Bootcamp.com - Cells and Organelles
1/215
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
216 Terms
what are the three main components in a cell membrane?
phospholipids; cholesterol; proteins
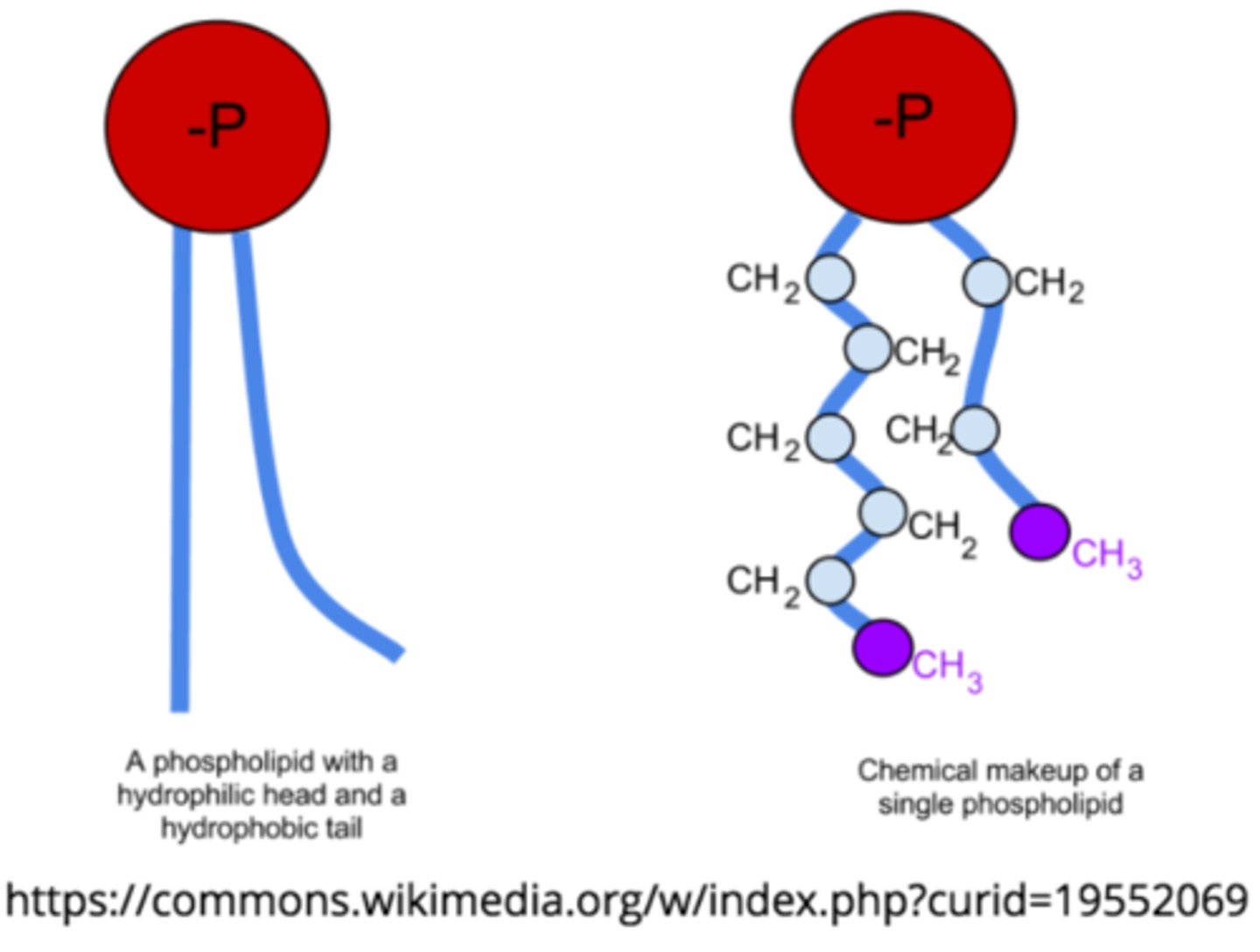
what is the structure of a phospholipid?
glycerol backbone, two fatty acid tails, and a hydrophilic phosphate group
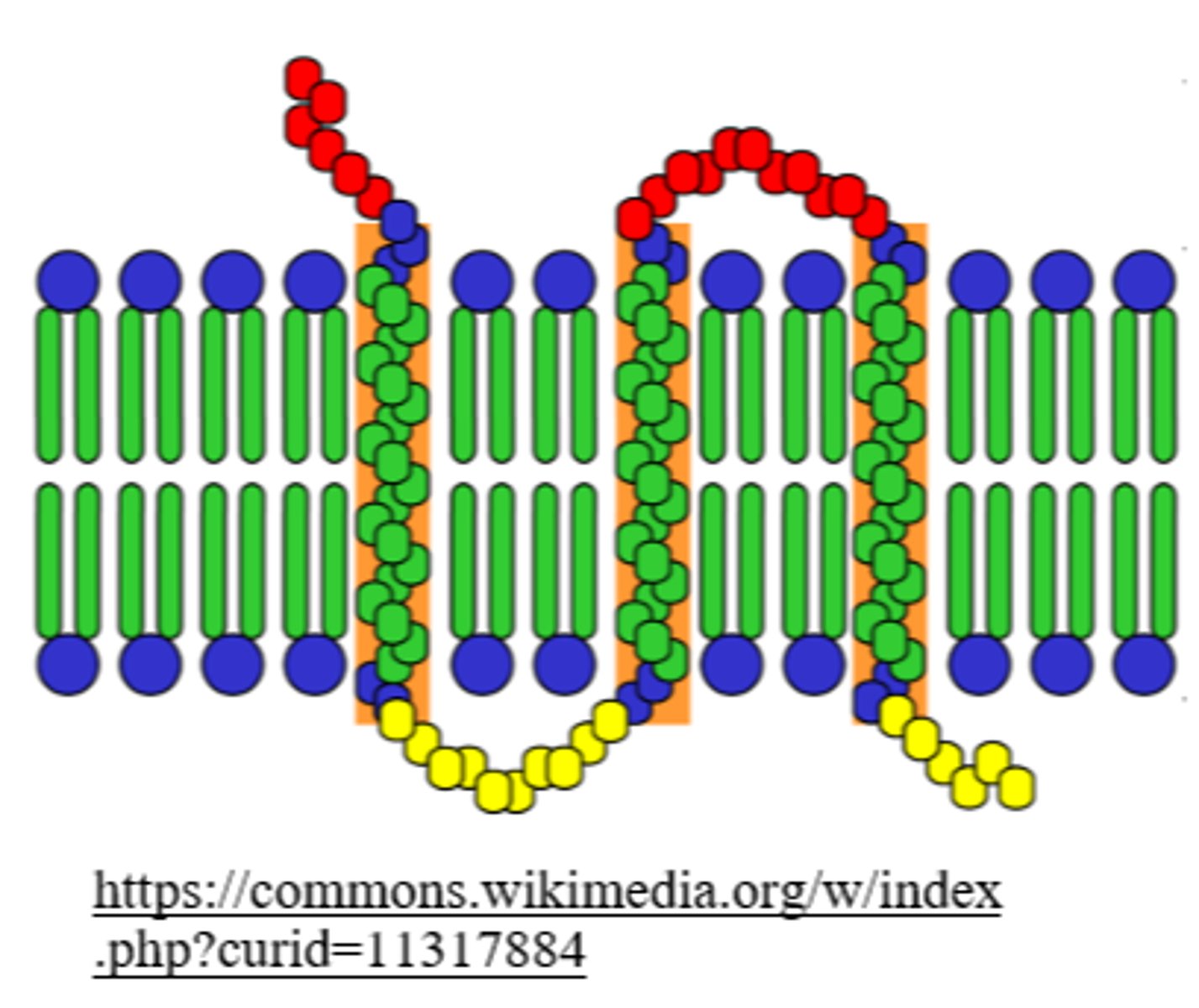
what are the two classes of membrane proteins?
integral; peripheral
_____ membrane proteins are embedded in the core of the plasma membrane
integral
many integral proteins are _____ proteins, meaning they extend all the way through the membrane
transmembrane
integral/transmembrane proteins may function in cell _____, but most tend to transport _____ molecules across the cell membrane
signaling; large, polar (hydrophilic)
_____ membrane proteins do not extend through the entire bilayer
peripheral
what are the three types of peripheral proteins?
receptors; adhesion proteins; recognition proteins
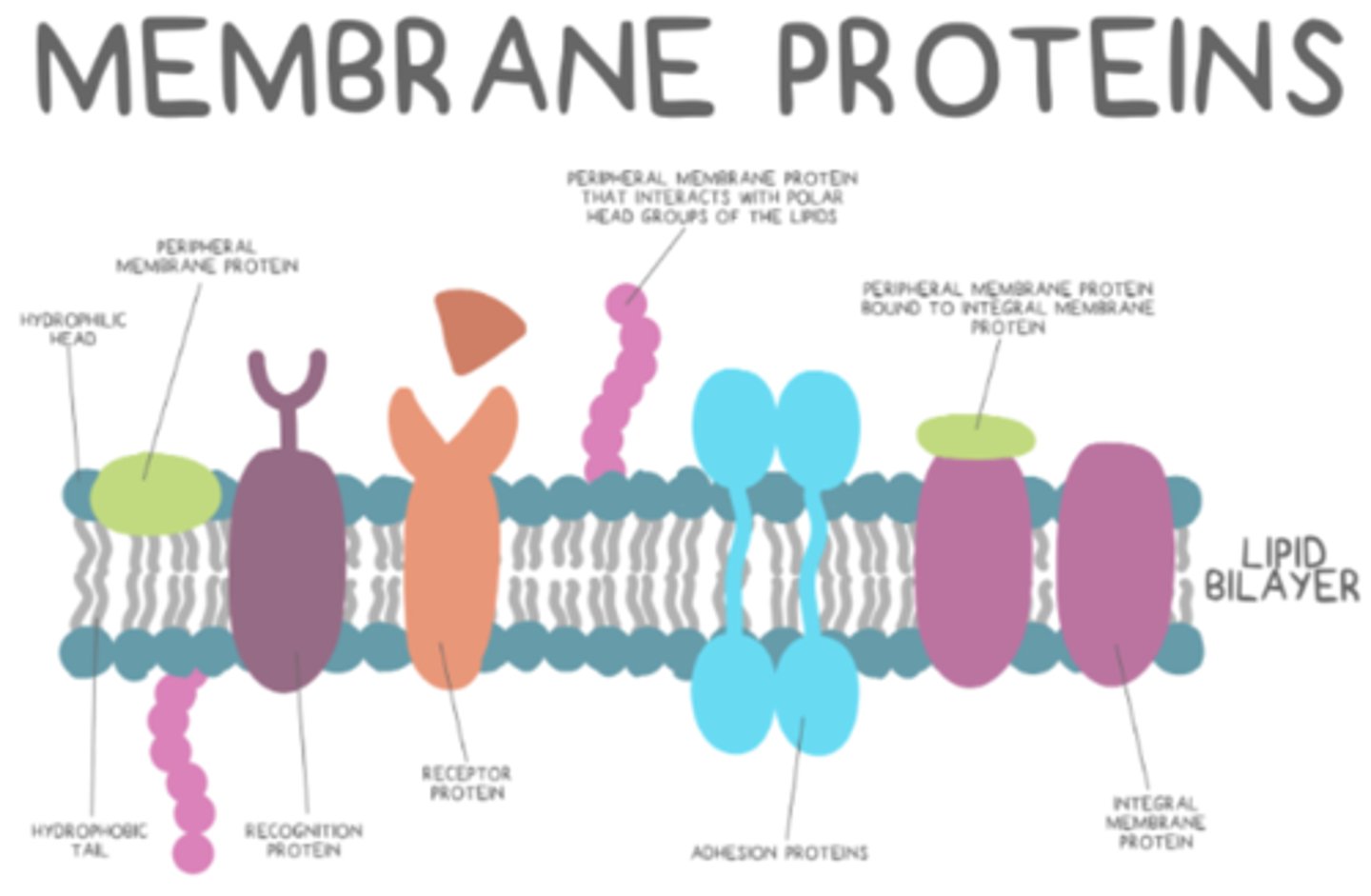
recognition proteins are also known as _____
glycoproteins
ligands that bind to a receptor protein and activate its response are called _______
agonists
ligands that bind to a receptor and prevent it from activating are called _______
antagonists
what are the three main factors that affect membrane fluidity?
temperature; cholesterol; the degree of phospholipid tail unsaturation
saturated fatty acids have the _______ possible number of hydrogens at each carbon, which gives them a _______ shape
highest; straight
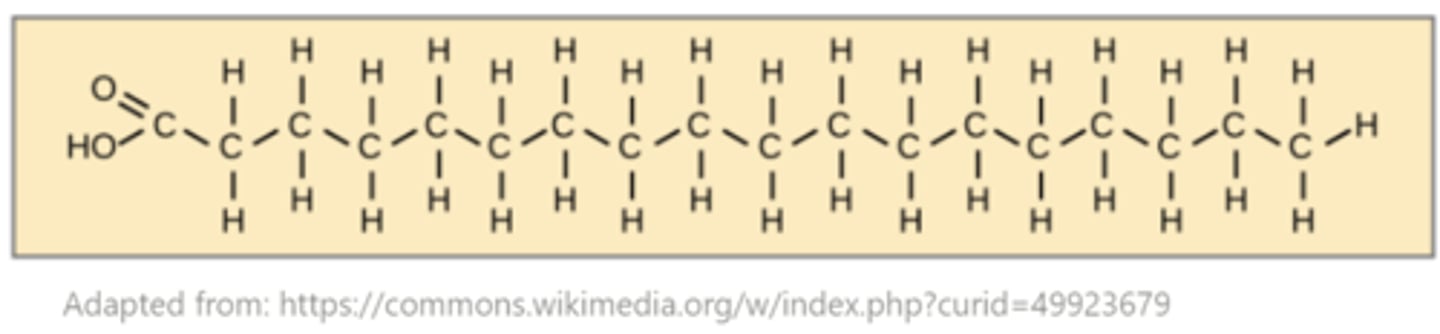
unsaturated fatty acids contain one or more _______
double bonds
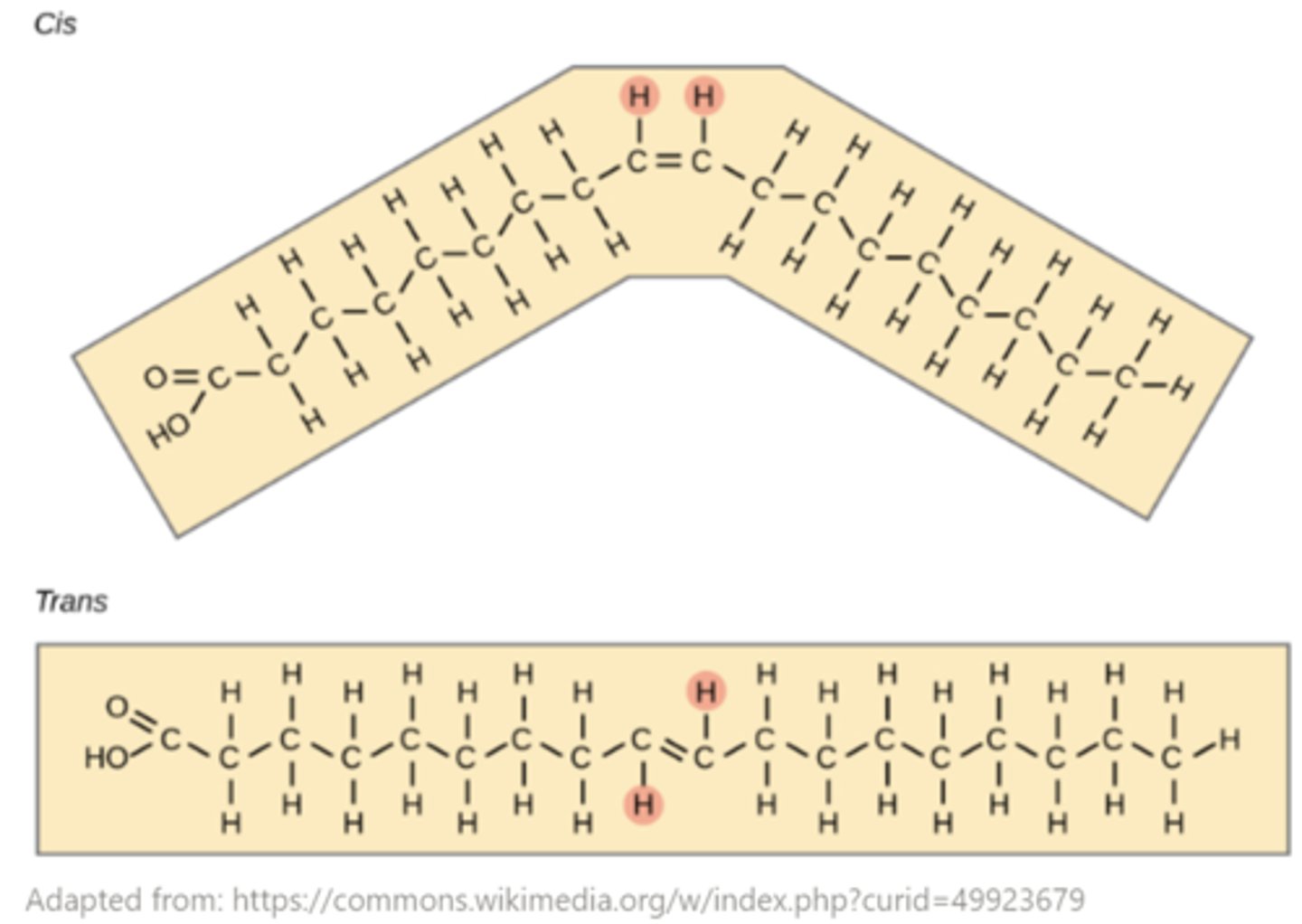
_____ particles can travel directly across the phospholipid bilayer via simple diffusion
small, uncharged, non-polar (hydrophobic)
simple diffusion is the flow of substances _____ their concentration gradient in a _____ consuming process
down; non-energy
_____ does not utilize proteins to help particles across the membrane
simple diffusion
osmosis is a type of _____
simple diffusion
Water is a _____ molecule that can cross the cell membrane via osmosis because it is _____
polar (hydrophilic) ; small
_____ molecules cannot travel directly across the bilayer
large, hydrophilic
_____ describes how large, hydrophilic molecules travel across the bilayer by transmembrane proteins
facilitated transport
what are the three main types of facilitated transport (direction)?
uniport; symport; antiport
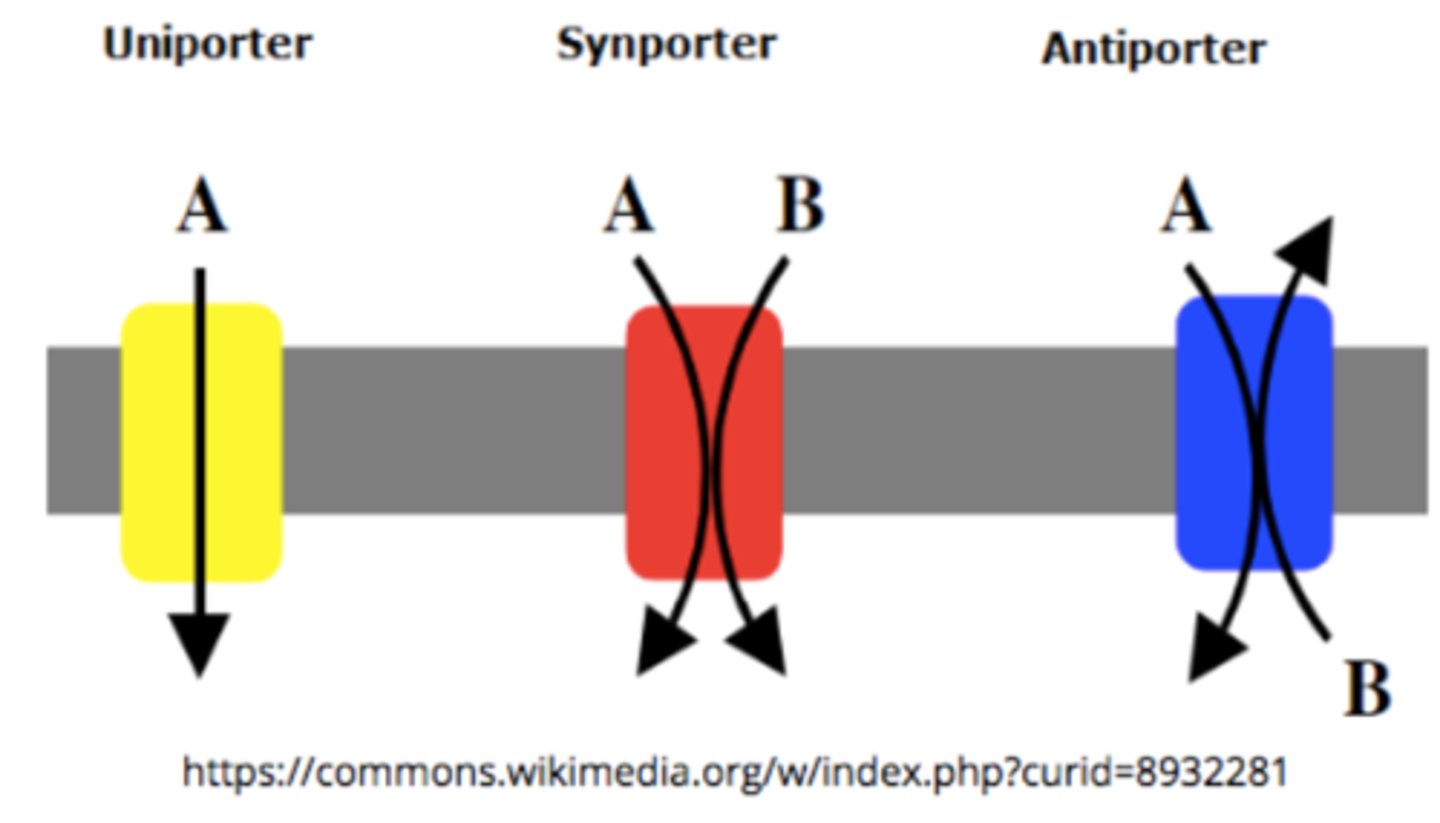
_____ move 1 molecule in 1 direction
uniporters
_____ move 2 molecules in the same (1) direction
symporters
_____ move 2 molecules in opposite (2) directions
antiporters
what are the two classes of transmembrane proteins involved with facilitated transport?
channel; carrier
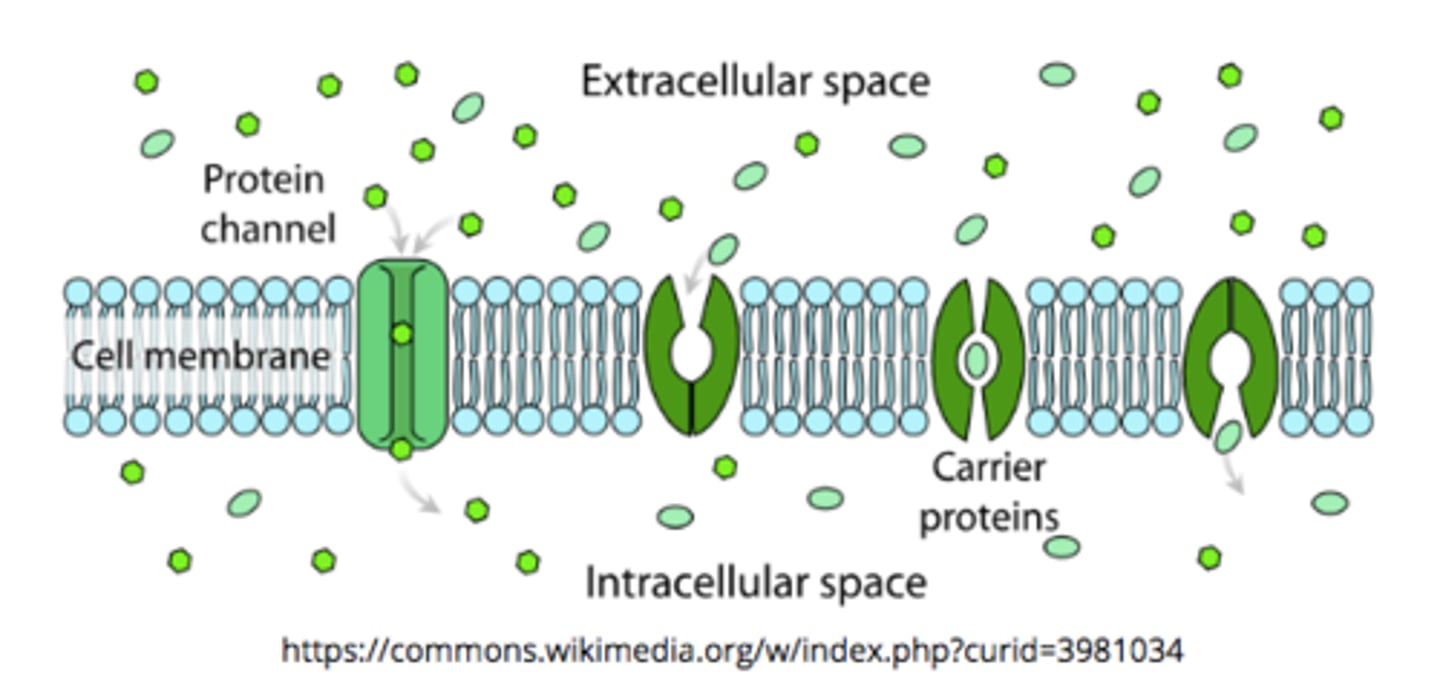
_____ proteins face both the extracellular and intracellular environments of the cell
channel
channel proteins are like tunnels for many _____
small, polar molecules and ions
_____ diffusion describes a type of facilitated transport of particles down their concentration gradient through a _____ protein
passive; channel
porins and ion channels are membrane proteins that aid _____ diffusion
passive
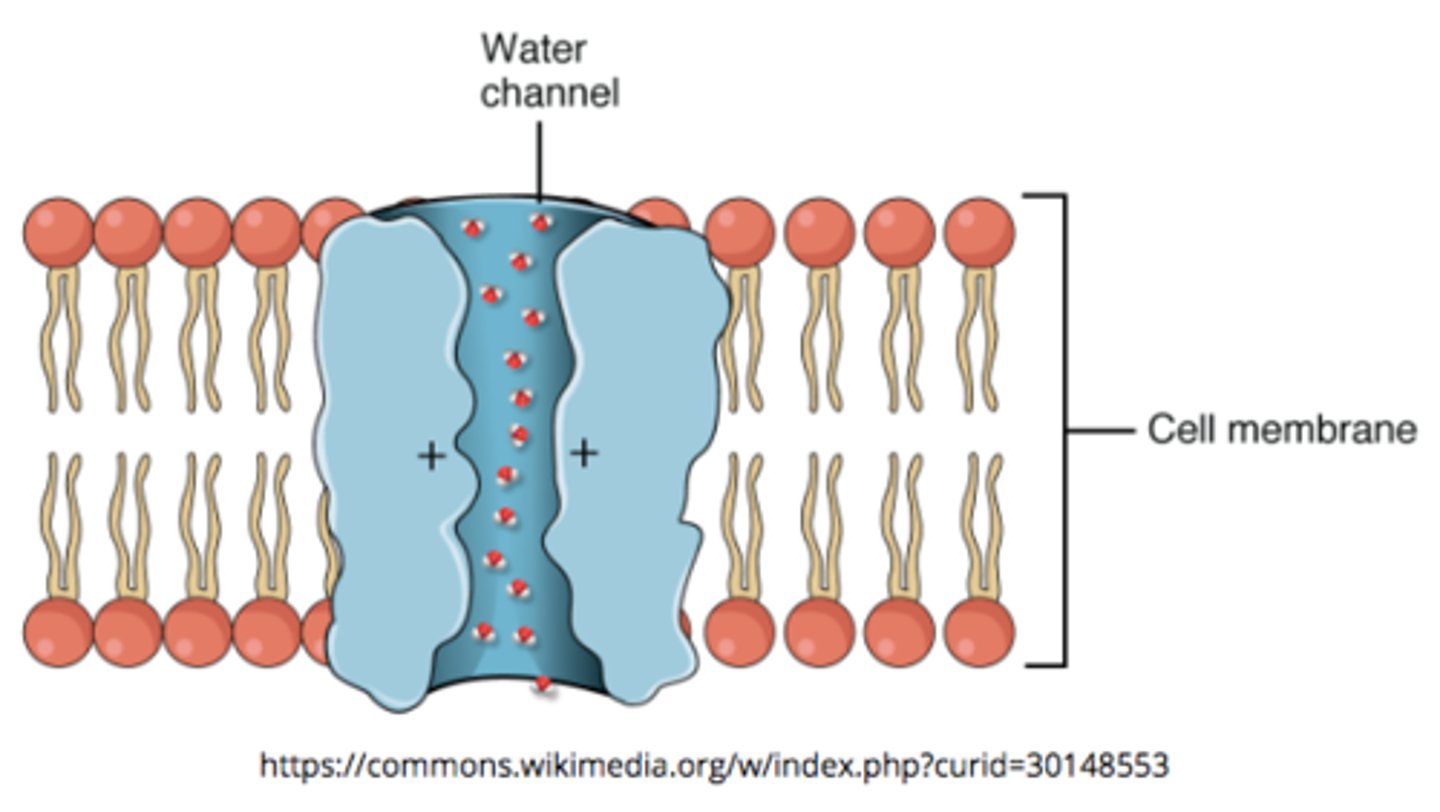
what are aquaporins?
particular type of porin that allows water to flow more rapidly than is possible through simple diffusion alone
_____ change their shape to facilitate the movement of molecules through the protein.
carrier proteins
_____ occurs when particles travel against their concentration gradient, which requires an energy input
active transport
active transport tends to rely upon _____ proteins
carrier
what are the two types of active transport?
primary; secondary
_____ active transport uses the energy released from ATP hydrolysis
primary
the Na+/K+ pump is a form of _____ active transport
primary
the Na+/K+ pump moves _____ out of the cell and _____ into the cell with the hydrolysis of 1 ATP
3 Na+; 2 K+
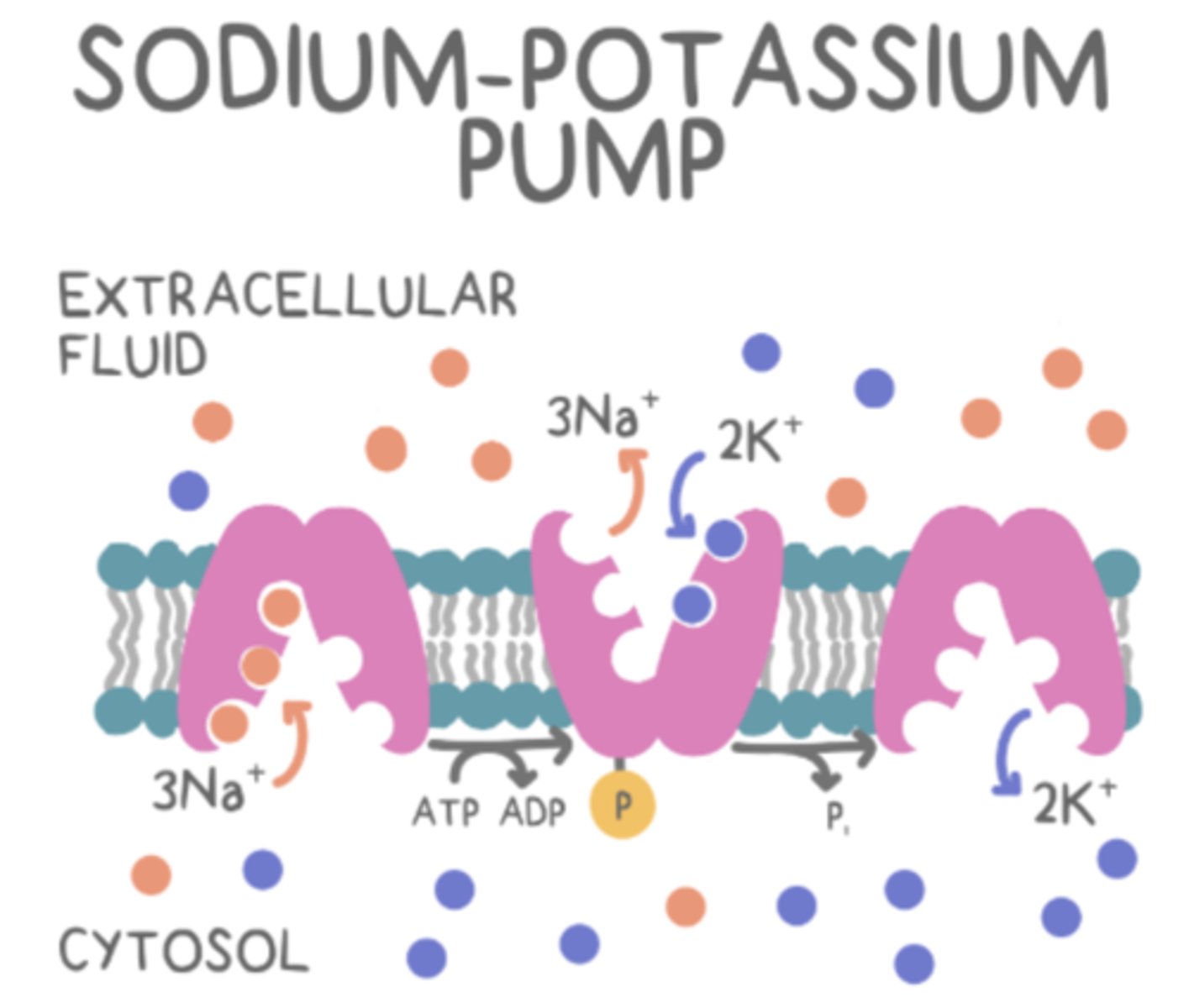
secondary active transport depends on _____ to generate free energy in the form of a concentration gradient
primary active transport
_____ active transport uses free energy to pump other molecules against their concentration gradient
secondary
_____ is bulk transport of large, polar (hydrophilic) molecules
cytosis
what are the two types of cytosis?
endocytosis (in the cell) and exocytosis (out of the cell)
_____ is a type of endocytosis where a cell engulfs undissolved materials
phagocytosis
(cellular eating)
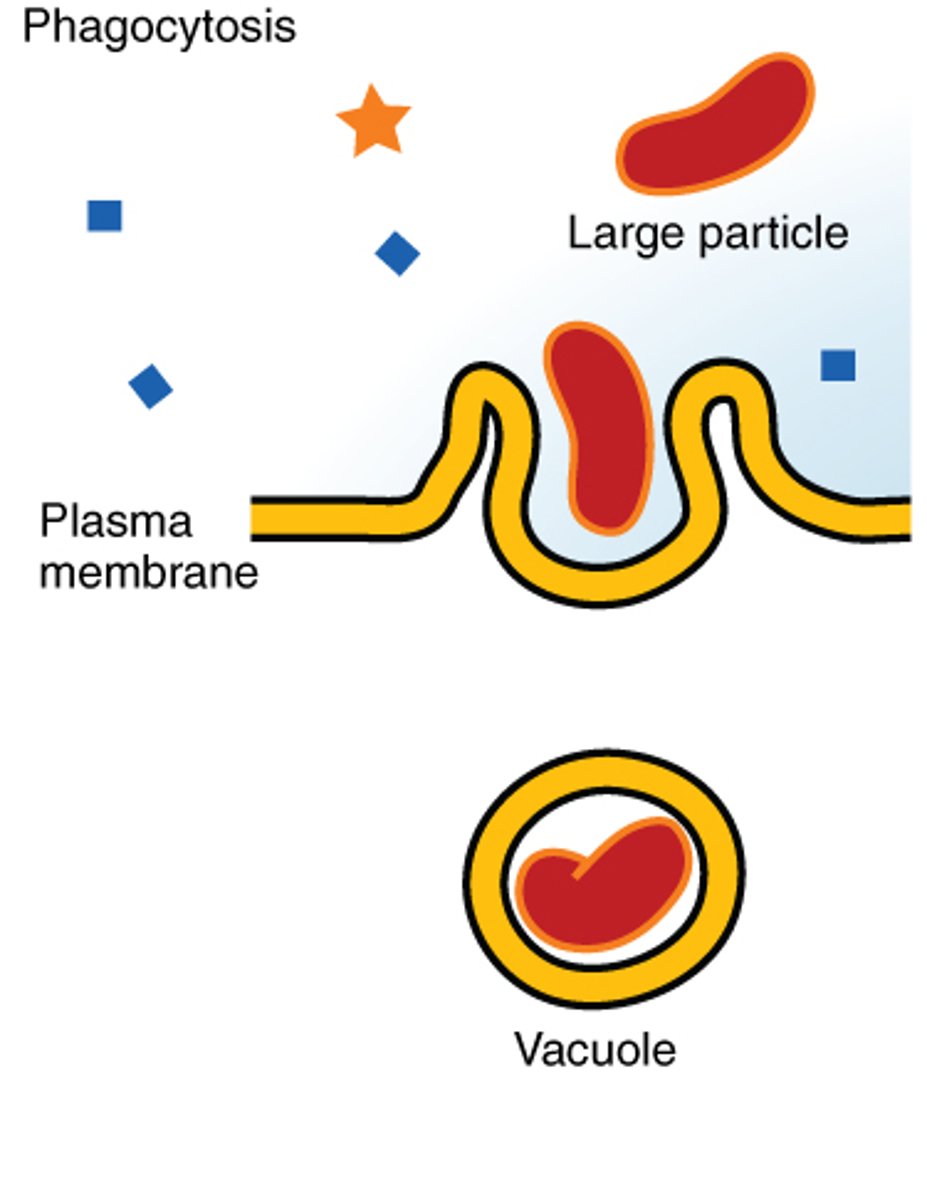
phagocytosis forms _____
vacuoles (phagosomes)
_____ is a type of endocytosis where a cell engulfs dissolved materials
pinocytosis
(cellular drinking)
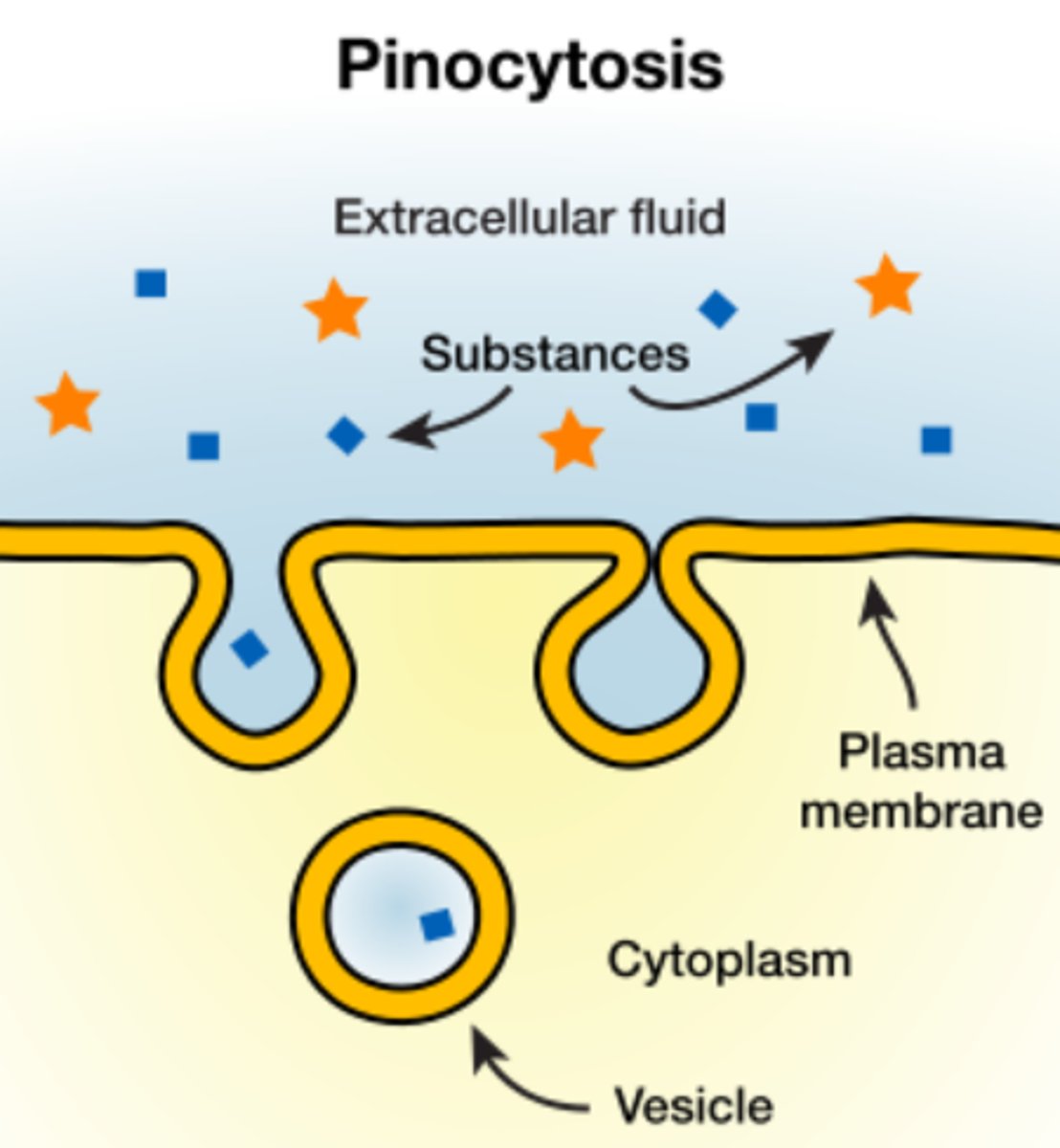
pinocytosis forms _____
vesicles
receptor-mediated endocytosis forms ______
vesicles
what is exocytosis?
process by which materials exit the cell (opposite of endocytosis)
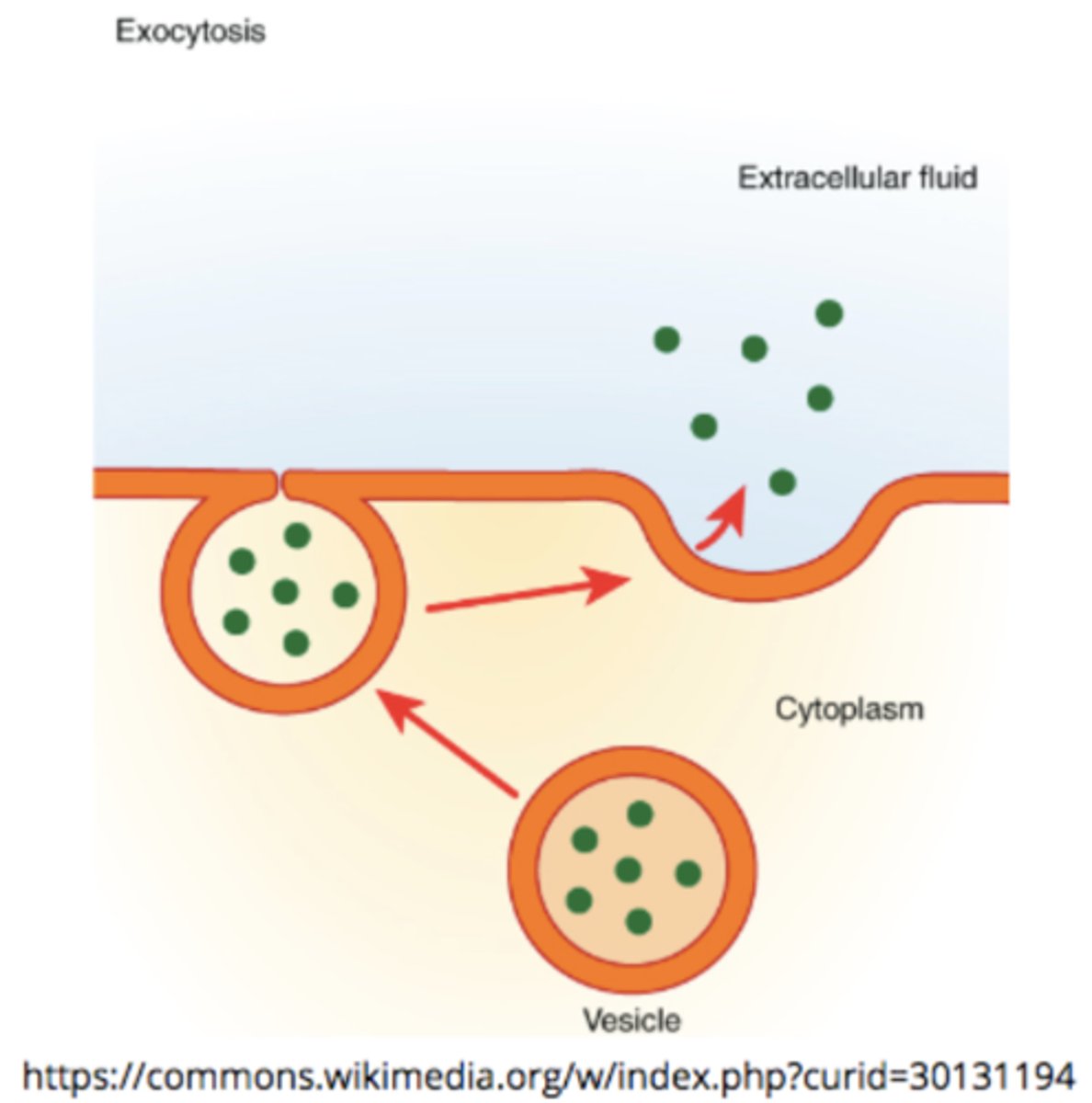
organelles are enclosed by a _____
phospholipid bilayer
membrane-bound organelles are predominately associated with which cell type?
eukaryotes
the _____ is the aqueous intracellular fluid
cytosol
the _____ is everything within the cell (fluid and organelles)
cytoplasm
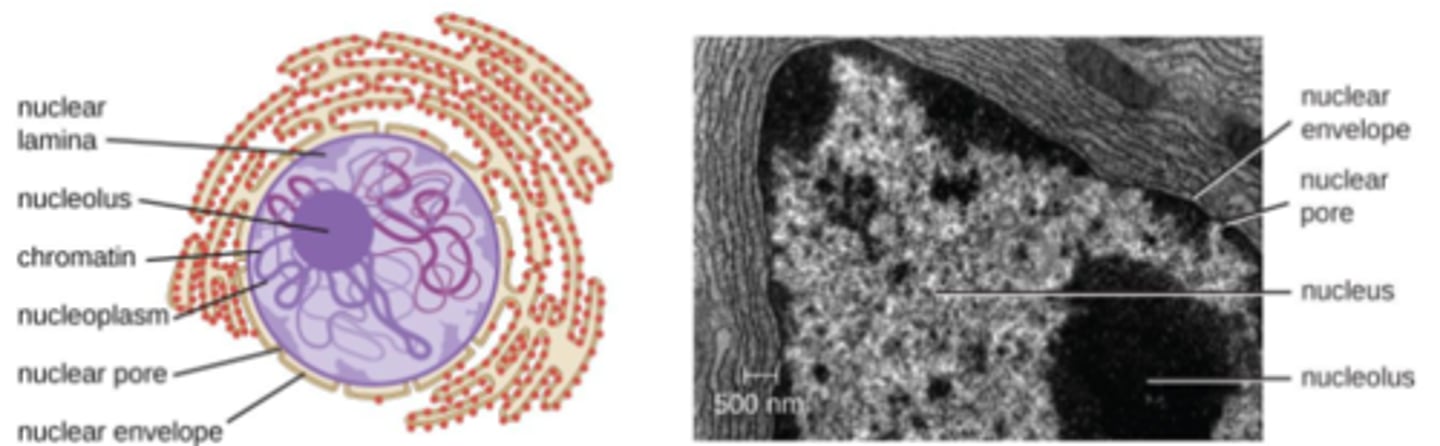
what is the nucleus?
a membrane-enclosed organelle that contains most of a eukaryotic cell's genetic material
do prokaryotes have a nucleus?
no - they have a nucleoid
the nucleus contains an aqueous _____
nucleoplasm
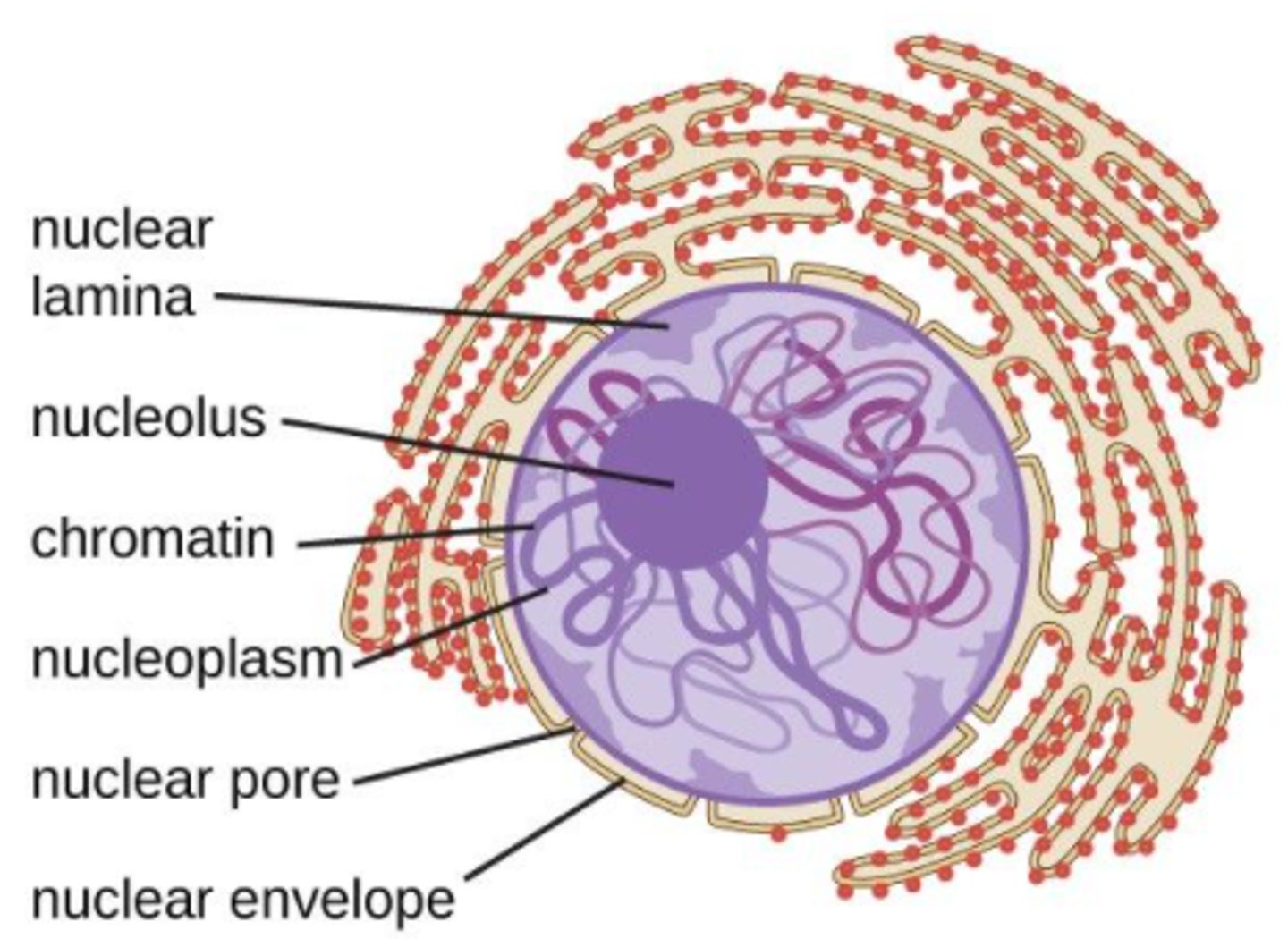
the nucleus has an inner and outer membrane, called the _____
nuclear envelope
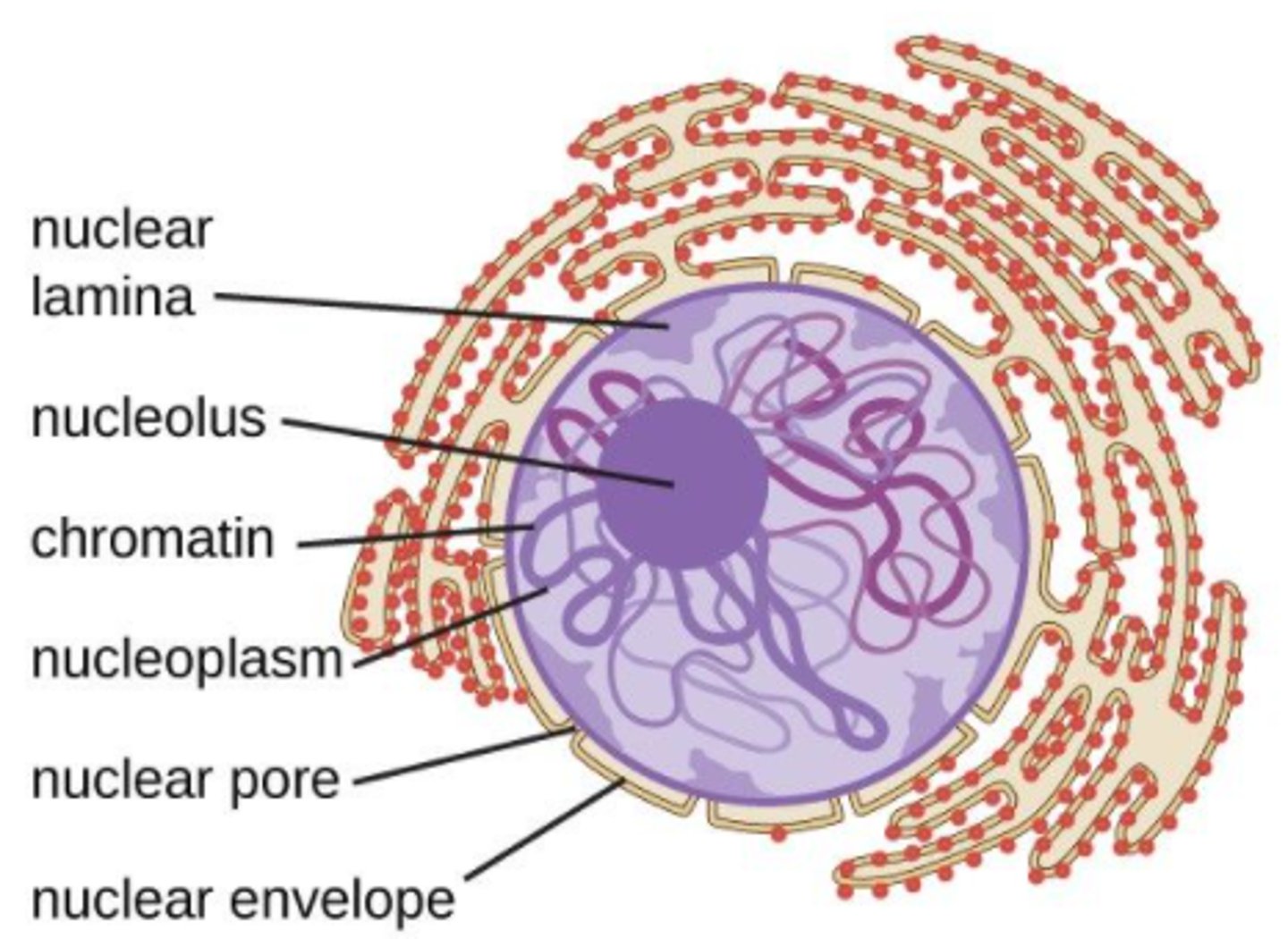
what is the space between the inner and outer nuclear membranes?
perinuclear space
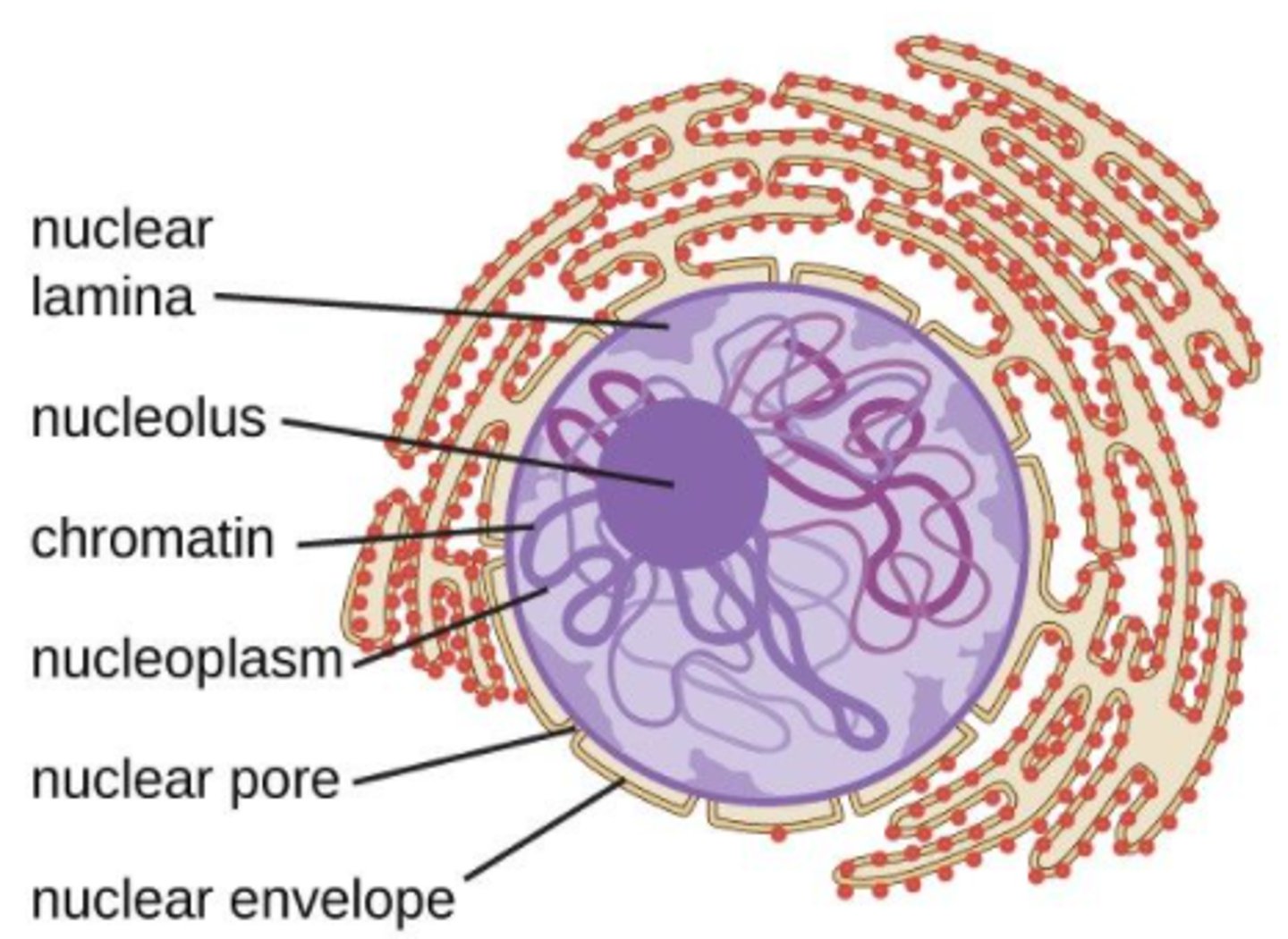
the _____ is a dense and fibrous network of proteins associated with the inner membrane of the nuclear envelope
nuclear lamina
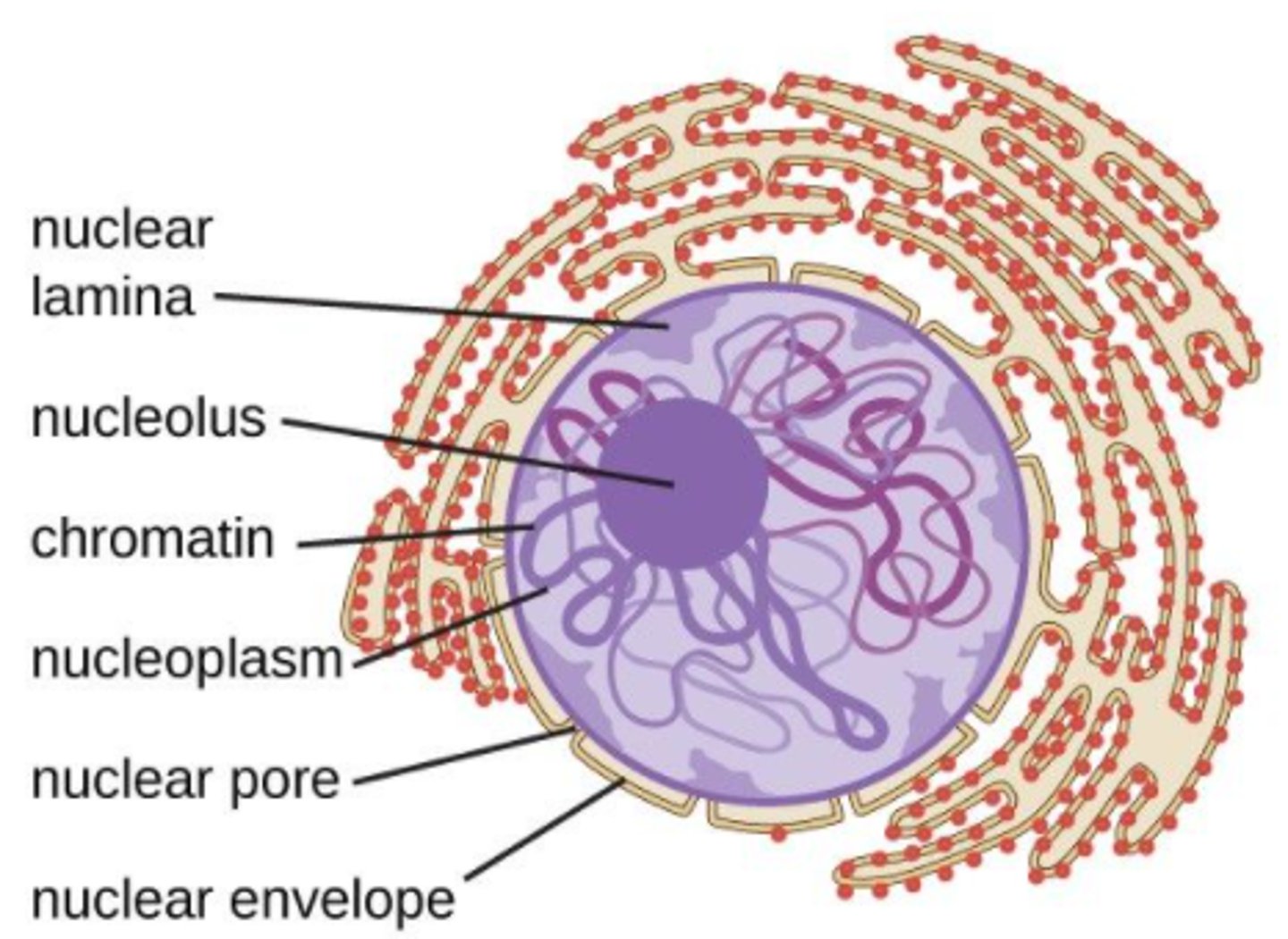
the nuclear lamina is made of _____
intermediate filaments
_____ are a type of intermediate filament that make up the nuclear lamina
lamins
the _____ functions to provide structural support to the nucleus; regulate DNA organization, DNA replication, and cell division
nuclear lamina
the nuclear envelope has holes called _____
nuclear pores
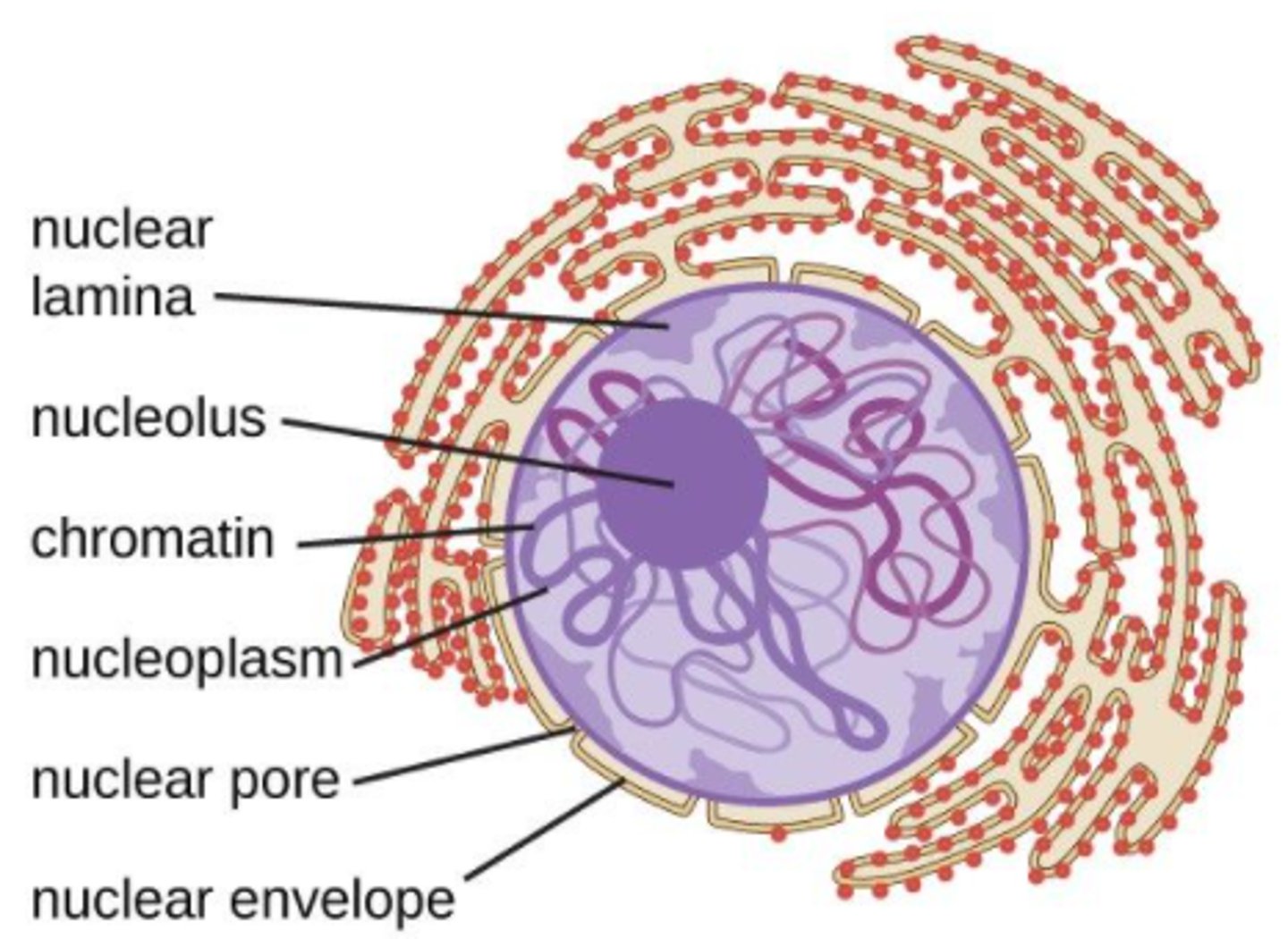
the _____ is a dense region in the nucleus, associated with ribosomal subunit assembly
nucleolus
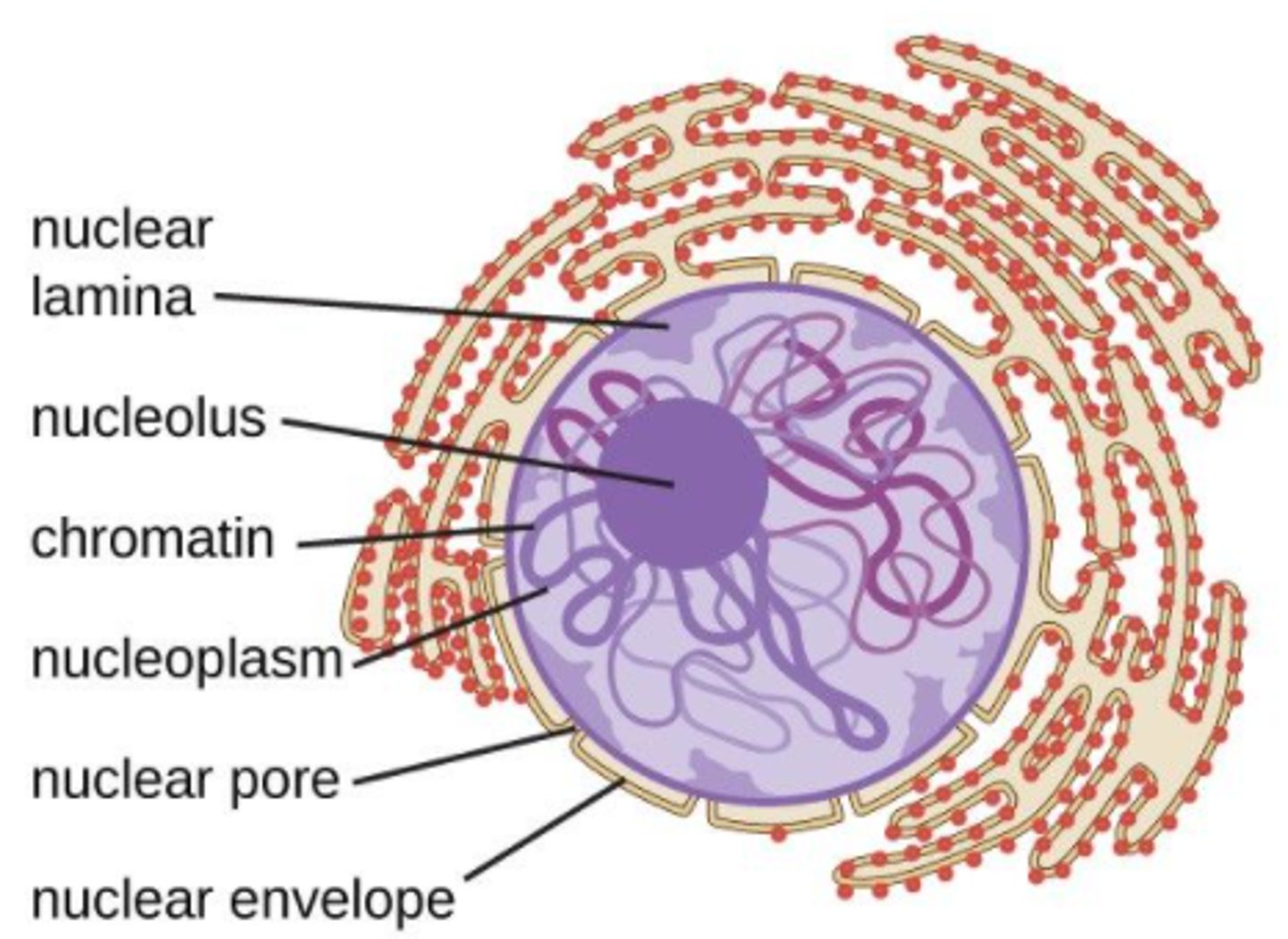
is the nucleolus an organelle?
no - it is not membrane bound
ribosomal subunits contain _____ and _____
ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA); proteins
eukaryotic ribosomal subunits are made in the _______ and assembled in the _______
nucleus; cytosol
what do ribosomes do?
function in the synthesis of proteins
(translation)
what is the structure of a eukaryotic ribosome?
60S + 40S = 80S
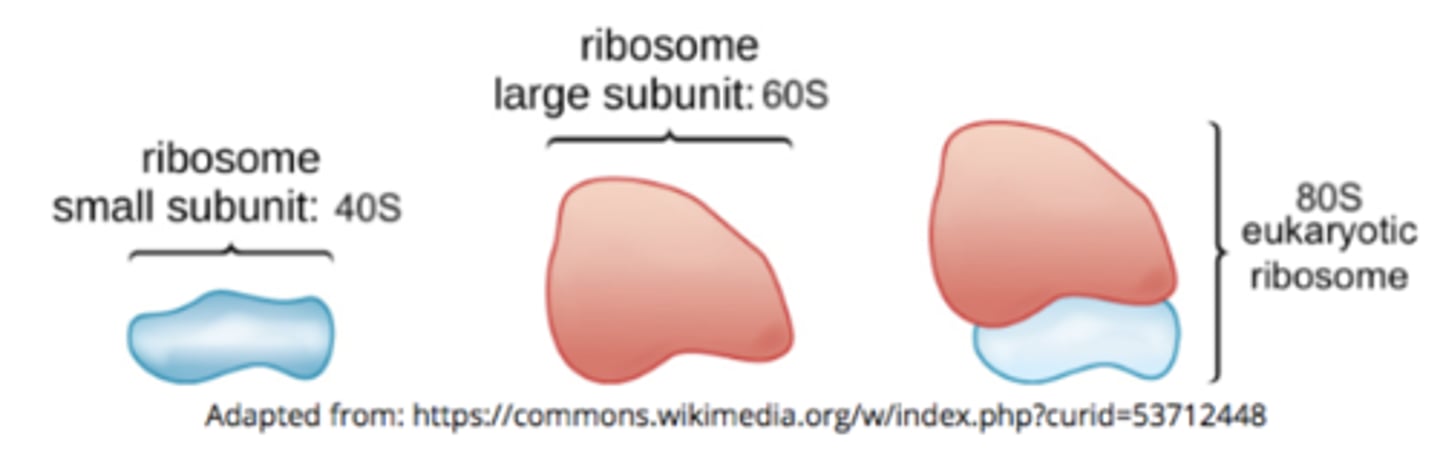
what is the structure of a prokaryotic ribosome?
50S + 30S = 70S
where are ribosomes found?
freely in the cytosol or attached to the rough ER
_____ ribosomes tend to make proteins that function within the cytosol of the cell
free
ribosomes that bind to the rough ER will synthesize proteins _____
into the rough ER lumen
the rough ER is continuous with the _____, which means the ER lumen is continuous with the _____
outer nuclear membrane; perinuclear space
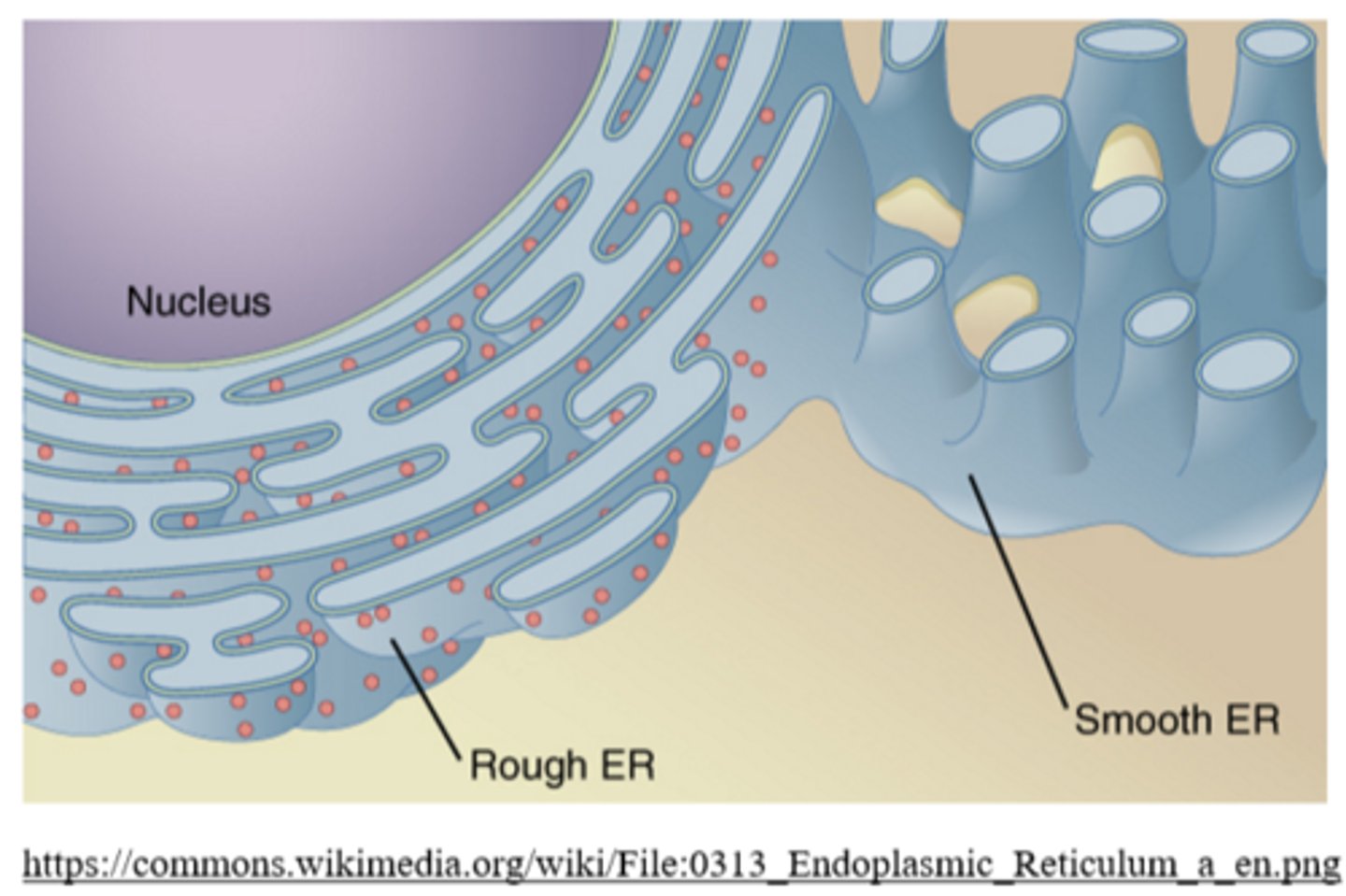
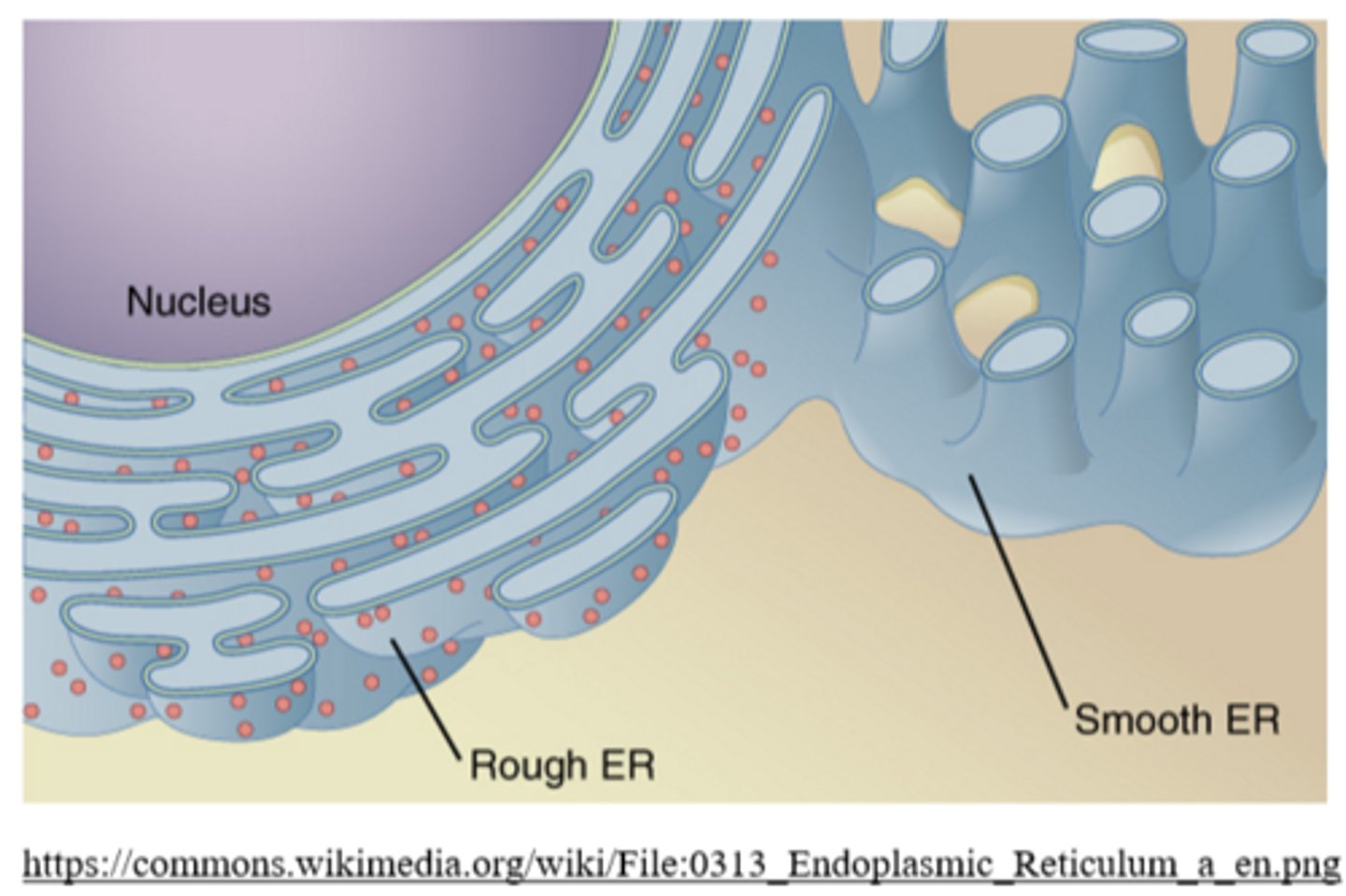
what happens to proteins inside the rough ER?
they are manipulated
what is a common manipulation for proteins in the rough ER?
glycosylation to make glycoproteins
what are the two fates of proteins that enter the lumen of the rough ER?
become a part of the cell membrane; exocytosis
the _____ synthesizes lipids and steroid hormones for export
smooth ER
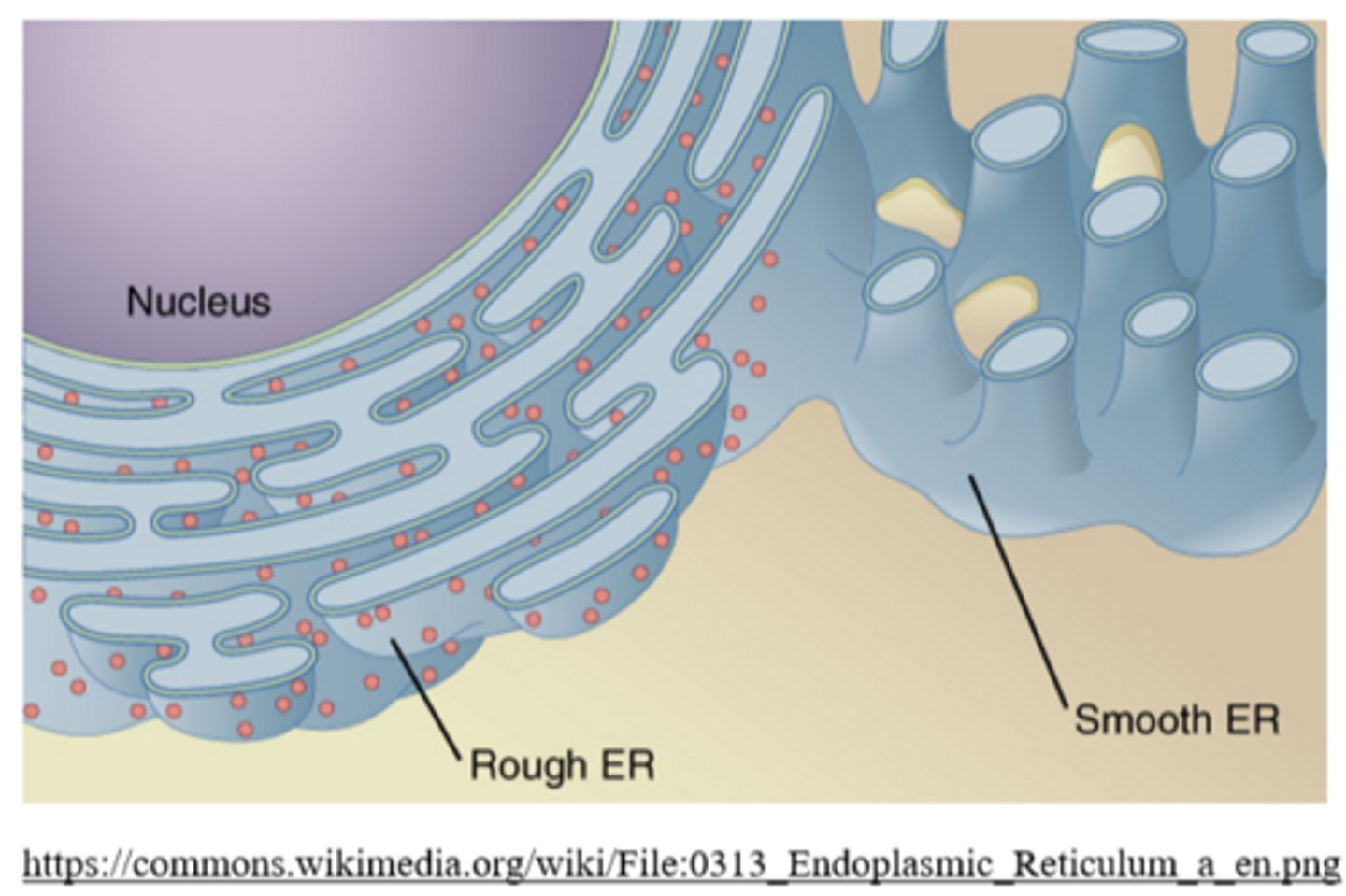
in some cells (ex: liver), the _____ functions in the breakdown of toxins and drugs
smooth ER
the _____ ER is not covered by ribosomes
smooth
the smooth ER is usually not attached to the _____
outer nuclear membrane
ERs send vesicles to the _____
cis-face of the Golgi
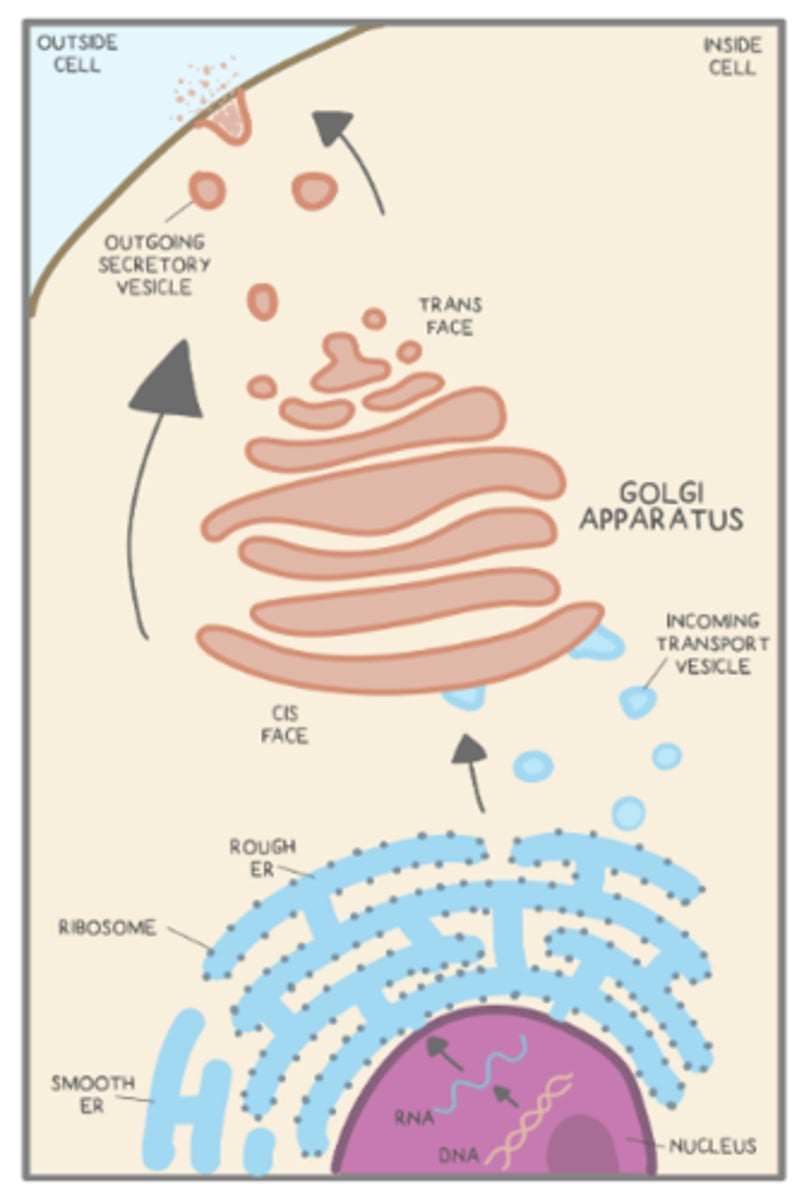
vesicles travel from the _____ to _____ of the Golgi, and the vesicle contents are manipulated along the way
cis-face; trans-face
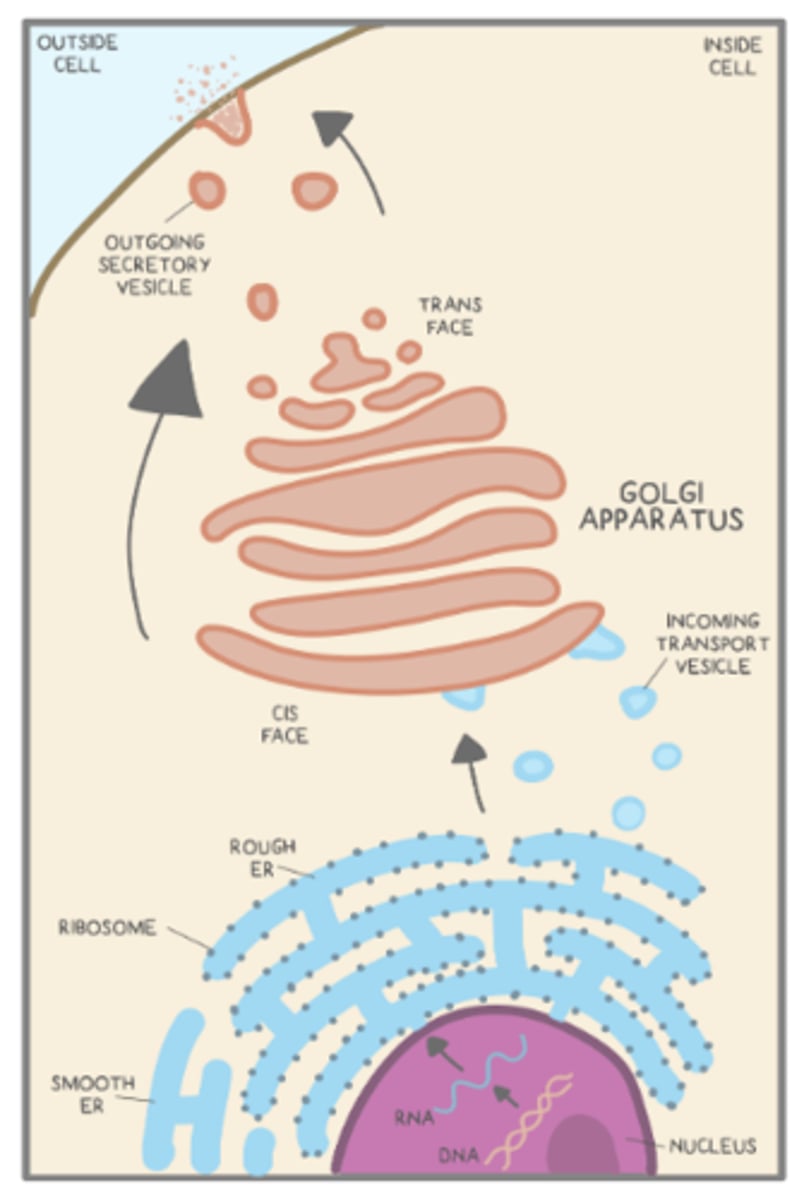
what is the main function of the Golgi apparatus?
directing molecules to their correct locations
which organelles break down nutrients/bacteria/cell debris?
lysosomes
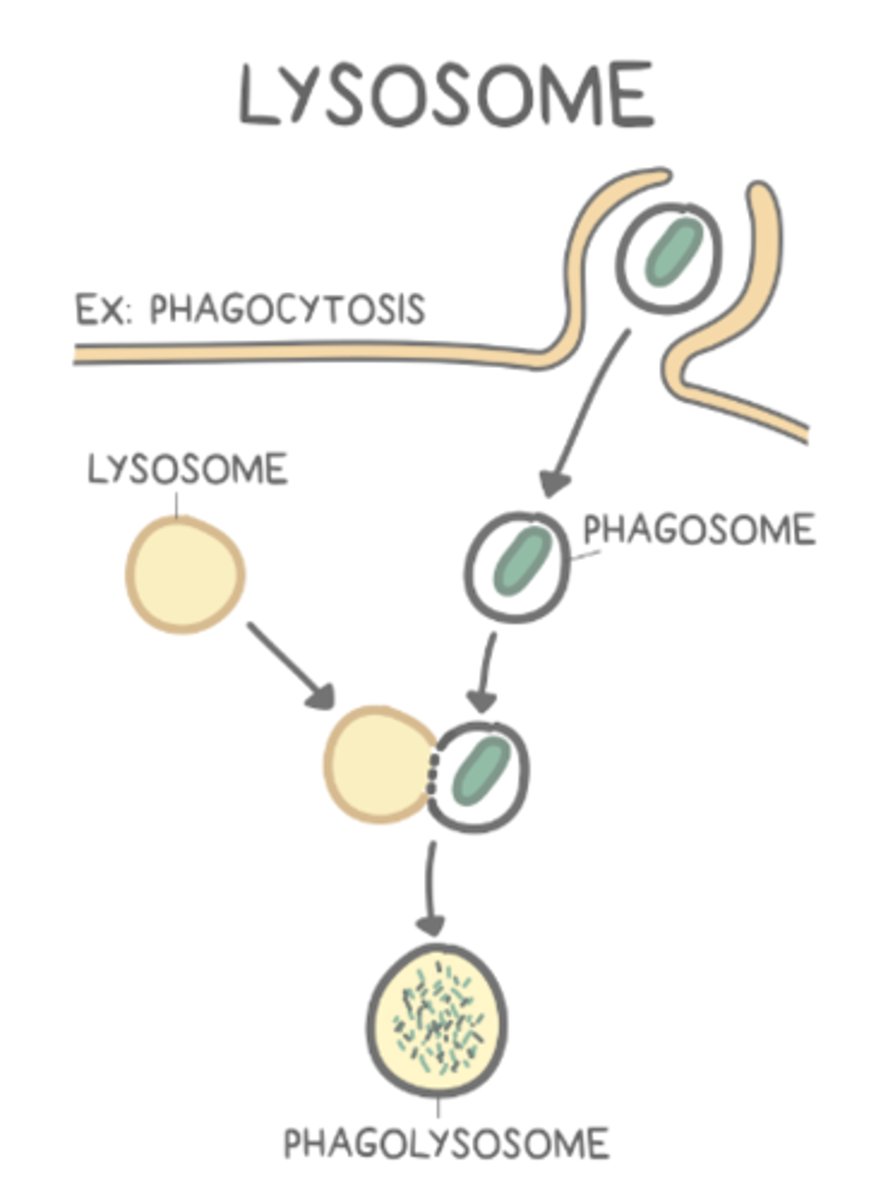
lysosomes receive vesicles containing digestive enzymes from the _____
Golgi apparatus
intracellular breakdown of unneeded/defective cellular components is called _____
autophagy
lysosomes function in _____ when they release their contents into the cell
apoptosis
which cells have vacuoles?
all plants and fungus; some animal, protist, bacteria
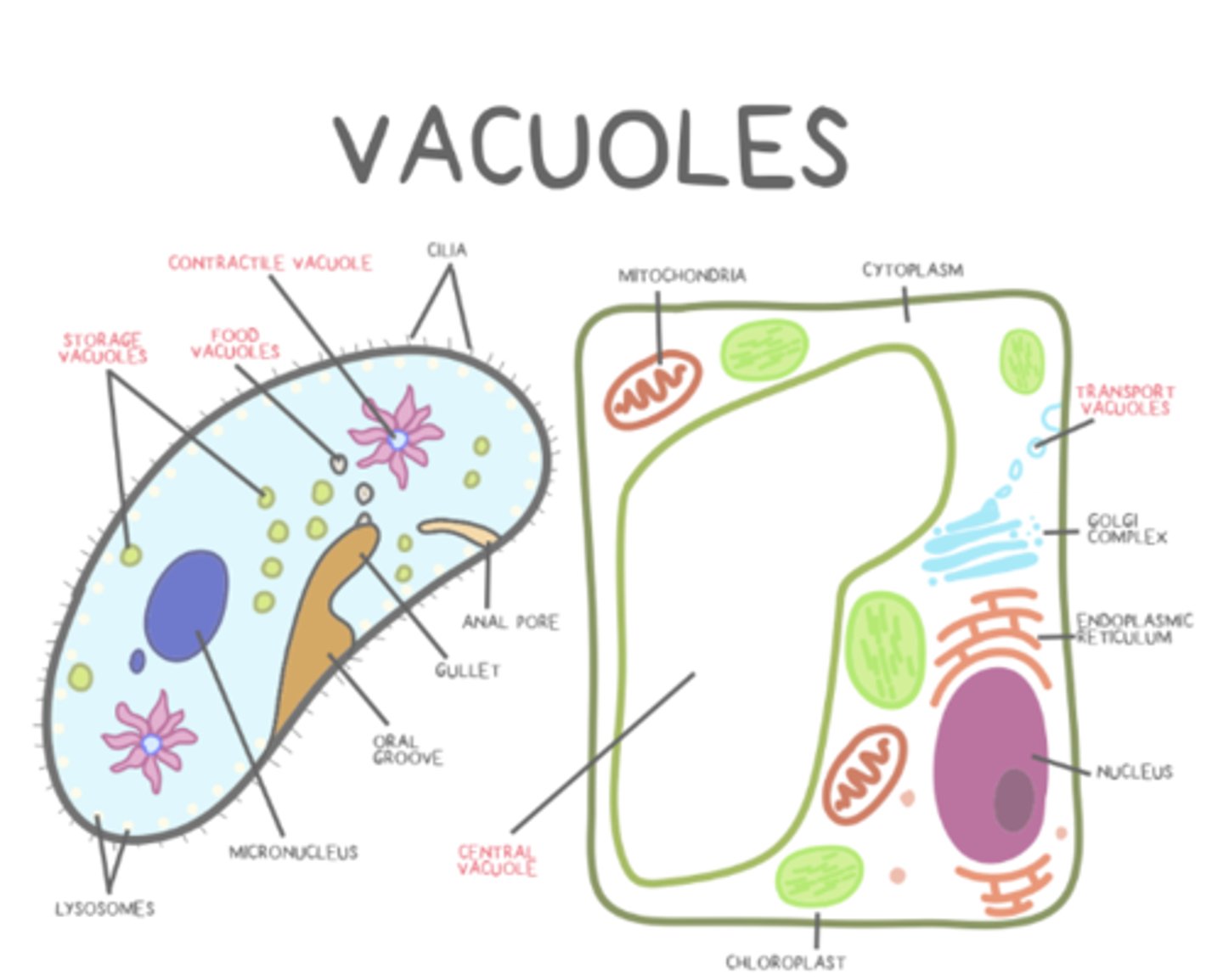
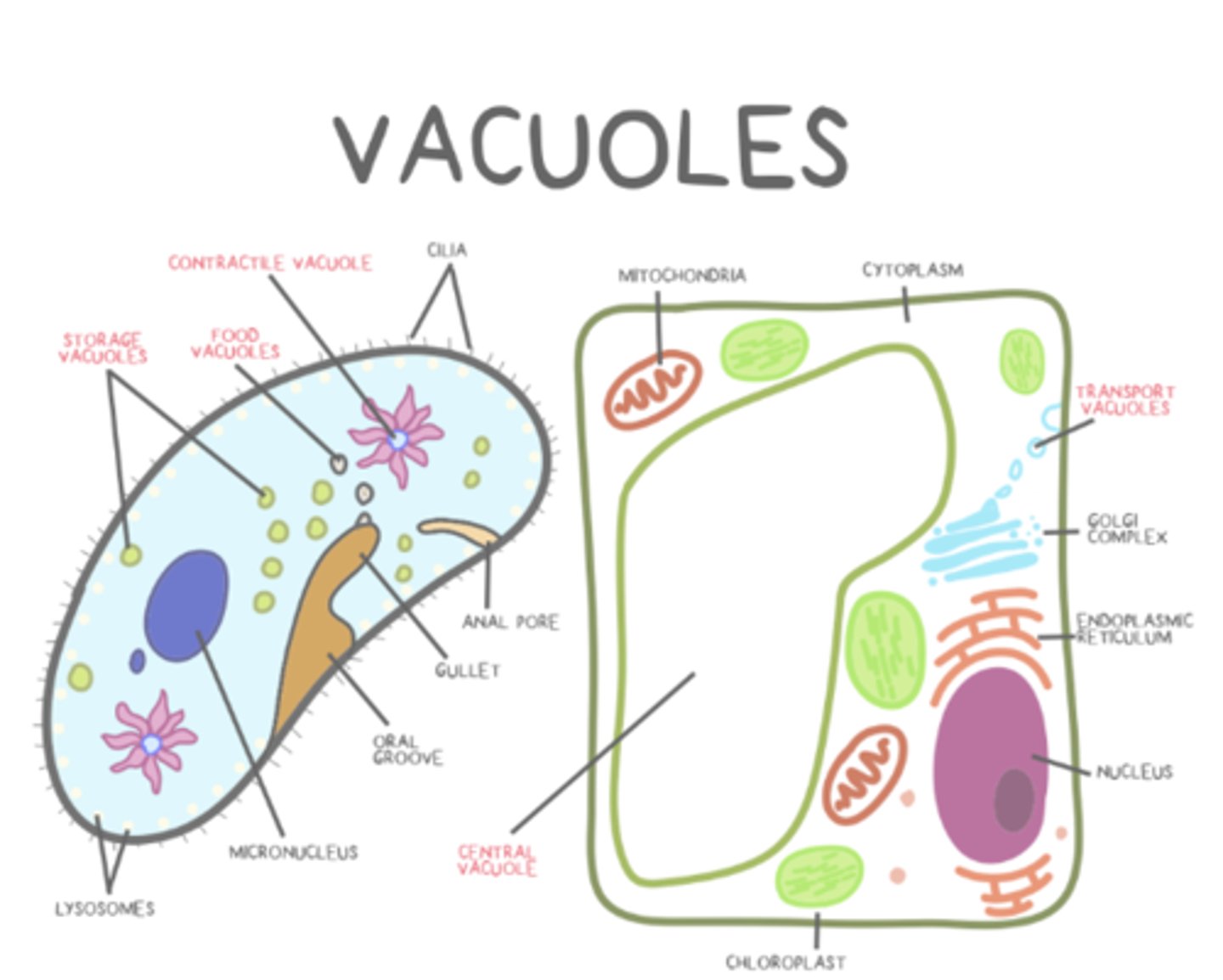
what are the types of vacuoles?
transport; food; central; storage; contractile
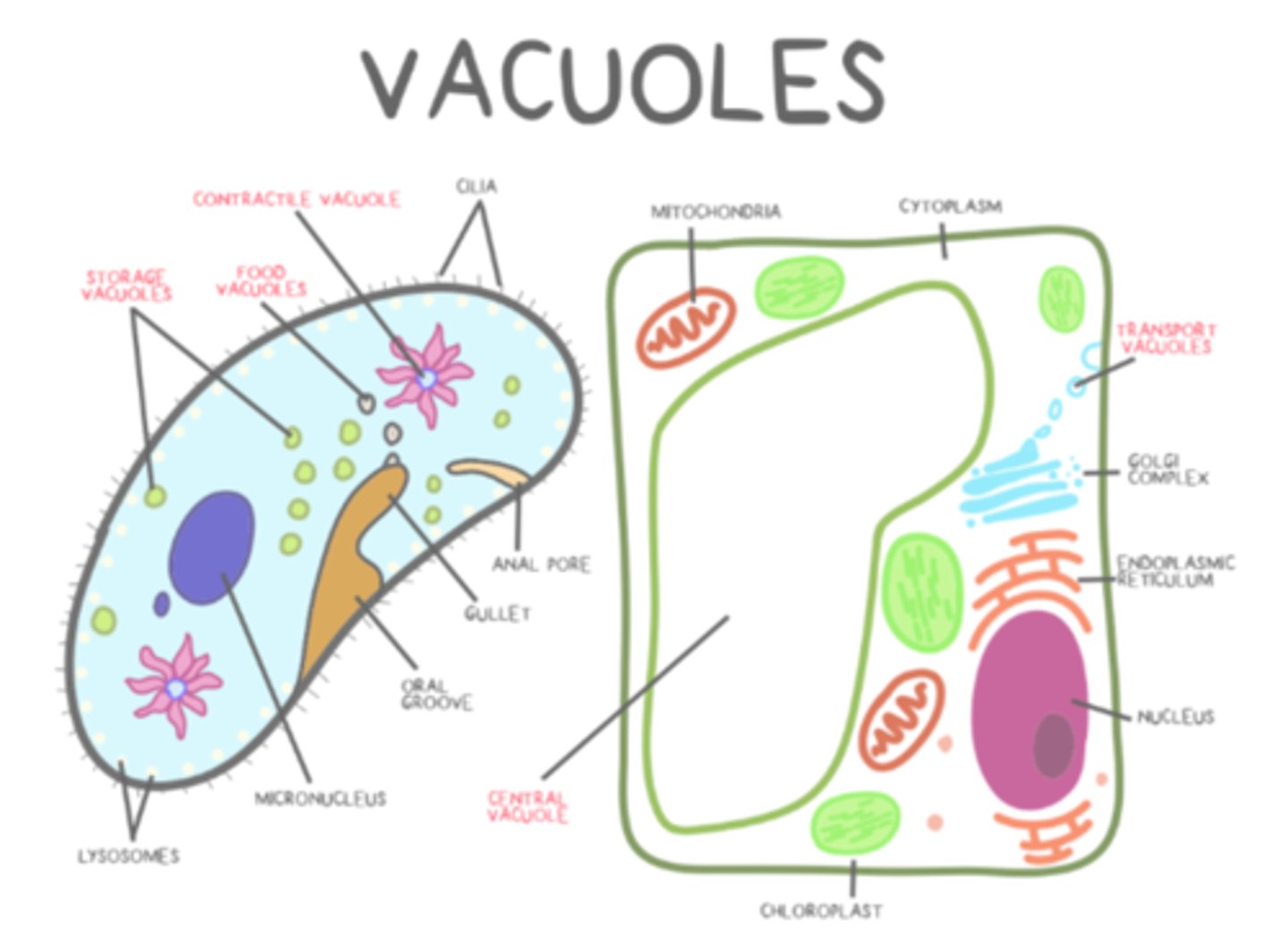
_____ vacuoles move materials from organelle to organelle or from organelles to the plasma membrane
transport
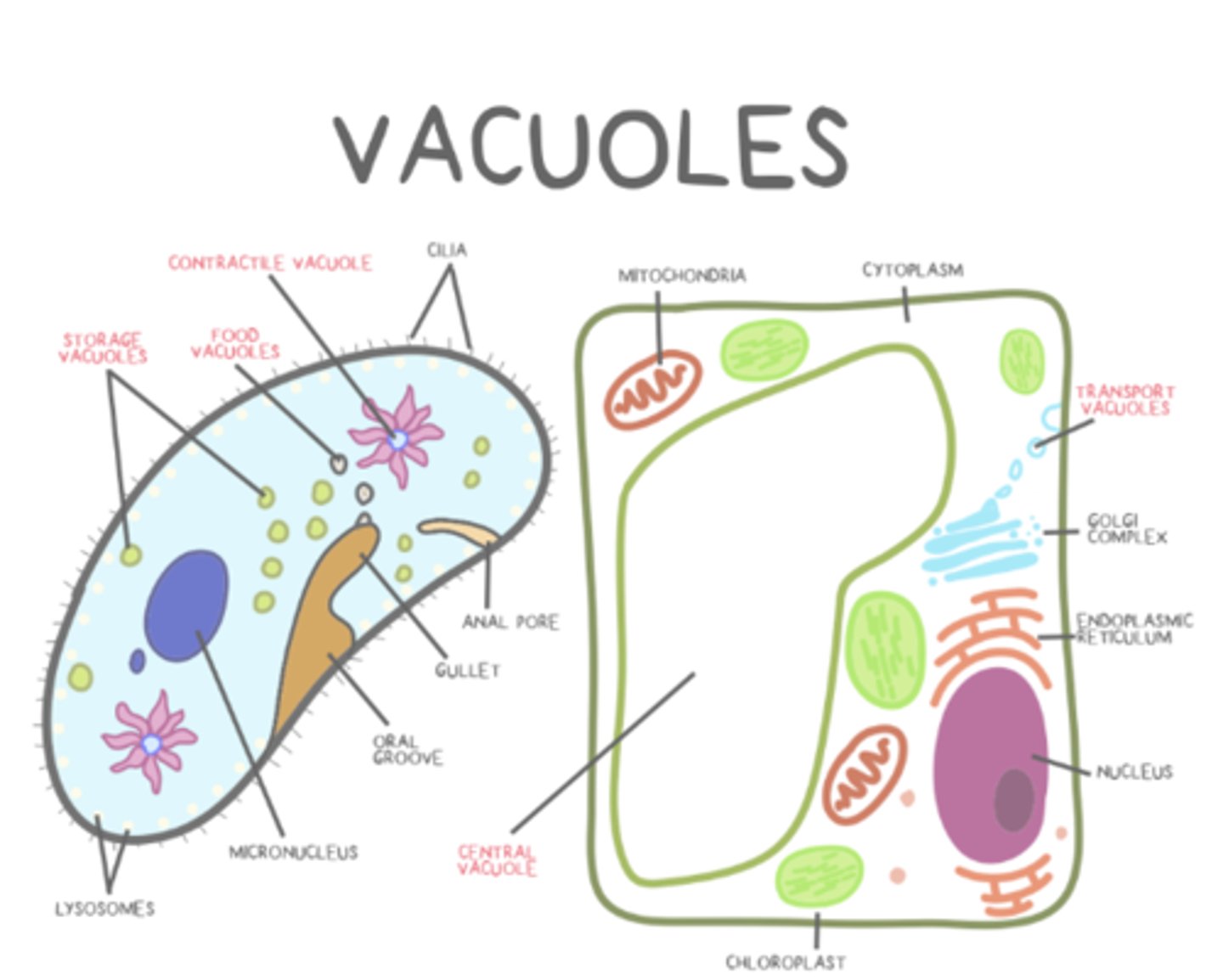
_____ vacuoles are temporary food holders that eventually merge with lysosomes for digestion
food
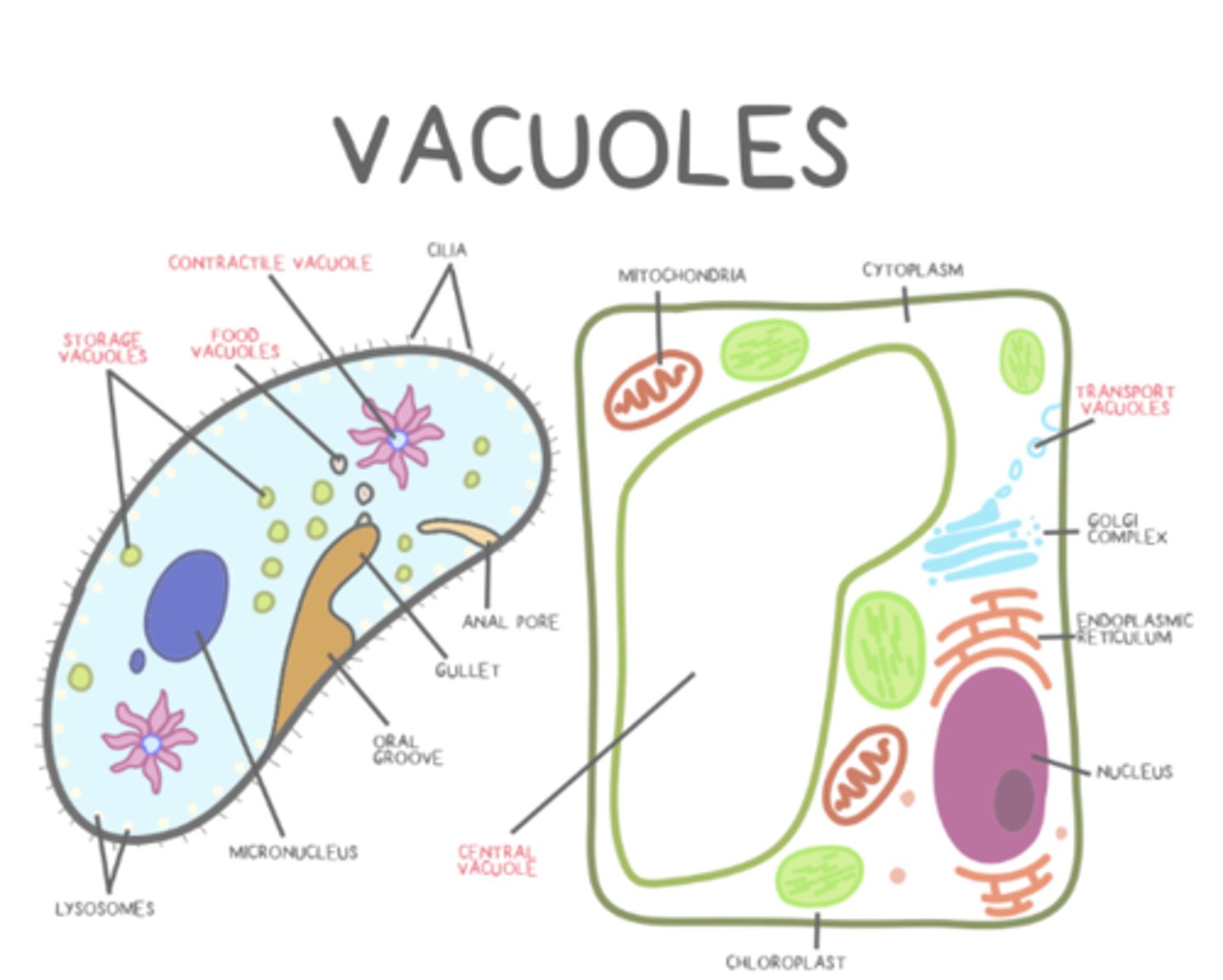
central vacuoles have a _____ and exert _____ when filled to maintain plant cell rigidity
tonoplast; turgor
_____ vacuoles (in plants) act similarly to lysosomes and storage vacuoles
central
_____ vacuoles tend to store starches, pigments, and toxic substances
storage
_____ vacuoles collect and pump excess water out of single-celled organisms
contractile
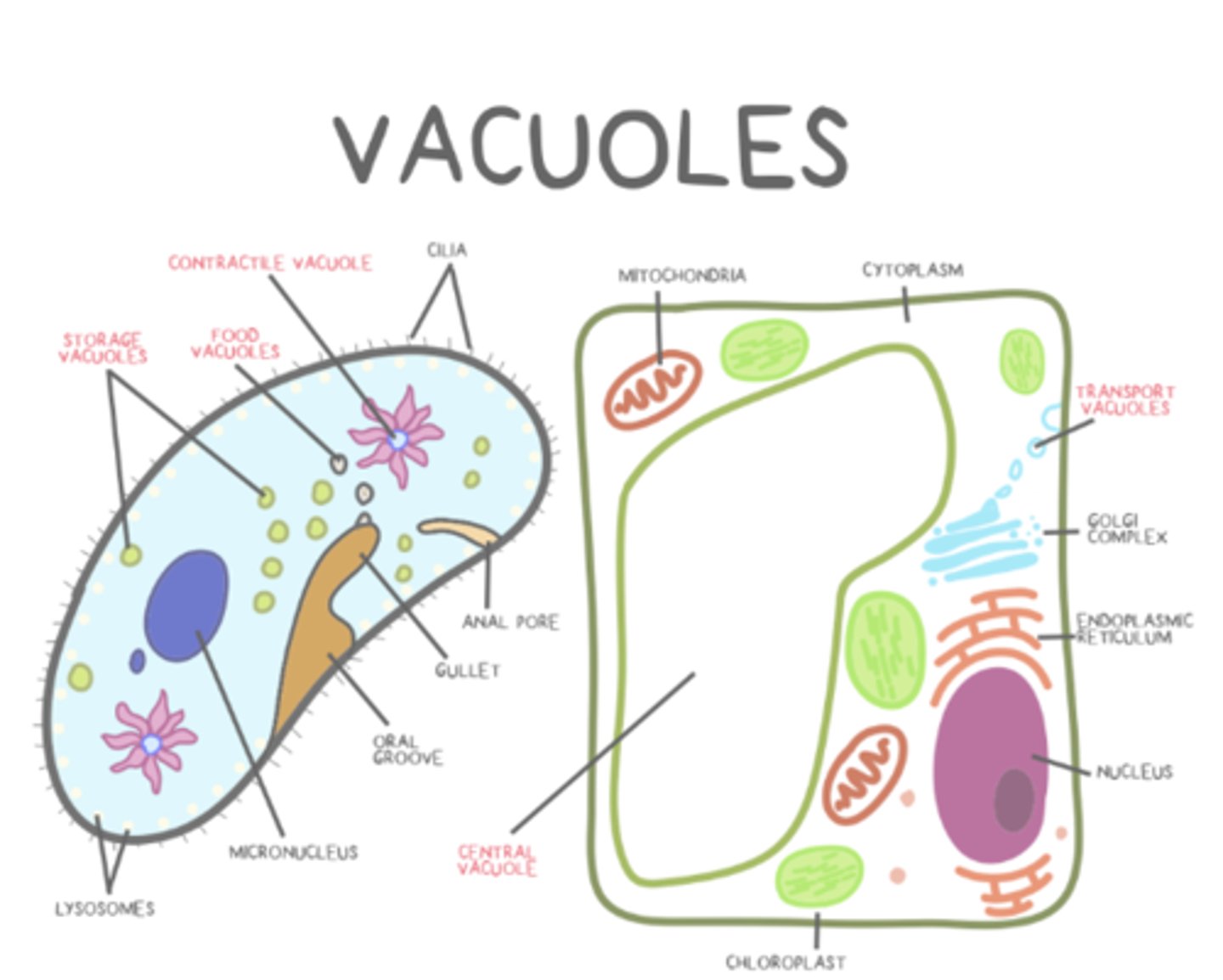
contractile vacuole use _____ transport
active
what is the endomembrane system?
group of organelles/membranes that work together to modify, package, and transport proteins and lipids that are entering/exiting a cell
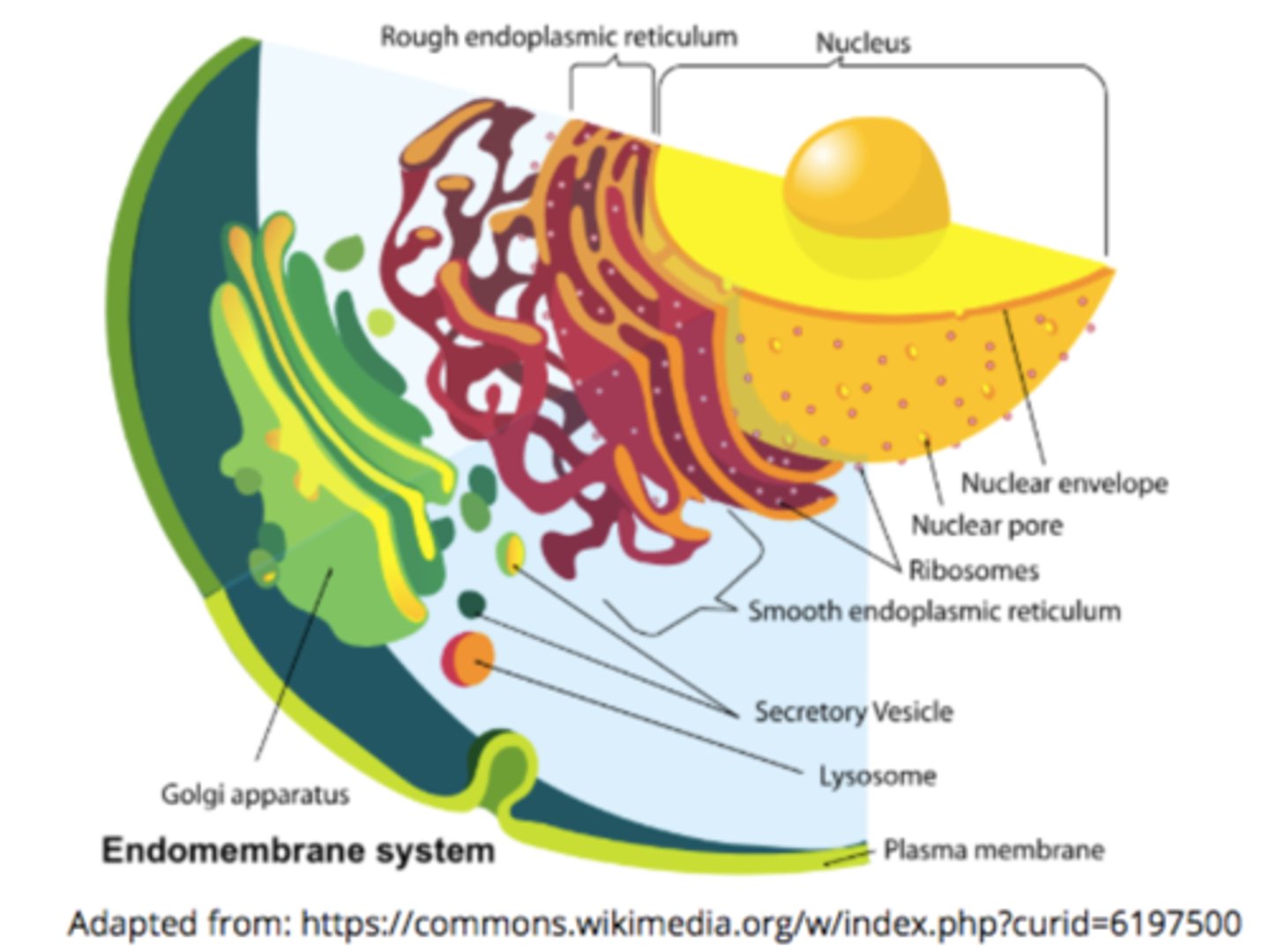
what are the components of the endomembrane system?
nucleus/nuclear envelope, rough and smooth ERs, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, and cell membrane
_____ break down fatty acids and some amino acids; also involved with detoxification
peroxisomes
alcohol detoxification occurs in the _____ of liver cells
peroxisomes and smooth ER