4 - The Cambrian Explosion
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is the Burgess shale
A Canadian fossil deposit from the mid Cambrian which preserved almost an entire ecosystem including soft tissues
List 8 organisms found in the Burgess Shale
Trilobites
Brachiopods
Annelidia → segmented worm
Priapulida → penis worm
Ottoia → worm containing a through gut
Hallucigenia → lobe limbed spiky worm
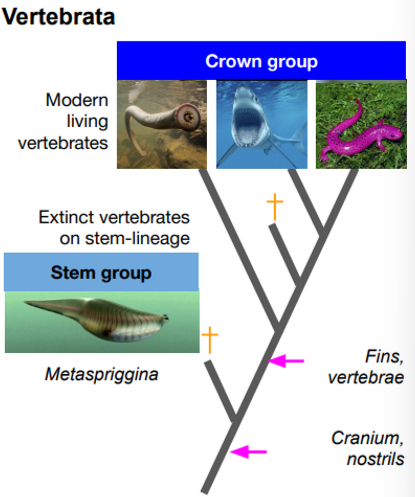
Metaspriggina → early vertebrate
Anomalocaris → arthropod
What is the defining fossil of the Cambrian
Treptichnus → worm burrow trace
Why is Metaspriggina considered a vertebrate
Has gill arches, paired eyes, muscles and a notochord
What was Gould’s interpretation of the Cambrian fauna
Classified each new weird and wonderful organism as its own new phyla → now outdates/dismissed approach which was understandable at the time
Current interpretation of the fauna
Most organisms are stem group members of modern phyla
How many modern phyla are there
30
What is a phyla
A group of organisms sharing a unique body plan
Modern interpretation of the Cambrian fauna in the context of evolution
Still a rapid ‘explosion‘, not to the same degree as Gould imagined (still getting progressively more varied and complex over time as Darwin imagined) just still more sudden and rapid tan he originally hypothesised
What was the rate of animal diversification in the Cambrian compared to normal
5x faster
List the main causes of the Cambrian explosion
Break up of Rodinia
Red queen hypothesis
Hox gene mutations
limited early competition so lots of available niches waiting to be filled
Explain how Rodinia breaking up contributed to the Cambrian explosion
Sea levels rising → shallow flooded continental shelves make great habitats
Regolith erosion → increased carbonate input into the ocean increasing alkalinity → more habitable and the origin of biomineralisation
Explain how the red queen hypothesis contributed to the Cambrian explosion
The predator prey arms race meant that they each had to evolve quickly to evade/catch the other respectively → spurs on the diversification of the other group increasing the complexity of the food web
Explain how hox gene mutations contributed to the Cambrian explosion
Hox genes are responsible for dictating what genes are expressed so how the body plan develops → relatively new so still ‘finding their feet‘ and ‘experimenting‘ → lots of new body plans in the early days of diversification → over time become more common and less deadly
Features of Anomalocaris
Large arthropod
shrimp like shape
Raptorial appendages → put food in mouth
Swimming appendages
Weaker than thought → could only eat soft prey
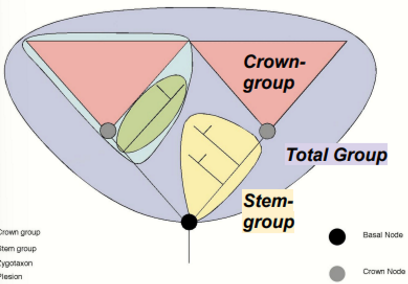
Define crown group
All living members of a clade, its common ancestor and all its descendants
Define Stem group
Extinct organisms outside the crown group with the shared most recent common ancestor
Example of a stem group organism
Metaspriggina is an extinct vertebrate on the stem linneage