Circulatory, Respiratory, Endocrine, Digestive, Nervous, Excretory Systems
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Circulatory system
Transport system that connects the organs of exchange with you body cells.
Function of circulatory system
Carries oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to cells, and removes waste products, like carbon dioxide.
Organs and other elements of the Circulatory system/Cardiovascular system
Heart
Vessels
Blood
Heart
Atria
top chambers (right and left, swapped)
Ventricles
bottom chambers (right and left, swapped).
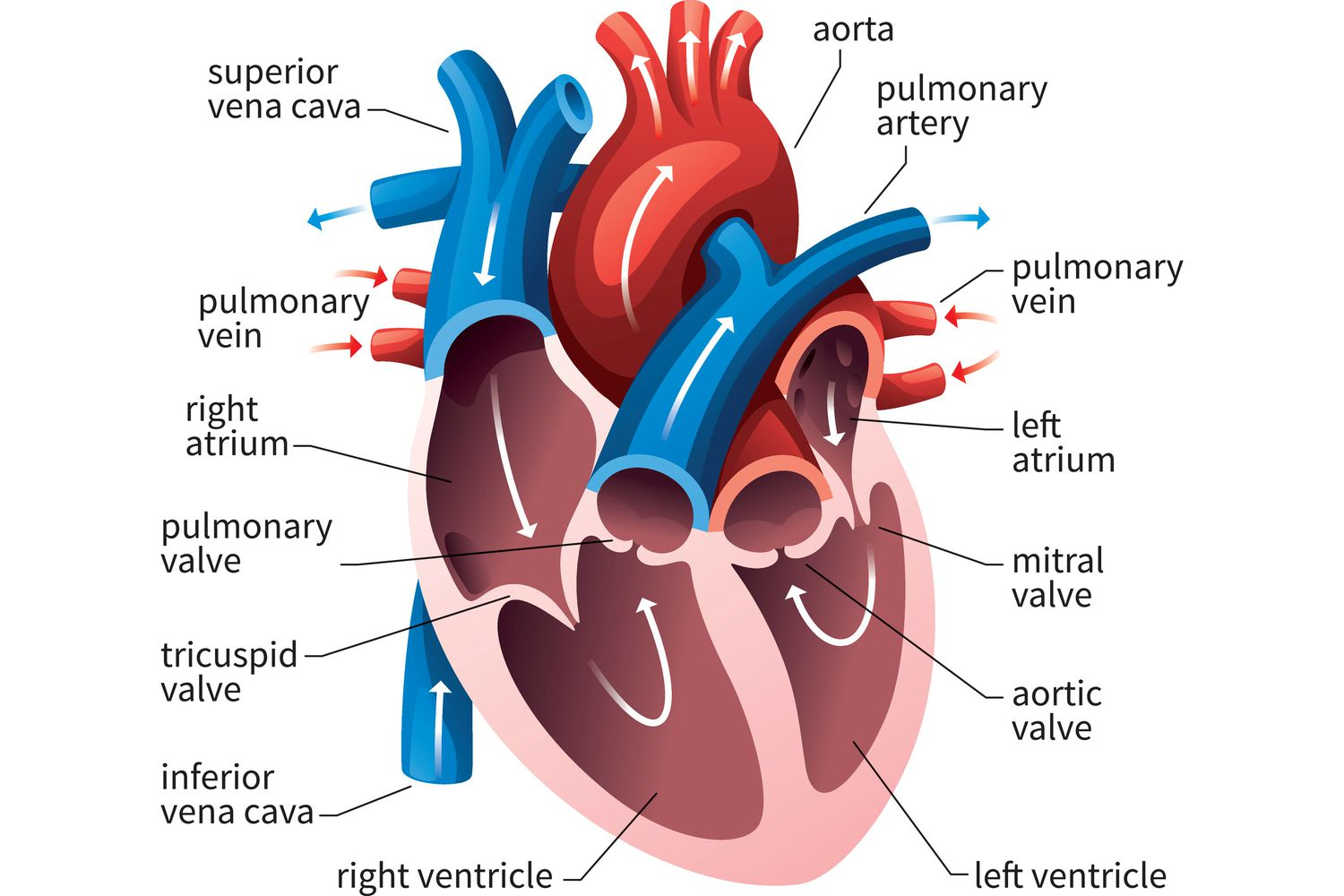
Vessels
Arteries
carries blood away
Veins
brings blood back
Capillaries
where oxygen and nutrients are exchanged for carbon dioxide and waste.
thin and small blood vessels
Blood (consists of)
Plasma (55%)
water
other dissolved substances
Cellular elements (45%)
red blood cells
white blood cells
platelets
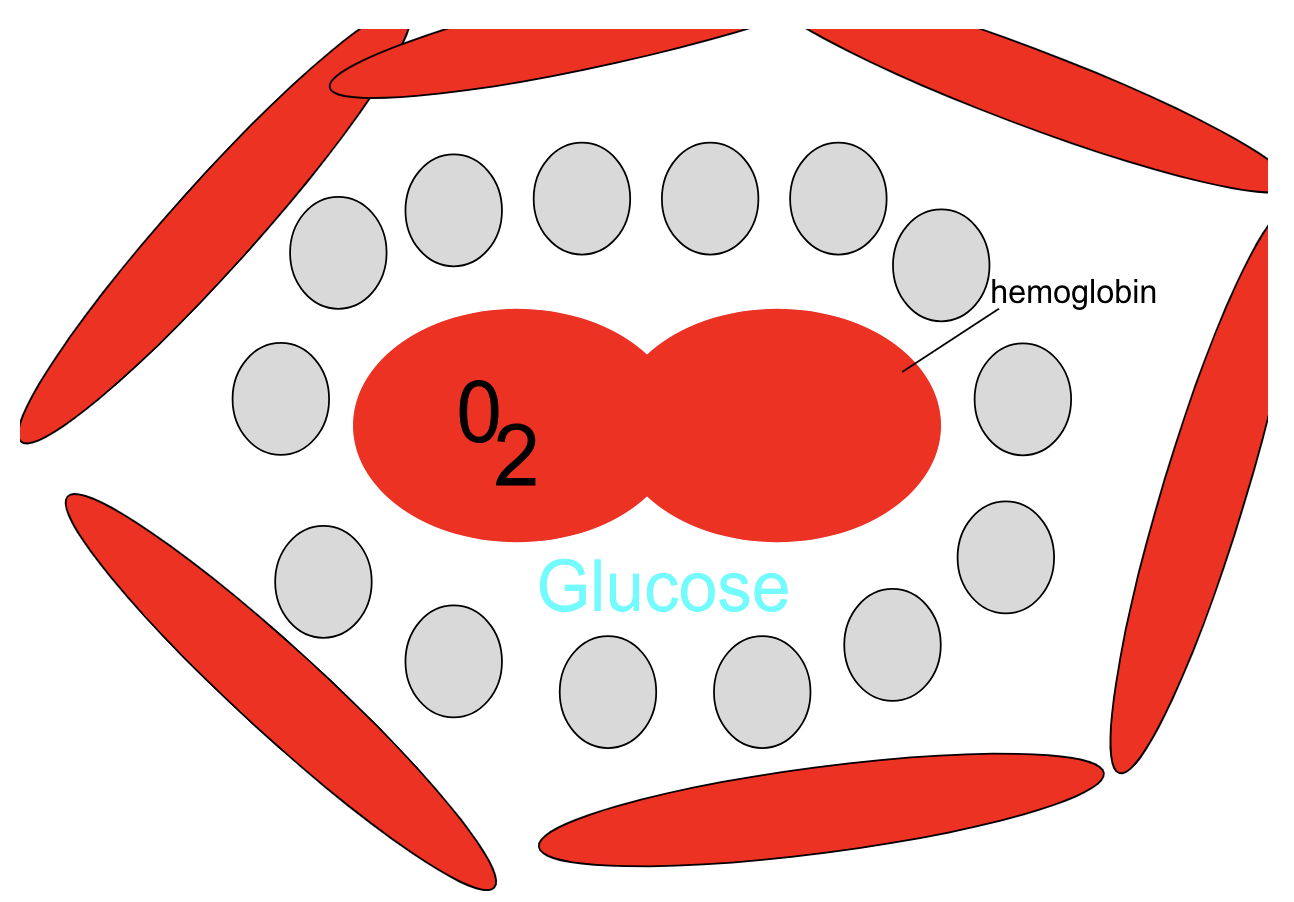
Red blood cells
carries oxygen in the hemoglobin
carry oxygen from the lungs to the entire body
White blood cells
helps fight diseases
count is important
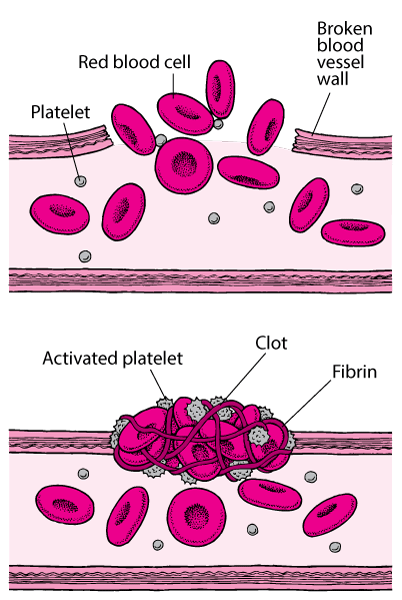
Platelets
Works with fibers to stop bleeding in the cell
How the heart pumps to receive oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body
Blood pumps bringing blood to the rest of the body, and the bringing blood to the lungs. The right side pumps oxygen poor blood to the lungs to bring back oxygen rich blood. The left side pumps oxygen rich blood to the rest of the body.
Respiratory system
Responsible for the process of gas exchange with the enviroment
Respiratory system function
Move fresh air into your body while removing waste gases
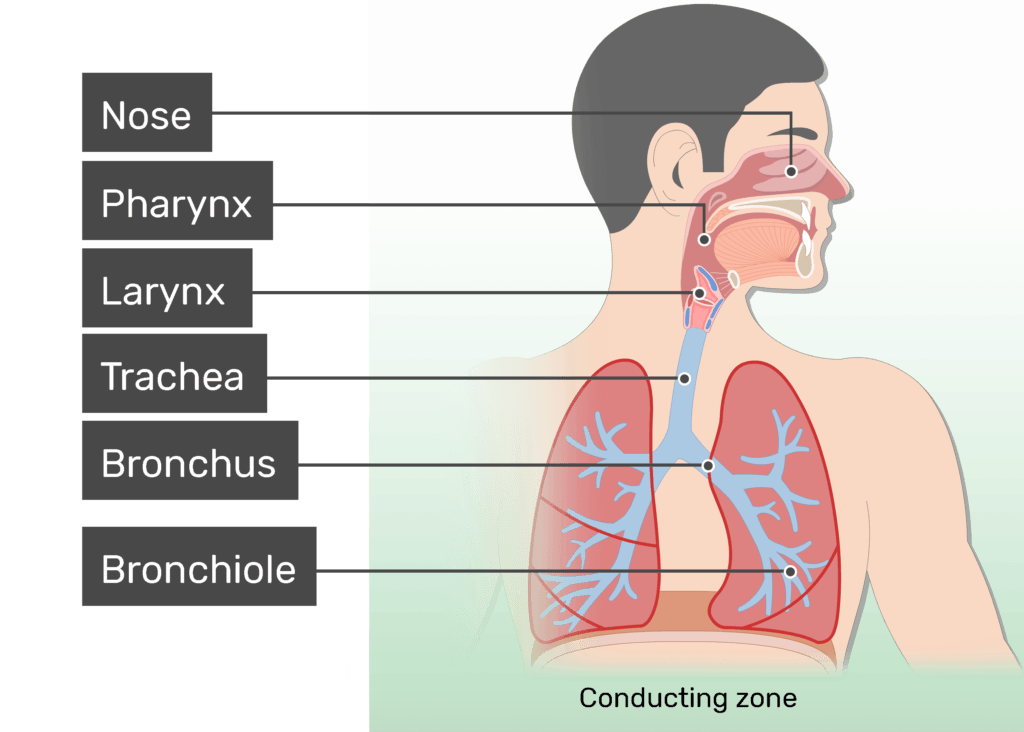
Parts involved with the Respiratory system
nose
filter, moisten, and warm the air
cilia
pharynx
lead the air
intersection
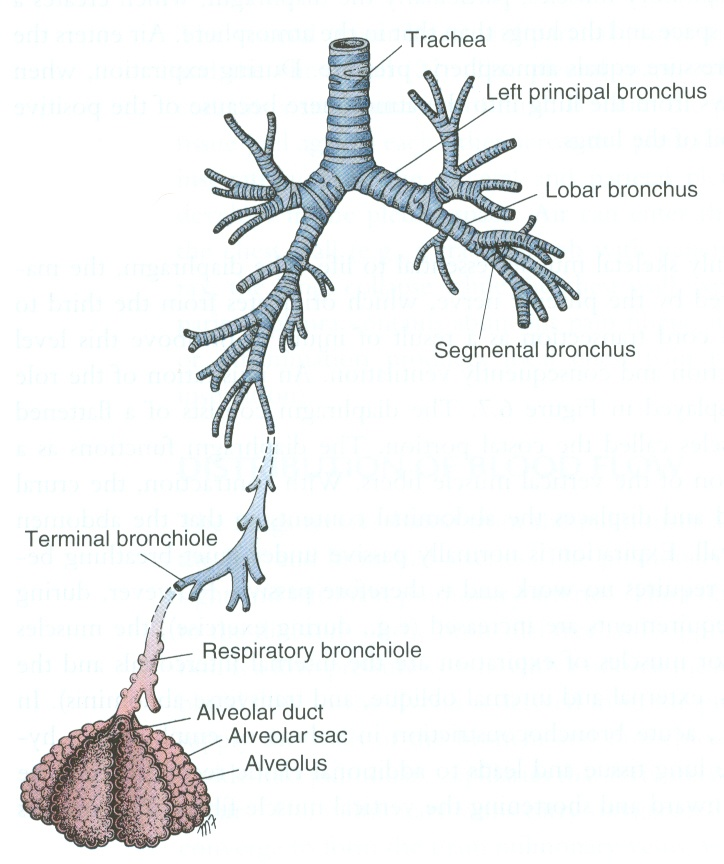
trachea
tissue with cartilage rings tube
epiglottis
covers the trachea when you swallow
bronchi
division of the trachea to direct oxygen
bronchioles
branches of the bronchus
alveoli air sacs on the broncioles.
Air sacs, alveoli
Exchange CO2 and O2 with blood from thin capillary net
Surrounded by capillaries
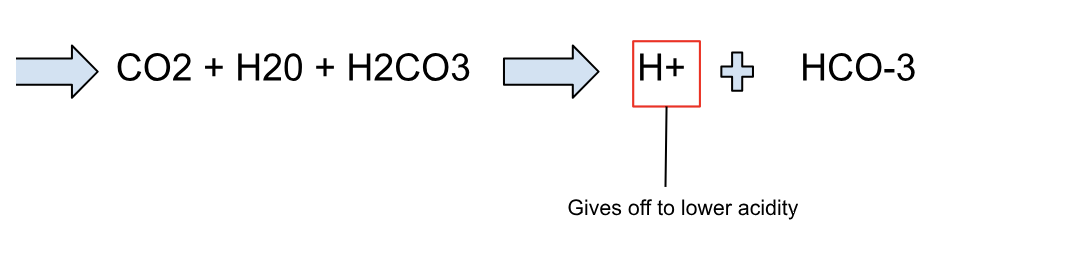
Gas Transport
oxygen (hemoglobin) and carbon dioxide (bicarbonate/carbonic acid)
The bicarbonate ion pulls the H+ ion out of the hemoglobin in the red blood cells, allowing it to bind with oxygen from the inhaled air in the lungs. The oxygen will then be carried by the hemoglobin back to the body's cells to be used in cellular respiration.
Endocrine system
Long-distance chemical communication that involves hormones and travels through the blood to a target cell. Acts as a master control system for the body responsible for homeostasis.
Function of Endocrine system
Maintain homeostasis, grow, and reproduce. Sends signals to maintain homeostasis, a master control system of the body.
Pancreas function
Regulate blood glucose by releasing insulin or glucagon.
Insulin
released when blood sugar is high, lowers blood glucose levels.
helps glucose go into cells.
Glucagon
released when blood glucose is low, raises blood glucose levels
tells liver to break glycogen into glucose.
Digestive System
Converts food into small molecules that can be used by the cells of the body.
Phases of food being processed
Ingestion
Digestion
Absorption
Elimination
Methods of Digestion
Mechanical
physically make smaller
Chemical
enzymes breaks bonds
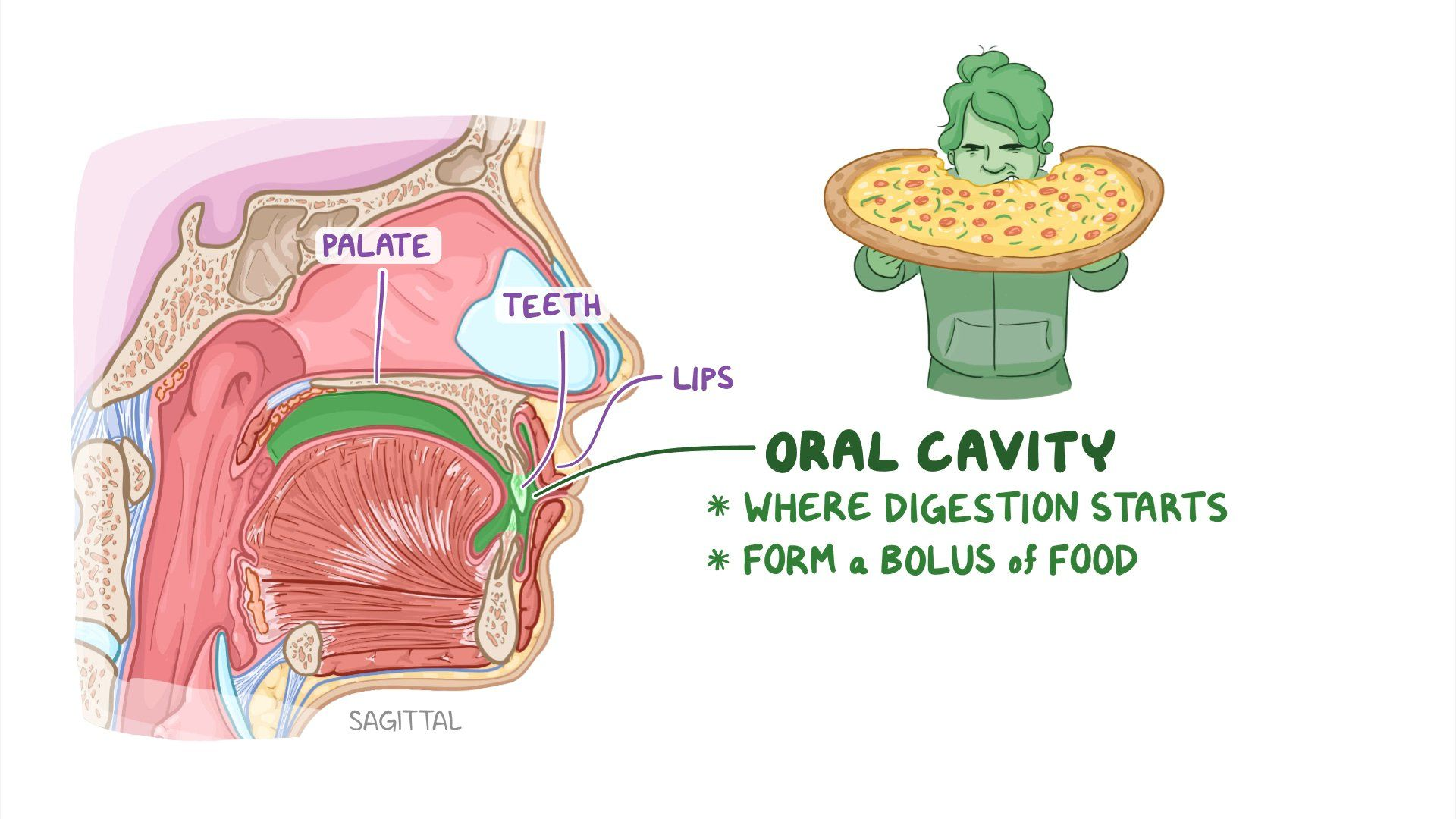
Oral Cavity
mainly mechanical digestion
some chemical digestion
starch
salivary glands
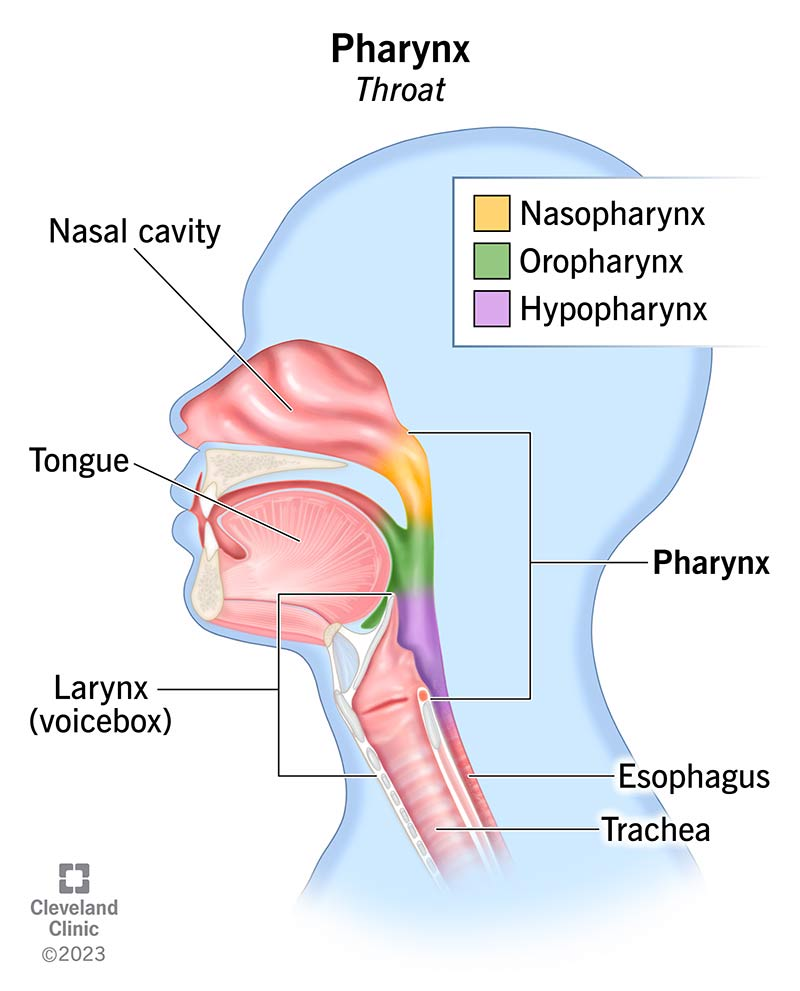
Pharynx
epiglottis
prevents food from entering your lungs
Esophagus
peristalsis
pushes the food down
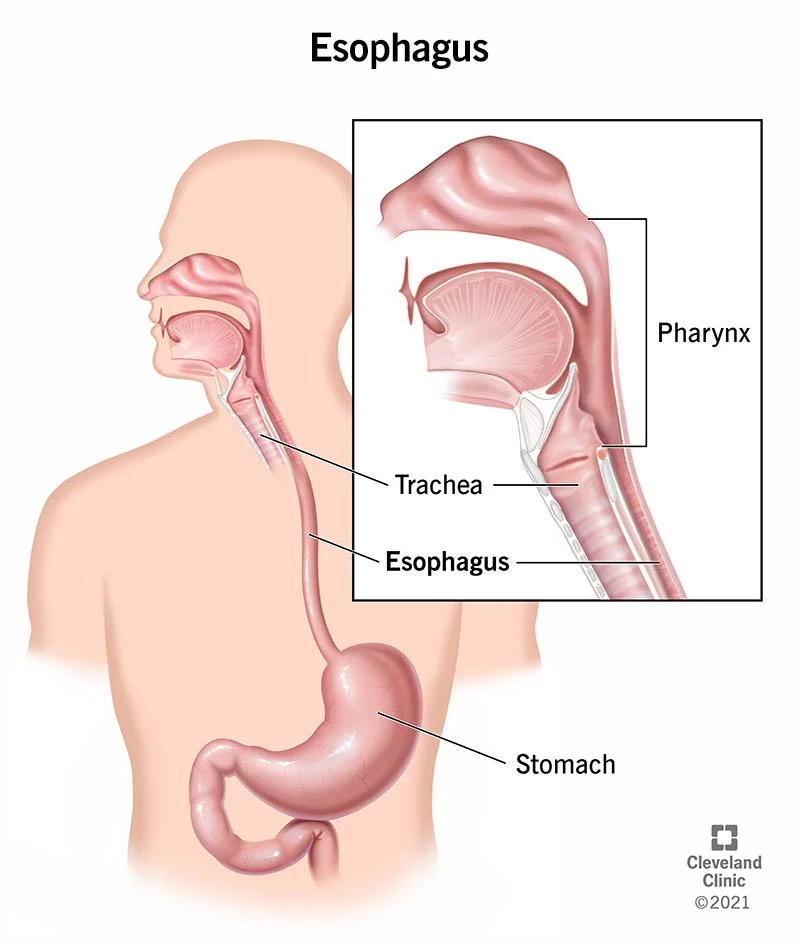
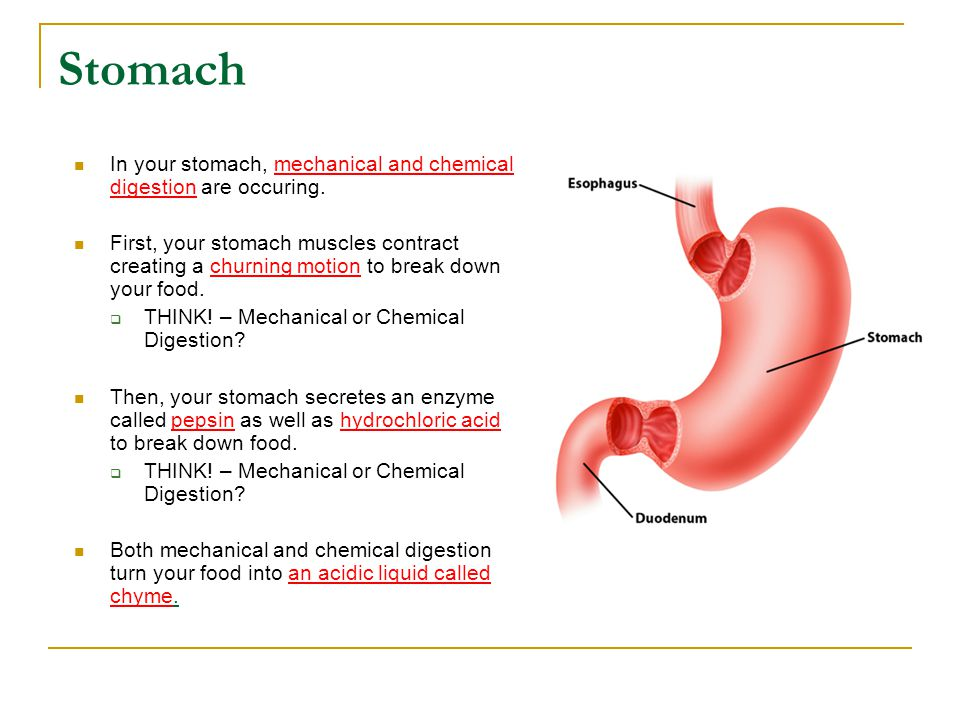
Stomach
some digestion
protein
acidic
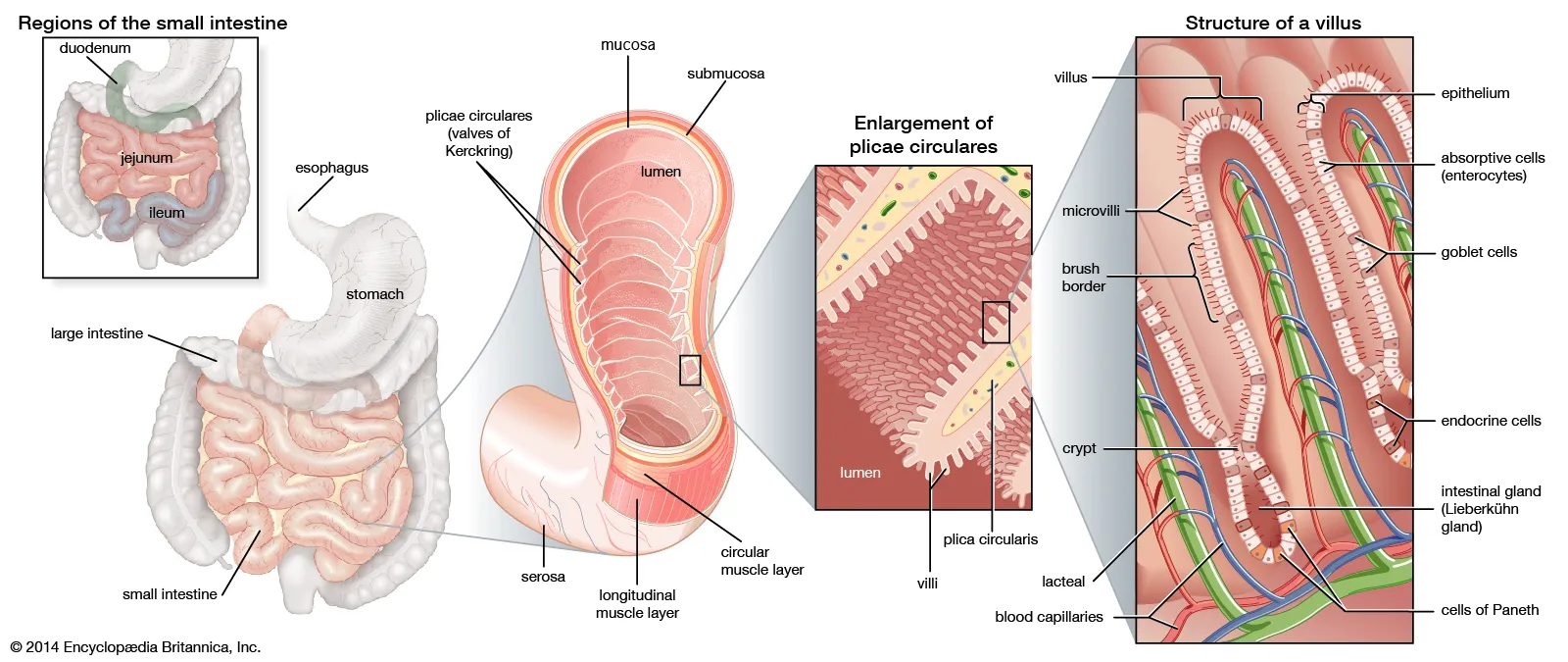
Small intestine
main area of digestion and absorption
villi, fingerlike projections
increase surface area.
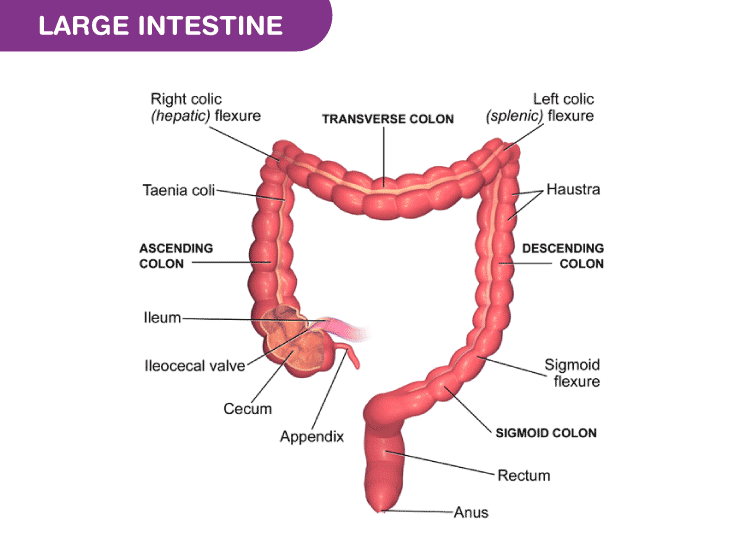
Large Intestine
absorbs water
removal of waste
Accessory Organs: Digestive system
Liver
produces bile
dissolves lipids
Pancreas
digestion of nutrients in small intestine
produces and bicarbonate
base for small intestine to neutralize acid
Thermoregulation
Adjusting the rate of heat exchange from a high to low concentration
Vasodilation
Your blood vessels expand, and more blood goes through and releases more heat.
when you’re hot
Vasoconstriction
Your blood vessels tighten, conserves heat
when you’re cold
Sweating
Cooling by evaporated heat loss
Shivering
Muscle activity that generates heat and warms the body
Nervous System
Collects information from the internal and external environment, processed the information, and responds.
Nervous System Function
Carries messages by electrical signals
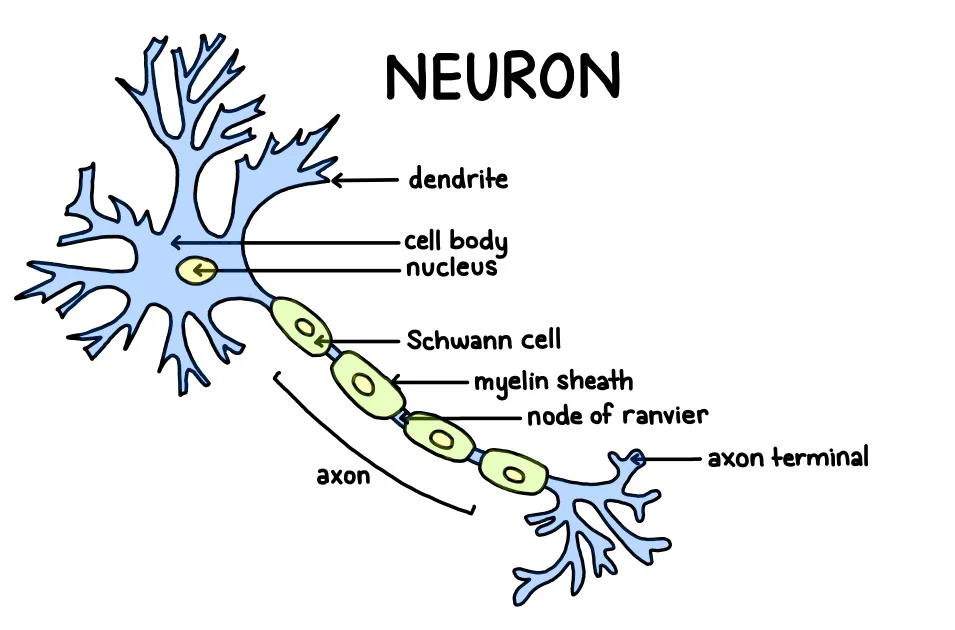
Nueron
Nerve cell
Parts:
dendrites
cell body
axon
Types:
sensory
motor
interneurons
Peripheral Nervous System
transmits information to and from the central nervous system
regulates the internal environment
Central Nervous System
processes and creates a response
brain and spinal cord
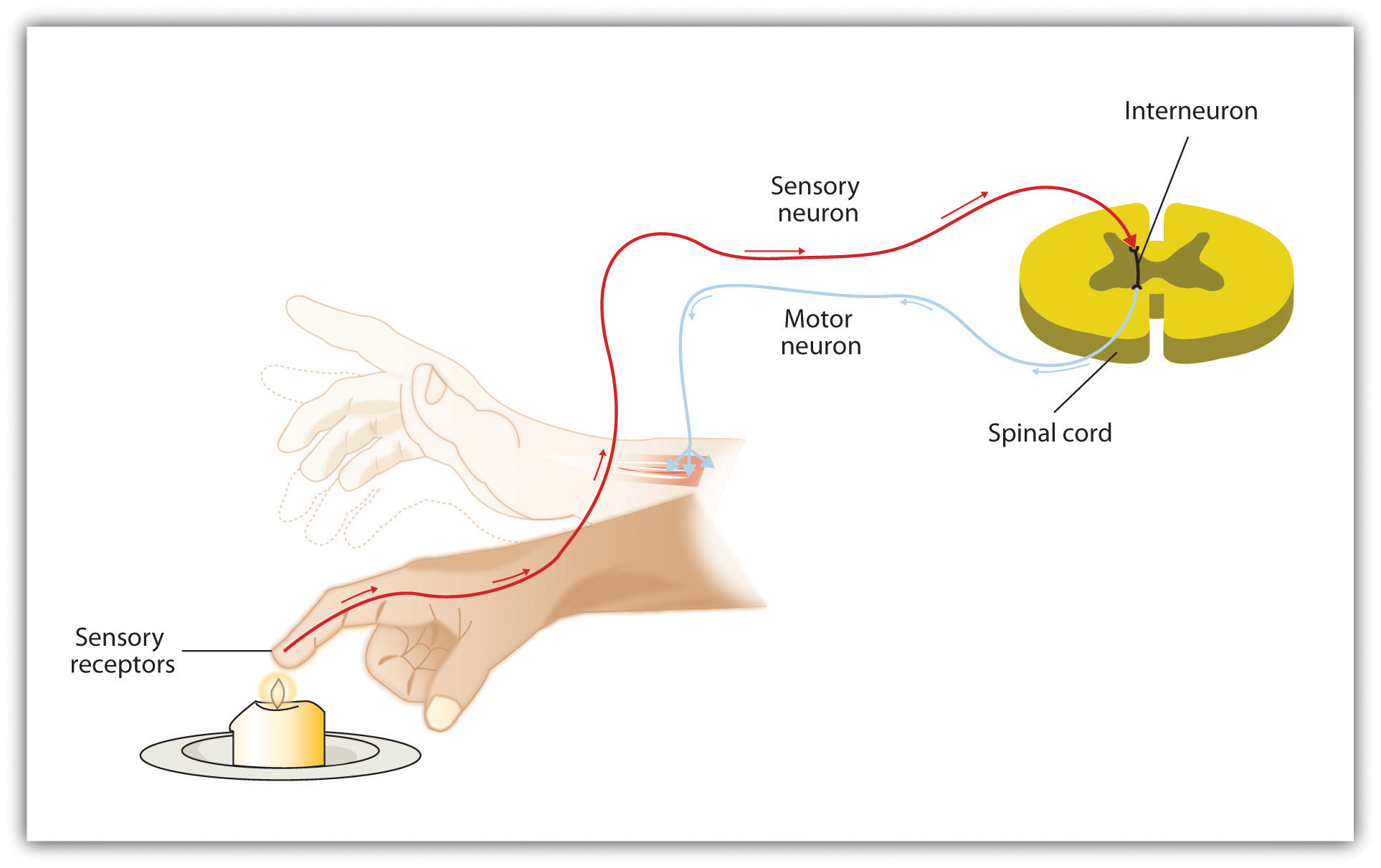
How Signals work
Your brain reads signals from your nerves to regulate how you think, move, and feel
Excretory System and Function
Responsible for eliminating metabolic waste
Skin: Excretory System
Excretes excess water, salts, and a small amount of urea
Lungs: Excretory System
Excretes carbon dioxide
Liver: Excretory System
Converts dangerous nitrogenous(CO2, NAH3) waste into urea
Kidneys: Excretory System
Filters out waste from the blood
Reabsorbs useful substances
Ureter: Excretory System
Transports urine from kidney to bladder
Bladder: Excretory System
Stores urine
Urethra: Excretory System
Releases urine from the body
Respiratory - Excretory Interaction
The respiratory system breathes out CO2 waste from the body
Respiratory- Circulatory Interaction
Circulatory system brings blood to the alveoli and capillaries to exchange CO2 and O2 for body usage
Circulatory- Endocrine Interaction
Endocrine system sends chemicals signals through the bloodstream (circulatory carries through the body)
Feedback
A response within a system (molecule, cell, organism, or population) that influences the continued activity or productivity of that system. Sends signals to create responses.
Making Connections Lab Overview
Control Group : Making Connections Lab
pulse rates before exercise
times clothes pins squeezed first time
Dependant Variable: Making Connections Lab
pulse rate
times clothes pins squeezed
Independent Variable: Making Connections Lab
exercising before
doing the experiment before or not
Experimental Group: Making Connections Lab
exercised before recording the pulse rate
doing the experimentH for the second time
Hypothesis: Making Connections Lab
If we test both groups, then the group exercising before will have a higher pulse rate because the blood needs to be pumped more since the body needs more oxygen.
If we test both groups, then the group that only tested once will have been able to squeeze the clothing pin more because the second group would have gotten muscle fatigue from waste and lactic acid build-up and energy stores being used.
Results: Making Connections Lab
The exercise groups pulse rate was higher than the group without exercise.
The group doing the experiment twice could not squeeze the pin as many times.
Dynamic Equilibrium
When the forward and reverse processes occur at the same rate, resulting in no observable change in the system
Homeostasis
A self-regulating process by which biological systems maintain stability while adjusting to changing external conditions
Feedback Mechanism
Regulation system in a living body that works to return the body to its normal internal state, or commonly known as homeostasis
Stimulus
Something that triggers an event
Signal
A method of communicating information between things
Response
Something you do after an event
Negative Feedback
The response will reserve or cause the opposite of the original stimulus. off/on
metabolic/ metabolism
The whole sum of reactions that occur throughout the body within each cell and that provide the body with energy
Insulin
A hormone released when blood sugar is high, lowers blood glucose.
Glycogen
Form of glucose that is a main energy source and is stored in your body.
Hormone
Chemical substances that act like messenger molecules in the body
Target cell/organ
Body organ or cell that comprises receptors on which the hormone act
Reflex Arc
A neural pathway that mediates or controls the reflex reaction of the body
Control
An element that remains unchanged or unaffected by other variables
Control Group
A group in the experiment which a variable is not being tested
Dependent Variable
What you measure in the experiment and what is affected during the experiment
Independent Variable
The variable that is manipulated during an experiment
Experimental Group
The group that receives the variable being tested in an experiment
Hypothesis
An educated guess as to what will happen during your experiment
Results
The outcomes of experiments, observations, or research studies