9- The relativity of time
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
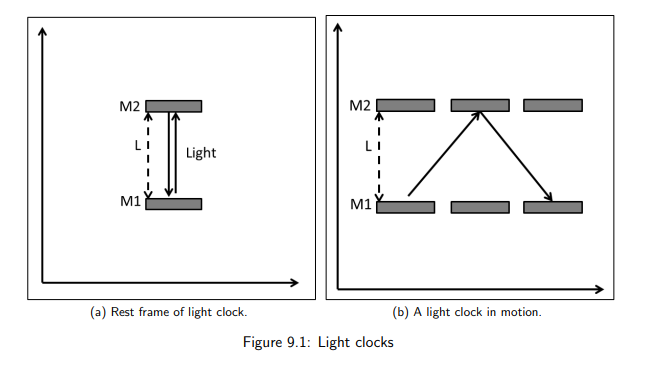
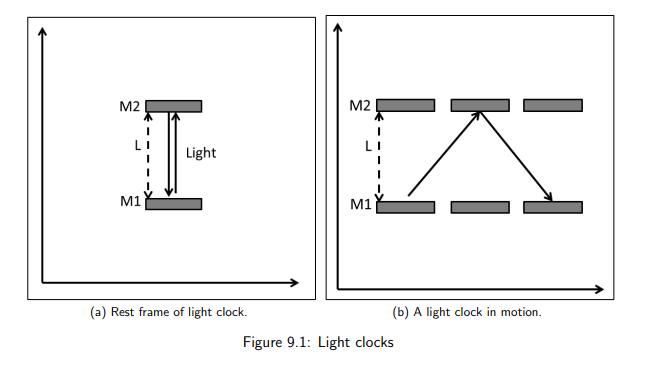
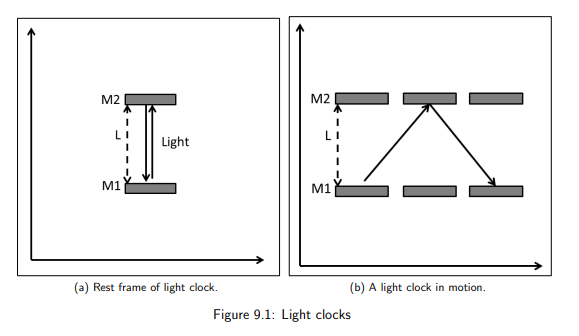
What is a light clock?
A clock that measures time using a pulse of light bouncing between two mirrors.
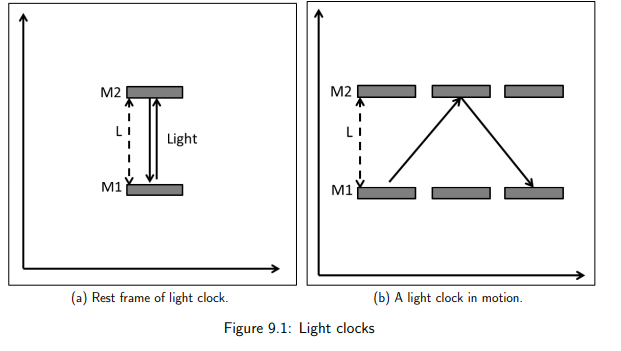
What two events define one ‘tick’ of a light clock?
E1: The pulse of light is emitted.
E2: The pulse of light returns to the lower mirror.
Why are light clocks useful in relativity?
Because they rely on the constant speed of light and provide a simple way to analyze time dilation.
What is proper time (Δt₀)?
Proper time is the time between two events that occur at the same location in an inertial reference frame (IRF).
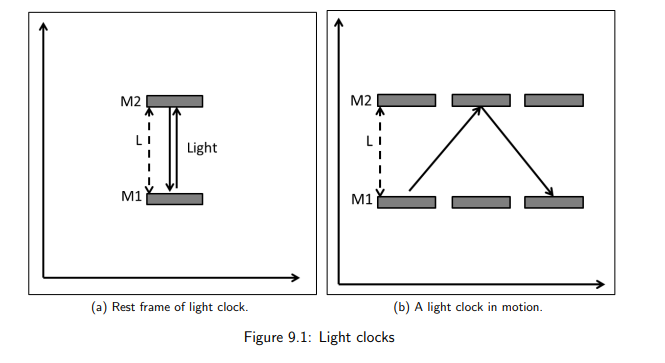
How is proper time measured using a light clock?
It’s the time interval for a light pulse to travel up and down between two mirrors when the clock is at rest relative to the observer.
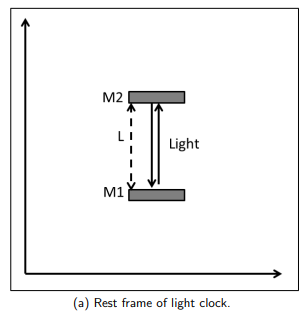
What is the formula for proper time in a light clock?
L is the distance between the mirror
c is the speed of light.
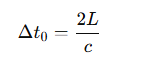
What happens to the path of light in a moving clock relative to an observer?
The light follows a longer, diagonal path instead of a straight vertical path.
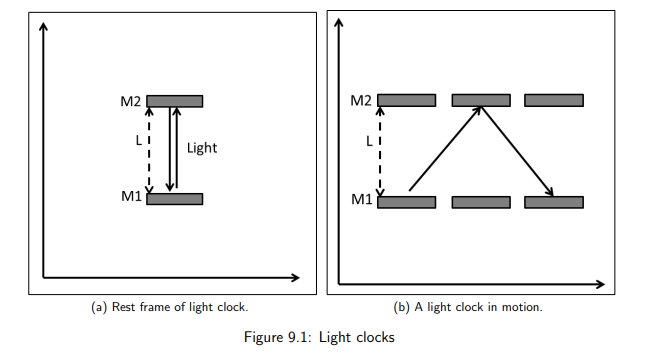
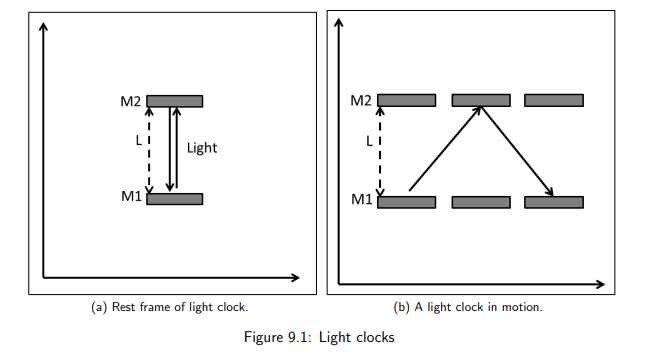
How does time measurement change for a moving clock?
The time interval Δt observed in a moving frame is longer than the proper time Δt₀
This means the moving clock ticks slower.
What is the formula for time dilation,Δt?
Δt₀= the proper time
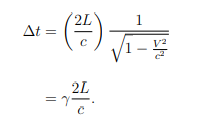
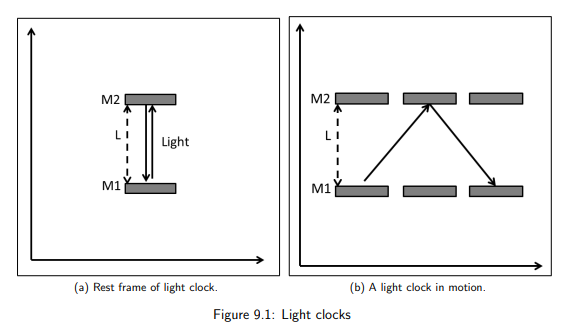
What is dialated time,Δt?
Its the time interval observed by a moving observer relative to the clock.
What is the physical meaning of time dilation?
Moving clocks run slower compared to stationary ones when viewed from another inertial reference frame.
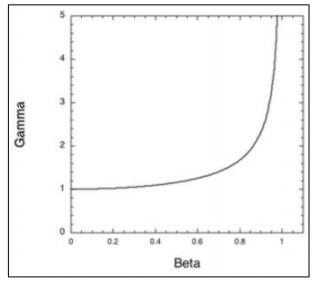
What happens to time as an object's speed approaches the speed of light?
As v → c, γ → ∞
This means time slows down significantly for the moving object as observed from a stationary frame.
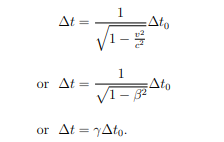
What is the key conclusion of time dilation?
Moving clocks run slow—time is not absolute but depends on the observer’s frame of reference.
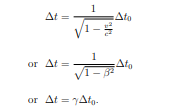
What happens to time dilation when an object is at rest (v = 0)?
There is no time dilation;
γ = 1, so Δt = Δt₀ (time appears normal).
How does the Lorentz factor (γ) behave for small speeds (v ≪ c)?
It approximates γ ≈ 1 + β²/2
This means time dilation is negligible at low speeds.
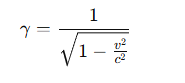
What does β represent in relativity?
β = v/c, the ratio of an object's speed to the speed of light.
What is the time dilation formula for low speeds (v ≪ c)?
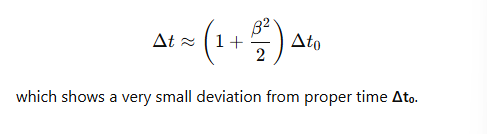
When does time dilation become significant?
As v approaches c, γ increases rapidly, meaning moving clocks slow down significantly.
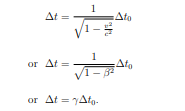
What happens to β as an object's speed approaches the speed of light (v → c)?
β → 1, meaning the object's speed is nearly equal to the speed of light.
What is the formula for the Lorentz factor,γ?
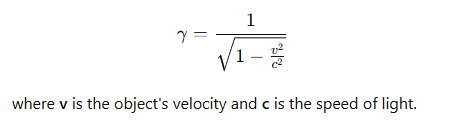
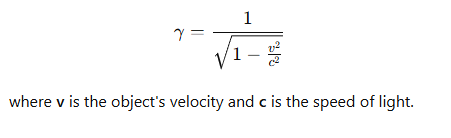
What happens to the Lorentz factor γ as v → c?
γ → ∞, meaning time dilation becomes extremely large.
What happens to the observed time interval Δt as v → c?
Δt → ∞, meaning time effectively stops for the moving object relative to a stationary observer.
Graph of γ as a function of β.