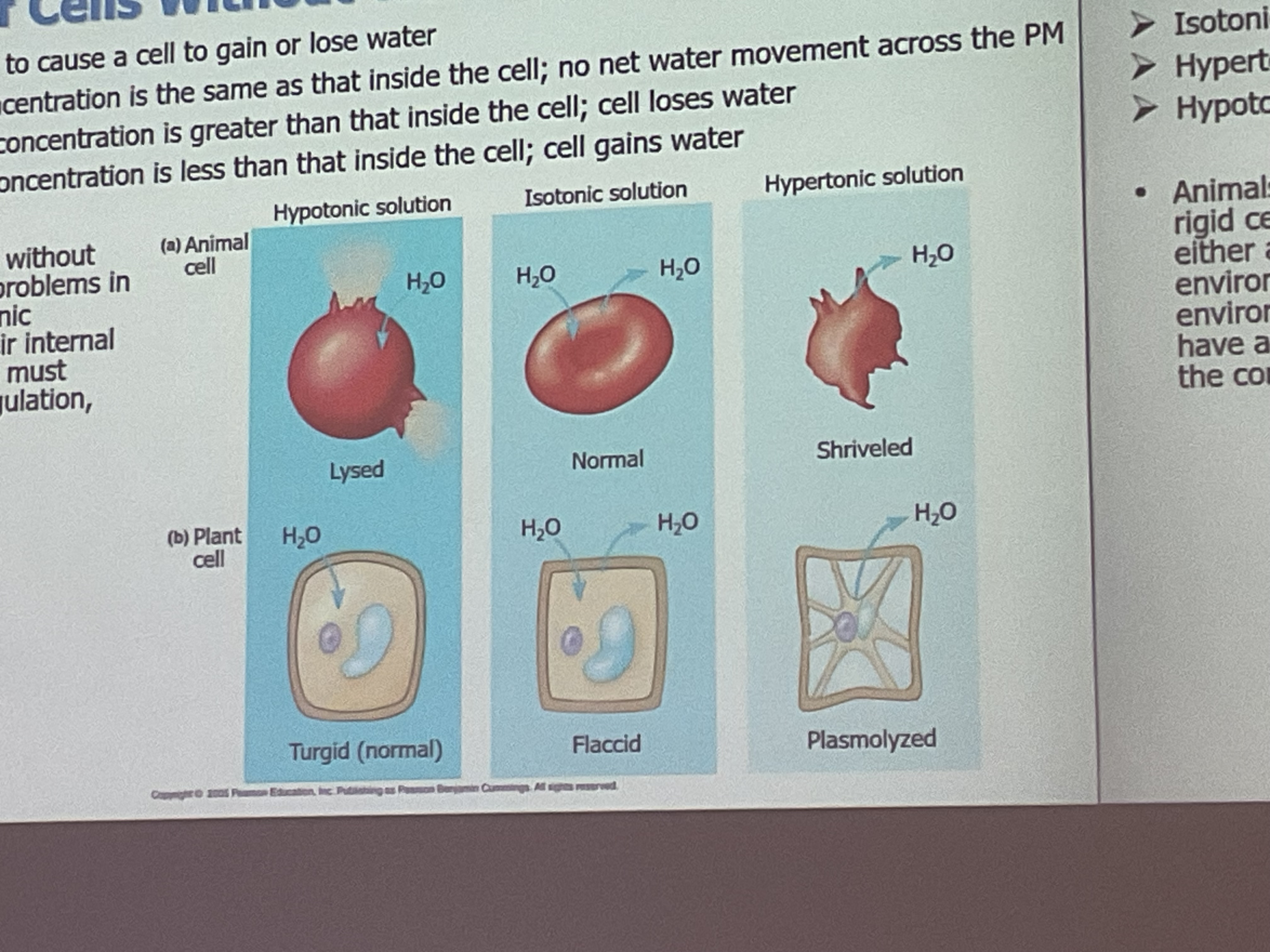
Cells without a _______ have osmoregulation problems and need a mechanism to maintain water balance into the cell.
Cells without a rigid cell wall have osmoregulation problems and need a mechanism to maintain water balance into the cell.
What is an Isotonic solution?
Concentration of solute is the same in and out of the cell—- no water movement.
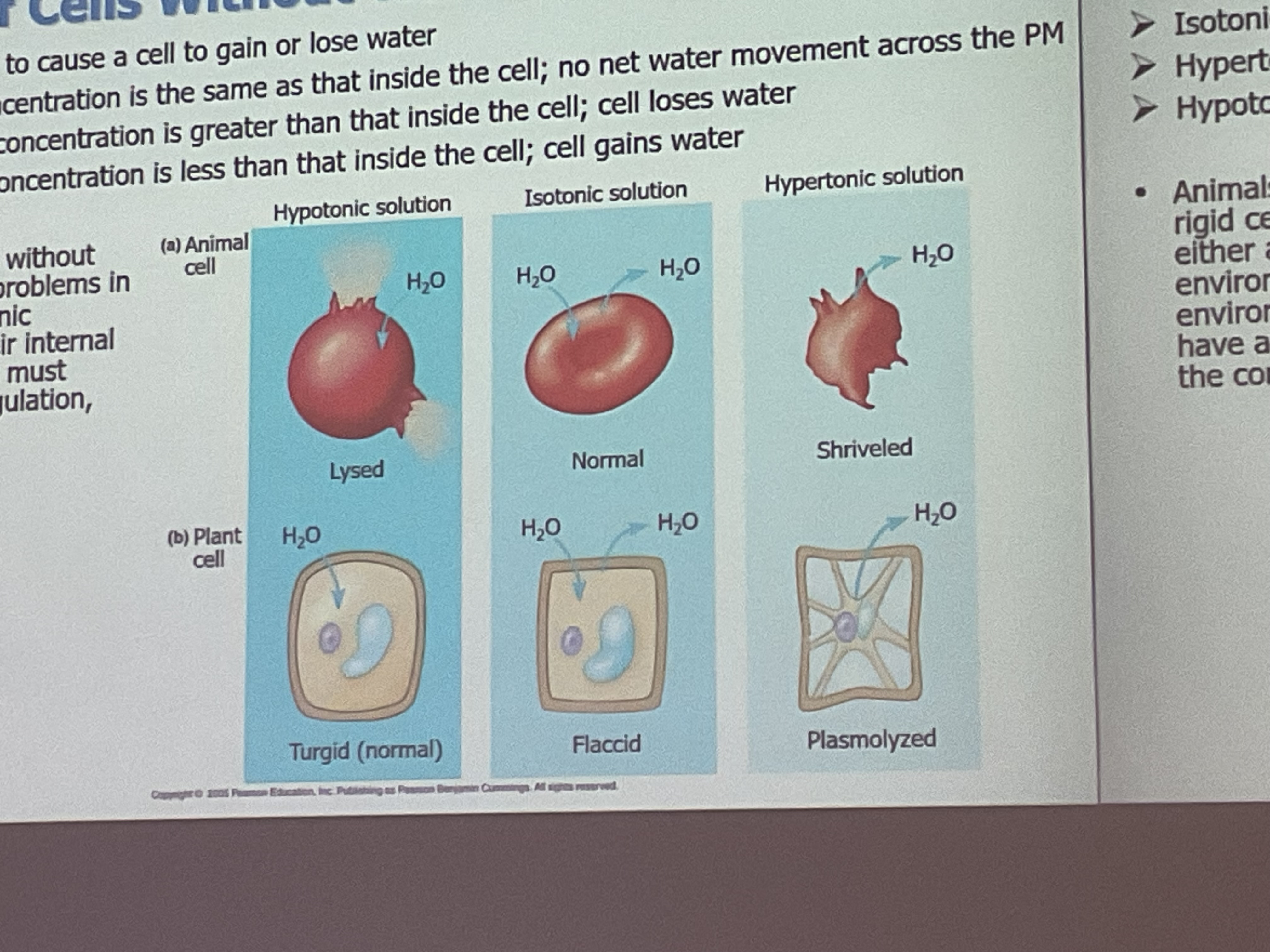
What is a Hypertonic solution?
Concentration of solute is greater out the cell —cell looses water(smaller)
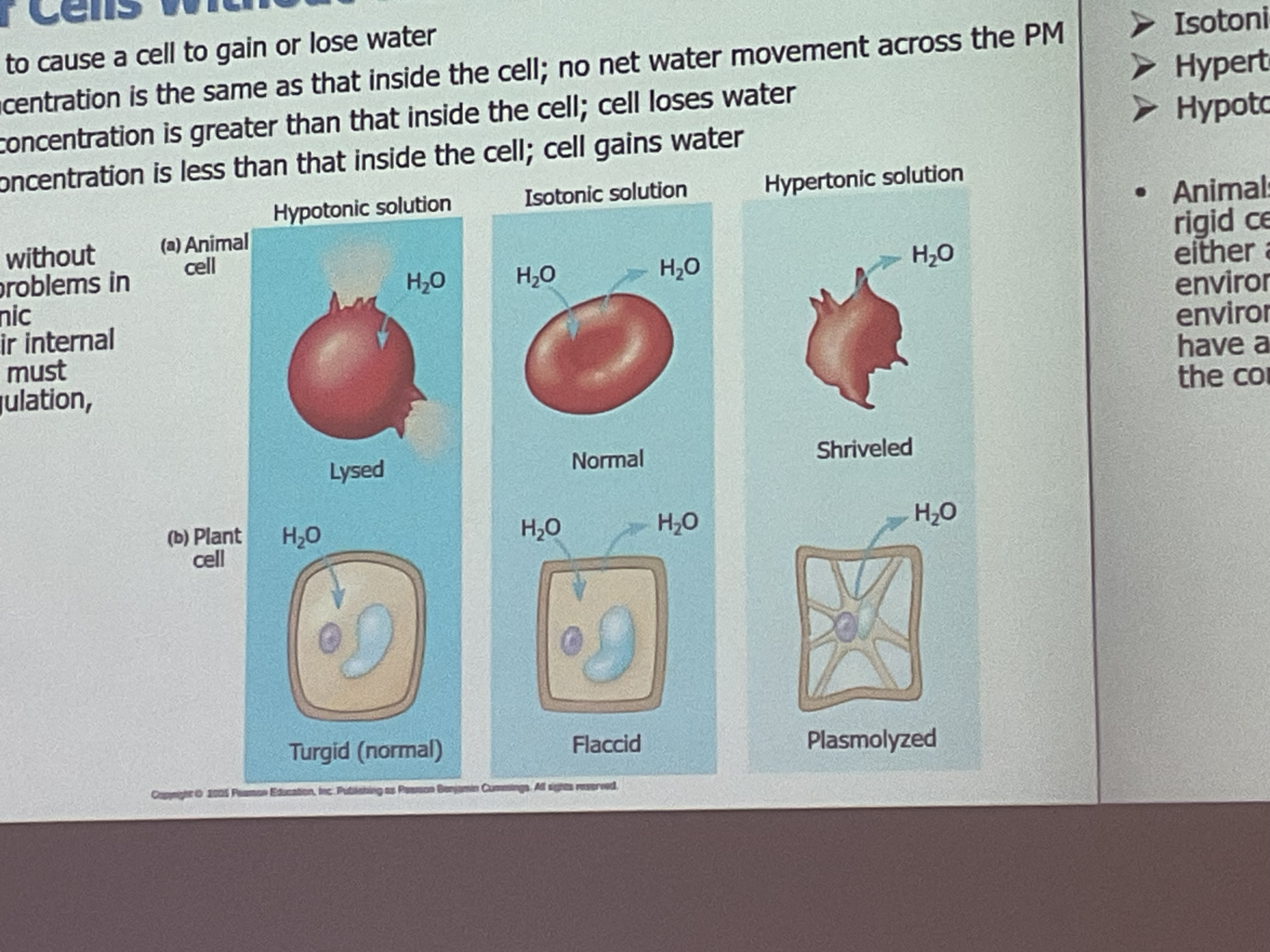
What is an Hypotonic Solution
Concentration of solute is greater in the cell—cell gains water( bigger)
Define facilitated diffusion?
It’s passive transport aided by transport proteins that aid movement of molecules
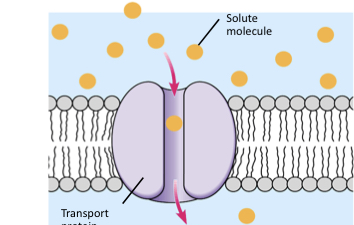
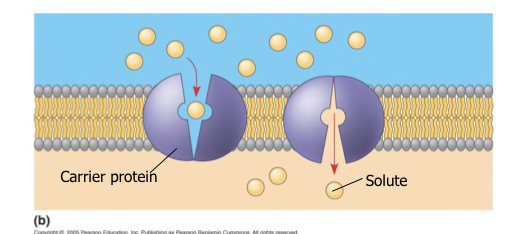
What are the two proteins that transport molecules in facilitated diffusion?
Channel proteins:specific ions to cross( always open) or pump
Carrier proteins: binds to solute and undergo change for it to go to the other side of the membrane (opens and closes)
What is active transportation?
Uses energy (ATP) to moves solute against the concentration gradient .
From low to high concentration
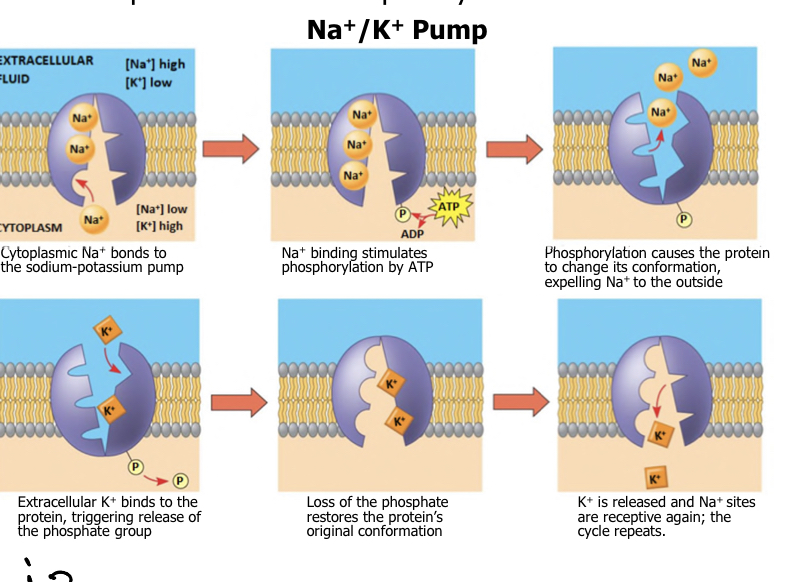
What is the most important active transport thing in animal cells?
The sodium-potassium pump
2K+ in (low conc. out and high conc. in the cell)
3Na+ out (high conc. out and low conc. in the cell)
What are the three classes of transporter for active transport?
Uniport
Symport
Antiport
Describe a uniport
one molecule goes one way (in OR out)
Describe a symport
Two molecules that travel the same direction in channel( in and in OR out and out)
Describe an antiport
Two molecules that move in opposite directions in the same channel (in and out)
What is cotransport?
It’s when the active transport of a solute activates automatically the transport of another solute
EX: cooperation of two transports
What are the types of active transport?
Primary Active Transport: energy comes from ATP breaking down
Secondary Active Transport:uses and electrochemical gradient created from active transport
ex: transport of glucose created by the gradient of the sodium-potassium pump
Endo and exocytocis
large molecules that cross the membrane via vesicles
Describe how exocytosis works
Active process of materials moving out(exit) the cell. Membrane-bound vesicles carry the materials and move to the exit. The membrane fuses to membrane then releases its content
Describe endocytosis
An active process of substances brought into a cell. The cell will form vesicles from the plasma membrane ( separates and like mutant formation)to intake macromolecules.
It’s the reverse of exocytosis with different proteins.