VCE Biology Unit 1
1/225
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
226 Terms
Independent Variable
What you change or manipulate. (Only 1 Variable)
Dependent Variable
What you measure (give units) that is changed.
Controlled Variable
What remains the same in an effort to reduce the chance of influence on DV.
Uncontrolled Variable
What is not kept constant. (Extraneous variable) Eg. How evenly the E.coli is spread across an agar plate.
Experimental Group
Group exposed to your IV. May be different levels of exposure (12 hrs, 36 hrs)
Control Group
Baseline comparison with experimental groups.
Negative Controls
Not exposed to any levels of IV.
Sometimes the negative control can be a placebo.
Positive Controls
Scientists apply a treatment which induces a well-understood effect on the DV.
Control Group ≠ Control Variable
Control Group ≠ Control Variable
Aim
Purpose of investigation
Make sure to use species name
Start with: 1. To investigate 2. To determine if
Hypothesis
A possible educated prediction that is a testable statement
Describes how you think IV will affect DV including direction of change (increase/decrease)
Either supported/non supported by results
Conclusion
Restate purpose/aim and summarise data
State if hypothesis was supported or unsupported
What further evidence is required
Risk Assessments
Identify, assess and control hazards, identify potential risks.
Quantitative Data
Data/variable that has a numerical value. Eg. 5cm
Continuous Variable
Results include decimal places. eg. Length, time, mass, temp
Discrete Variable
Whole number and not in parts. Eg. NUmber of bubbles, chromosomes, WBCs
Qualitative Data
Data/variable that has a description. Eg. Colour, smell, texture
Primary Data
Data collected by the person directly involved in the investigation.
Secondary Data
Data collected by someone else.
Accuracy
Close to the true value of the quantity being measured.
Precision
When two or more measurements are close to each other in value.
Outliers
A single data point that goes far outside the average value of a group of statistics.
Personal Error
Human mistakes or miscalculations
A type of random error
Random Error
Unpredictable variations that affect precision.
Can be observational or environmental.
Eg. Weighing a moving insect on scales, reaction time with stopwatch, error in reading due to change in wind.
Effects of random error can be reduced by:
Making more repeated measurements and calculating a new mean by refining measurement method or technique.
Systematic Error
Have a clear cause and can be eliminated
Affect the accuracy of a measurement and cause readings to differ from true value consistently. Accuracy cannot be improved by repeating measurements.
Eg. A clock is 5 minutes slow, leaking gas cylinder, scales read 0.2g with nothing (calibration is wrong).
Repeatability
When scientists, using the methods they designed, can obtain the same result multiple times under the same conditions (people, equipment, laboratory).
Reproducibility
When a group of scientists, using methods designed by others, can obtain the same results as another group’s experiment under different conditions (different people, equipment, laboratory).
Improvements to Experimental Design
Control group/placebo group
Controlling more variables
Repeating experiments and averaging results
Increasing randomisation to reduce sample bias
Blind: Recipient don’t know which treatment given, experimenter knows
Double Blind: Experimented and recipient don’t know which treatment given
Limitations to Experimental Design
Size of sample group
Range of IV is too small: 5c-25c
Cost
Availability of resources
Time
Ethical issues
Prokaryotic Cells
Minimal defined internal structure
No membrane-bound organelles
Lack defined structure (nucleus) to house DNA
Prokaryotic Cell Examples
Bacteria, Archaea
Eukaryotic Cells
Complex structure
Many membrane bound structures
Contain a nuclear envelope
Some are unicellular, some multicellular
Eukaryotic Cell Examples
Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Similarities
Have chromosomes
DNA
Ribosomes
Cytoplasm
Plasma Membrane
Vacuoles
Nucleus/Nucleolus
Enclosed in nuclear envelope
Contains genetic material
Ribosome assembly
Cytoplasm/Cytosol
Cytosol is the fluid that organelles float in, and cytoplasm is the combination of cytosol and all organelles inside a cell.
Cell Membrane
Made from phospholipid bilayer
Controls movement of substances inside and outside of cell
Outer surface of cells
Cell Wall
Not membrane bound
Strengthens, supports, protects
Ribosomes
Not membrane bound
Produces protein
Attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Smooth/Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Transport and synthesizes proteins
Smooth makes lipids
Rough makes proteins and exports out of the cell
Golgi Apparatus
Membrane bound
Modifies and packages proteins
Creates vesicles for exocytosis
Lysosomes
Membrane bound vesicle
Contains enzymes
Destroy unwanted/damaged cell parts
Vacuoles
Larger in plant cells
Stores waters
Creates turgor pressure, gives structure.
Mitochondria
Produces energy, ATP
Enclosed in double membrane
Breaks down glucose to carbon dioxide and water to release energy
Chloroplasts
Contains chlorophyll
Traps sunlight to make glucose (photosynthesis)
Double membrane
Vesicles
Transports proteins around the cell or to the outside of the cell.
Cytoskeleton
Not membrane bound
Backbone of the cell, allows movement and shapes
Cilia/Flagella
Assists cell in movement. Tiny hairs or whip-like tail.
Plant Cell Vs Animal Cells
Plants:
Cell wall
Larger vacuoles
Chloroplasts
Lack centrosomes and lysosomes
Animal:
No cell wall
Smaller vacuoles
No chloroplasts
Has lysosomes and centrosomes
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Comparison of the amount of SA (cell membrane) available for absorption and secretion of substances (oxygen and glucose), compared to the V (cytoplasm).
Surface Area to Volume Ratio Formula
Obtained by dividing an object's area by its volume.
Cell Size: SA:V Ratio
Smaller cell= SA:V increased, more efficient.
Bigger cell= SA:V decreased, less efficient
Methods to Overcome Size Challenges:
WBCs can grow more nuclei to supply enough proteins and RNA.
Some have lots of folds throughout the membrane. These can increase surface area.
Some cells can divide into two smaller cells.
RBC’s can lose organelles (nucleus included), to make more space for oxygen carrying haemoglobin.
Biomolecules
Polymers
Organic molecules
4 Major Molecules
Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids and Nucleic Acid
Proteins
Chains formed from the joining of monomers called amino acids.
The joining of amino acids to form proteins occurs in the ribosomes.
Each protein has a unique function and its own specific sequence/chain of amino acids.
Functions of Proteins
Enzymes to speed up reactions, antibodies in the immune response, assist with transport across cell membranes, carry oxygen in RBCs.
Carbohydrates
Polymers (many monomers).
The monomers of carbs (building blocks) are monosaccharide.
An important source of energy.
Examples of Carbohydrates
Glucose, Lactose, Cellulose, Starch
Lipids
Not true polymers
Insoluble in water
Made from fatty acids and glycerol
Make up membranes and some human hormones eg. sex hormones
Nucleic Acid
Main information carrying molecule in the cell.
Two main classes: DNA and RNA.
Made up of nucleotides (monomers) which contain a nitrogenous base, a phosphate and a sugar (ribose - RNA, deoxyribose - DNA)
Water
Most abundant compound.
Highly cohesive (attracted to each other) and adhesive (attracted to other things).
Found in the blood, tissue fluid and lymph outside of cells.
Also found in cytosol and organelles.
Plasma Membrane
Semi-permeable barrier of the cell.
All cells have one.
Structure of the cell membrane is called the fluid mosaic model.
Fluid Mosaic Model
Phospholipid bilayer with proteins embedded.
Molecules that make up the membrane are not held static in one place.
Fluid as the phospholipids that make up the membrane move laterally (side to side)
It is a mosaic as it made up of more than one thing.
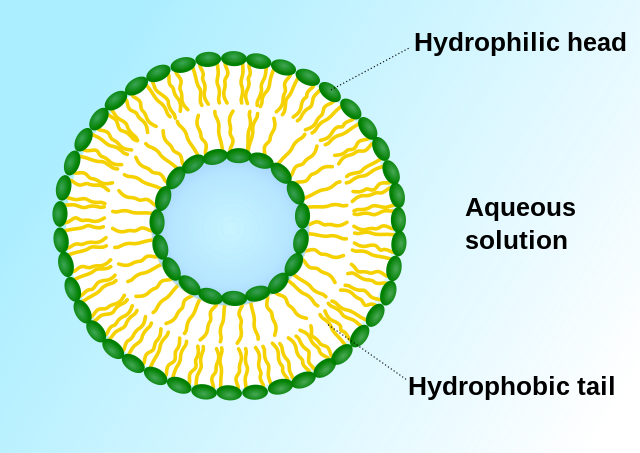
Phospholipids
Hydrophobic tails, face away from water (Non-polar)
Hydrophilic heads, face water solution (Polar)
Embedded Proteins
Peripheral: Attached to the surface or one side of the membrane
Transmembrane: Integral protein embedded in the membrane
Glycoproteins: Proteins with carbohydrates attached
Glycolipid: Proteins with lipids attached.
Glycoproteins and Glycolipids
Cellular recognition, Immune recognition
Cholesterol
Regulates fluidity in the cell.
Substances That Can Pass through the Membrane
Lipid-soluble substances dissolve: Alcohol, Chloroform
Tiny hydrophilic/polar molecules through osmosis: H20
Small hydrophobic/non polar molecules: O2, CO2
Substances That Cannot Pass through the Membrane
Medium sized hydrophilic substances: Ions, Amino acids
Polar monomer molecules: Glucose
Large molecules use bulk transport: Hormones and proteins
Passive Transport
Transport that takes no energy. The energy comes from the chemiosmotic potential due to the concentration gradient.
Types of Passive Transport
Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
Diffusion
The passive movement of particles from an area of higher concentration of a substance to lower concentration, in order to achieve equilibrium. If a solute can cross the semipermeable membrane, it will move to achieve the same concentration on both sides of the membrane.
Facilitated Diffusion
When charged particles or medium sized water soluble molecules (e.g. ions, glucose, amino acids) diffuse across a membrane through channel proteins or with the aid of carrier proteins.
Osmosis
The passive NET movement of WATER across a semipermeable membrane along the concentration gradient.
When a solute (eg: salt, sugar, protein, etc.) cannot pass through a membrane but the solvent (water) can. Water always moves towards the more concentrated solution of solute, to make both inside and outside equal in dilution.
Isotonic
Concentrations both inside and outside of the cell are the same.
Animal Cell Tonicity
Hypertonic: High solute, water leaves cell causing it to shrivel (crenation).
Hypotonic: Low solute, water enters the cell, causing it to swell, potentially burst (lysis).
Plant Cell Tonicity
Hypertonic: High solute, water leaves cell, cytoplasm shrinks, but cell wall maintains structured shape (plasmolysis/flaccid).
Hypotonic: Low solute, water enters the cell, cytoplasm expands, but unable to burst because of pressure from cell wall (turgor).
Active Transport
Moves ions or molecules against a concentration gradient using energy (ATP).
Examples of Active Transport
Plants move minerals (inorganic ions) into their roots.
The gills of marine fish can remove salt from the body by pumping it into the salt water.
Bulk Transport
Endocytosis and Exocytosis are used for materials that are too big to pass through the plasma membrane (eg. proteins). Transport occurs through the formation of vesicles.
Endocytosis
Cell engulfs material to bring it into the cell.
Endocytosis of fluids is PINOCYTOSIS.
Endocytosis of solid material PHAGOCYTOSIS.
Exocytosis
Moves material to the outside of the cell.
Vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane and discharges contents to the outside.
Fusion of vesicles to the plasma membrane adds membrane to the cell surface.
Light Microscopes
Magnification: 300x or 2000x
Whole parts, can be living
Outer details, some structures inside
Electron Microscopes
Magnification: 2 million x
Must be dead
Detailed structures
Cell Theory
All living things are made of cells.
Cells are the smallest basic units of life.
All cells come from pre-existing cells.
Domains and Kingdoms of Life
3 Domains: Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya.
Bacteria and Archaea are all prokaryotes, and Eukarya is eukaryotic and divided into distinct Kingdoms.
MRSGREEN Criteria for Organism Consideration
Movement
Respiration
Sensitivity to stimuli
Growth
Reproduction
Equilibrium (Homeostasis)
Excretion
Nutrition
Multicellular Organism Order
Cell: Basic unit of life.
Tissue: Group of cells with similar structure and function. Eg. Smooth muscle cells= Smooth muscle tissues.
Organ: Grouping of tissues into distinct structures to perform a specialised job.
System: Group of organs work together to perform a particular task. Eg. reproductive system.
Binary Fission
The one circular chromosome replicates and the copies attach to the cell membrane. Plasmids will also replicate
The cell begins to grow.
The cell continues to grow, elongating further.
The cell membrane (and cell wall) pinches inwards to divide the cell into two. (Cytokinesis)
Two daughter cells are produced, each genetically identical to each other and the original cell.
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm and formation of two daughter cells.
Septum
A dividing wall formed during binary fission.
How is cytokinesis different in plant and animal cells?
Animal cells form a cleavage furrow, then pinch apart.
Plant cells form a cell plate in the middle from vesicles accumulating, and new cell walls are formed.
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
A molecule that is the blueprint of all living things.
Contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive and reproduce.
DNA Structure
Two strands or "backbones"made of phosphate bonded together and twist around each other: A double helix.
Backbones are bonded together by hydrogen bonds.
Each "rung" of the ladder is made up of two smaller molecules, known as bases: Adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C).
Base pairs are complementary.
Adenine (A) and Thymine (T) join together: A–T
Guanine (G) and Cytosine (C) join together: G–C
DNA Molecule
The DNA molecule is made up of small parts (monomers) called nucleotides. A DNA nucleotide itself has 3 parts:
A phosphate group
A deoxyribose sugar
A nitrogenous base (one of A, T, C or G)
DNA Replication
DNA replication needs to occur so that there is enough DNA for cell division (mitosis or meiosis). It ensures that each new cell made by cell division gets a copy of the genome.
DNA replication is semi-conservative, meaning that each strand in the DNA double helix molecule acts as a template for the synthesis of a new, complementary strand.
The hydrogen bonds of the DNA double helix unwind, and the helix opens. Each strand of DNA acts as a template for synthesis of a new complementary strand. Complementary pairs are added to each strand, and replication produces 2 identical DNA double helices, with one new and one old strand.
Chromosomes
Made of chromatin, a single long strand of DNA coiled around proteins called histones.