Lecture 1: Types of Innovation and Technological Change
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
1
New cards
What is Innovation?
* The ability of generate new and useful ideas
* Creation of a new idea or a new technology
* *"the specific instrument of entrepreneurship. It is the act that endows resources with a new capacity to create wealth. Innovation, indeed, creates a resource"* (Drucker, 1985)
* *"…Includes both improvements in technology and better methods or ways of doing things..[innovations] shift competitive advantage"* (Porter, 1990)
* Creation of a new idea or a new technology
* *"the specific instrument of entrepreneurship. It is the act that endows resources with a new capacity to create wealth. Innovation, indeed, creates a resource"* (Drucker, 1985)
* *"…Includes both improvements in technology and better methods or ways of doing things..[innovations] shift competitive advantage"* (Porter, 1990)
2
New cards
Why does innovation matter?
"Under capitalism, innovative activity - which in other types of economies is fortuitous and optional - becomes mandatory, a life-and-death matter for the firm" (William Baumol, 2002)
Innovation is the **long-term engine of growth** for organizations and economies alike.
Innovation is the **long-term engine of growth** for organizations and economies alike.
3
New cards
Innovation For people and society:
* Plastic-Munching Bacteria can make trash biodegradable
* Genetic fortune telling babies will get report cards at both predicting their chances of getting a disease
* Gene Editing to treat deadly diseases
* Drones applications in the Covid-19 crisis
* Genetic fortune telling babies will get report cards at both predicting their chances of getting a disease
* Gene Editing to treat deadly diseases
* Drones applications in the Covid-19 crisis
4
New cards
Innovation For the corporate world:
* Share price
* Growth in product usage
* Growth sales
* Profits
* Growth in product usage
* Growth sales
* Profits
5
New cards
Types of innovation
**Focus:**
* Product vs Process Innovation vs Service Innovation
**Change:**
* Radical vs Incremental Innovation
* Competence enhancing vs Competence destroying innovation
* Component vs Architectural Innovation
**Impact**
* Sustaining vs Disruptive Innovation
**Strategy**
* Business Model innovation
* Open vs Closed innovation
* Platform Innovation
* Product vs Process Innovation vs Service Innovation
**Change:**
* Radical vs Incremental Innovation
* Competence enhancing vs Competence destroying innovation
* Component vs Architectural Innovation
**Impact**
* Sustaining vs Disruptive Innovation
**Strategy**
* Business Model innovation
* Open vs Closed innovation
* Platform Innovation
6
New cards
Product vs process
**Product innovation** can enable process innovation
* Development of advanced robots (PRODUCT) enables the implementation of processes that allow using robots in manufacturing to increase the speed and efficiency of production (PROCESS
**Process innovation** can enable product innovation
* A new metallurgical technique (PROCESS) enabled the development of the bicycle chain which in turn enabled the development of multiple-gear bicycles (PRODUCT)
What is a product innovation for one organization might be a process innovation for another
* UPS creates a new distribution service (product innovation) that enables its customers to distribute their goods more widely or more easily (process innovation)
* Development of advanced robots (PRODUCT) enables the implementation of processes that allow using robots in manufacturing to increase the speed and efficiency of production (PROCESS
**Process innovation** can enable product innovation
* A new metallurgical technique (PROCESS) enabled the development of the bicycle chain which in turn enabled the development of multiple-gear bicycles (PRODUCT)
What is a product innovation for one organization might be a process innovation for another
* UPS creates a new distribution service (product innovation) that enables its customers to distribute their goods more widely or more easily (process innovation)
7
New cards
Radical vs incremental
\
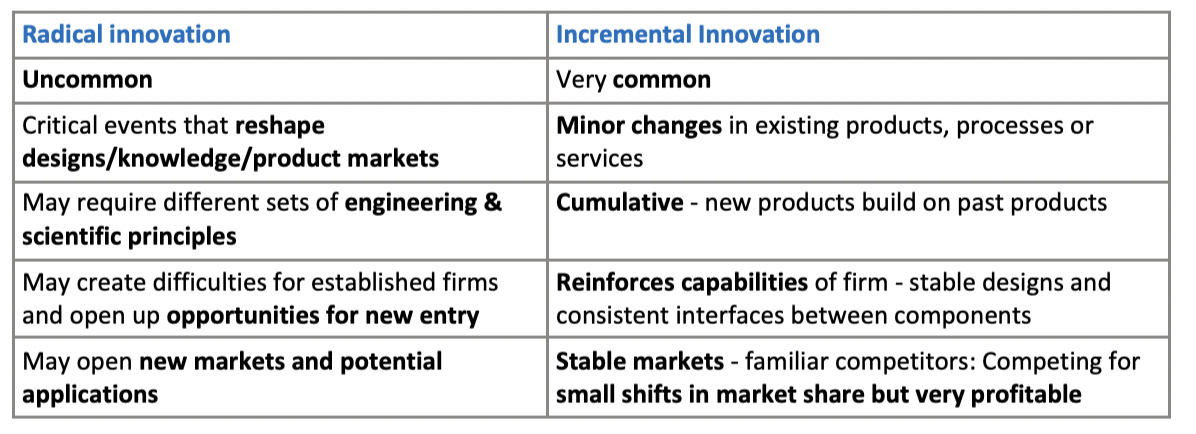
8
New cards
Competence enhancing vs destroying innovation
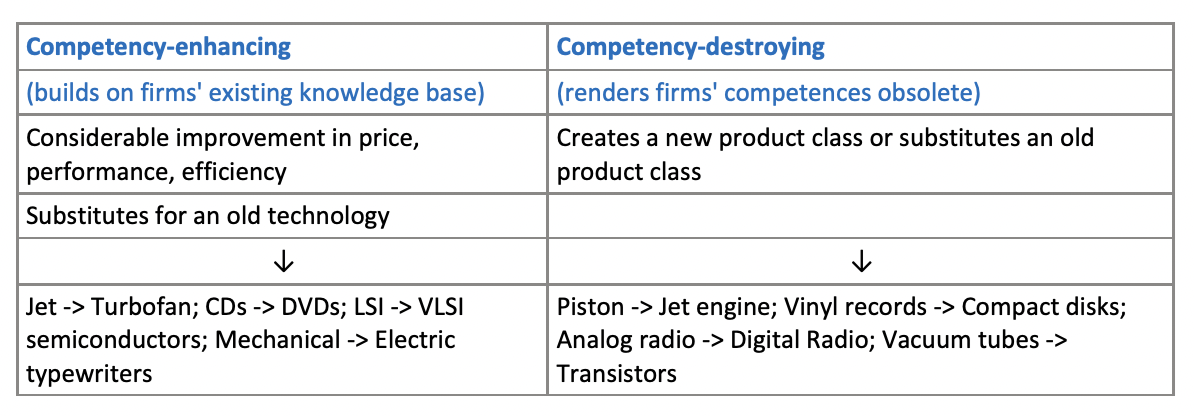
9
New cards
Component vs Architectural
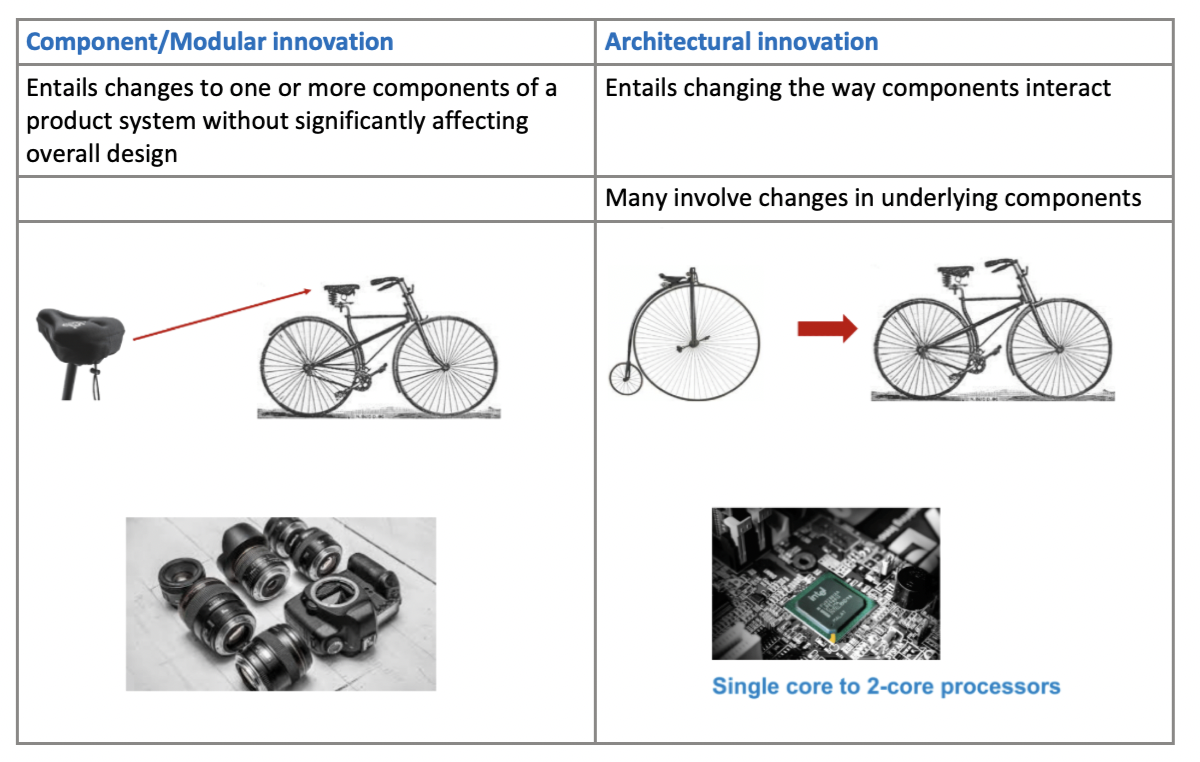
10
New cards
Sustaining vs Disruptive
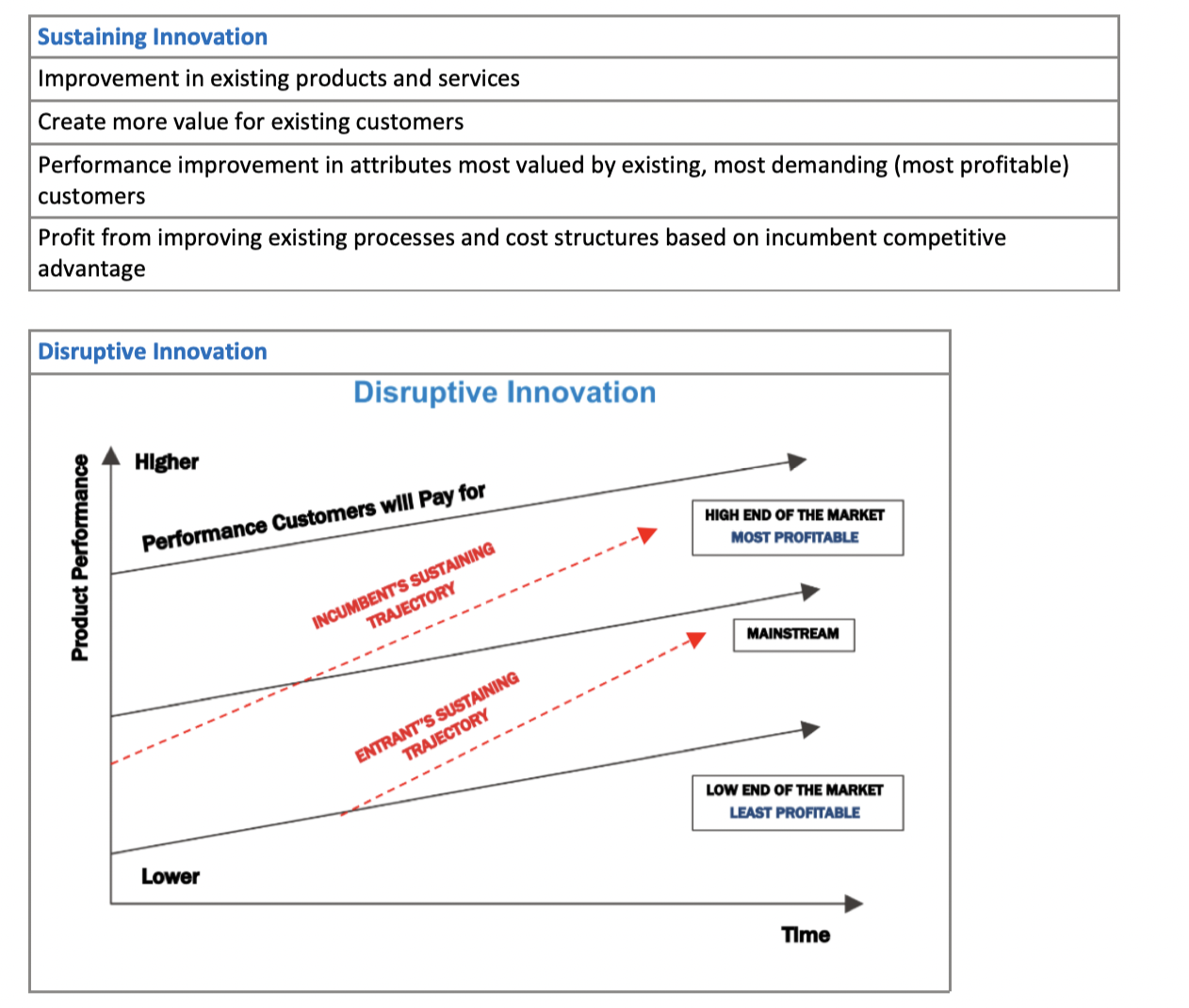
11
New cards
Disruption in the **steel industry:** Integrated steel companies vs Mini Mills
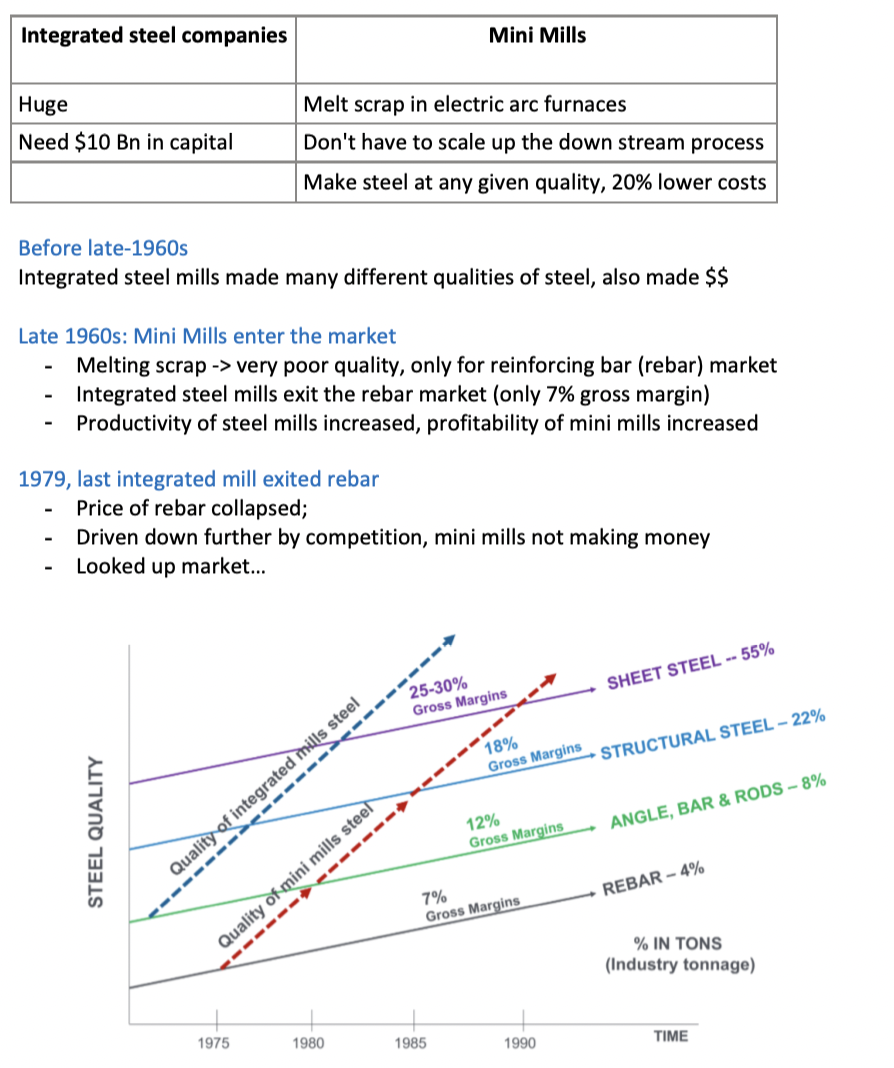
12
New cards
__Disruptive innovation: The innovator's dilemma__
"The highest performing companies, therefore, have well developed systems for killing ideas that their customers don’t want. As a result, these companies find it very difficult to invest adequate resources in disruptive technologies –lower margin opportunities that their customers don’t want –until their customers want them. And by then it is too late.” (Christensen, 1997, p. 265) \n \n **The Dilemma**: The logical, competent decisions of management that are critical to the success of their companies are also the reasons why they lose their positions of leadership
13
New cards
How useful is the theory of Disruptive Innovation?
The theory of disruptive innovation provides:
* “a generally useful warning about managerial myopia”
* “a useful reminder of the importance of testing assumptions, seeking outside information, and other means of reducing myopic thinking”
* “describes case examples of dysfunction and failure, __not what the average business may do__"
* “a generally useful warning about managerial myopia”
* “a useful reminder of the importance of testing assumptions, seeking outside information, and other means of reducing myopic thinking”
* “describes case examples of dysfunction and failure, __not what the average business may do__"
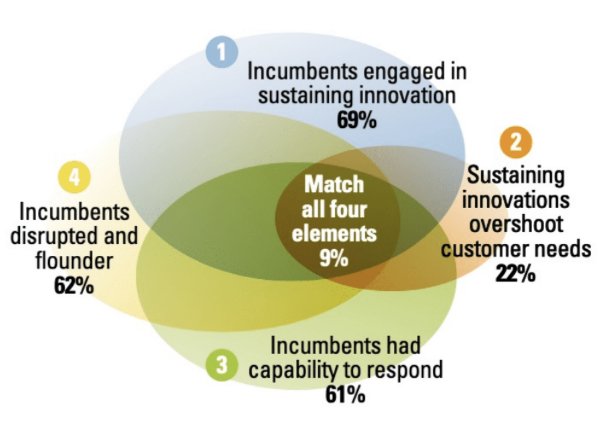
14
New cards
The inflection point
"The **inflection point** - is a change in the business environment that dramatically shifts some element of your activities, throwing certain taken-for-granted assumptions into question. Someone, somewhere, sees the implications, but all too often they are not heard. That someone might be you!”
15
New cards
__Types of Innovation:__ __**Business Model**__
Business model articulates the **customer value proposition**, it identifies a **market segment**, and it specifies the **revenue generation mechanisms**

16
New cards
Open vs Closed Innovation
**Open innovation** - is a **distributed innovation process** based on **purposively managed knowledge** flows across **organizational boundaries**, using **pecuniary** and **non-pecuniary mechanisms** in line with each **organization’s business model**
**Platform innovation** - a platform is a business based on enabling value-creating interactions between external producers and consumers. The platform provides an open, participative infrastructure for these interactions and sets governance conditions for them
**Platform innovation** - a platform is a business based on enabling value-creating interactions between external producers and consumers. The platform provides an open, participative infrastructure for these interactions and sets governance conditions for them
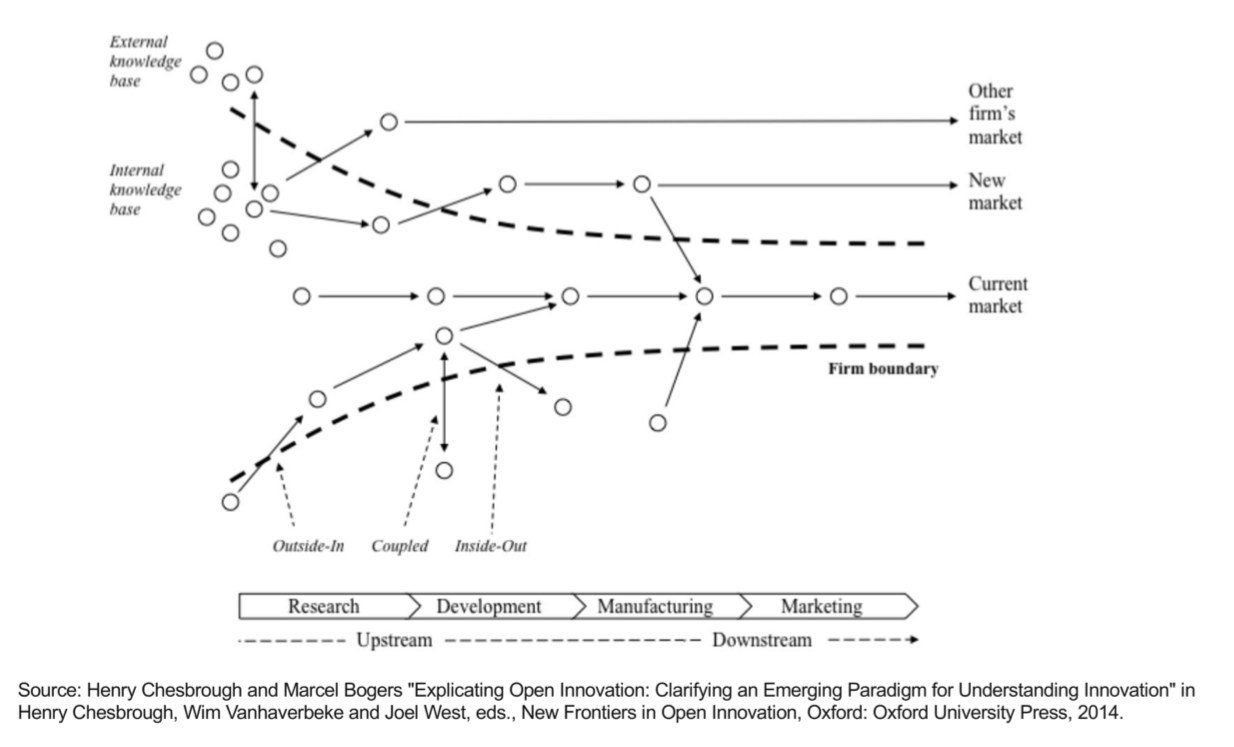
17
New cards
Path dependency, paradigms and trajectories
**Technological Paradigms**
* Thought structure or way of thinking (about a problem)
* Paradigms identify the problems to be addressed, and close off other approaches
**The Cumulative Nature of Technological Knowledge**
* Technologies build on one another
* Path Dependent Trajectories
“...we shall define a ‘t**echnological paradigm**’ as ‘model’ and a ‘pattern’ of solution of selected technological problems, based on selected principles derived from natural sciences and on selected material technologies...As ‘normal science’ is the ‘actualization of a promise’ contained in a scientific paradigm, so is ‘technical progress’ defined by a certain ‘technological paradigm’.
We will define a **technological trajectory** as the pattern of ‘normal’ problem solving activity(i.e. of ‘progress’) on the ground of a technological paradigm”
* Thought structure or way of thinking (about a problem)
* Paradigms identify the problems to be addressed, and close off other approaches
**The Cumulative Nature of Technological Knowledge**
* Technologies build on one another
* Path Dependent Trajectories
“...we shall define a ‘t**echnological paradigm**’ as ‘model’ and a ‘pattern’ of solution of selected technological problems, based on selected principles derived from natural sciences and on selected material technologies...As ‘normal science’ is the ‘actualization of a promise’ contained in a scientific paradigm, so is ‘technical progress’ defined by a certain ‘technological paradigm’.
We will define a **technological trajectory** as the pattern of ‘normal’ problem solving activity(i.e. of ‘progress’) on the ground of a technological paradigm”
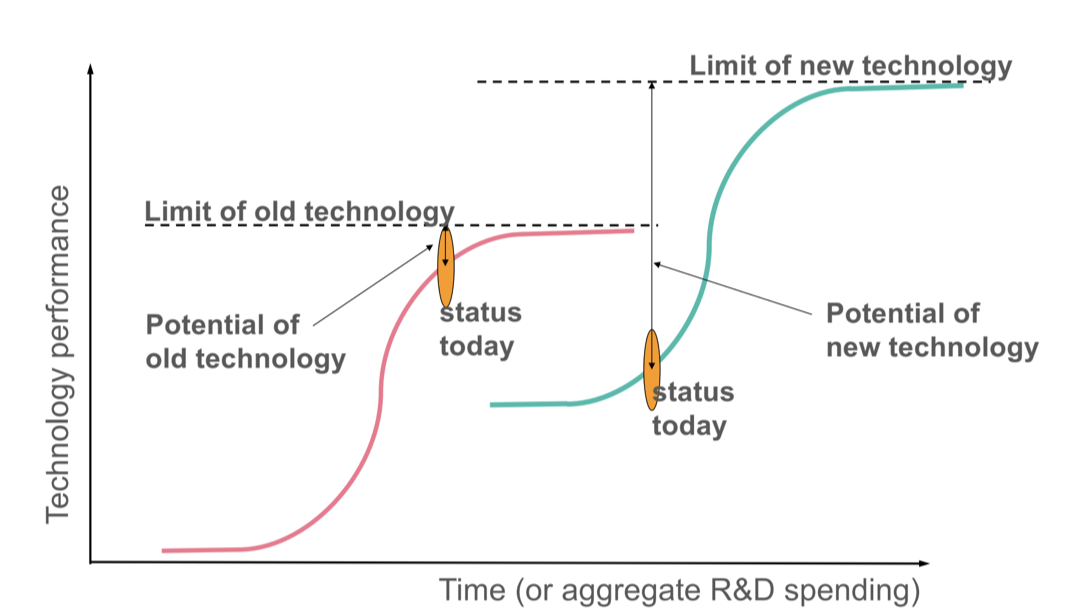
18
New cards
Consequences of technological change
* Newly emerging technologies attract **investments**
* New skills and expertise **(human capital)** are generated
* New **industries** begin to evolve
* New technological opportunities lead to a **redistribution** of profitable activities from old sectors to new sectors
* New patterns of **industrial relations**, national/international **regulations** emerge
* New skills and expertise **(human capital)** are generated
* New **industries** begin to evolve
* New technological opportunities lead to a **redistribution** of profitable activities from old sectors to new sectors
* New patterns of **industrial relations**, national/international **regulations** emerge
19
New cards
Technological change: key learning points
* Technological change is typically **cumulative** and **evolutionary**
* Technological development is **not a smooth, automatic process**
* Some changes can be retrospectively identified as ‘**revolutionary**’ in nature, leading to ‘**technological revolutions**’ or new ‘**techno-economic paradigms**’
* Technological change has major **implications** for the **competitiveness** of firms
* Technological development is **not a smooth, automatic process**
* Some changes can be retrospectively identified as ‘**revolutionary**’ in nature, leading to ‘**technological revolutions**’ or new ‘**techno-economic paradigms**’
* Technological change has major **implications** for the **competitiveness** of firms