Labor & Birth: Procedures, Complications, & Nursing Care
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key terms and definitions related to labor and birth procedures, complications, and nursing care.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
External Cephalic Version (ECV)
An attempt to turn the fetus from a breech or shoulder presentation to a vertex presentation for birth.
Bishop Score
A scoring system used to assess the favorability of the cervix for induction of labor.
Non-Stress Test (NST)
A non-invasive test in the 3rd trimester which monitors the fetal heart rate response to fetal movement.
Interpretation
Reactive if two accelerations in 20 minutes
Otherwise it is categorized as non-reactive
Biophysical Profile (BPP)
A combination of fetal heart rate monitoring and ultrasound to visualize movement and responses
Measures:
§ Fetal Heart Rate (NST) max. 2 pts
§ Fetal breathing movements max 2 pts
§ Gross body movements max 2 pts
§ Fetal tone max 2 pts
§ Qualitative amniotic fluid volume max 2 pts
Biophyssical porfile (BPP) score
Score of 8-10 is normal, low risk of asphyxia
Score of 4-6 abnormal, suspect chronic fetal asphxia
Score of less than 4 is abnormal, strongly suspect chronic fetal asphyxia
what is asphyxia
A condition arising from insufficient oxygen supply to the body, particularly affecting the brain and other vital organs, often leading to serious complications in the baby
techniques for inductioon
1st-Cervical ripening if necessary
Chemical methods (prostaglandins)
Mechanical methods (dilators, laminaria)
2nd-Oxytocin (Pitocin) administration
Diluted in IV fluids and given as a secondary infusion May require one-on-one nursing care at the bedside
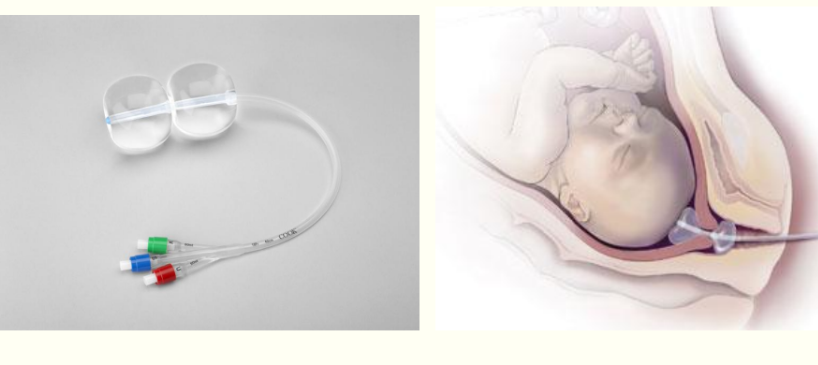
cooks catheter
cervical ripening balloon
opens up the cervix more
augmentation of labor
When labor starts spontaneously but progress is slow, it is often augmented through
• Oxytocin administration
• Amniotomy (AROM)
nurses role
Education: reasons, what to expect
• Electronic monitoring: assess FHR & contractions Q15 min and with every change in dose during the first stage of labor; Q5 min during the active pushing phase of the second stage of labor.
• Monitor maternal VS Q30-60 minutes and with every change
in dose
tachysystole: more than five contractions in 10 minutes averaged over a 30-minute window.
nurses role continued in induction and augmentation
• Monitor for Pitocin side effects, including N/V, HA, and water
retention
Assess fluid balance.
• Limit IV intake to 1000 mL in 8 hrs.
• Urine output
• Monitor for complications including tachysystole, placental abruption, and uterine rupture
• Perform vaginal examination as indicated
• Psychosocial support of laboring family
• Document
nurses role in amniotomy
• Education
• Assess FHR rate before
• Place extra chux pads to absorb fluid
• Assist provider with positioning for SVE
• Note TACO
• Time
• Amount
• Color
• Odor
• Reassess FHR
• Risk for prolapsed cord if fetal head is not engaged
• Ongoing assessment: s/s of infection
external cephalic version
An attempt to turn the fetus from a breech or shoulder presentation to a vertex presentation for birth
§ At 37 weeks, the success rate for ECV is approximately 65% and the risk for cesarean birth is reduced by 50%
§ Ultrasound scanning used during procedure
§ NST and Informed consent before procedure
§ Contraindications to ECV
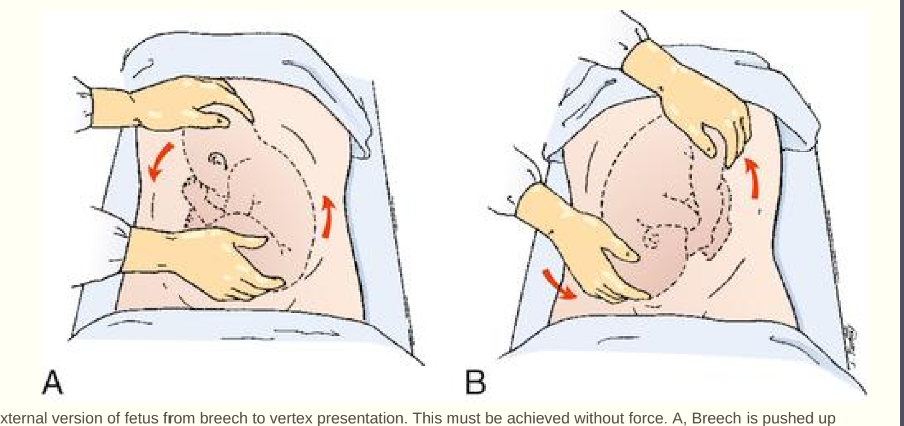
nurses role in ecv
during: fhr monitoring, maternal vs and comfort
after: maternal vs, uterine activity and bleeding, fhr monitoring at leaser one hour, RH ig admin
Shoulder Dystocia
When the anterior fetal shoulder cannot pass under the maternal pubic arch during delivery.
Risk factors:
• Fetal size >4000g
• Maternal pelvic abnormalities
• Maternal diabetes
• Hx of shoulder dystocia
• Prolonged 2nd stage of labor
shoulder dystocia
Remember the HELPERR mnemonic
§ H: Call for help
§ E: Evaluate for episiotomy
§ L: Legs (McRoberts maneuver)
§ P: suprapubic pressure
§ E: Enter for rotational maneuvers
§ R: Remove the posterior arm
§ R: Roll the patient to hands and knees
Cesarean Birth
Delivery of the fetus through a transabdominal incision of the uterus.
indication for c section
Reasons a cesarean happens:
§ Previous cesarean with vertical uterine incision
§ Multiple previous cesareans
§ Dystocia
§ Fetal malpresentation (breech, footling, etc.)
§ Non-reassuring FHR
§ Multiple gestation
§ Suspected fetal macrosomia
§ Suspected cephalopelvic disproportion (CPD)
§ Placenta previa
Placenta Previa
Condition where the placenta is implanted in the lower uterine segment near or over the internal cervical os.
hree types
• Complete placenta previa
• Marginal placenta previa
• Low-lying placent
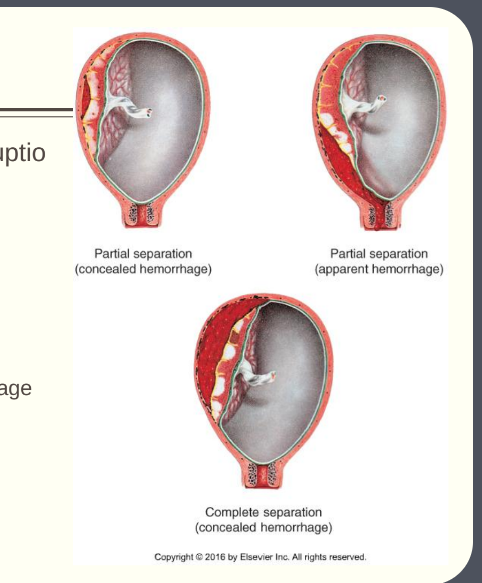
placental abruption
§ Premature separation of placenta (abruptio placentae)
§ Can be marginal, partial or complete
§ Classification systems
§ Grades 1 (mild), 2 (moderate), 3 (severe)
§ With or without visible bleeding
§ Visible bleeding = apparent hemorrhage
§ Non-visible bleeding = concealed hemorrhage
§ Risks: Maternal hypertension, trauma, oxytocin administration
§ Pain? yes
TOLAC
Trial of Labor after Cesarean, an attempt to have a vaginal birth after a previous cesarean.
VBAC
Vaginal Birth after Cesarean, a delivery option for women who previously had a cesarean.
Amniotic Fluid Embolus (AFE)
A serious condition involving respiratory and circulatory collapse due to amniotic fluid entering circulation.
Prolapsed Umbilical Cord
A medical emergency where the umbilical cord slips ahead of or alongside the presenting part of the fetus.
Obesity in Pregnancy
A condition where a pregnant woman has a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater, posing increased risks for complications.
Obese pregnant women are at increased risk for complications:
§ Spontaneous abortion and stillbirth
§ Pregnancy-associated hypertensive disorders
§ Gestational diabetes
§ Fetal congenital abnormalities
§ Cesarean birth
§ Venous thromboembolism
inteprofessional care for obesity
§ Intrapartum Challenges:
§ Standard furniture may not be large enough
§ Fetal monitoring can be difficult
§ Routine procedures require more time and effort
§ Mobility may be a problem
§ Postoperative Challenges:
§ increased risk for blood clot formation
§ Keeping the incision clean and dry to prevent wound infection and promote healing
§ pannus causes area to remain moist
Forceps Delivery
Operative vaginal birth using curved blades to assist in the delivery of the fetus.
Vacuum Extraction
A technique used during labor where a vacuum cup is placed on the fetal head to assist in delivery.
Uterine Rupture
A rare but serious complication during labor, particularly in women with previous uterine surgery.