Protein Building Blocks
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Proteins are biological macromolecules that act as enzymes, hormones, receptors, channels, transporters, antibodies, and support structures inside and outside cells. Proteins are composed of twenty different amino acids linked together in polymers. The composition and sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain is what makes each protein unique and able to fulfill its special role in the cell. Here, we will start with amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, and work our way up to three-dimensional protein structure and function.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are proteins?
Proteins are biological macromolecules with various functions such as enzymes, hormones, receptors, channels, transporters, antibodies, and structural support.
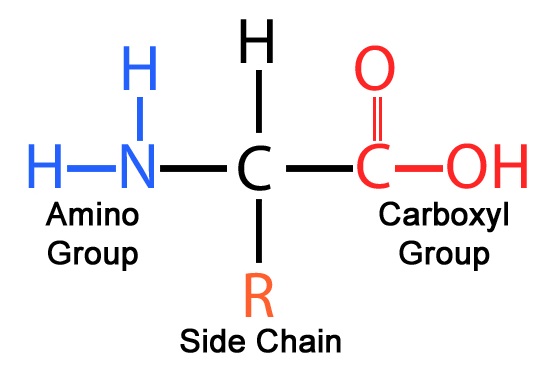
What are amino acids?
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, composed of
a central carbon atom (α-carbon),
an amino group (-NH₂),
a carboxyl group (-COOH),
a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain (R-group).

What is the α-carbon in an amino acid?
The central carbon atom in an amino acid

What is the function of the amino group (-NH₂) in an amino acid?
The amino group is basic and can accept protons (H⁺) in aqueous solutions.
** Basic means that it has the ability to accept protons. Hydrogen is the simplest element while nitrogen is group 15 — more reactive since it has more electrons and wants to achieve a stable electron configuration.

What is the function of the carboxyl group (-COOH) in an amino acid?
The carboxyl group is acidic and can donate protons (H⁺) in aqueous solutions usually to the amino group.

What is the variable side chain (R-group) of an amino acid?
The R-group is a unique chemical group that distinguishes each amino acid and determines its specific properties, such as hydrophobicity, hydrophilicity, or charge.

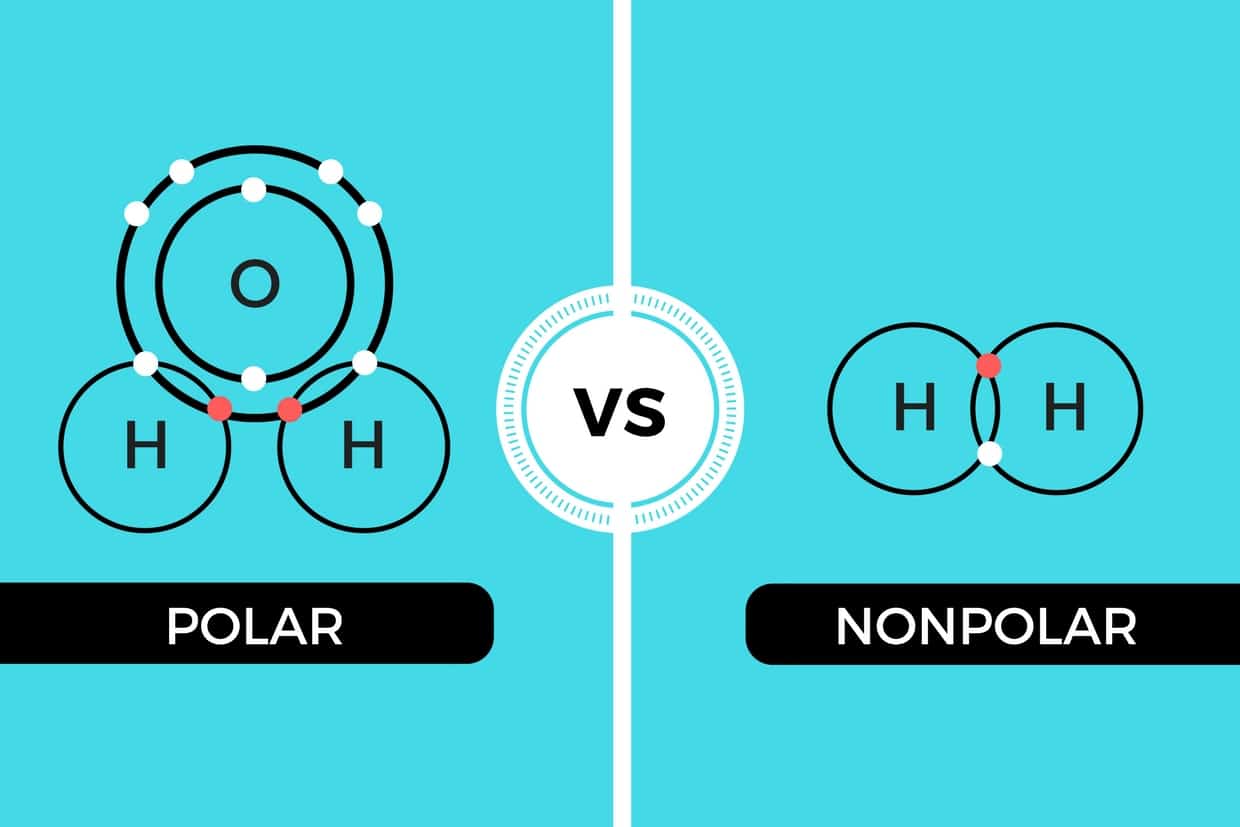
What is the difference between polar and nonpolar?
Polar: molecules/parts of molecules that have regions with partial positive and negative charges
arises due to differences in electronegativity between atoms in molecule
act differently with water-based environment like cells
have affinity for water because water is polar too (hydrophillic)
they can hydrogen bond to make them soluble
when there is a significant difference in electronegativity between two atoms in a covalent bond, the bond is considered polar !!!
Non-polar: does not have regions with significant differences in electronegativity between atoms
have an even distribution of electrons between atoms
lipids, oils and fats are usually nonpolar and are used for energy storage and cellular membranes — steroid hormones
typically hydrophobic because water is polar
How are amino acids named?
Amino acids are named based on their side chain properties. For example, alanine has a methyl group (-CH₃) as its side chain, while serine has a hydroxyl group (-OH).

Why is the sequence of amino acids important in proteins?
The sequence of amino acids determines the structure and function of proteins, as it dictates how the protein folds into its three-dimensional shape and interacts with other molecules.
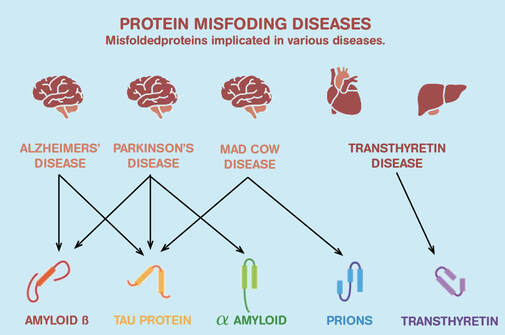
Proteins fold into specific three-dimensional structures primarily due to the interactions between their amino acid building blocks and the surrounding environment.
The shape of a protein allows it to interact with specific molecules like enzymes, it stabilizes the molecule and minimizes unfavorable interaction — also to achieve the favorable state of energy. it lowers the energy of system by optimizing the interactions between amino acid residues
If this is not achieved correctly, it could cause protein misfolding and contribute to Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and cystic fibrosis
What are some functions of proteins in living organisms?
Proteins serve as
enzymes (catalysts),
hormones (regulators),
receptors (signal transmitters),
channels (transport facilitators),
transporters (molecule carriers),
antibodies (immune defenders),
and structural components (support builders).

Why are proteins important in biochemistry and biotechnology?
Proteins play crucial roles in biochemical reactions, cellular functions, and are used in biotechnology for various applications like drug development, biocatalysis, and molecular engineering.
What makes each of the twenty amino acids unique?
Each amino acid is unique due to its side chain (R-group), which determines its chemical properties and functions in proteins.

What are the important properties of amino acid side chains?
Side chain properties include shape, charge, ability to hydrogen bond, and their capacity to act as acids or bases, influencing protein structure and function.

How are hydrophobic (nonpolar) amino acids characterized?
Hydrophobic amino acids have aliphatic or aromatic side chains (e.g., glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan).
They repel water and are typically found inside folded proteins.

What distinguishes polar amino acids?
Polar amino acids have side chains that are polar enough to form hydrogen bonds with water but not strongly acidic or basic. Examples include serine, threonine, and tyrosine.

Which amino acids are acidic?
Glutamic acid and aspartic acid have carboxylic acid functional groups in their side chains, making them acidic and negatively charged at physiological pH.

Name the basic amino acids.
Lysine, arginine, and histidine have basic R-group side chains. They are positively charged at physiological pH, with histidine being unique in its ability to act both as an acid and a base.

What is unique about histidine among basic amino acids?
Histidine has a side chain with a pKa close to physiological pH, allowing it to be protonated or deprotonated, which is important for its role in enzyme catalysis.

What is histamine, and how does it relate to histidine?
Histamine is a small molecule involved in allergic responses and inflammation. It is not an amino acid and should not be confused with histidine, which is an amino acid.
What are sulfur-containing amino acids?
Amino acids with sulfur-containing side chains include cysteine (containing a thiol group) and methionine (containing a thioether group).
What distinguishes cysteine from methionine in terms of polarity?
Cysteine is polar due to its thiol group (SH), while methionine is nonpolar due to its thioether group (S).
What is the unique structural feature of proline?
Proline has a secondary α-amino group covalently bonded to its side chain, forming a distinctive ring structure.
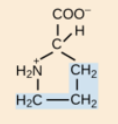
How does proline affect protein structure?
Proline introduces kinks in protein chains, influencing protein folding and stability.
