Physics P6: Waves
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What needs to be used to prevent alpha, gamma and beta particles travelling?
Alpha- paper
Beta- Aluminium
Gamma- thick lead
What is an isotope?
an isotope is an atom of a chemical element that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons compared to other atoms of the same element
What is the radius of an atom?
1×10-10m
What are some uses of radiowaves
TV, Radio
What are some uses of visible light waves
Vision, optical fibres
What are some uses of U-V waves
tanning, energy efficient bulbs
Uses of x-rays?
Medical scan, airport security
Uses of gamma rays?
radiotherapy, sterilisation
What are ‘the waves’ , in order
Radio, Micro, Infrared, Visible, U-V, X-Ray, Gamma
Which waves are ionising?
U-V, X-Ray, Gamma
What is the speed of light?
300,000,000m/s
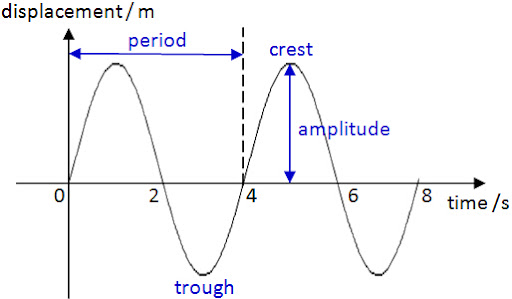
What is the definiton of these?
Period- time taken for 1 full wave movement
Crest- top part of a wave
Trough- bottom part of a wave
Frequency- number of waves that occur every second
Amplitude- distance from the equilibrium to the crest
Wavelength- distance from 2 identical points
What are transveral waves
waves that travel perpendicular to the direction of travel (up and down)
what are longitudinal waves
waves that travel parallell to the direction of travel (left and right)