L11 Corneal Signs
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
what are clinical descriptors to describe what you are viewing (6)
shape, location, size, borders, color, and other
when describing general shape what are some ways to describe what you are seeing (4)
round, oval, linear, or irregular
when describing unique shape what are some ways to describe what you are seeing (4)
dendritic, disciform, geographic, nummular
when trying to describe the location of a lesion you can attempt to see what ___ of cornea is affect or what ____
layer, region
what are tools to use to check which layer of the cornea is affect while in the slit lamp (2)
optic section, vital dyes
what layers can be affects based on location (6)
epithelial (superficial)
subepithelial
anterior stroma
mid stroma
posterior stroma
endothelial( at or within endothelium)
what region can be affected based on location (5)
central (w/i visual axis)
paracentral (outside visual axis)
Mid periphery: btwn paracentral and periphery
periphery: near limbus
limbal: at limbus
while describing the size of something you are seeing something in the slit lamp (2)
qualitative and quantitive
while describing something you are seeing in the slit lamp what are some qualitative descriptors (3)
small, medium, large
what are some quantitive measures while try to describe how big something is (2)
measure in mm HxV
photodocument
what is a trick to measure the Height and width of a lesion in the slit lamp
use the slit lamp beam to match the height and width and use a ruler to measure it
qualitative = ___ assessment
quantative= ___ assessment
subjective, objective
while describing a lesion and determining borders you should ask yourself if they are
distinct or indistinct border
what is considered a well defined or distinction (2)
- able to draw an imaginary shape
- contained lesion with minimal involvement of adjacent cornea
what is considered a ill defined or indistinction (2)
unable to draw imaginary shape
may or may not have significant adjacent corneal involvement
describing color: white
may be from infiltrates, scar tissue, calcium, ...
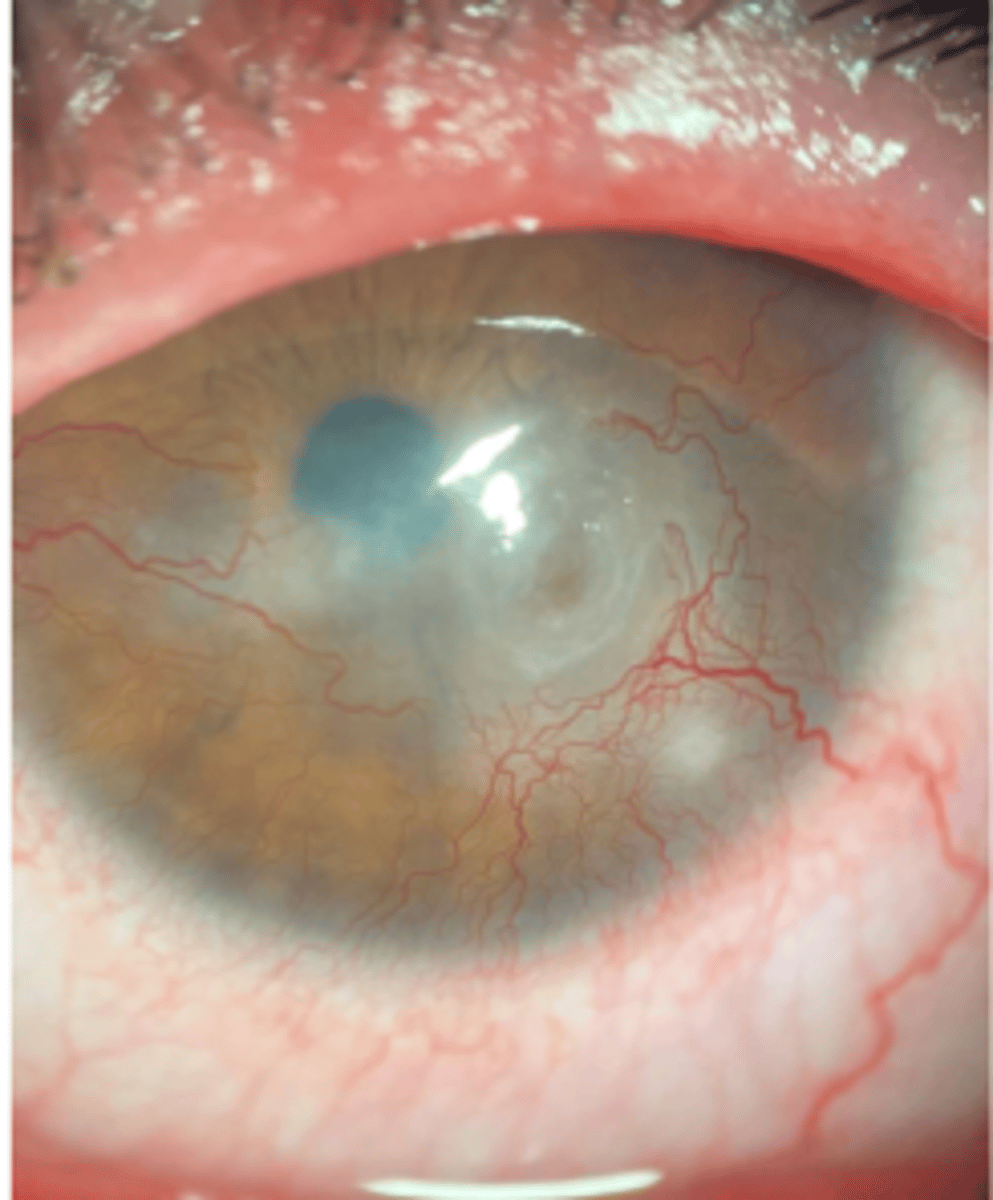
color: red
from blood or RBC dusting
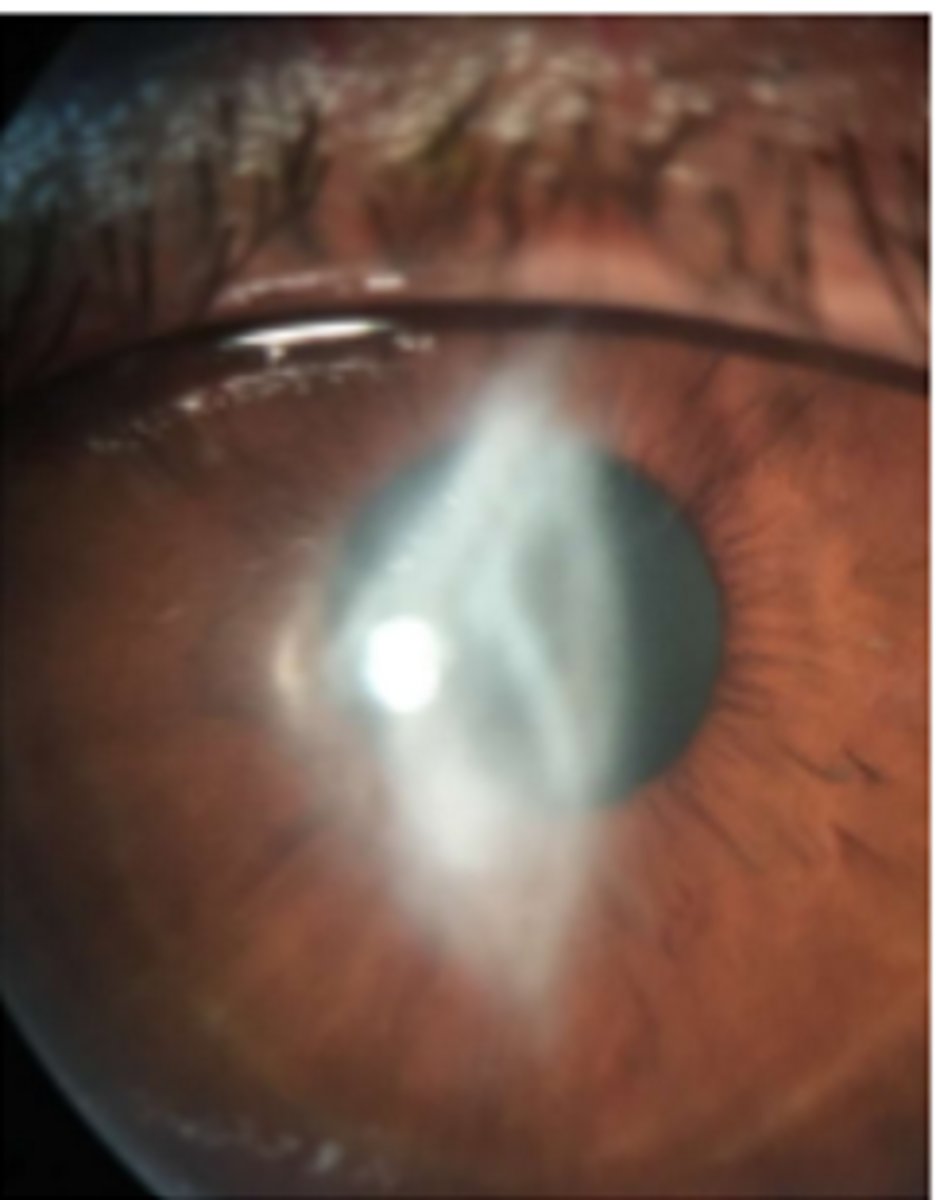
color: blue gray
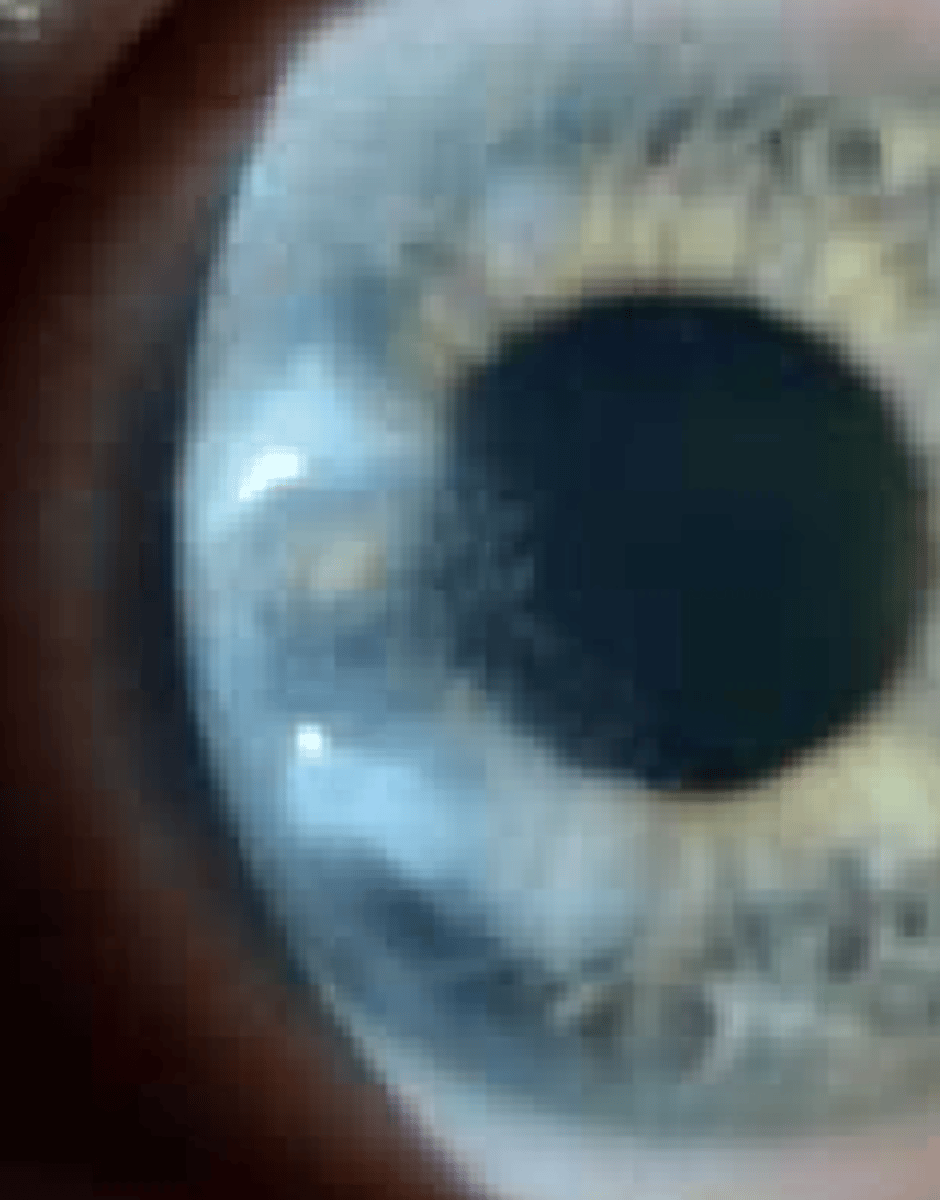
color: brown
may be from: pigment, copper, iron
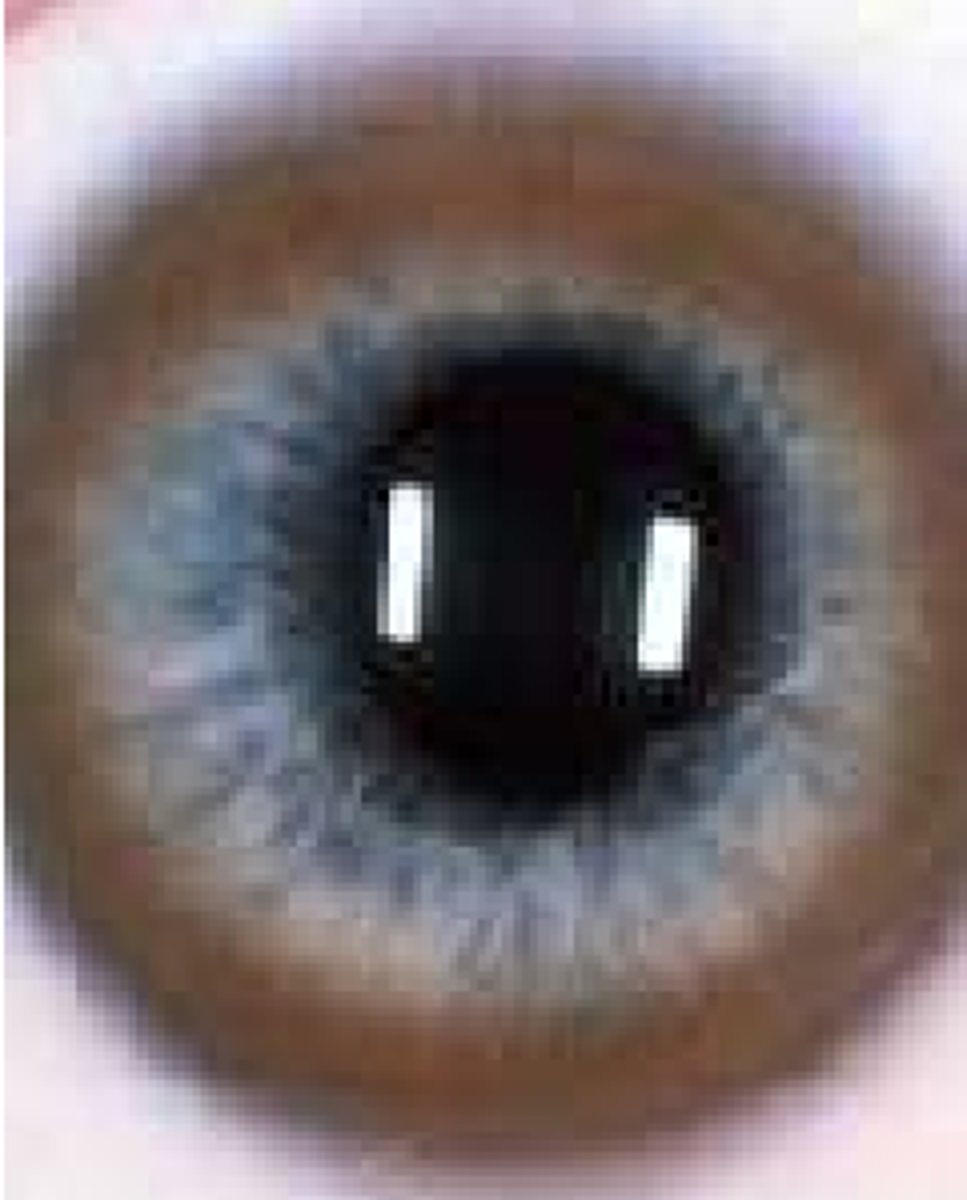
color: yellow
may be from: from white-yellow to dark yellow
fatty, lipid deposits
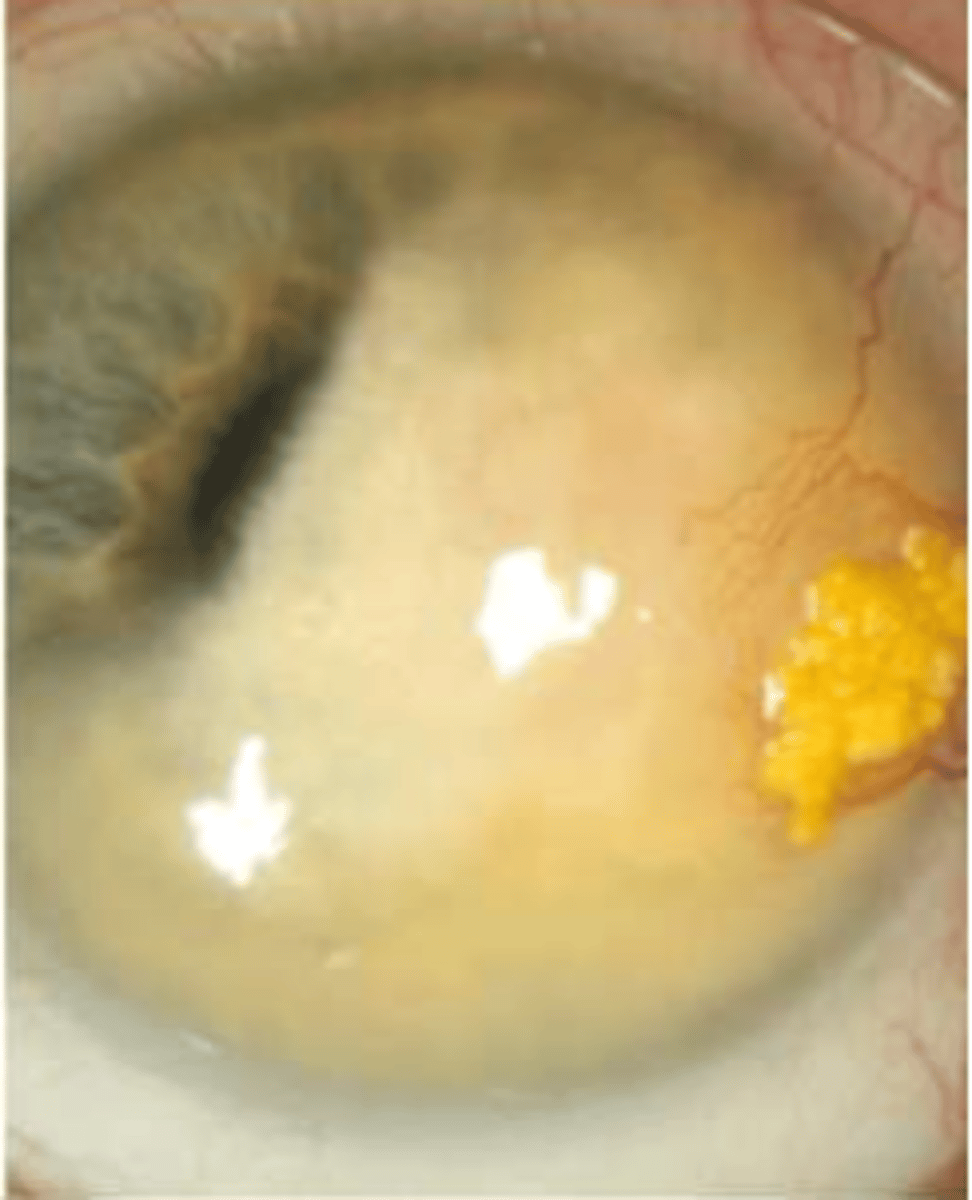
space: diffuse
widespread
space: focal
specific localized
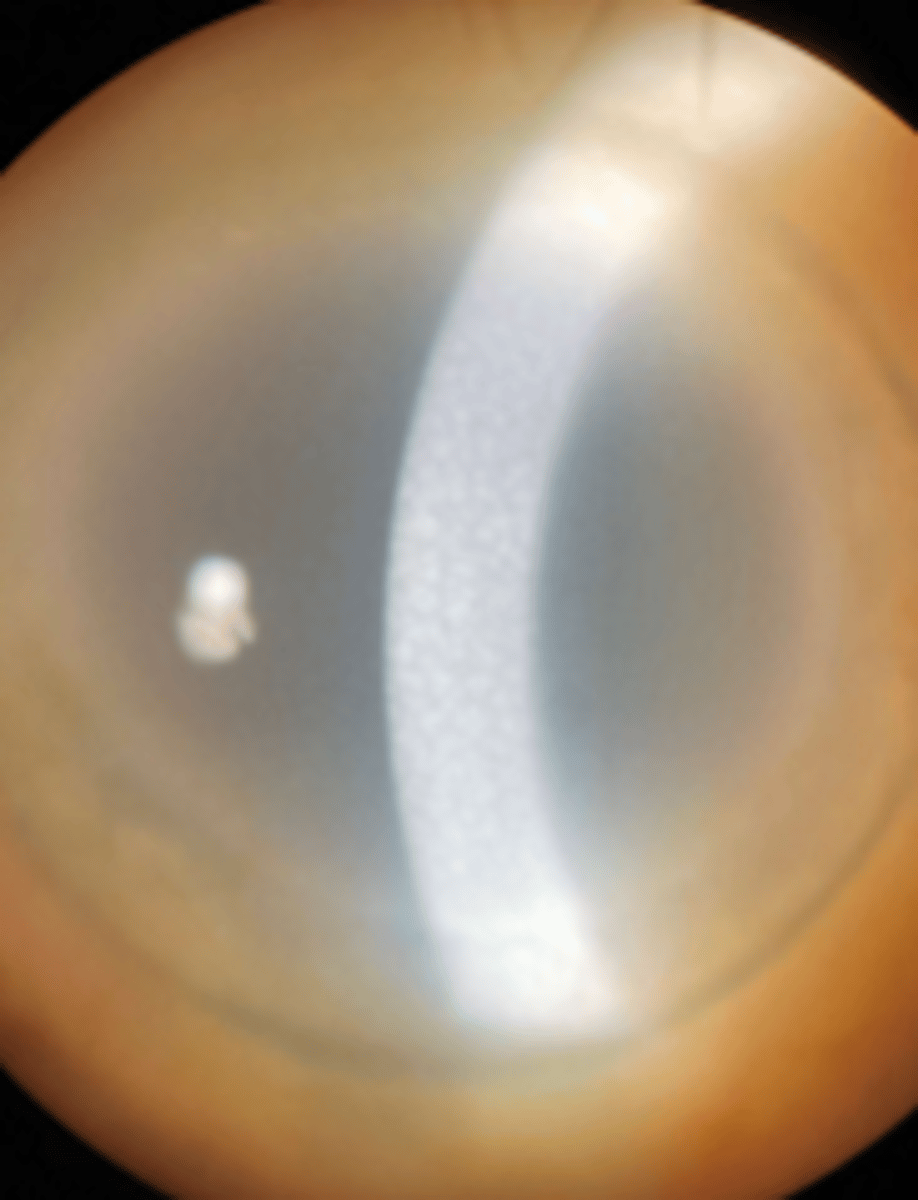
space: marginal
near the border
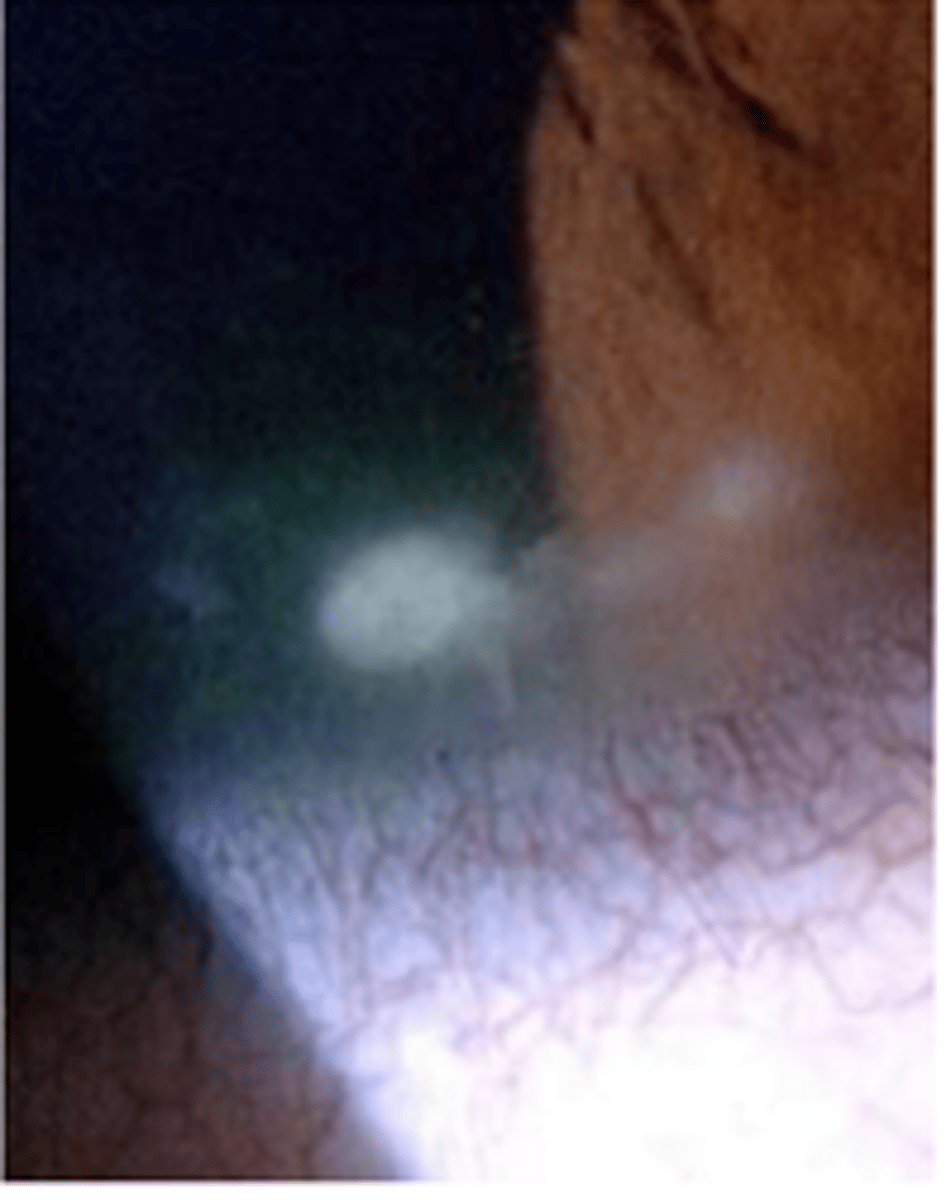

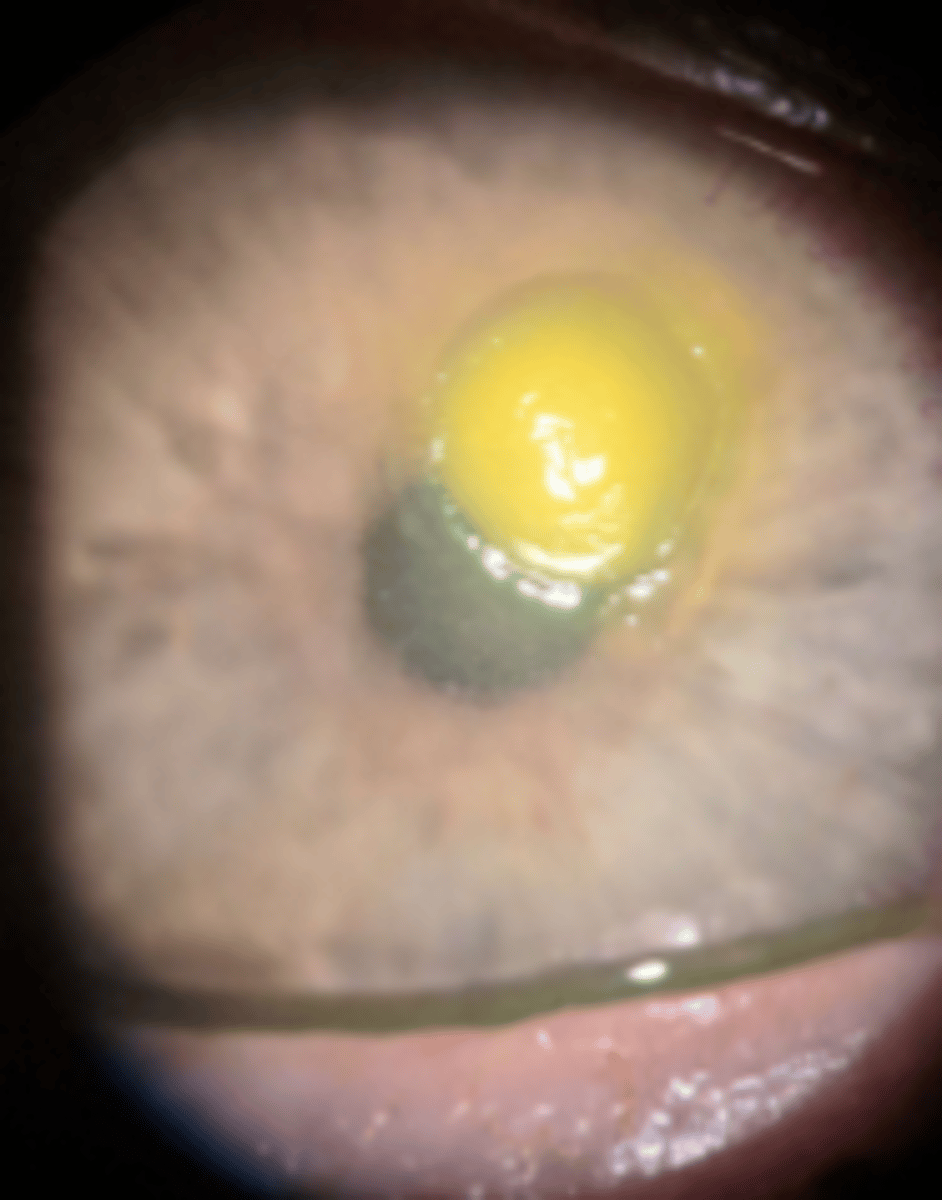
space: interstitial
spaced between cells
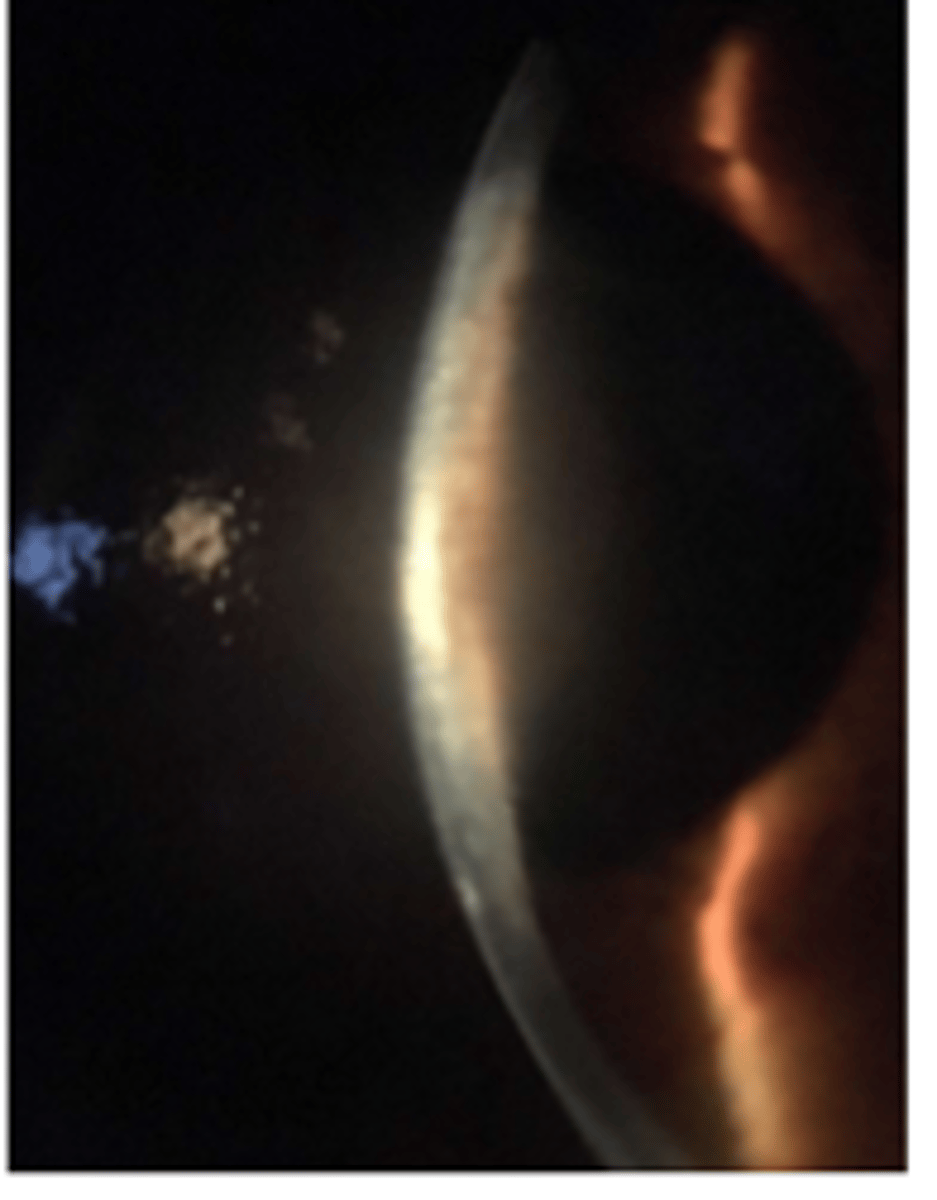
space: circumferential
outside edge
consistency, transparency, quantity, and company it keeps are other clinical ____
descriptors
what are two tools to measure ocular clincial signs
mm ruler and slit lamp light height/ width
what are slit lamp techniques to asses ocular signs (4)
sclerotic scatter
specular reflection
optic section
indirect illumination
what vital dyes can be used to asses ocular signs (2)
superficial
postive vs negative staining
what filters can be used while assessing ocular signs (2)
cobalt with wratten filter
neutral density vs no filter
what is the central thickness of the cornea
555 microns
what is the thickness of the cornea peripherally
670 microns
epithelium is ___ microns
50
corneal stroma is ___ microns
500
endothelium is ____ microns
5
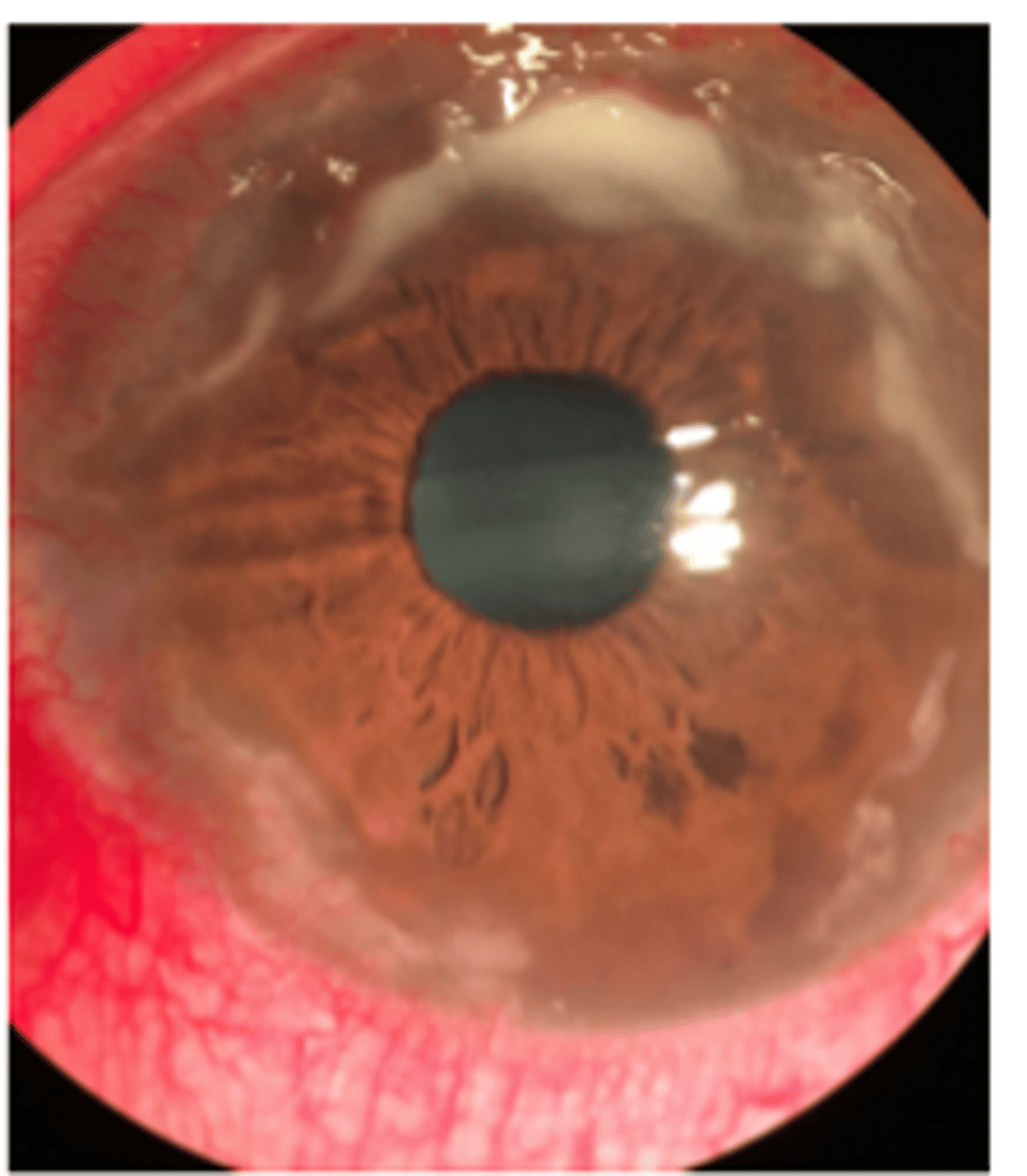
what is pannus
superficial subepithelial fibrosis derived from conjunctival or superficial episcleral plexus
____ ___ is
- non specific response
- lacks blood supply
- appears as subepithelail haze made of various collagenous components
- can occur in many conditions including PRK and salzmann nodular degeneration
avascular pannus
____ ___ is
- fine sheet of fibrosis with blood vessels
can be present in mild or chronic inflammation with varying severity
vascular pannus
what is stromal neovascularization
formation of new blood vessel
___ ___ ___ is
- located subepithelial or anterior stromal
- response to superficial disease
- arises from ACA to conjunctival or superficial episceral plexuses
superficial stromal neovascularization
___ ____ ___
- located from mid stroma
- chronic inflammation
- arises from PCA to deep episcleral plexus vessels
middle stromal neovascularization
__ ___ ___
- located in the posterior stroma
- chronic inflammation
- arises from PCA to deep episcleral plexus vessels
deep stromal neovascularization
superficial stromal neovascularization
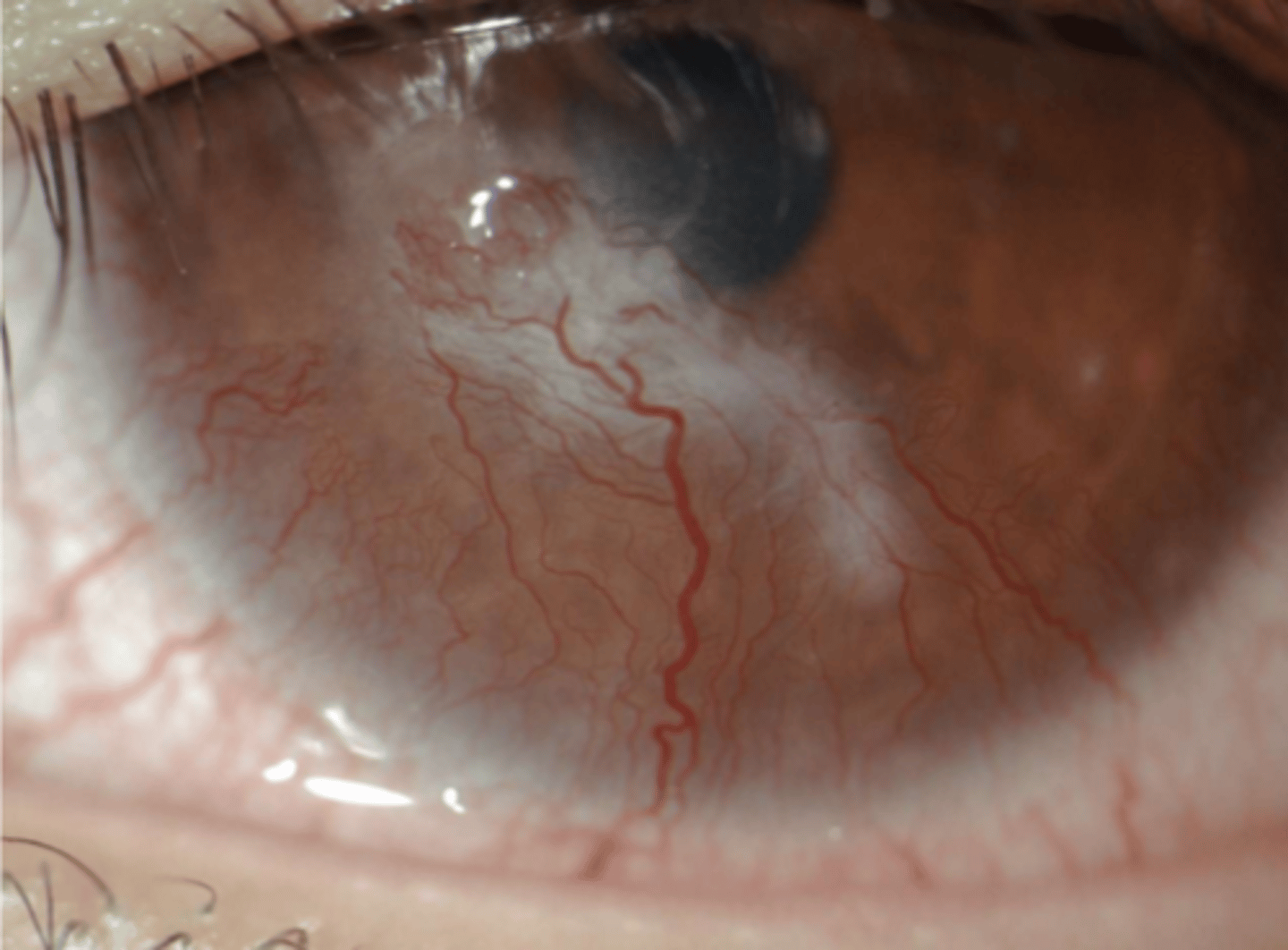
middle stromal neo
middle stromal neo
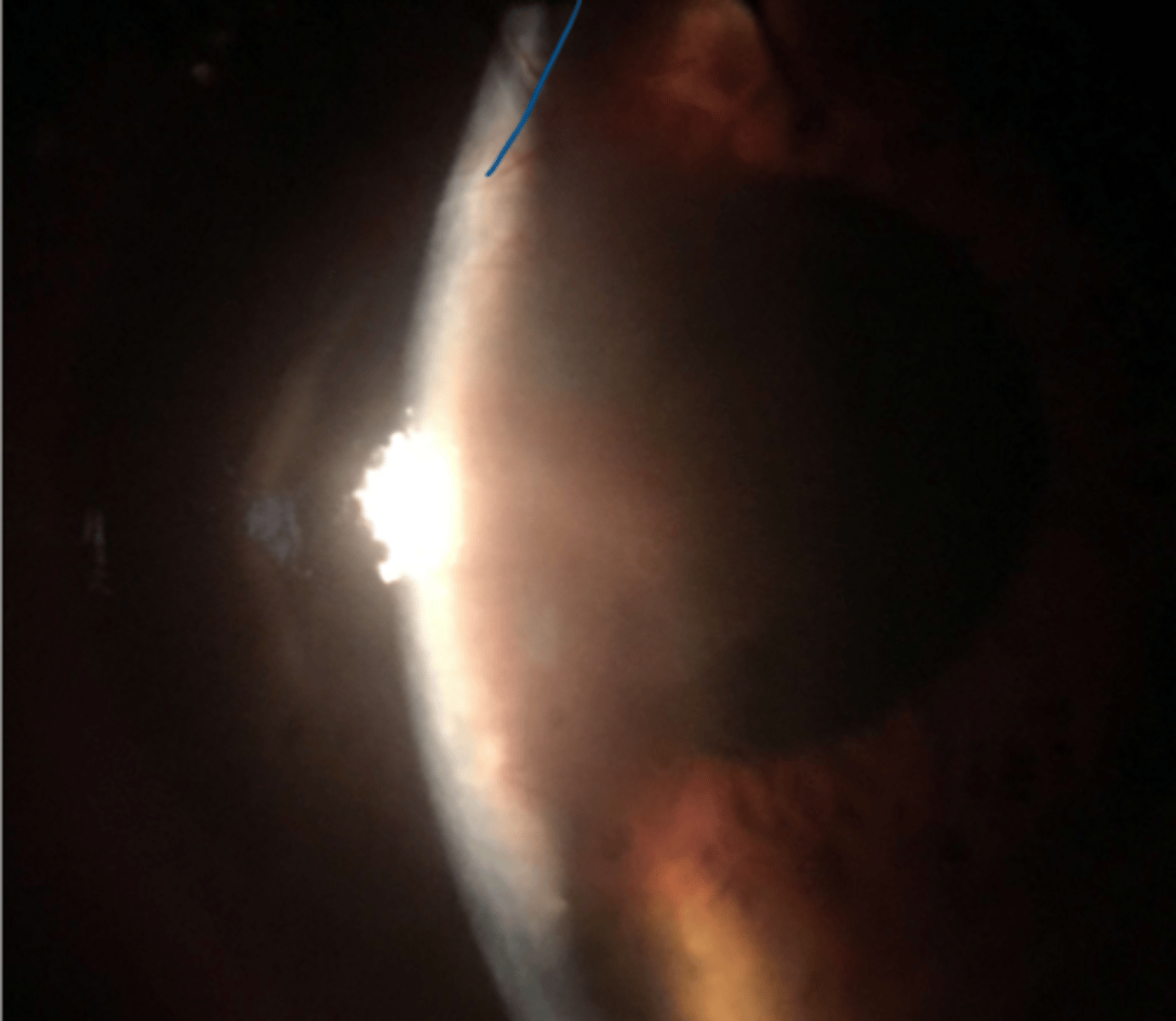

deep stromal neo
inactive neo-> ghost vessels
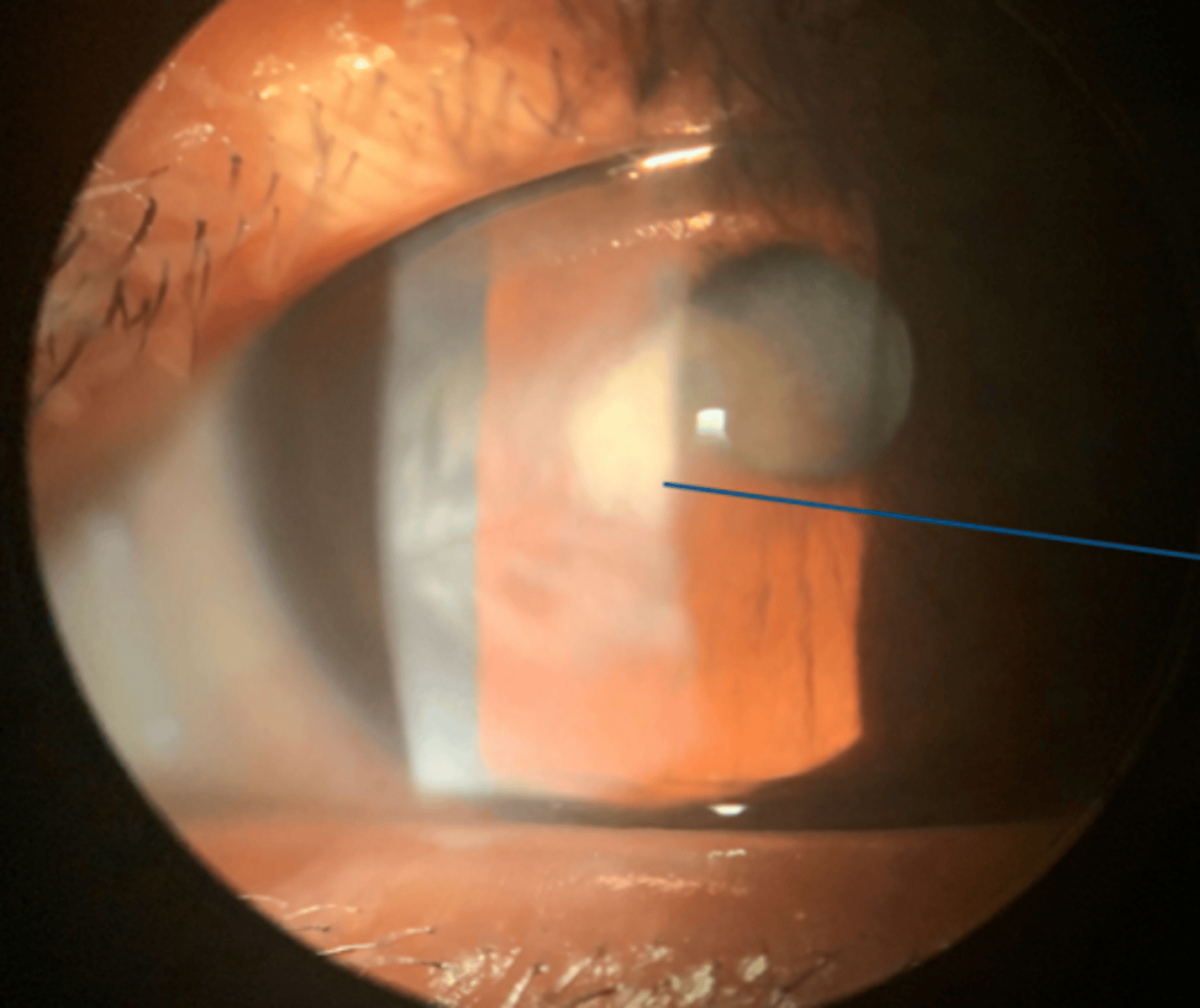
___ ____ is
- regression of stromal neo
- white and quiet eye
- potential to reactivate
ghost vessels
an inciting event such as microbe, trauma, or autoimmune can lead to : ___ (4) in chronicological order
hyperemia, stromal neovascularization, inflammatory cells and then clinical presentation such as infilitrates with chance of edema & suppuration
what are infiltrates?
inflammatory cells composed of leukocytes
are infiltrates single, multiple, diffuse or all of the above
all of the above
when there is a immune response it will manifest as ___ in the cornea
infiltrates
if there is there is infiltrates in the epithelium it is known as
epithelial infiltrates
if there are infiltrates in the corneal anterior stroma it is known as (2)
subepithelial infiltrates OR stromal infiltrates
if there are infiltrates in the corneal middle stroma OR posterior stroma it is known as
stromal infiltrates
if there are infiltrates in the corneal endothelium it is known as (2)
keratic precipitates
corneal epithelium infiltrates
subepithelial epithelial infiltrates
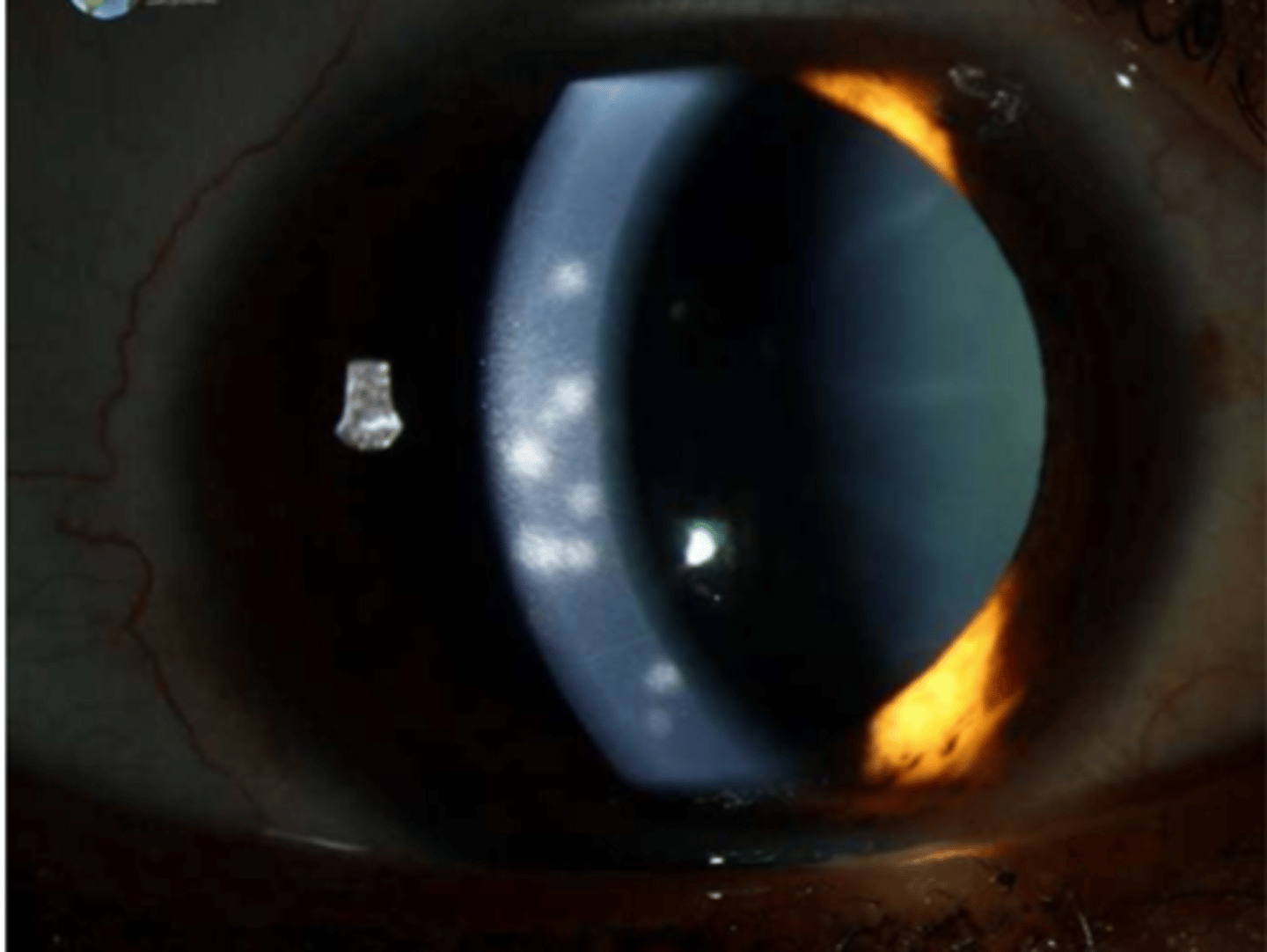
t/f subepithelial epithelial infiltrates can be located in the anterior stroma
true
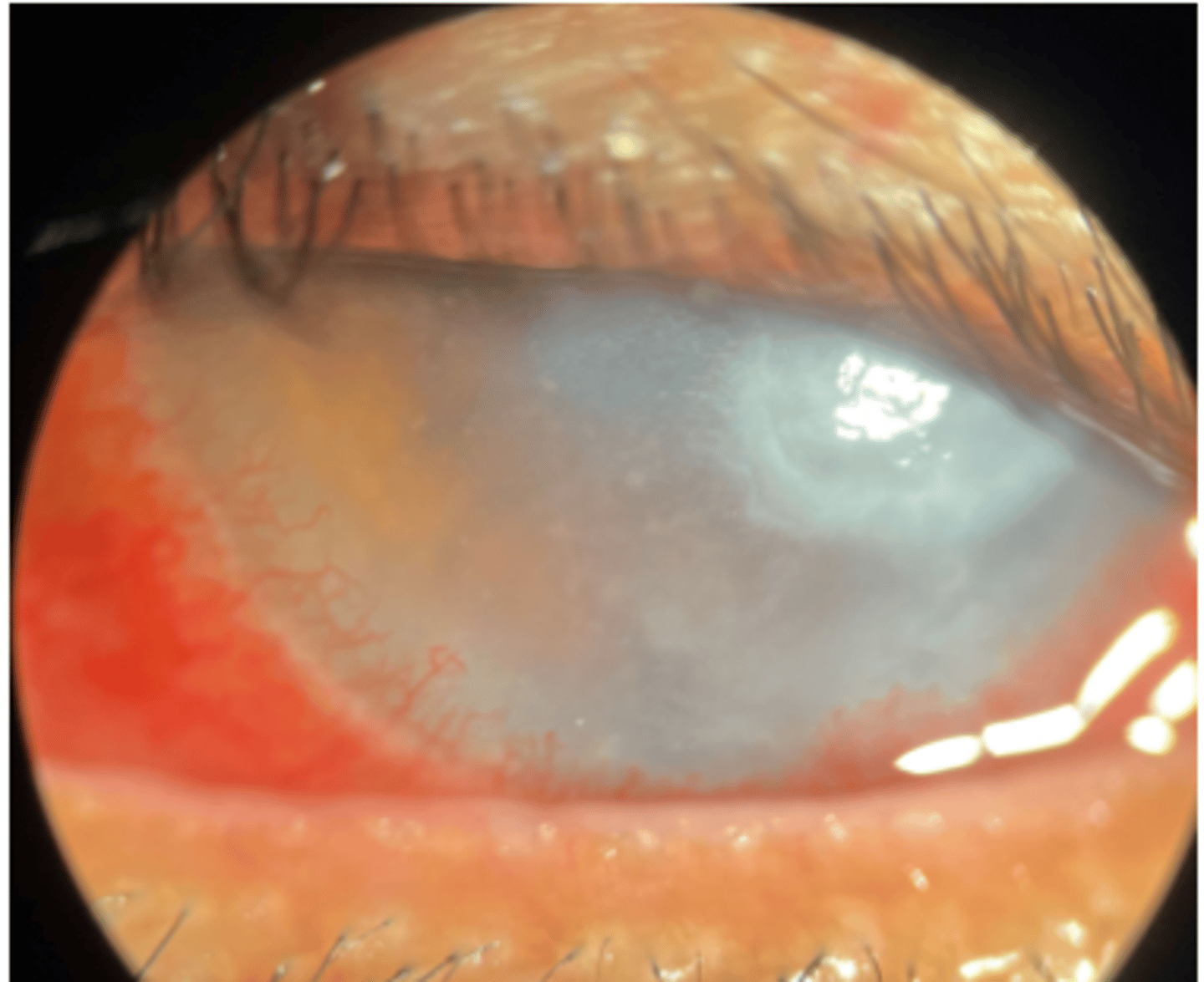
t/f a characteristic of stromal infiltrates is that it can be indistinct faint to sense grainy haze
true
can stromal infilitrates present present and without edema? yes or no
yes
stromal infiltrates
___ ___
- inflammatory leuokcytespresents on the back of the endothelium
- shows in various shapes such as fine dusting, large greasy round stellate
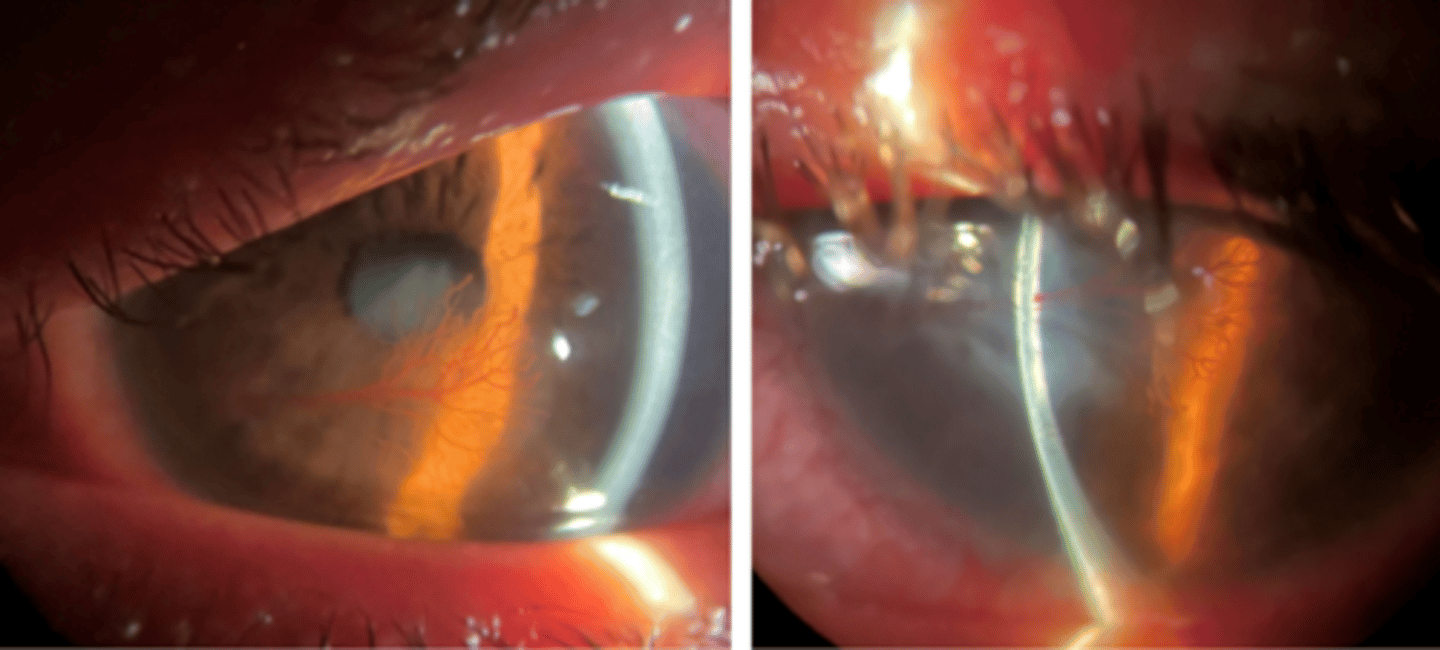
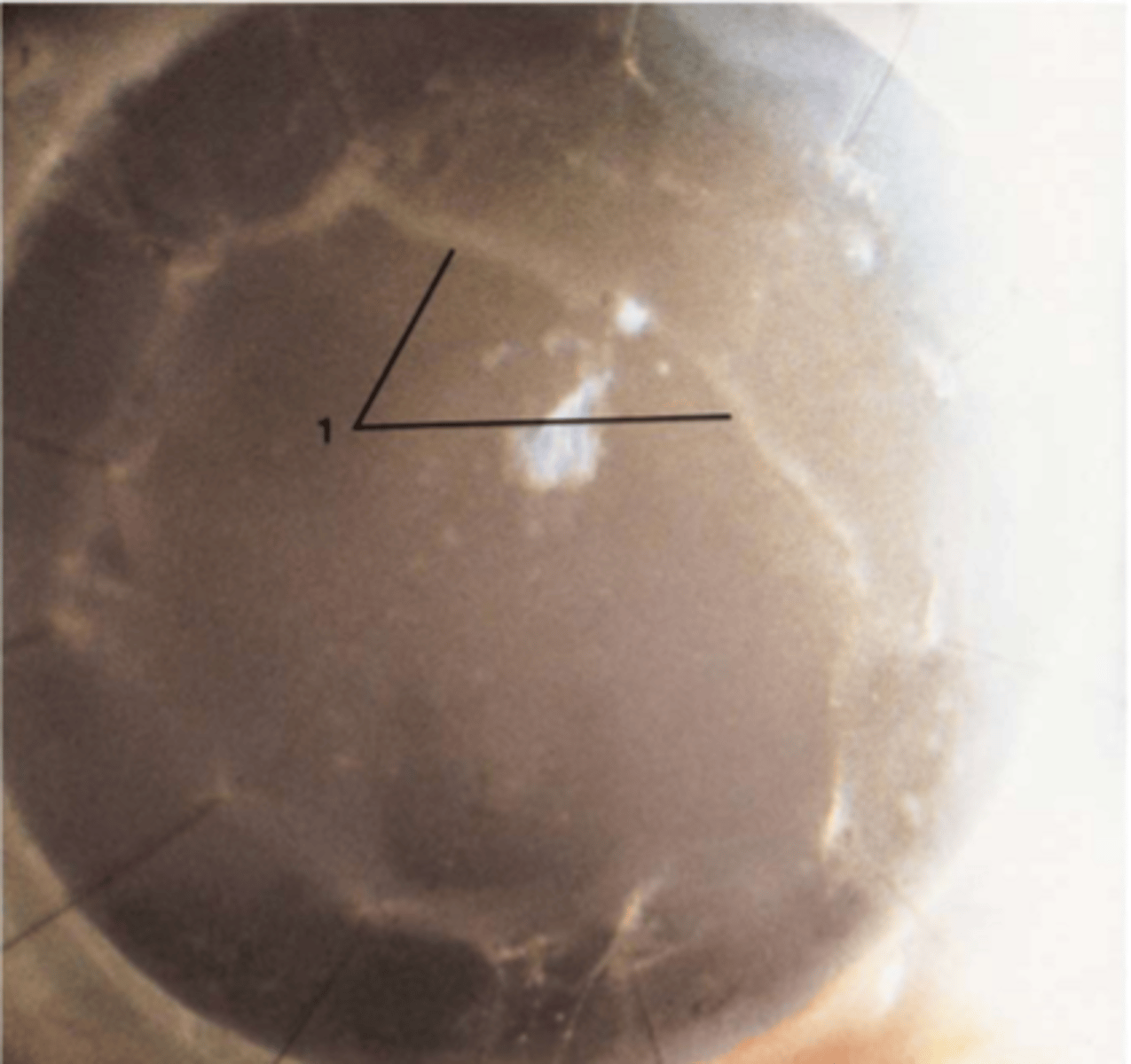
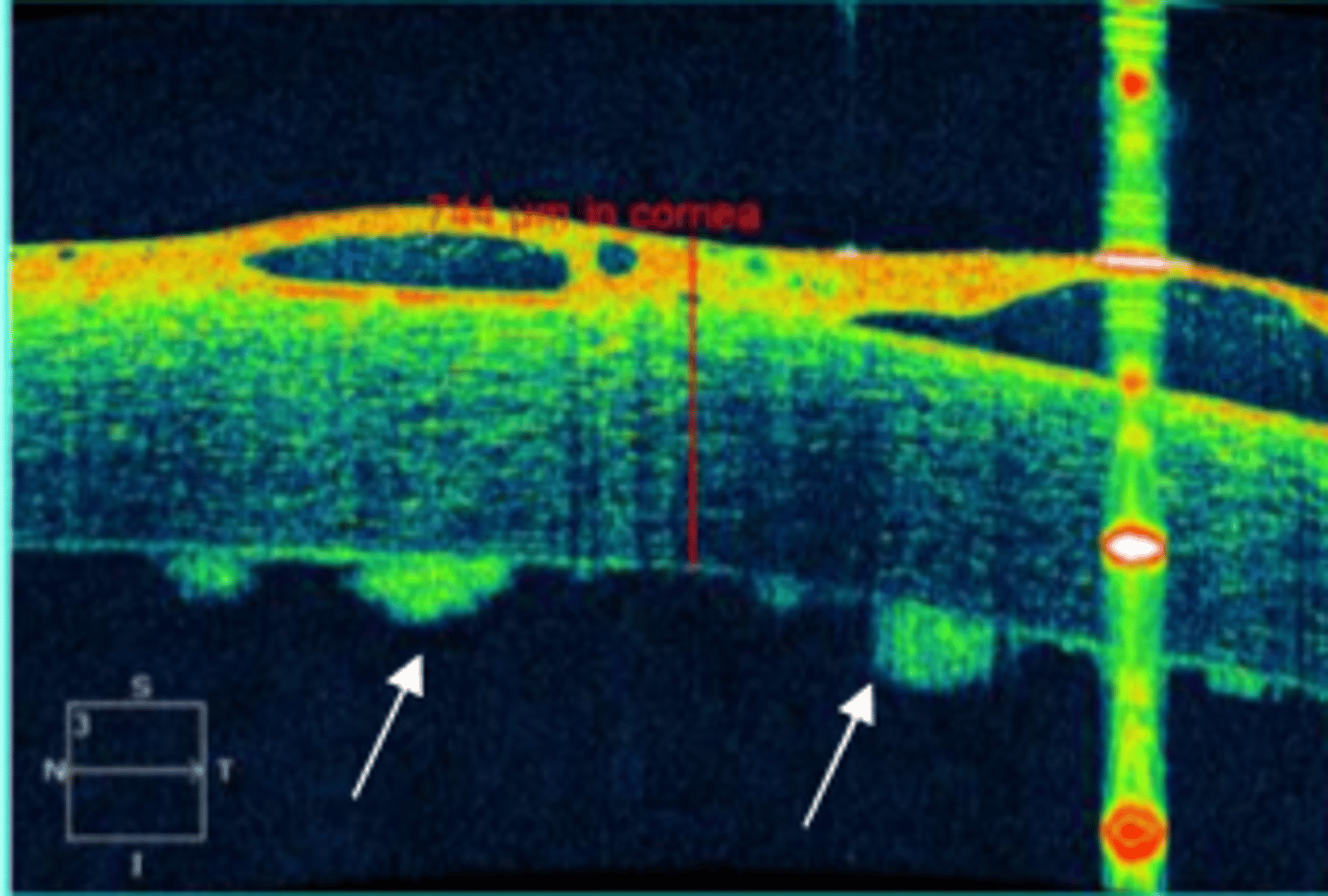
keratic precipitates
keratic precipitates
keratic precipitates on series OCT
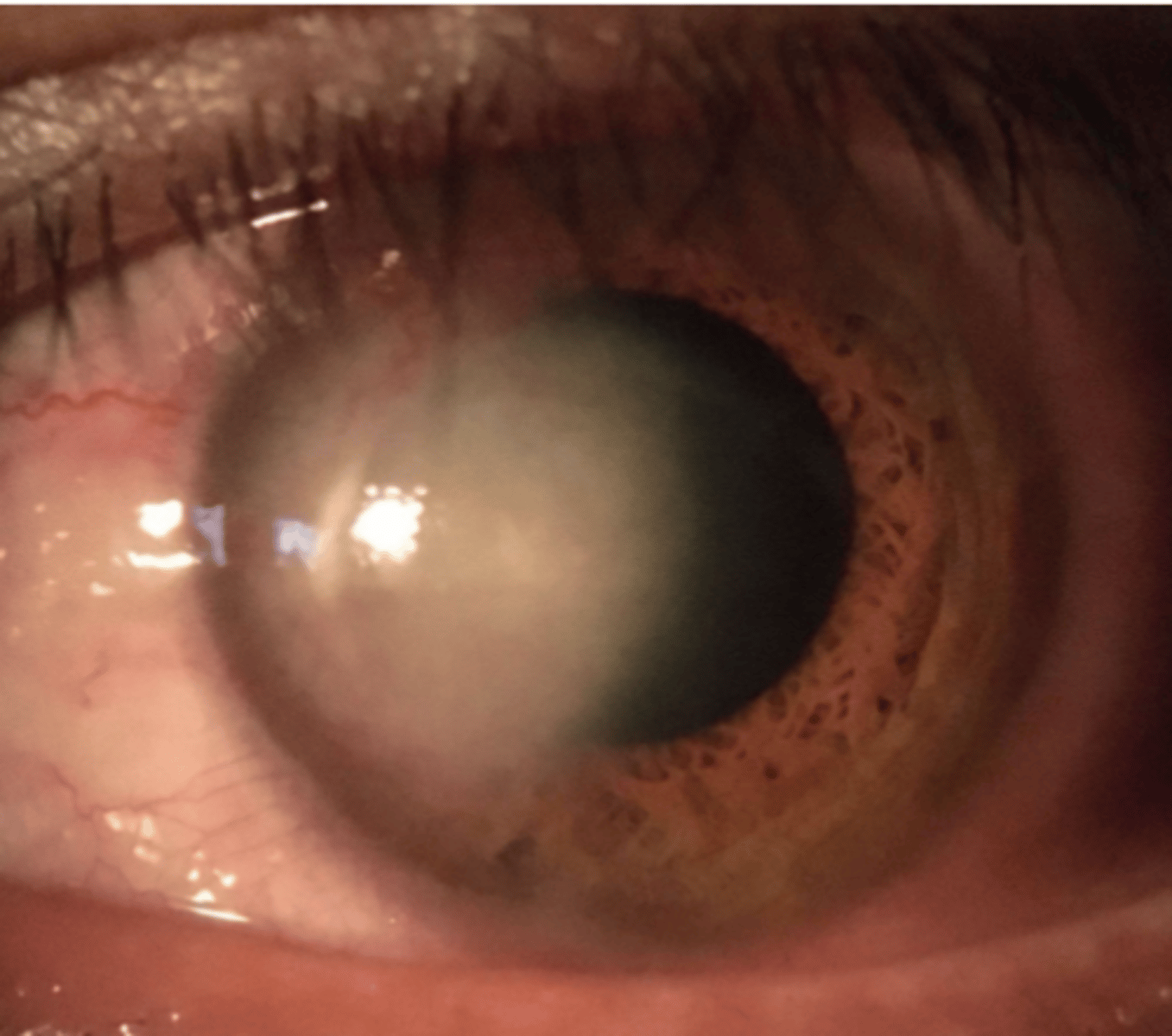
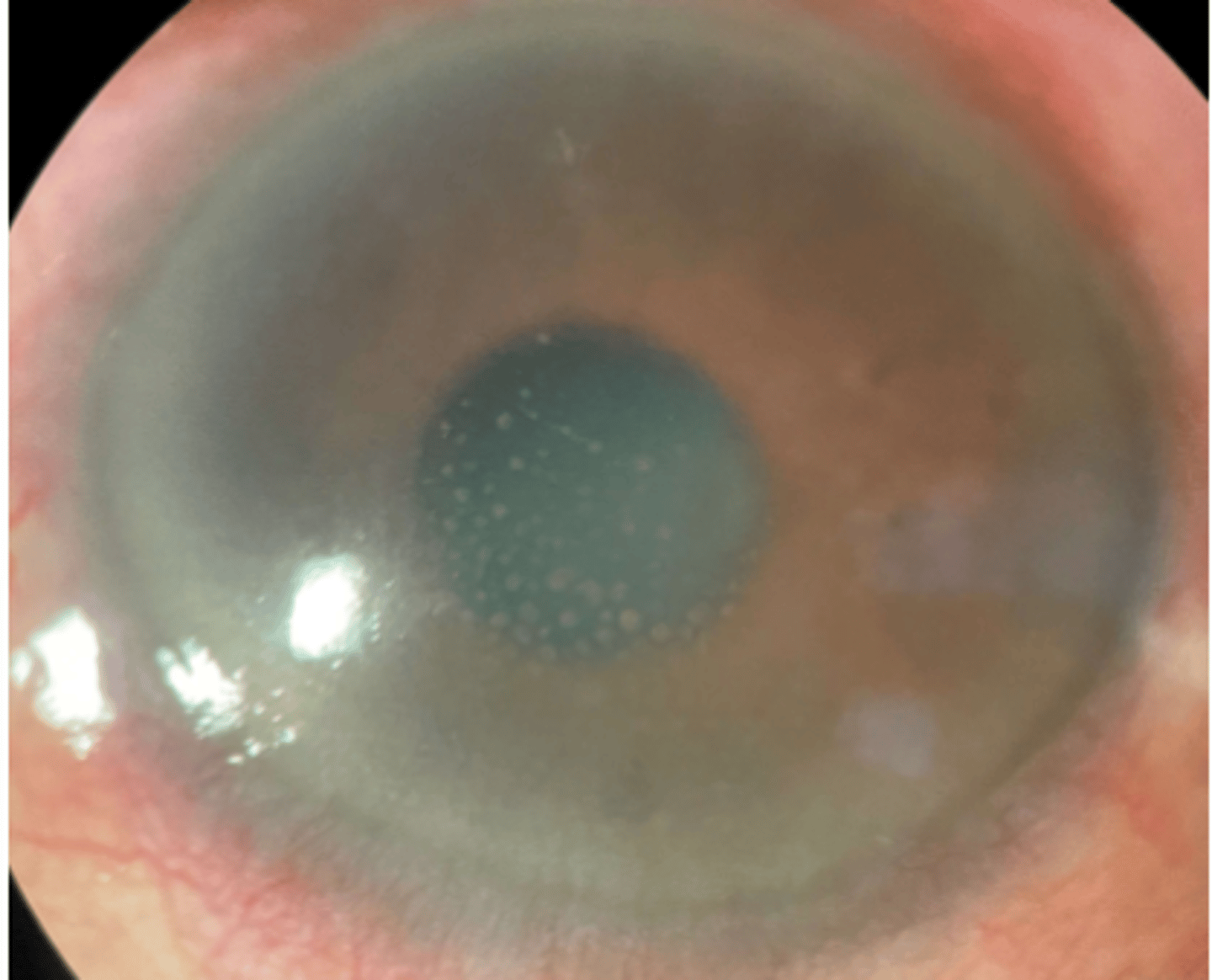
guttata in central cornea

what is guttata
abnormal thickening of descemets resulting in endothelial cell destruction
a break or tear in descemet
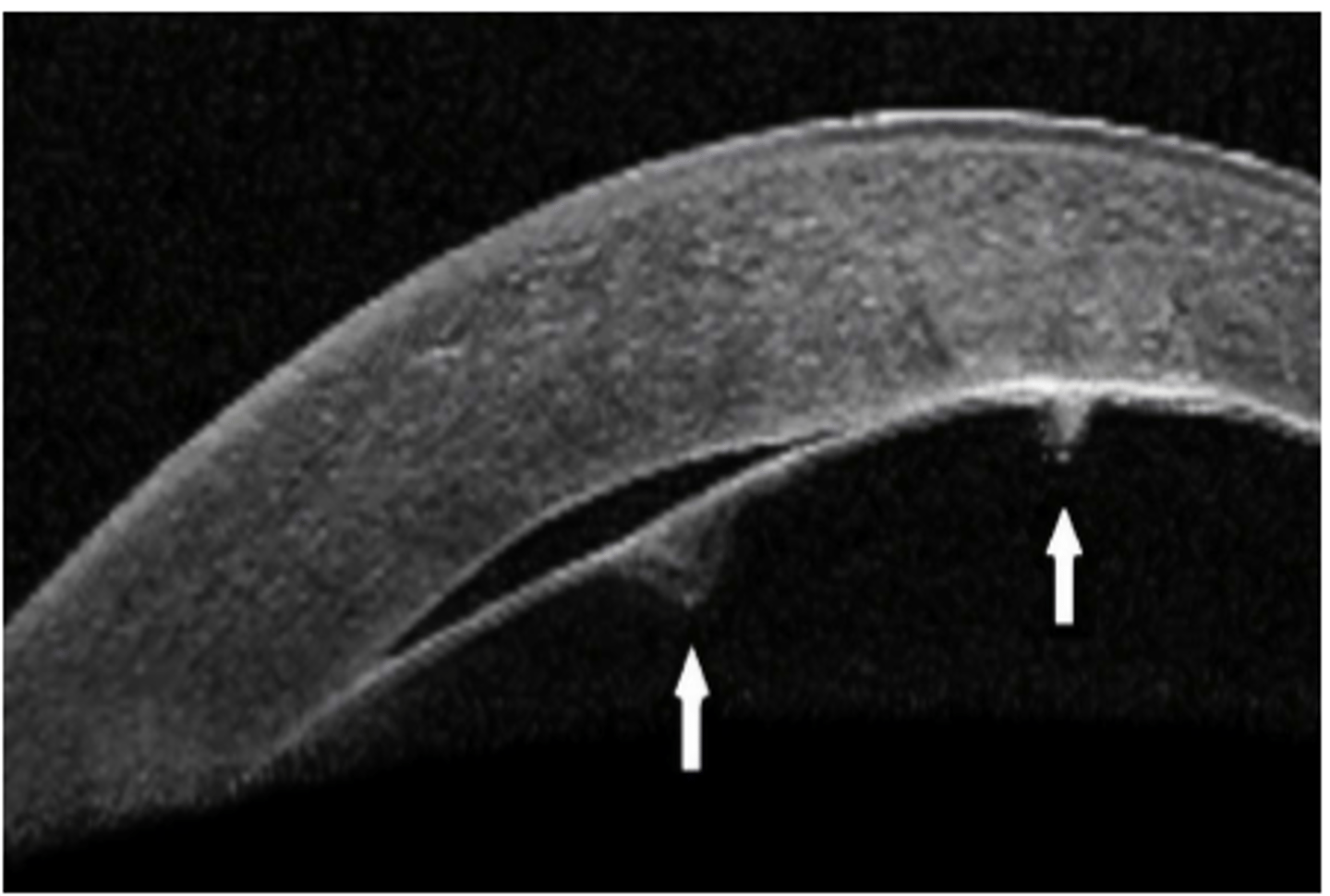
t/f vital dyes can be used to detect epithelial defects
true
sodium fluorscein can be used to detect ___ epithelial cells
MISSING
rose bengal can be used to stain?
dead or devitalized epithelial cells
lissamine green can be used to stain?
dead or devitalized epithelial cells
NaFl detecting missing epithelial cells
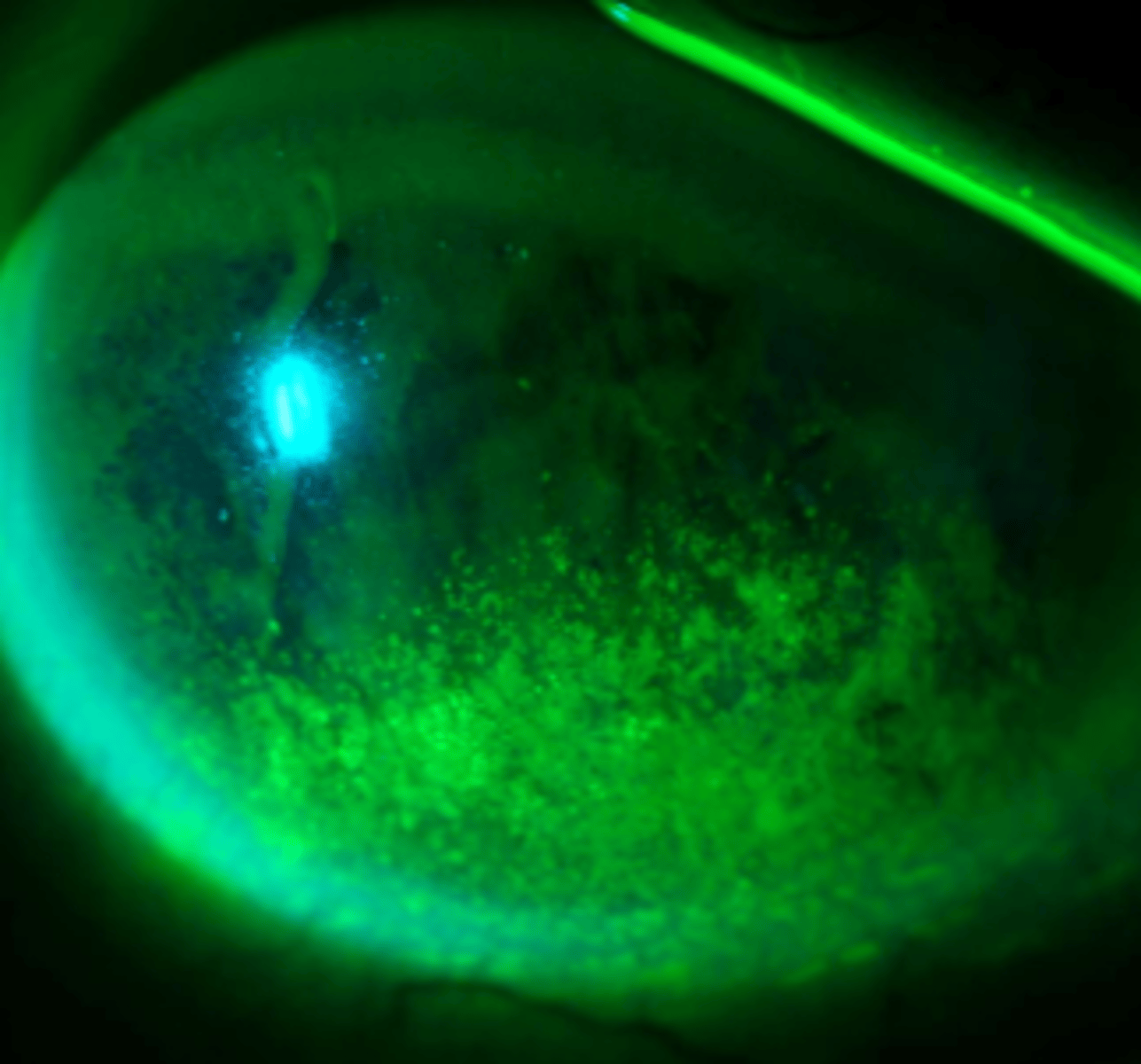
dead or devitalized epithelial cells
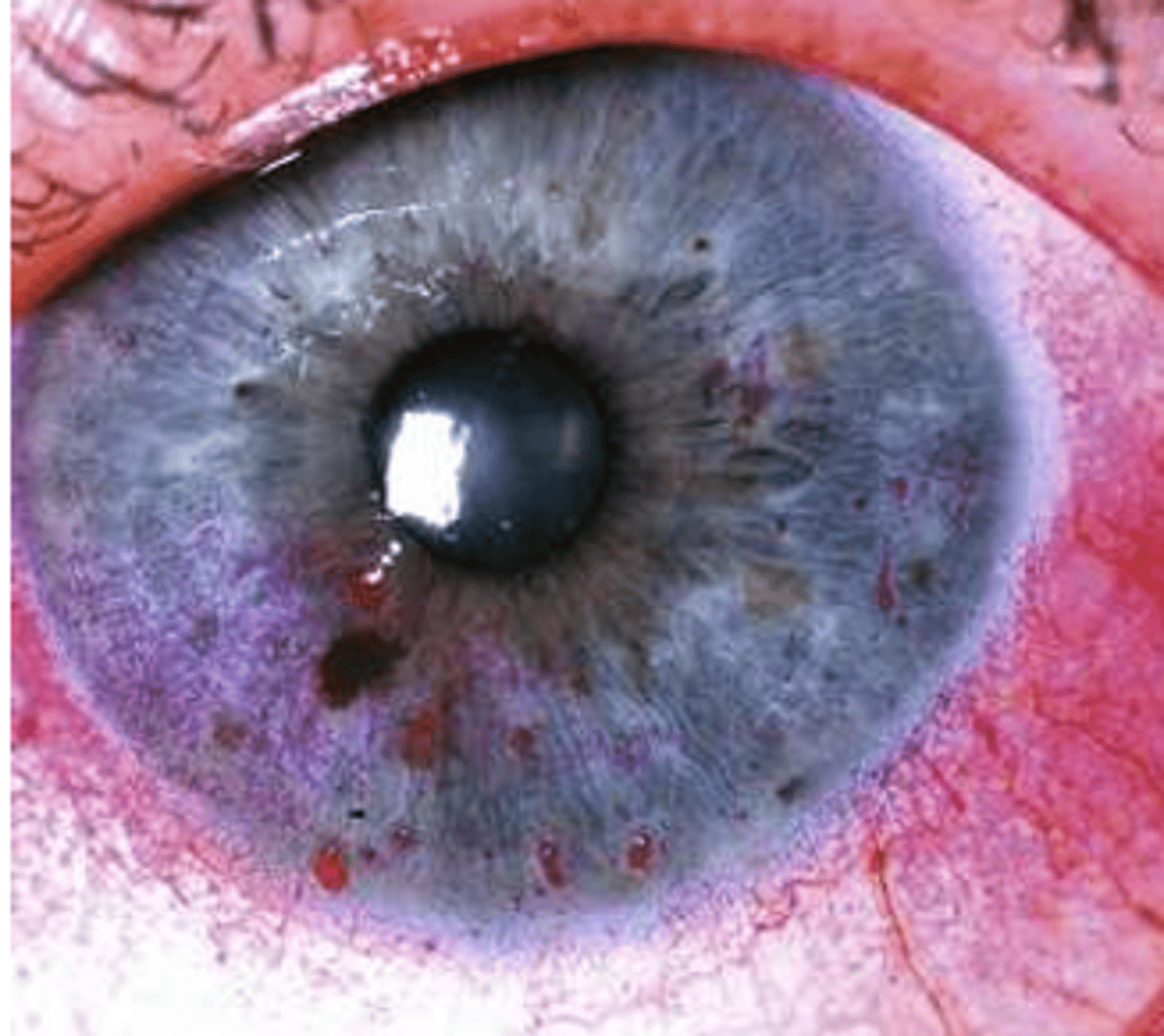
what 4 types of micro epithelial defects
superficial punctate staining
superficial punctate keratitis
punctate epithelial erosions
persistent epithelial defects
__ ___ ___ is punctate staining without inflammation
superficial punctate staining?
___ ___ __ is small fine staining accompanied by inflammation
superficial punctate keratitis
__ __ __ is punctate staining with repetitive breakdown of epithelium
punctate epithelial erosions
__ ___ ___ is chronic epithelial break that fail to heal in the expected time period
persistent epithelial defect
difference between superficial punctate staining (SPS) and superficial punctate keratitis (SPK) is that __ ___ __ is staining without inflammation, hyperemia, edema, or pain. it also only stain with NaFl. whereas __ ___ ___ does punctate staining with inflammation along with hyperemia, edema and pain. in addition, it can stain with any of the dyes
SPS, SPK
superficial punctate keratitis and punctate epithelial erosions could be similar except punctate epithelial erosion is
repetitive breakdown of the corneal epithelium and there is no improvement with treatment
t/f SPK usually responds well to treatment?
true
SPK
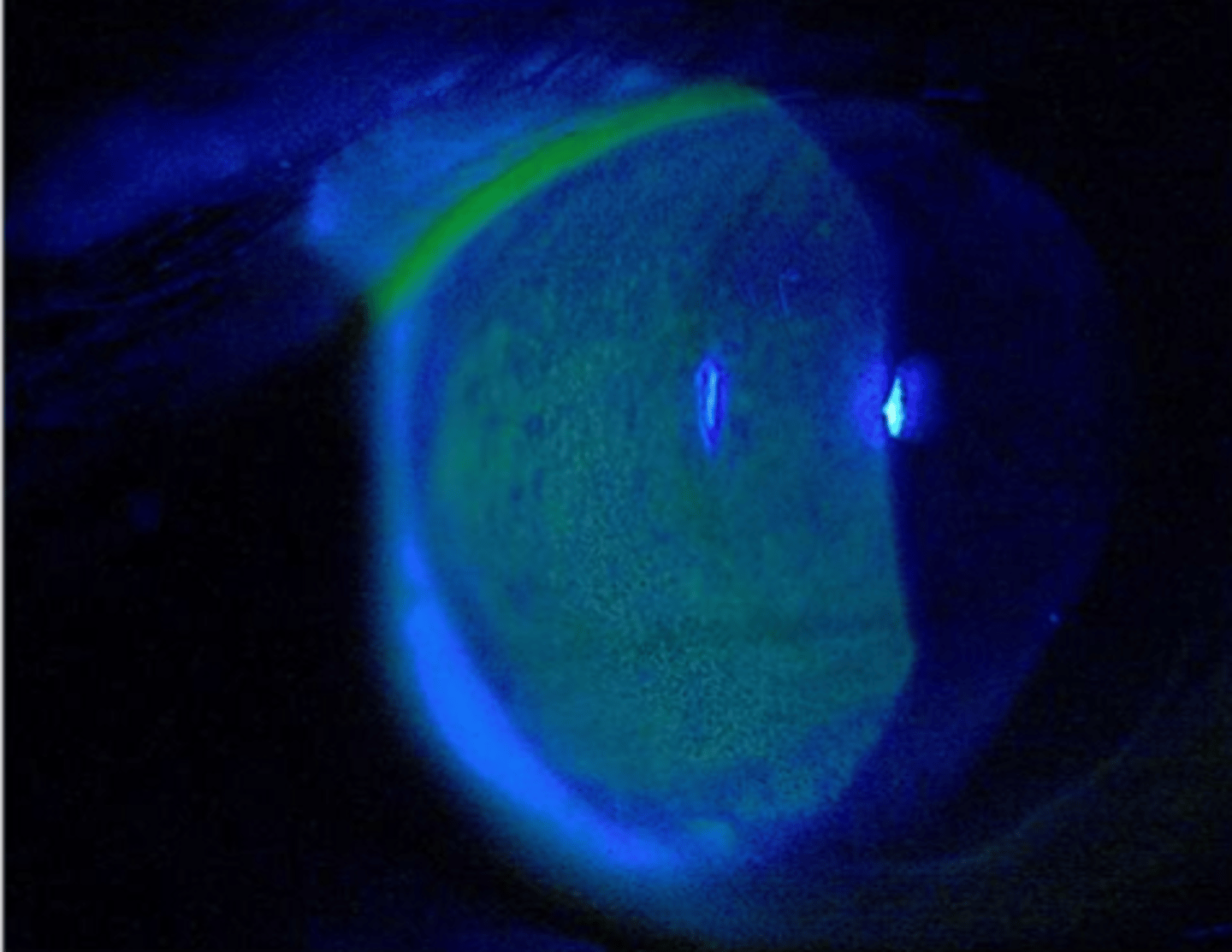
PEE with confluent staining
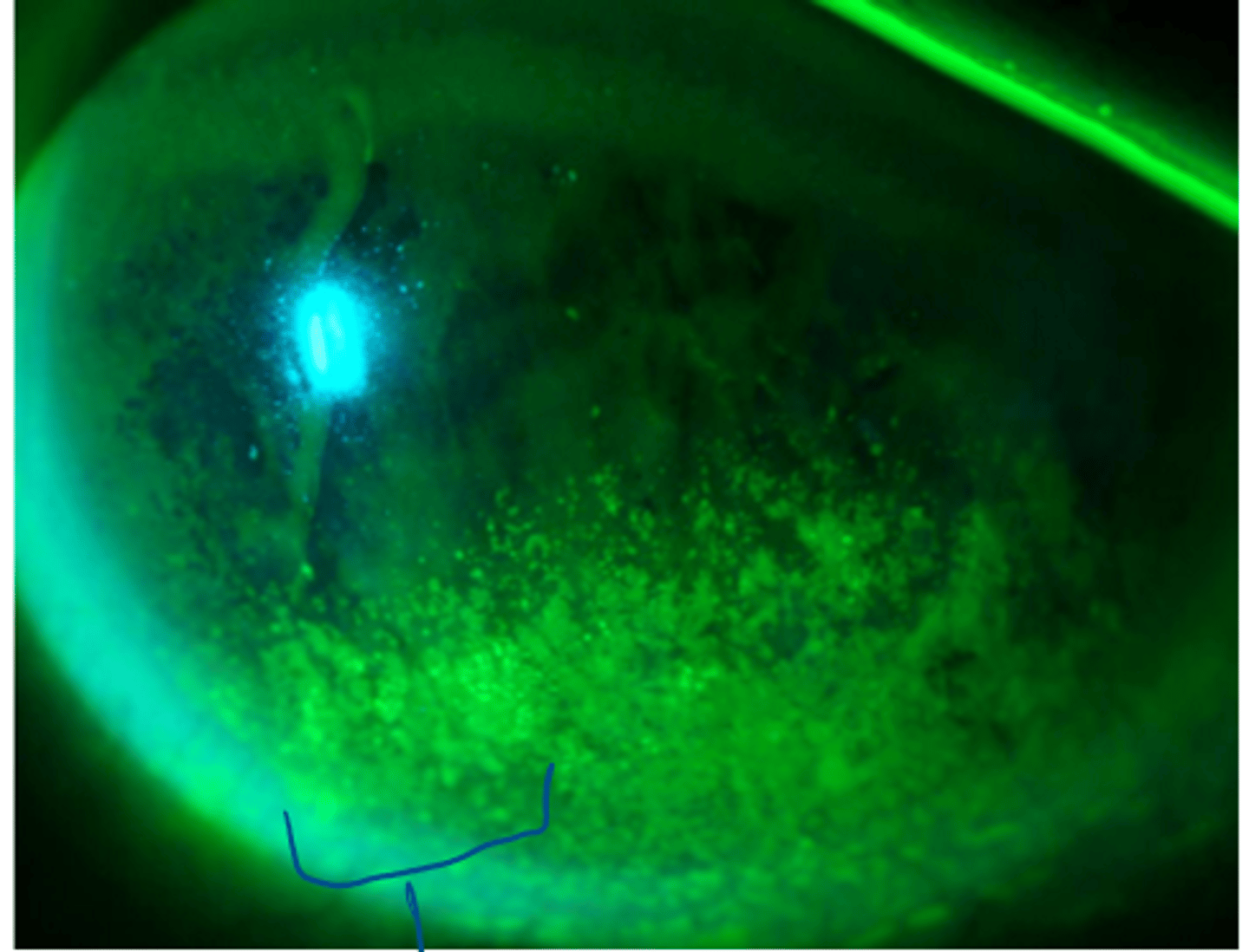
what is confluent staining?
like a concentration of affected cells in a region
T/F punctate epithelial erosions can lead to persistent epithelial defect
true
loose / missing epithelium can lead to __ ___ __
persistent epithelial defect
what are the 4 types of excavation and/or pseudoexcavation
corneal dellen, corneal ulceration, desemetocele, corneal perforation
what is corneal dellen
pseudo-excavation; desiccation of cornea with al layers intact next to an adjacent area of elevation
___ ___ is excavation with loss of epithelial layer and some stroma
corneal ulceration
___ is excavation with complete loss of epithelium and stroma, leaving only Descemet and endothelium
descemetocele (precursor to perforation)
what 3 reasons a corneal dellen can form
poor rgp fit
bulbar elevation
inflammation or surgery
how does poor fit contribute to corneal dellen
excessive edge lift
How does bulbar elevation contribute to corneal dellen
pinguelca or pterygium
dermoids
blebs
how does inflammation or surgery contribute to corneal dellen
conj edema or chemosis
t/f corneal dellen is not truly an excavation since it has intact layers
true
corneal dellen
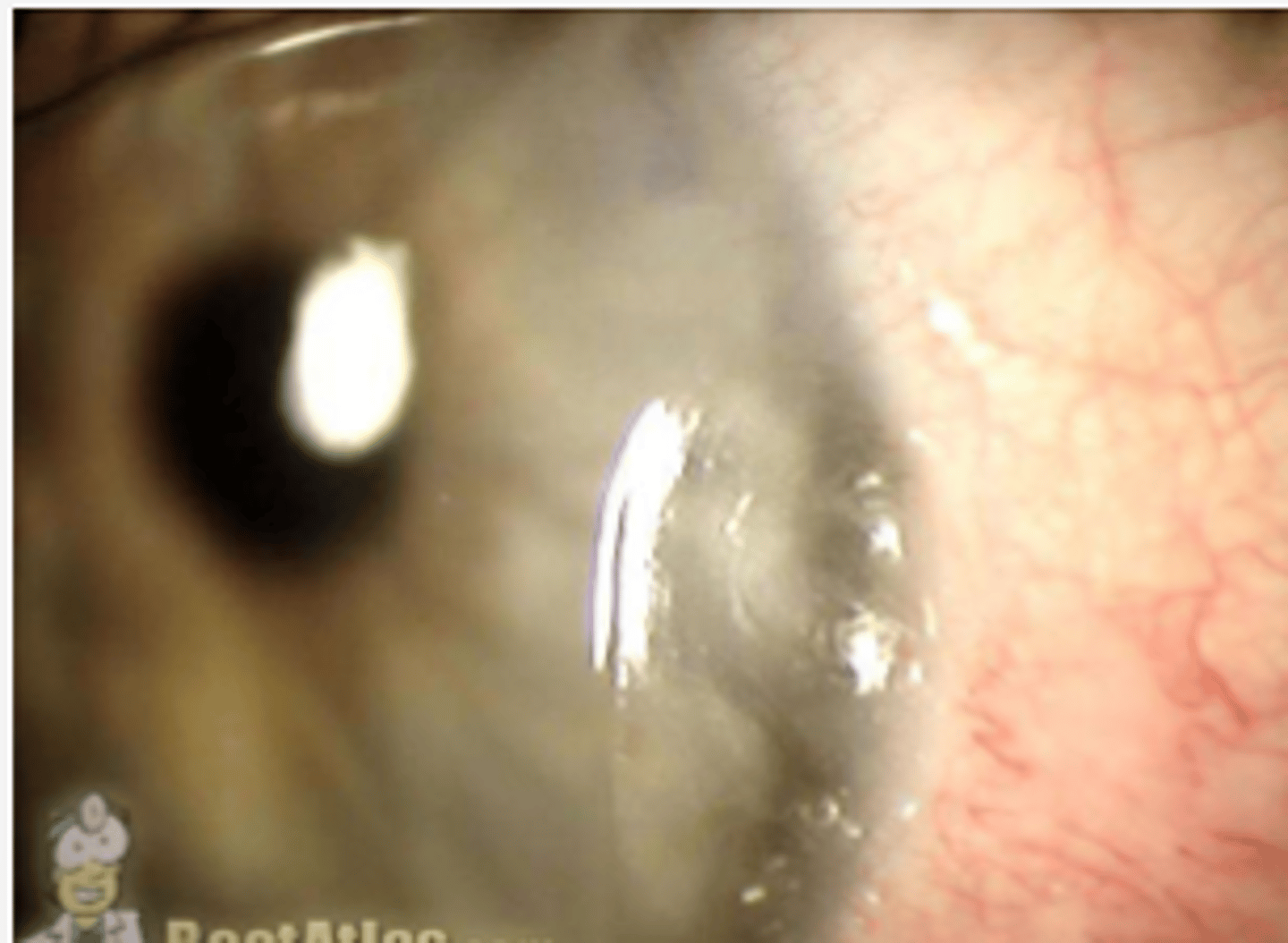
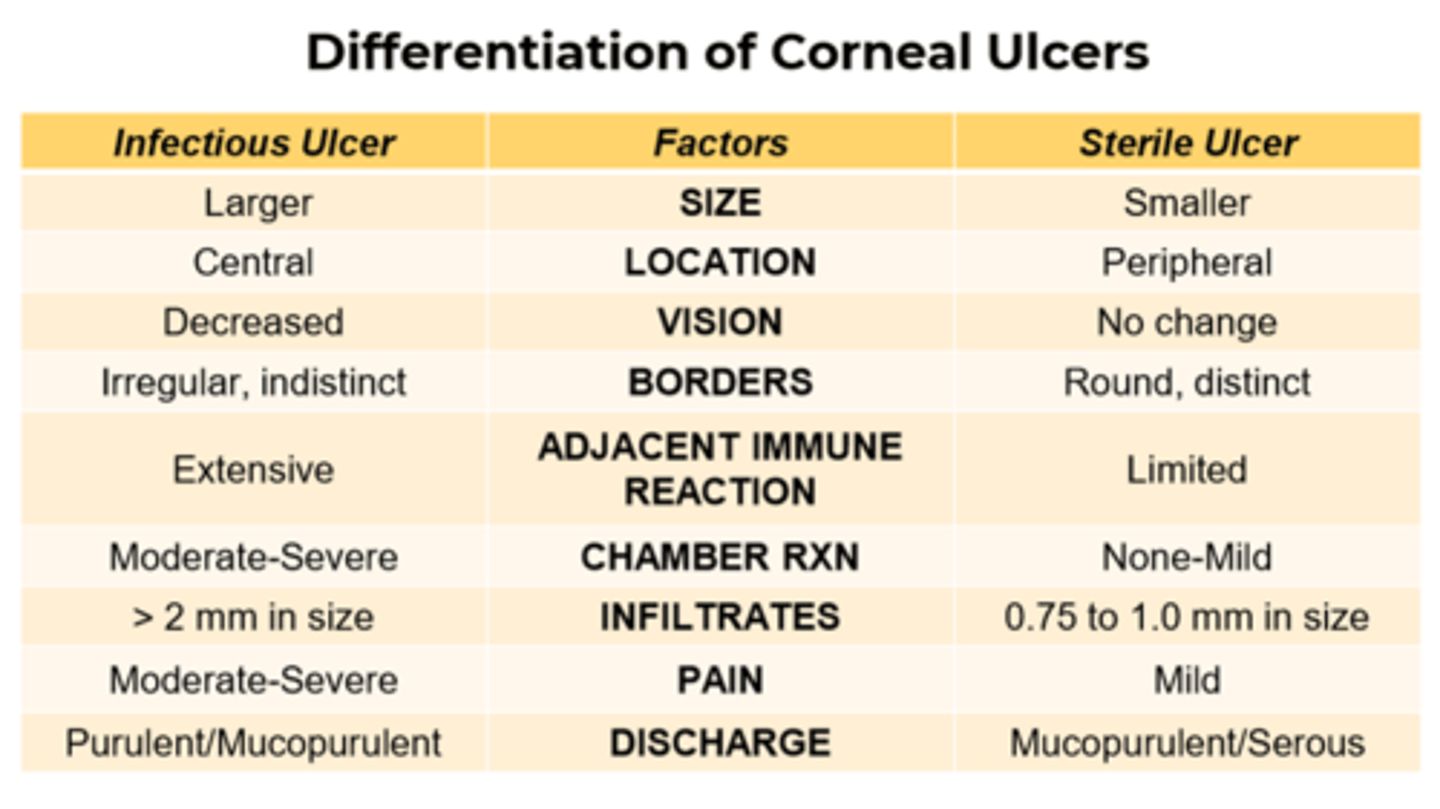
how do you confirm if a corneal ulcer is infectious or not?
confirm with culture, stain, pcr
what is keratolysis
process of progressive necrosis of corneal stroma