Exam 1: Diabetes
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Types of Prevention (Diabetes) (3)
- Primary prevention (BEFORE Diabetes diagnosed or onset)
- Secondary prevention (Diabetes already diagnosed, treat/prevent complications)
- Tertiary prevention (Diabetes complications, but want to prevent further problems)
Categorize the intervention by whether it is primary, secondary, or tertiary prevention:
1. Provide education about exercise, healthy weights, and healthy diets to reduce risks before the patient develops diabetes
2. Conduct a screening program to detect if a patient has diabetes
3. The patient has diabetes and you want to prevent worsening of the disease
1. Primary prevention
2. Secondary prevention
3. Tertiary prevention
According the DM video, which of the following statements are TRUE?
- Insulin is secreted by the liver
- Insulin helps glucose enter cells
- Glucose is the primary source of energy for the body's cells
- Insulin helps glucose enter cells
- Glucose is the primary source of energy for the body's cells
Why do we use guidelines? (6)
• Improve the quality of clinical decisions
• Offer explicit recommendations for specific situations
• Potential to change beliefs
• Prove outdated practices wrong
• Improve consistency of care
• Evidence Based Guidelines can clarify in interventions are beneficial, call attention to ineffective/dangerous practices
Diabetes Guidelines
• Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes
– American Diabetes Association
– Current is 2025
– Updated annually (January)
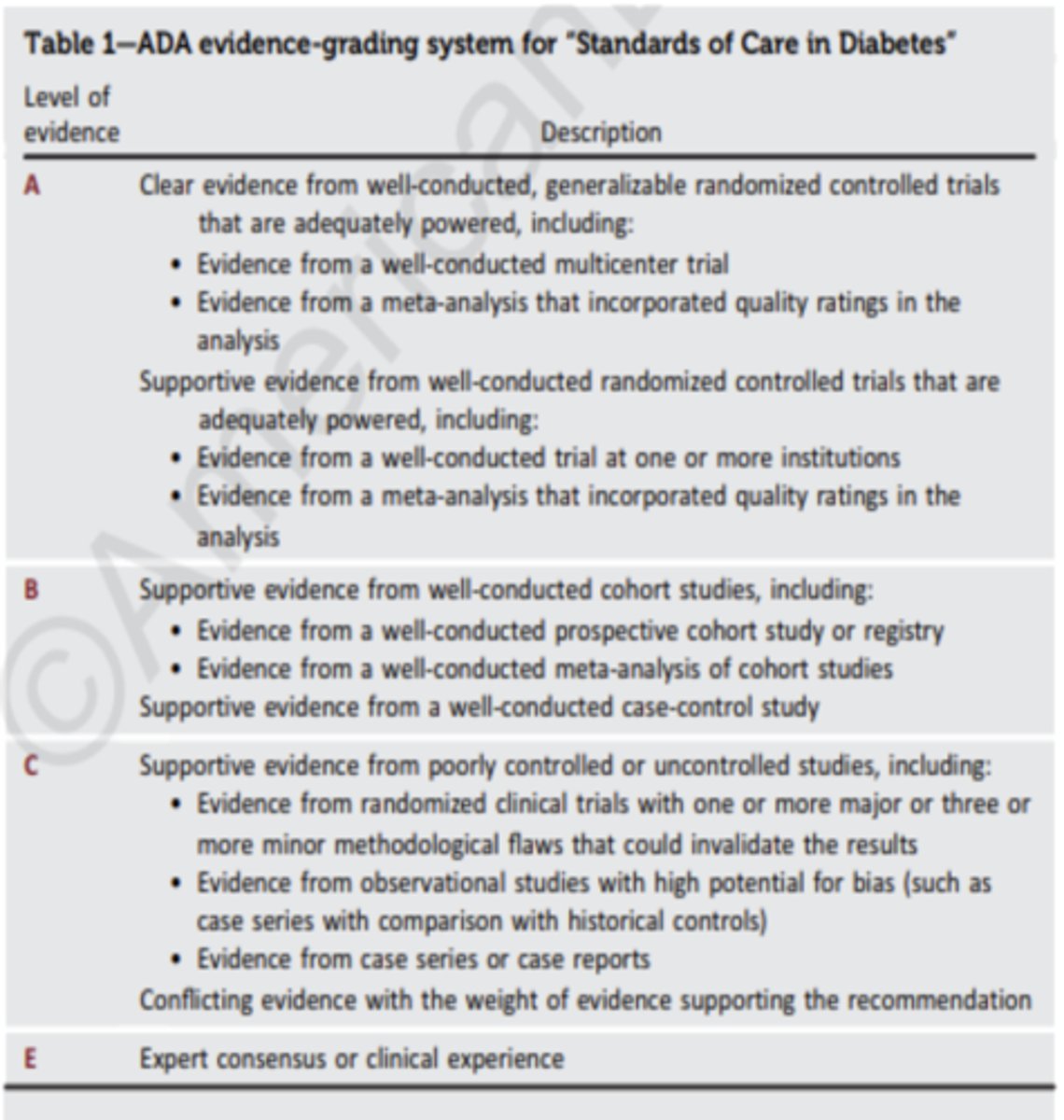
What does A, B, C, E recommendation mean?
A - clear evidence from well-conducted, generalizable randomized controlled trials (highest level)
B - supportive evidence from well-conducted cohort studies
C - supportive evidence from poorly controlled or uncontrolled studies (lowest level)
E - expert consensus or clinical experience
Risk factors
characteristics/conditions that can increase a person's risk for developing a disease
Modifiable risk factors can (for the most part)...
be changed or addressed
Non-modifiable risk factors...
cannot be changed; innate; irreversible
What are the risks based on the online diabetes test? (7)
- Age
- Gender
- History of gestational diabetes
- 1st degree relative with diabetes
- Hypertension diagnosis
- Physical activity
- Ethnicity
Risk Factors or Criteria Screening for T2DM in asymptomatic adults:
A. Overweight or obesity (Level of Evidence ___)
- BMI > __________ kg/m2
- (If Asian > _________ kg/m2)
- Level of evidence: B
- BMI > __25__ kg/m2
- (If Asian > __23__ kg/m2)
Risk Factors or Criteria Screening for T2DM in asymptomatic adults:
B. Age > ______ years (Level of Evidence _____)
- Age > __35__ years
- Level of evidence: B
Risk Factors or Criteria Screening for T2DM in asymptomatic adults:
C. Family history of diabetes from a _______ degree relative
1st degree relative
(parent, child, sibling)
Risk Factors or Criteria Screening for T2DM in asymptomatic adults:
D. Race/Ethnicity: (4)
- African American
- Asian American
- Latino
- American Indian
Risk Factors or Criteria Screening for T2DM in asymptomatic adults:
E. History of ______
History of CVD
Risk Factors or Criteria Screening for T2DM in asymptomatic adults:
F. Hypertension
> _____________ OR on meds for __________
> __130/80__ OR on meds for HTN
Risk Factors or Criteria Screening for T2DM in asymptomatic adults:
G. _______________ HDL (<35 mg/dL) and/or ____________ TG (>250 mg/dL)
- Low HDL (<35 mg/dL) and/or High TG (>250 mg/dL)
Risk Factors or Criteria Screening for T2DM in asymptomatic adults:
H. For women ____________________ syndrome (B)
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
Risk Factors or Criteria Screening for T2DM in asymptomatic adults:
I. Physical ____________
physical inactivity
Risk Factors or Criteria Screening for T2DM in asymptomatic adults:
J. Others (2): ___________________ nigricans and severe _______________
- acanthosis nigricans
- severe obesity
Risk Factors or Criteria Screening for T2DM in asymptomatic adults:
K. History of Pre-___________
L. History of _________________ diabetes
M. Sex?
- Pre-diabetes
- gestational diabetes
- male
Ideally, where should screening be carried out? Why?
- within a health care setting (including appropriately resourced pharmacies)
- the need for follow-up and treatment
T/F: Community screening outside a healthcare setting IS recommended
FALSE
it is generally NOT recommended because people with positive tests may not seek/have access to appropriate follow-up care
- may be poorly targeted
In what situations might community screening be considered?
where an adequate referral system is established beforehand for positive tests
What is fasting?
>= 8 hours with no caloric intake
What is A1c/HbA1c?
- sugar attaches to hemoglobin in RBC
- A1c measures the % of your RBC with attached sugar
- RBCs regenerate about every 3 months, measures average blood glucose for about 3 months
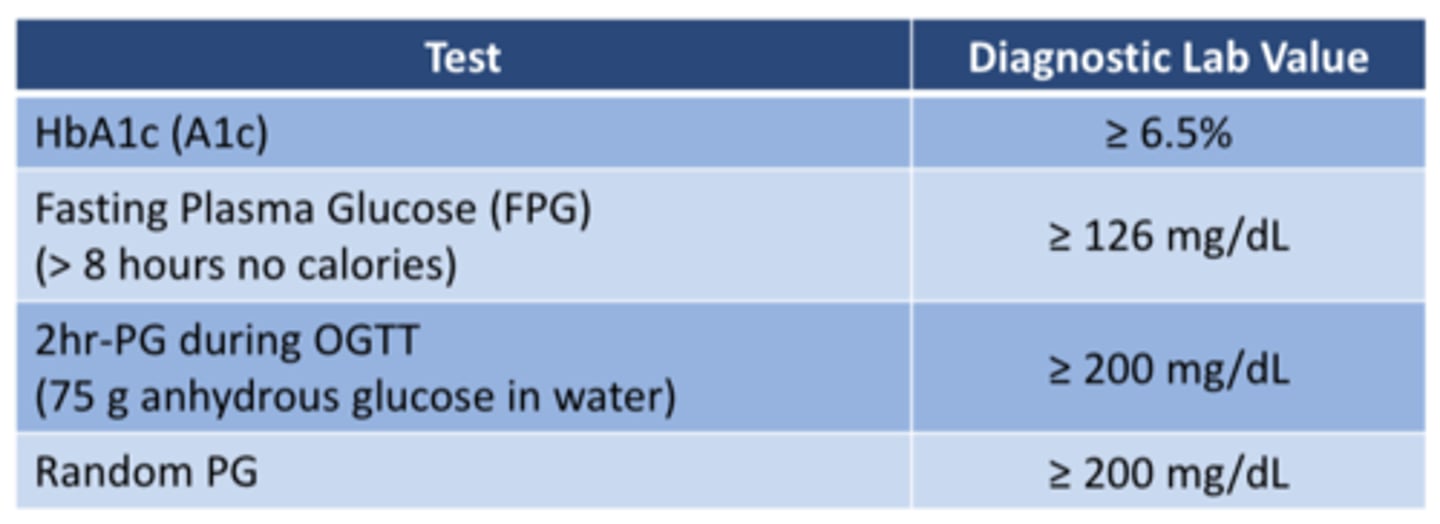
Criteria for "normal" Non-diabetics:
A1c (%):
Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG):
2 hour Plasma Glucose during 75 g (OGTT):
- A1c (%): <5.7%
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG): <100 mg/dL
- 2 hour Plasma Glucose during 75 g (OGTT): <140 mg/dL
Criteria for Pre-diabetes:
A1c (%):
Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG):
2 hour Plasma Glucose during 75 g (OGTT):
- A1c (%): 5.7-6.4%
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG): 100-125 mg/dL
- 2 hour Plasma Glucose during 75 g (OGTT): 140-199 mg/dL
Diagnostic values for Diabetes:
A1c (%):
Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG):
2 hour Plasma Glucose during 75 g (OGTT):
Random PG:
- A1c (%): ≥ 6.5%
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG): ≥ 126 mg/dL
- 2 hour Plasma Glucose during 75 g (OGTT): ≥ 200 mg/dL
- Random PG: ≥ 200 mg/dL
What is done after a positive diabetes screening?
Confirm the diagnosis: A second test is required for confirmation of the diagnosis
What is a clear diabetes diagnosis?
Hyperglycemic Crisis or Classic Symptoms + Random PG of ≥200mg/dL
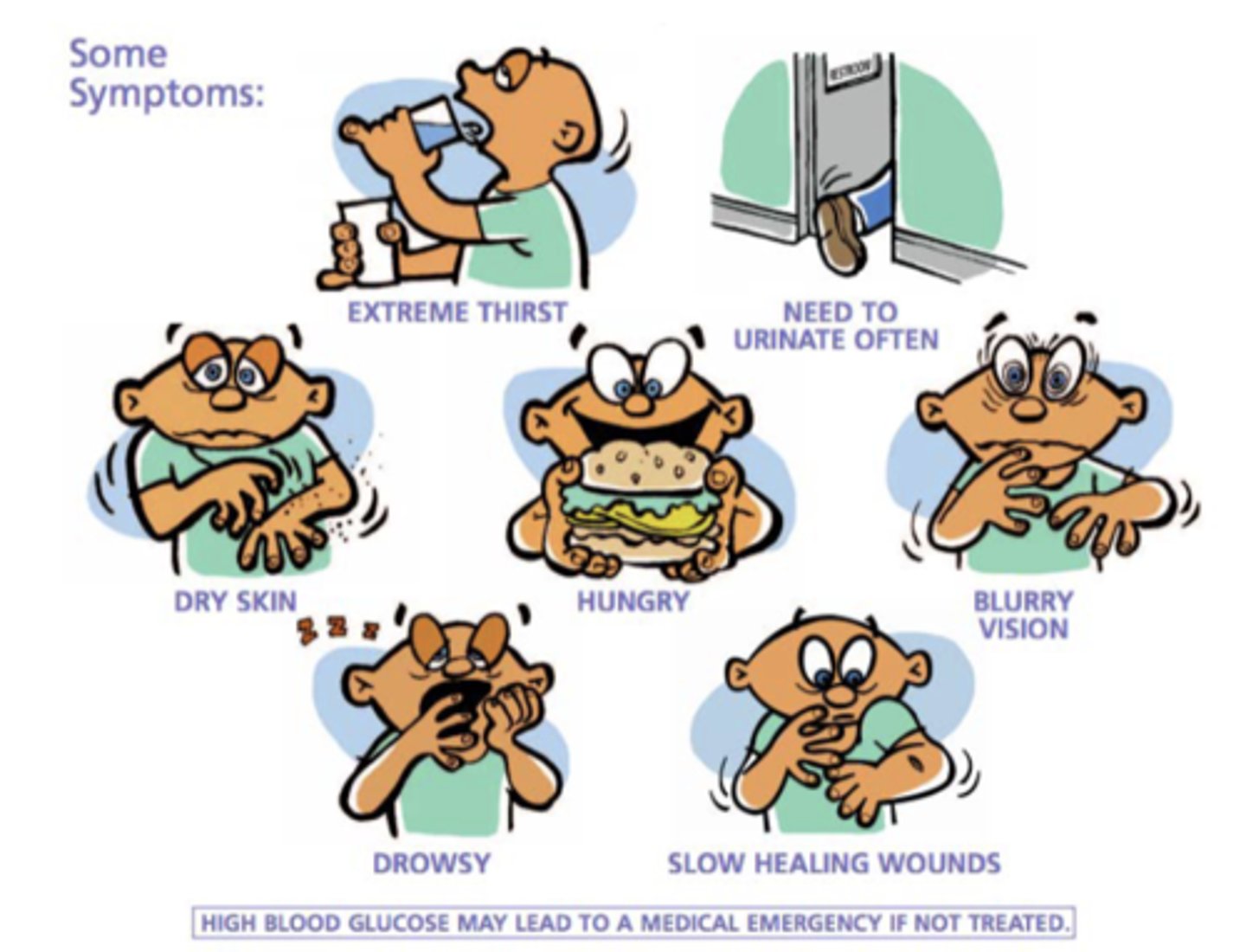
Symptoms of Hyperglycemia (Uncontrolled T2DM) (7)
o Extreme thirst
o Need to urinate often
o Blurry vision
o Slow healing wounds
o Drowsy
o Dry skin
o Hungry
- High blood glucose may lead to a medical emergency if not treated
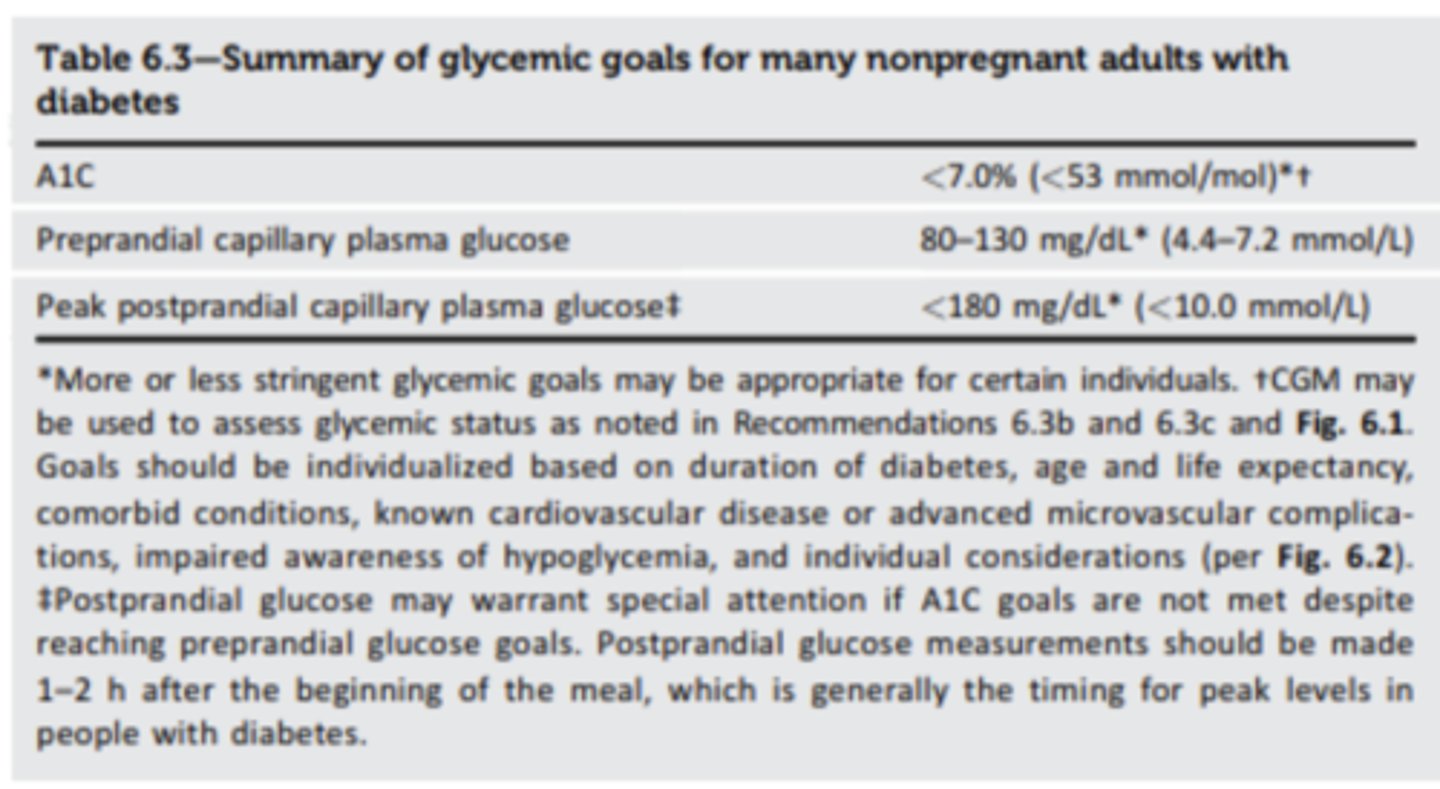
What are the maintenance goals for blood sugar for those already diagnosed with T2DM?
A1c:
Fasting capillary glucose:
Post prandial capillary glucose (1-2 hours after starting meal)(2 hour PPG):
- A1c (%): <7.0% (A) or < 154 mg/dL
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG): 80-130 mg/dL
- Post prandial capillary glucose: <180 mg/dL
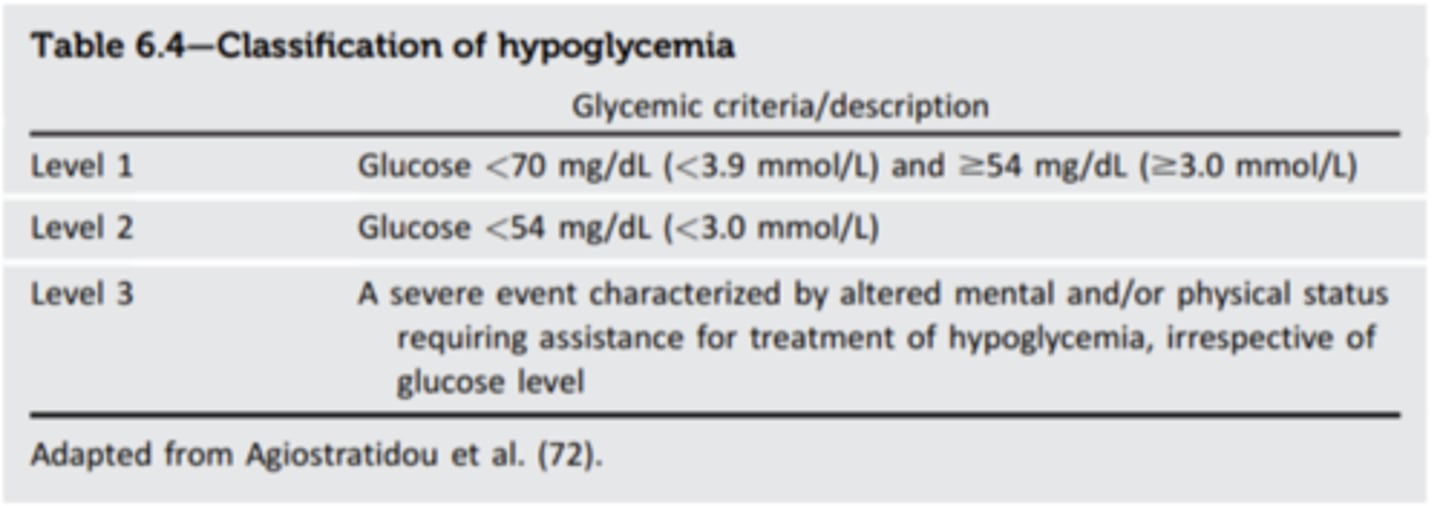
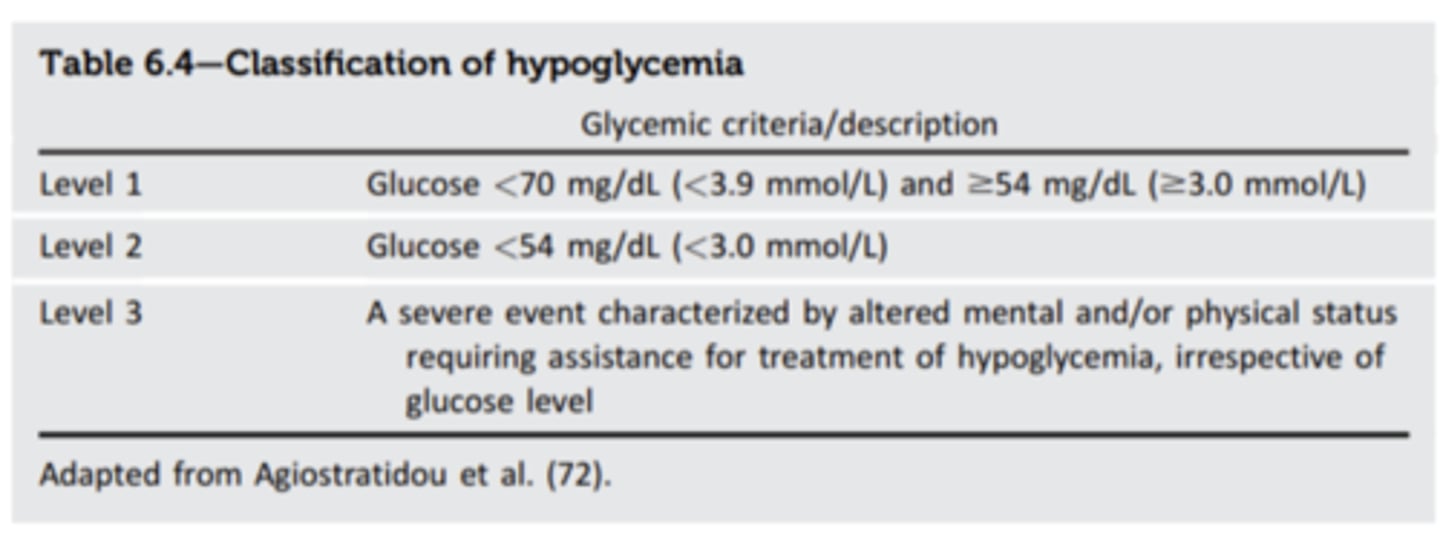
What is Level 1 hypoglycemia?
glucose < 70mg/dL
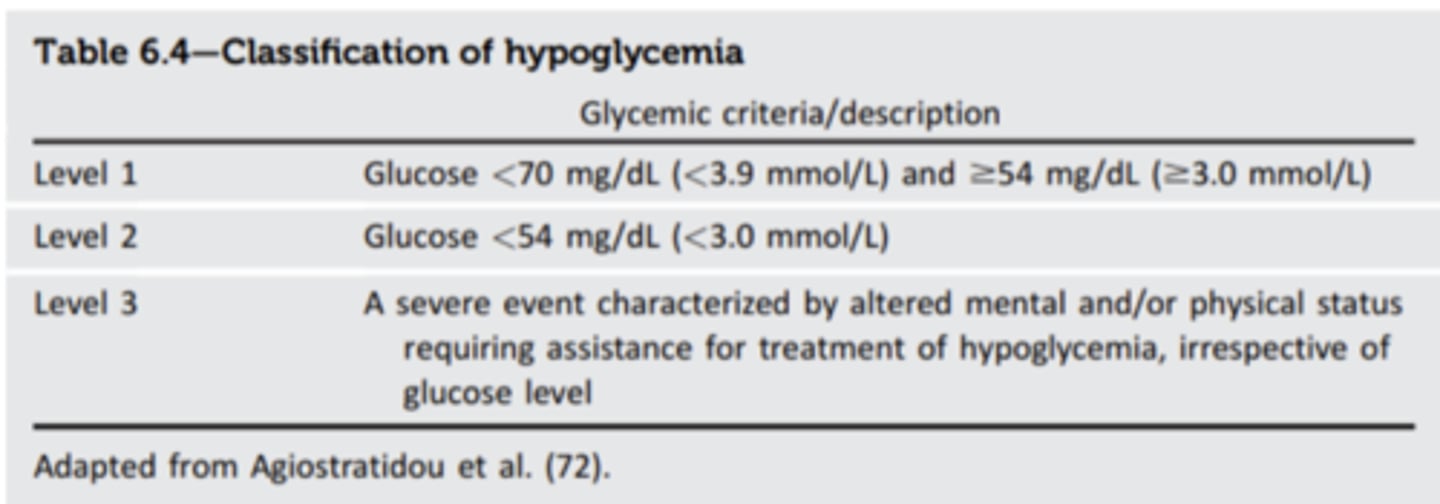
What is Level 2 hypoglycemia?
glucose <54 mg/dL
- clinically significant
What is Level 3 hypoglycemia?
No specific value
- severe hypoglycemia characterized by altered mental &/or physical status requiring assistance for treatment of hypoglycemia
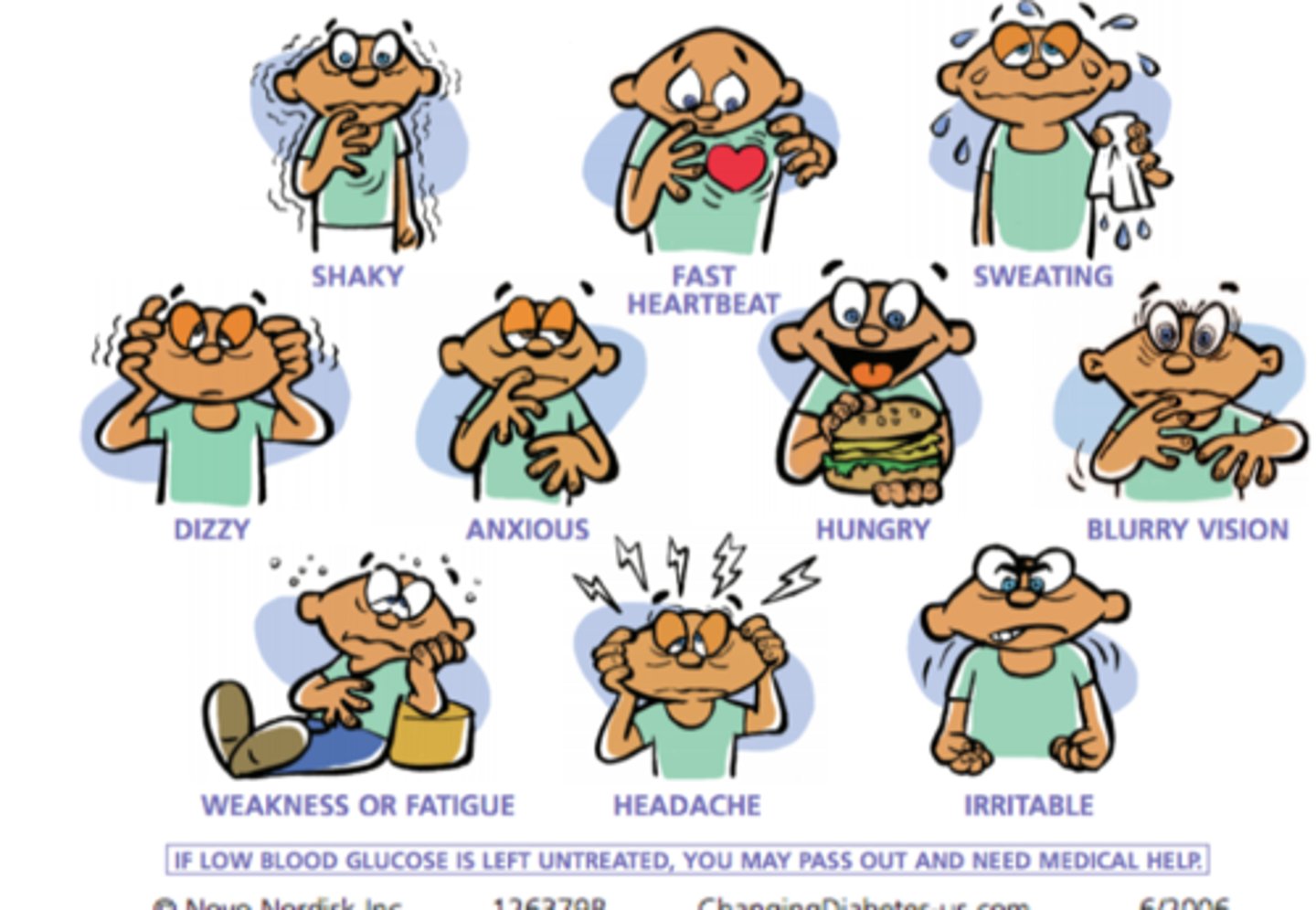
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia (Uncontrolled T2DM) (11)
o Shaky
o Fast heartbeat
o Sweating
o Dizzy
o Anxious
o Hungry
o Blurry vision
o Irritable
o Weakness
o Fatigue
o Headache
o Irritable
If low blood glucose is left untreated, you may pass our and need medical help
How many calories in 1 gram of carbohydrate?
4 calories/gram
Management of hypoglycemia: 15:15 rule
- If having hypoglycemia of <70 mg/dL, ingest 15-20 grams (60 calories) of glucose (carbs)
- Recheck in 15 minutes
- If BG is still <70 mg/dL, then repeat (15 grams carbs (60 calories), wait 15 minutes)
- When BG > = 70 mg/dL, eat a small snack
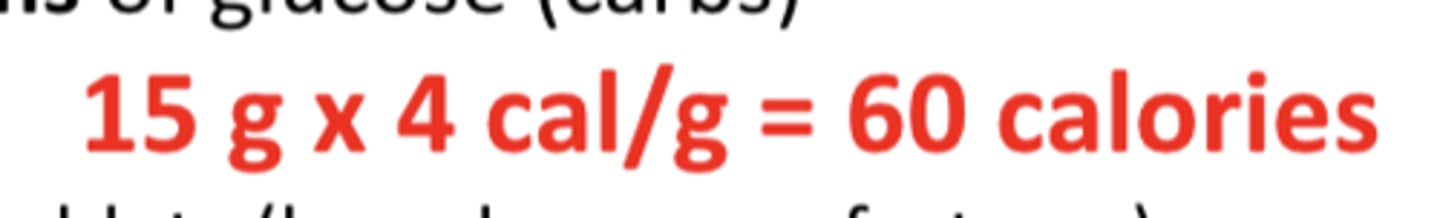
How many calories of carbs are needed to treat low BG? How many grams?
60 calories, 15 grams
Examples of what to use to treat low BG: (7)
- 3 to 4 glucose tablets (based on manufacturer)
- About 4 oz of fruit juice
- About 4 oz or half a can of non-diet soda
- 3 to 5 hard candies (jolly ranchers, peppermints)
- Glucose gel (dosing based on manufacturer)
- Icing tubes (read label)
Can you use proteins or fats to treat low BG?
no, although they can play a role in stabilizing blood sugar levels over time, they are digested slowly & don't provide the immediate glucose boost needed to treat low blood sugar the way carbs do
T/F: Glucose tablets can be swallowed whole or sucked on
FALSE
glucose tablets are NOT to be swallowed whole or sucked on
- tablets should be chewed
T/F: Glucose gel can be swallowed or dissolved in mouth
TRUE
Do glucose tablets and gels have expiration dates?
Yes
What is the diagnosis according to a FPG <100 mg/dL?
Non-diabetic
What is the diagnosis according to an A1c of 5.7-6.4%
Pre-diabetes
What is the diagnosis according to a random PG > 200 mg/dL
Diagnostic for diabetes
What is the diagnosis according to an A1c < 7.0%?
Maintenance goal for someone that already has DM
Which of the following are symptoms of hyperglycemia?
- sweating
- hungry
- extreme thirst
- urinating frequently
- weakness
- hungry
- extreme thirst
- urinating frequently