PHRM- OVERVIEW OF DRUG ANALYSIS
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
OVERVIEW OF DRUG ANALYSIS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
pharm analysis mostly refers to
lab based evaluation of drugs and associated substances inc drug formulation or dosage form
involves drug analyte assessment in a sample of
bulk/unformulated drug substance
drug formulation/ dosage form
biological medium
purpose of pharm analysis assay can be
QUANTITATIVE
determination of amount of analyte within sample
QUALITATIVE
determination of presence and or ID of the analyte in sample
type of analytical/assay tech for drug analysis dependent on
purpose
nature of drug
properties like-
solubility, ionisability, acid-base nature, stability and spectral features
for drug formulation and biosample analysis, method of choice dependent on
type of dosage form
biomedium
assay quality
simplicity
cost/availability of eq/reagents and analyst skills set
DRUG SAMPLE USUALLY NEEDS FURTHER PROCESSING TO PRODUCE AN AQ SOLUTION FOR ANALYSIS
wide variety of analytical tech are available
titrimetry
spectrophotometry
HPLC
mass spectrometry
fluorimetry
HPCE
NMR spectroscopy
IR spectroscopy
Analysis of drug substances
pre-formulation
QUANTITATIVE analysis of drug compound
inc titrimetry and spectrophotometry
QUALITATIVE analysis for verification of drug ID
assay methods- rapid and simple
major app areas for drug substance analysis are
QUALITY ASSURANCE/CONTROL
drug discovery and dev
determination of drug properties
Drug Percentage Purity
measure actual drug amount/mass in drug sample and compare to mass of sample used for assay
range 95%-105%
Drug percentage purity formula

impurities represent
trace substances
H2O
salts
Assay for drug substances- 3 stage procedure
sampling
random selection of a representative portion or units from drug sample/batch for appraisal purposes
sample prep
pre-analysing treatment/processing of assay sample to produce suitable form to analyse
may inc drug isolation/separation and purification procedures
sample analysis
app of assay tech to obtain desired drug data
Assay for drug substances
selection of small drug quantity by MASS <0.5g
NOT need lengthy sample prep
NEED PREP OF SAMPLE SOLUTION FOR ANALYTICAL PURPOSES
Assays for drug substances part 2
prep of drug solution involves solvation/dissolution of specified drug mass- assay sample- in specified vol of solvents and or reagent solution
solvents used are-
H2O
OH- EtOH
reagent solutions-
dilute aq acids and bases like HCl or NaOH
used to dissolve acidic/basic drugs
key quality assessment criteria for assay inc
ACCURACY
closeness of true value
PRECISION
closeness between series measurements obtained
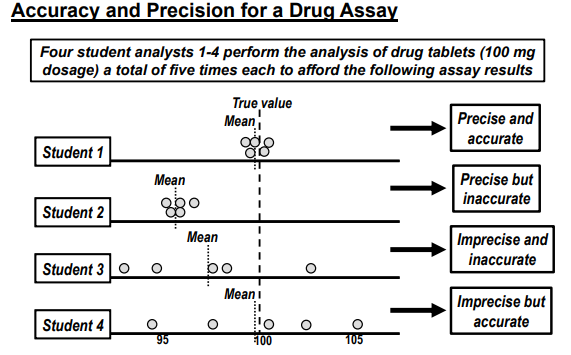
Quality of pharm assays have 3 levels
repeatability/ intra-assay precision
needs to be precise on separate days for same analyst and assay conditions
over short time
same analyst
intermediate precision/within lab reproducibility
in lab reproducibility
same lab conditions
different analysts
different days
reproducibility/ between lab reproducibility
precision between different analysts in diff labs
transferred to another part of company
Other important assay quality/validation parameters
robustness
measure capability of assay to cope with subtle change in procedure/conditions
specificity/ selectivity
measure assay by ability to detect analyte alone or with other substances
alone is selective, analyte with other substance is non-selective
range
limits of analyte can be accurately/precisely measured by assay
sensitivity
measure assay responsiveness to small variations in analyte amount or conc
high assay sensitivity means can measure extreme low analyte levels