Hazard risk, perception & responses
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
risk
the likelihood that humans will be seriously affected by a hazard
What three risk factors intersect to determine hazard risk?
hazards
exposure (elements at risk)
vulnerability (coping capacity)
What factors determine hazard risk?
geographical location
human responses
population density
hazard perception
nature of the hazard
wealth
LIC, NEE or HIC
What physical factors can affect hazard risk?
environmental factors
spatial concentration
regularity
magnitude
frequency
duration
areal extent
speed of onset
What human factors can affect hazard risk?
social factors
economic factors
political factors
geographical factors
technology factors
What aspects of a person’s background can impact their perception of hazards?
economic background
social background
cultural background
What factors can impact a person’s perception of hazards?
wealth
religion
education
past experiences
personality
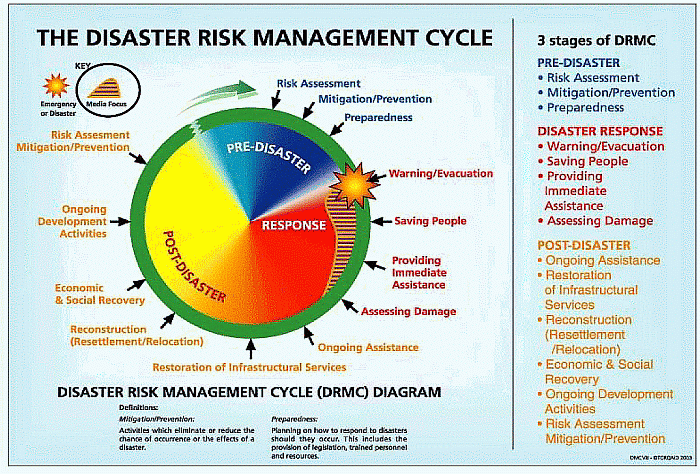
What is The Hazard Management Cycle?
an ongoing process where governments, businesses, and society plan for and reduce the impact of disasters, react to disasters, and take steps to recovery after the event
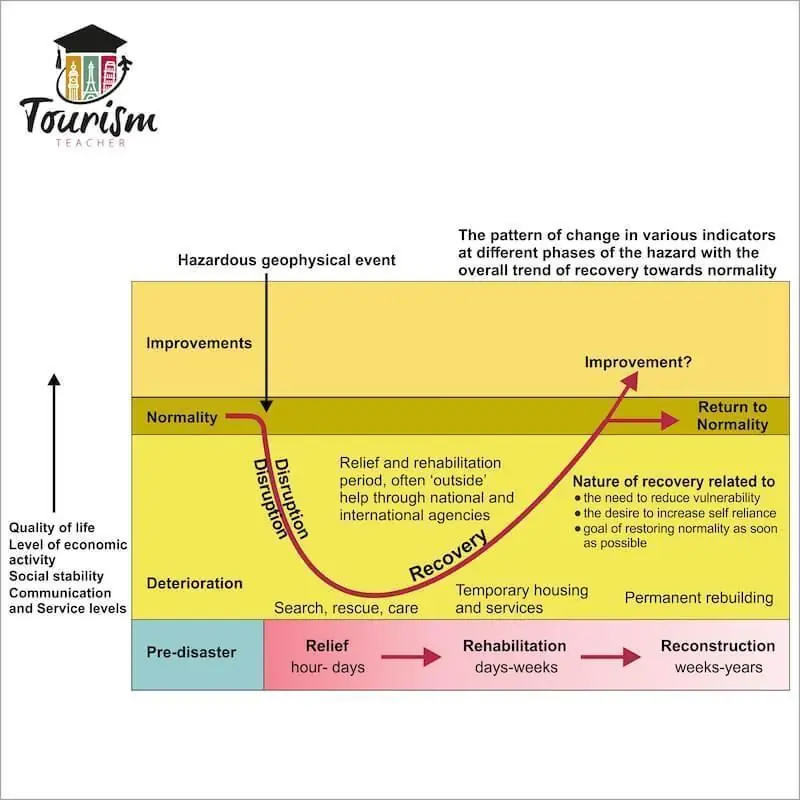
What is Park’s disaster-response model?
a model of the impact of a disaster from before the event to after the event (each hazard will have a different response curve)
What physical factors can affect responses to hazards?
climate
topography of region
accessibility of location
type of hazard
What human factors can affect responses to hazards?
level of community preparedness
scientific understanding and expertise
technological resources
level of education and training
wealth of region
political framework
quality of infrastructure
number of people involved/affected
What are some examples of responses to hazards?
prediction
prevention
risk sharing
mitigation
fatalism
coordinating responses
prediction
it may be possible to give warnings that would enable action to be taken quicker
prevention
it involves things like building flood defences which costs money but is not always possible
risk sharing
buying insurance and sharing the cost
mitigation
reducing or minimising the impacts (e.g., bury food or medical supplies to be dug up after flooding, moving expensive items upstairs to avoid floods, training emergency services)
fatalism
accepting that hazards happen and sometimes nothing can be done (sometimes the belief in God’s will)
coordinating responses
governments or organisations working together to provide relief