Swimming
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
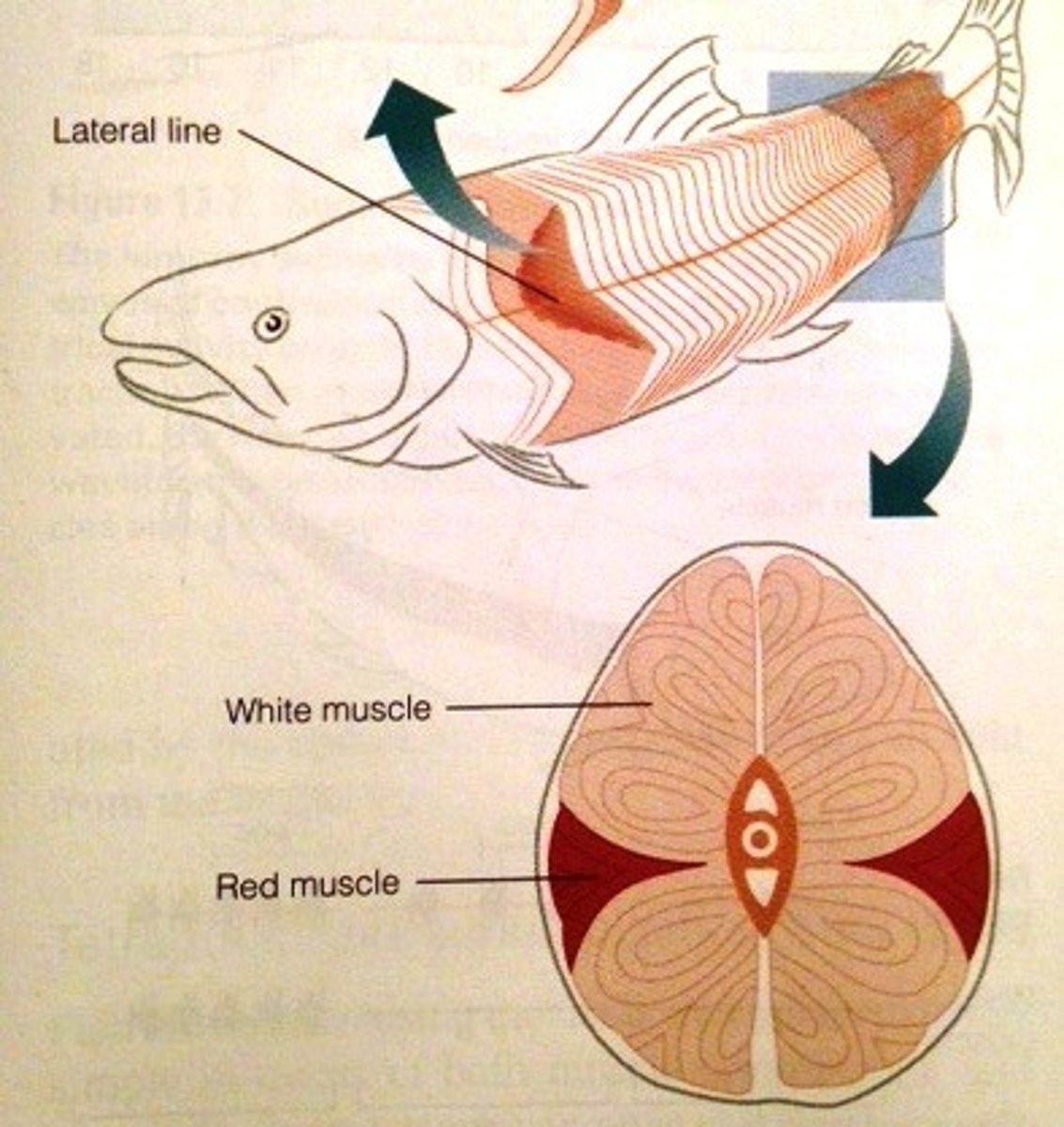
White muscle
this is best for:
-quick bursts
-has little vascularization
-has few mitochondria
-low myoglobin
-Anaerobic respiration (glycolysis)
-Higher power production
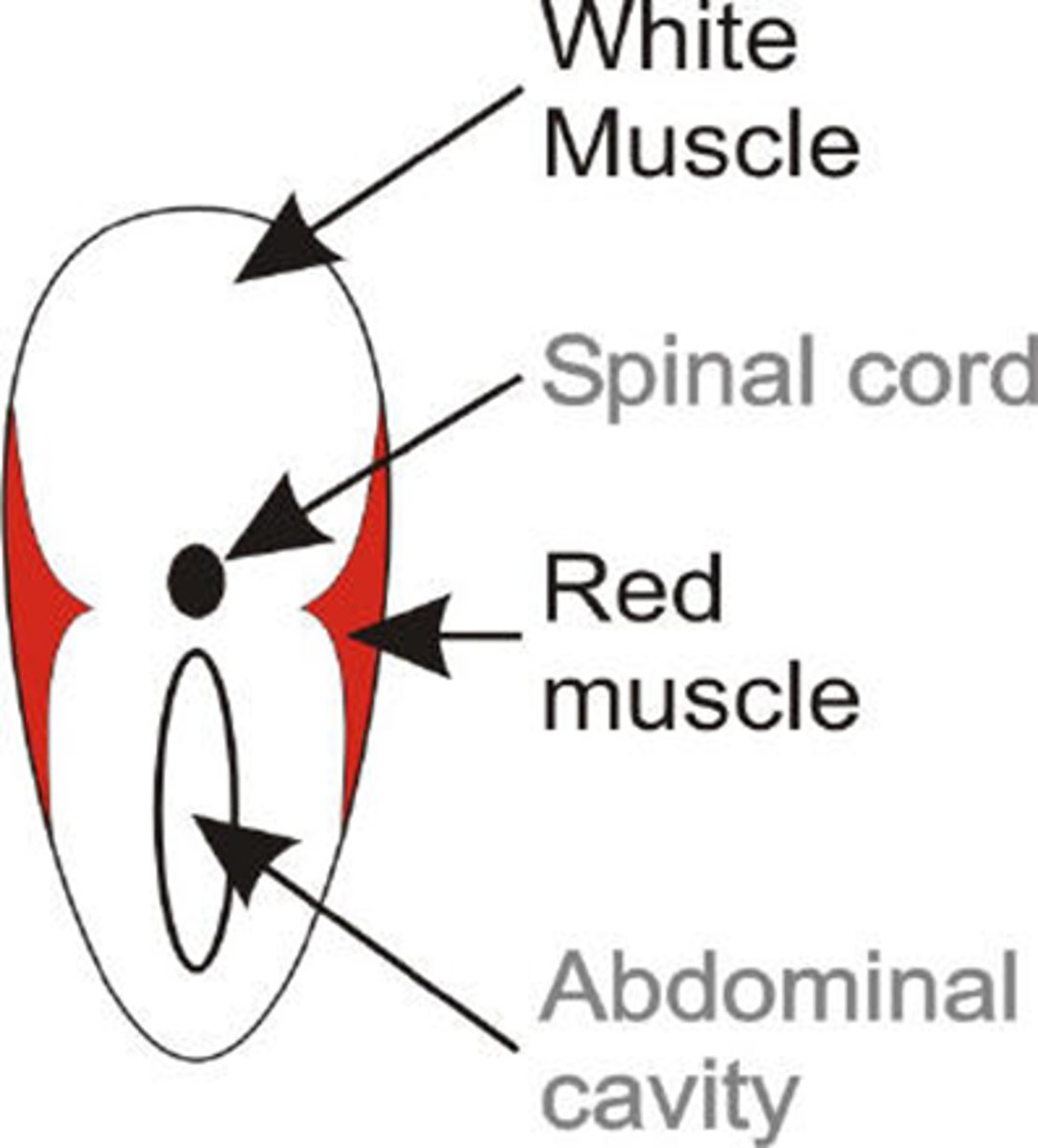
Red Muscle
This is best for:
-slow, cruising
-has high vascularization
-Many mitochondria
-High myoglobin
-Aerobic respiration (oxidative)
-lower power production
Pink Muscle
this is best for:
-Oxidative capacity
-Sustained swimming
-intermediate swimming speeds
-Power swimming at cold temps
Undulation
wavelengths pass down length of body

Oscillation
When fins move back and forth, pivots on a base
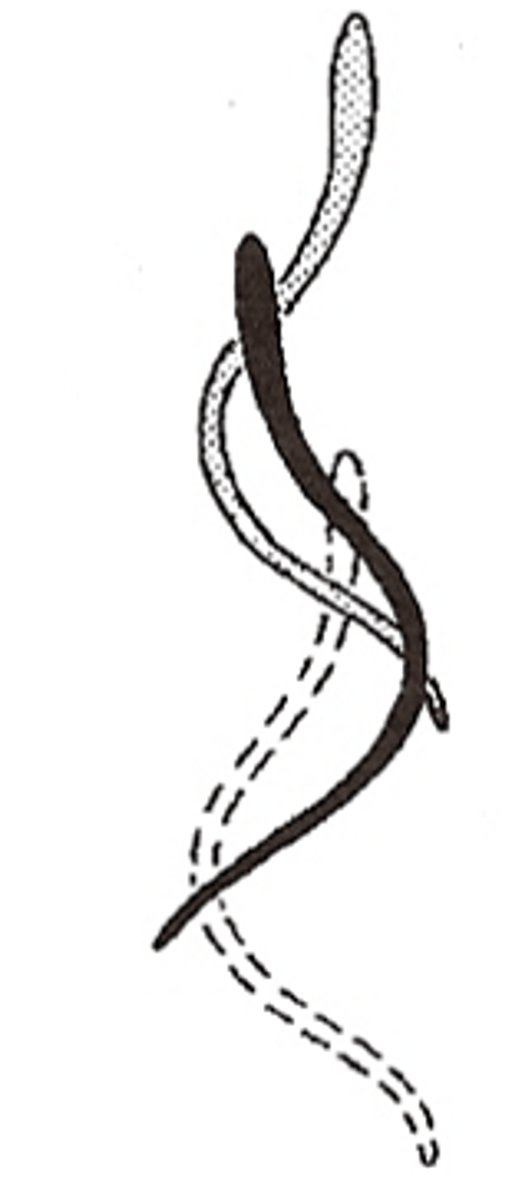
Anguilliform swimming
-Force: Entire body undulates
-Form: Undulations that are s shaped
- body goes rigid to stop

Suction based propulsion
-sucks water towards itself to move forward
-creates a pocket of low pressure water
Subcarangiform swimming
propulsion comes from undulation of the entire body, but the tail moves more than the head
-Force: posterior portion of body (2/3 to 1/2)
-Form: Undulation
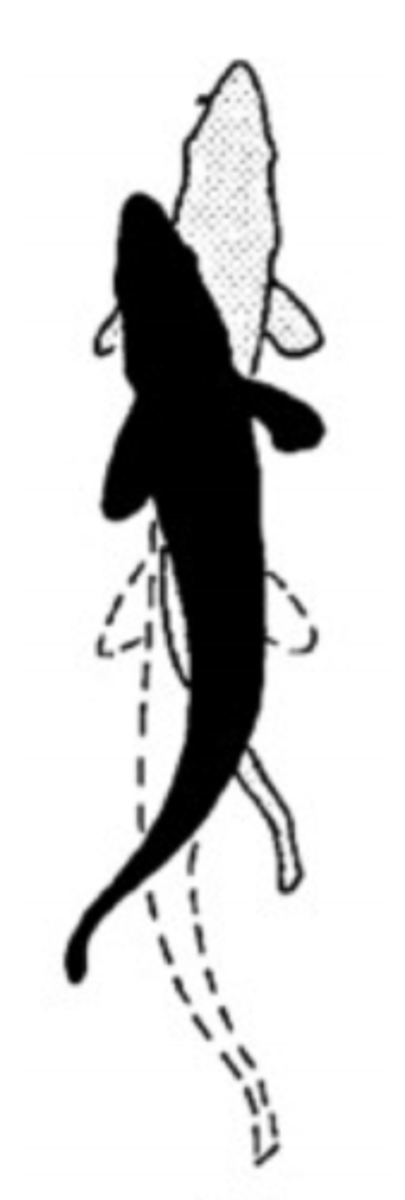

Carangiform swimming
propulsion comes from undulation of the posterior of the body and the tail
-Force: less than 1/2 to 1/3 of body flexes
-Form: side to side undulations are confined to last third of body length
-stiff and deeply forked caudal fin to reduce turbulence and frictional drag
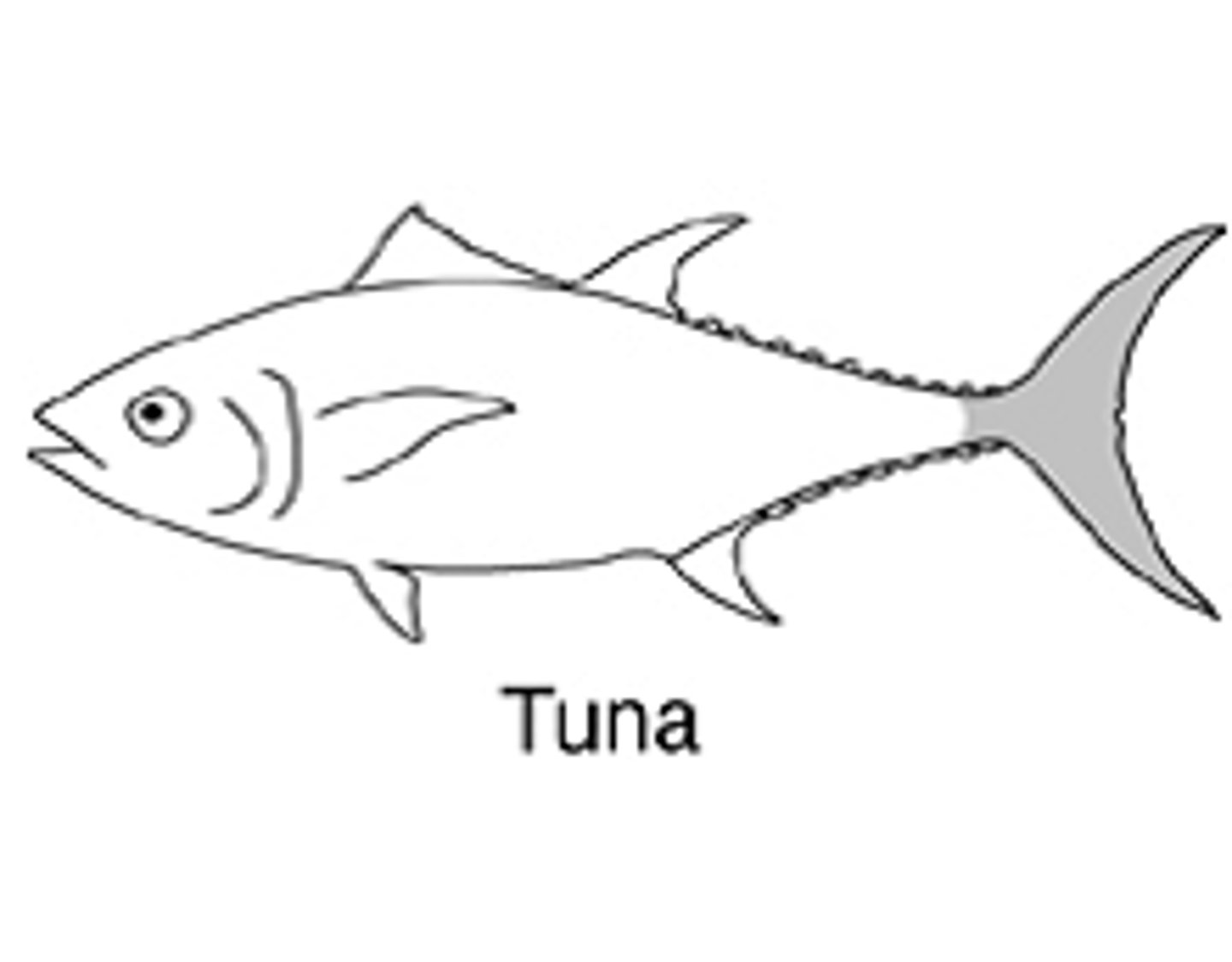
Thunniform swimming
propulsion only comes from undulation of a narrow peduncle and deeply forked caudal fin
"wing on a stick"
Rajiform Swimming
Slow undulation of pectoral fins, with wing-like 'flapping'
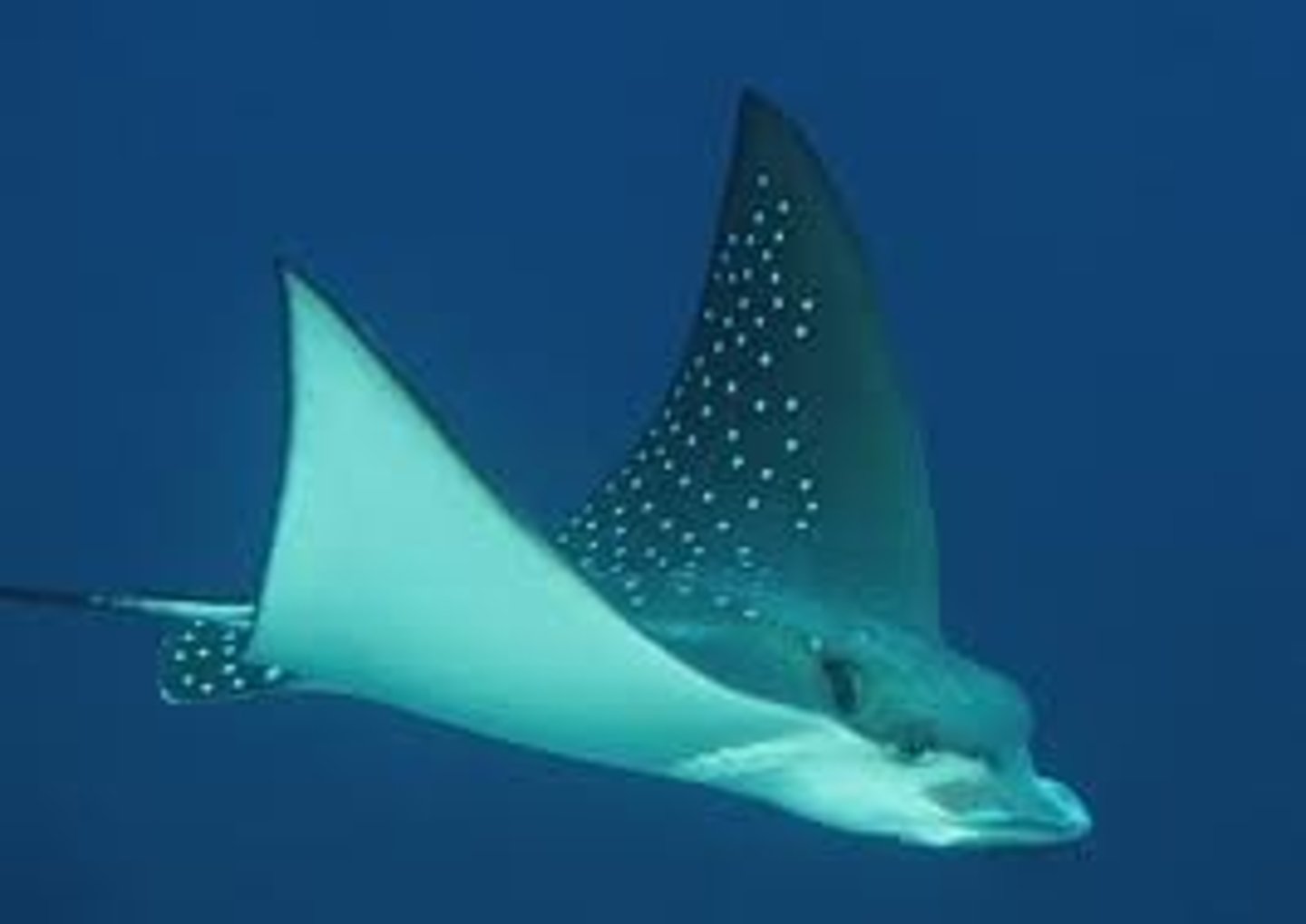

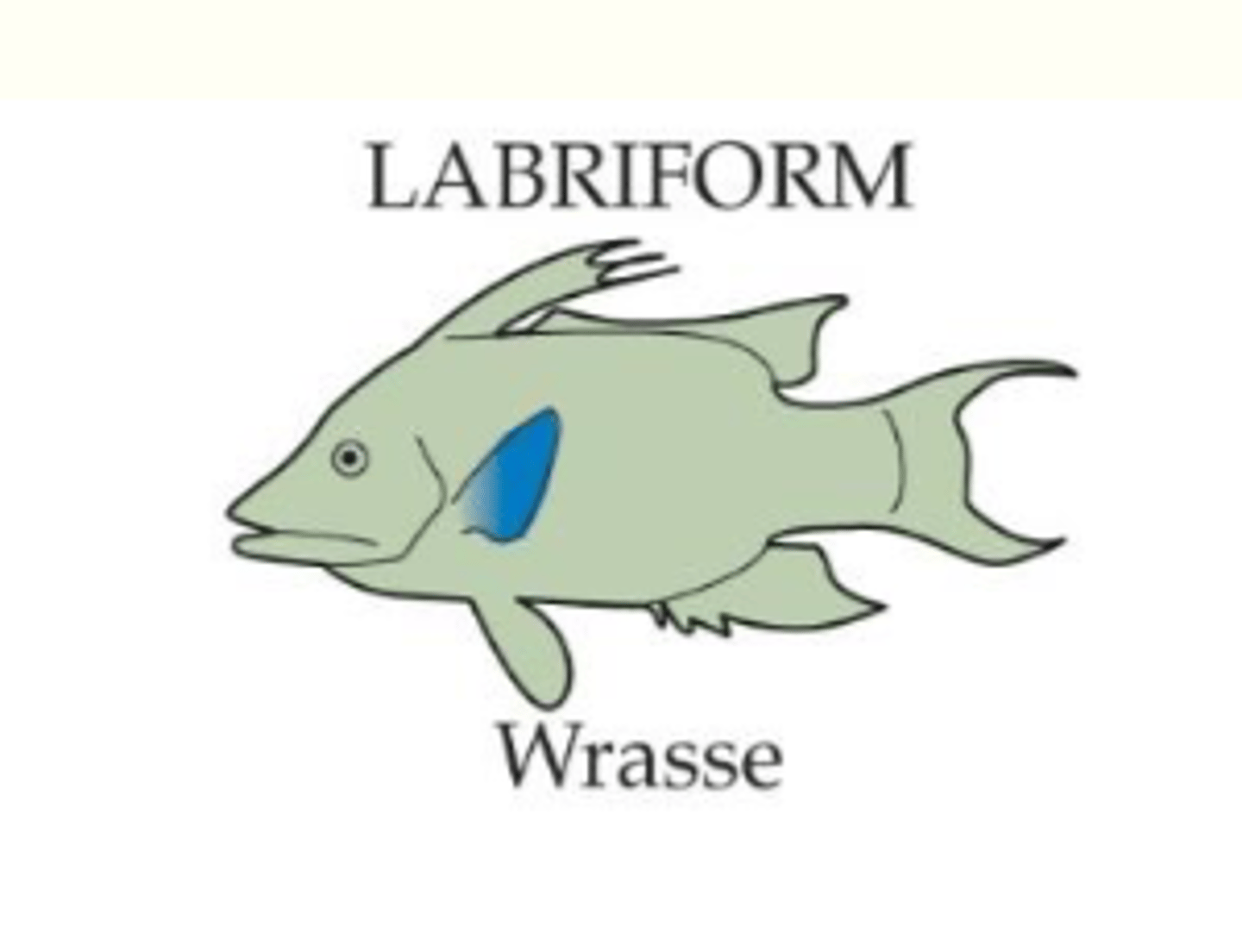
Labriform swimming
Propulsion by rapid undulation of the pectoral fins
-oscillate pectorals sculling and maneuvering
Amiiform swimming
undulation along dorsal fins
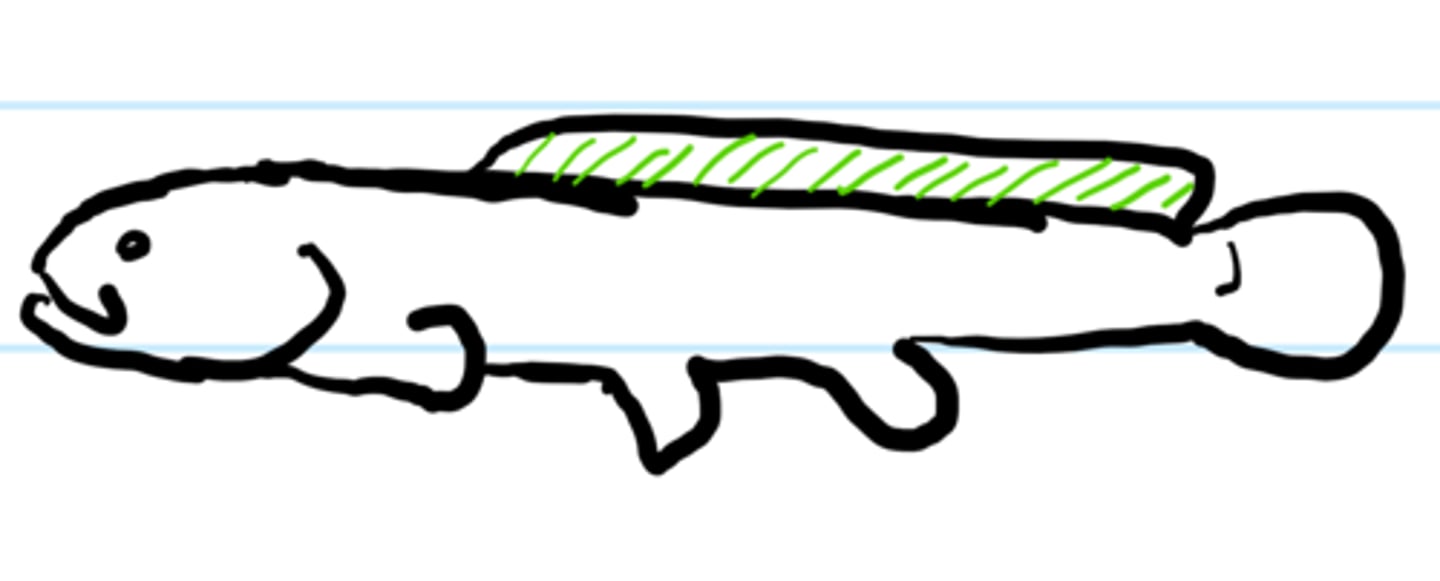

Gymnotiform
Undulation along anal fin
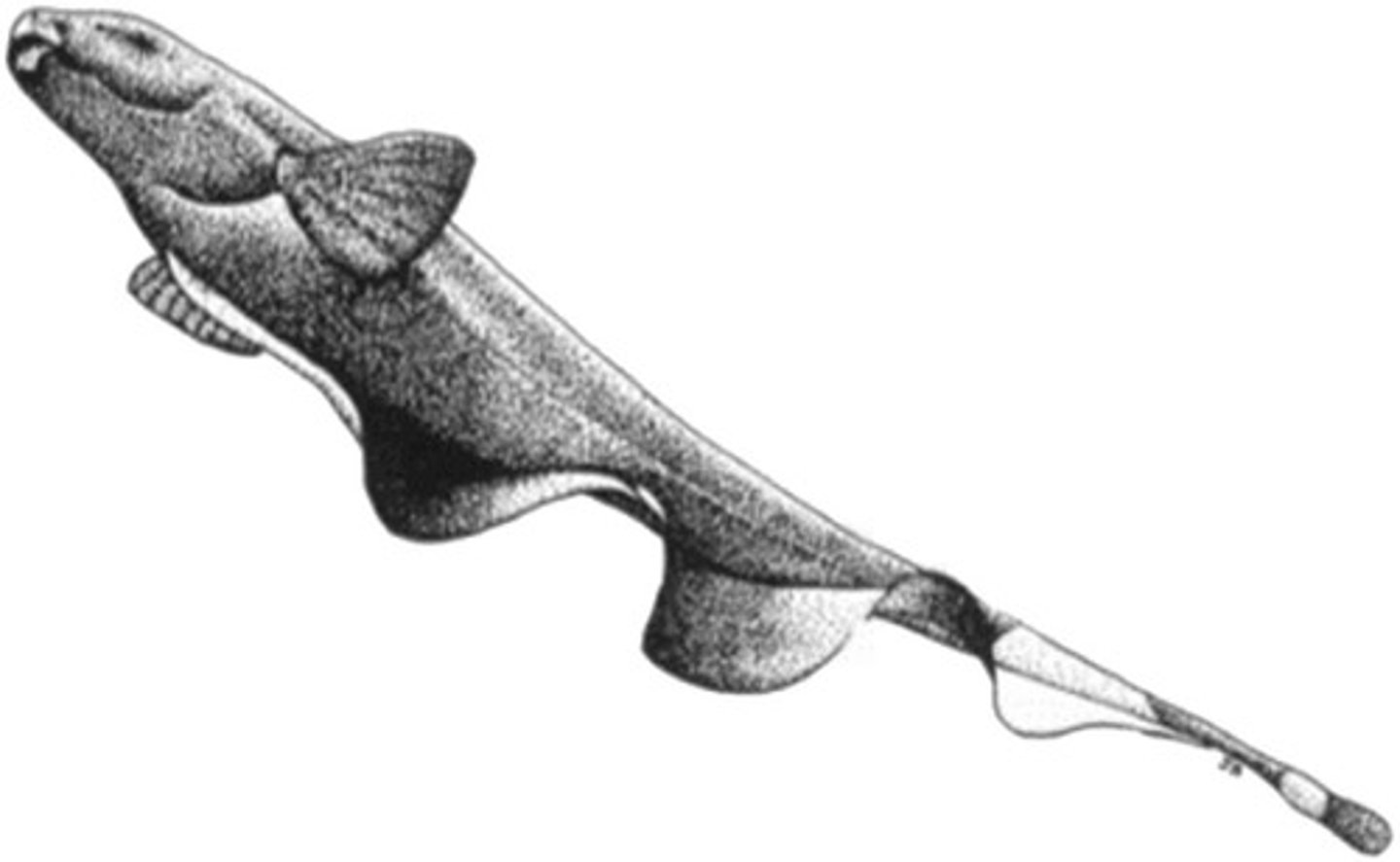
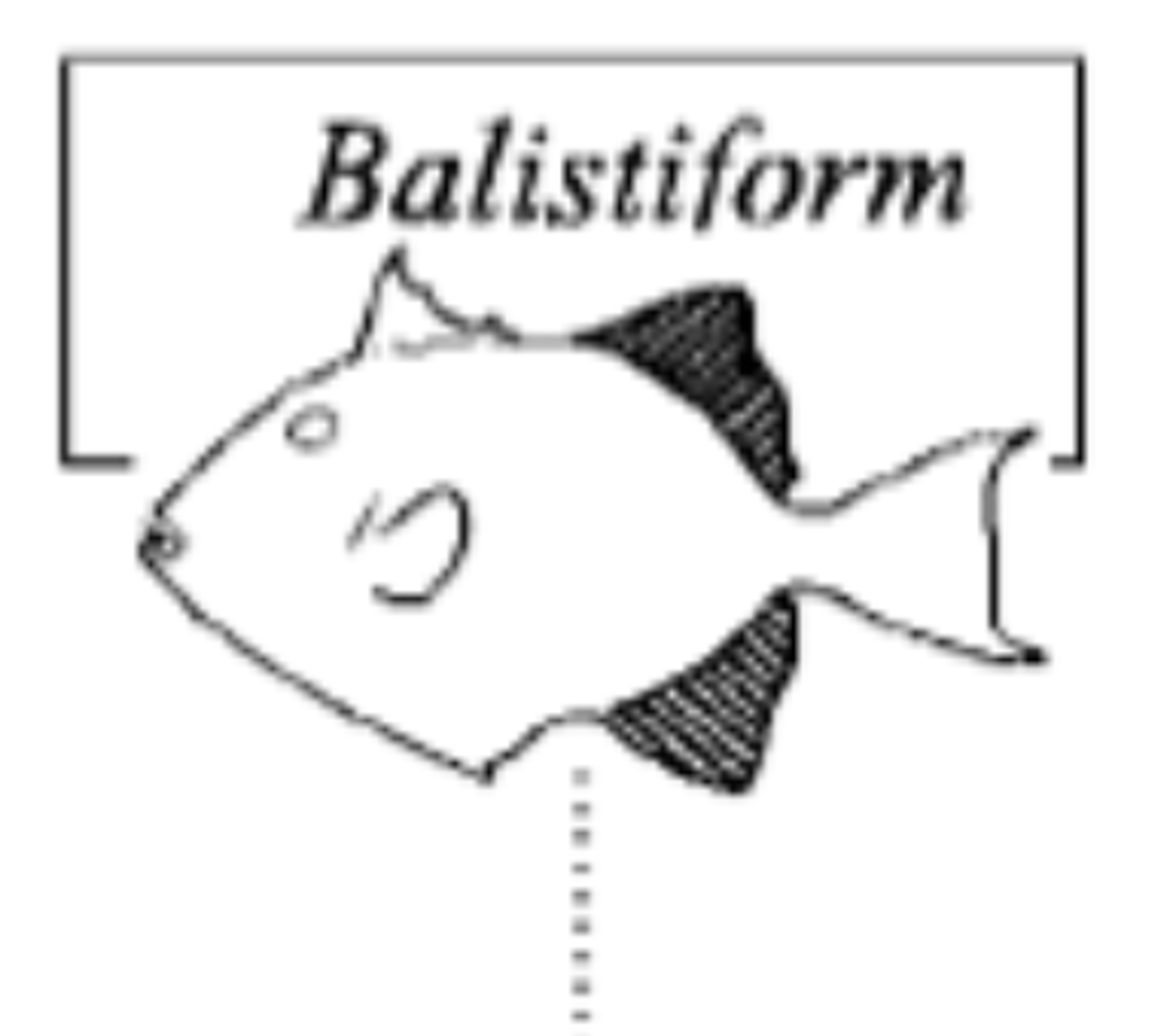
Tetraodontiform swimming
Asynchronous oscillations of dorsal and anal fins.

Syngnathiform swimming
-Seahorses
-all fins more or less at same time
