Nervous System
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Central Nervous System
(CNS) brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous system
Body Nerves that connect to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Connects the central nervous system to the body's organs and limbs.
Autonomic Nervous System
Controls involuntary bodily functions (not consciously controlled), such as breathing, the heartbeat, and digestive processes
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary bodily functions (consciously controlled), such as controlling skeletal muscles
2 Major Functions of Nervous System
1. Sensory Reception-end of peripheral neurons monitor conditions( light,sound,temperature)
2. Integrative Functions- Sensory messages that get sent repeatedly get remembered "motor functions" (subconscious actions)
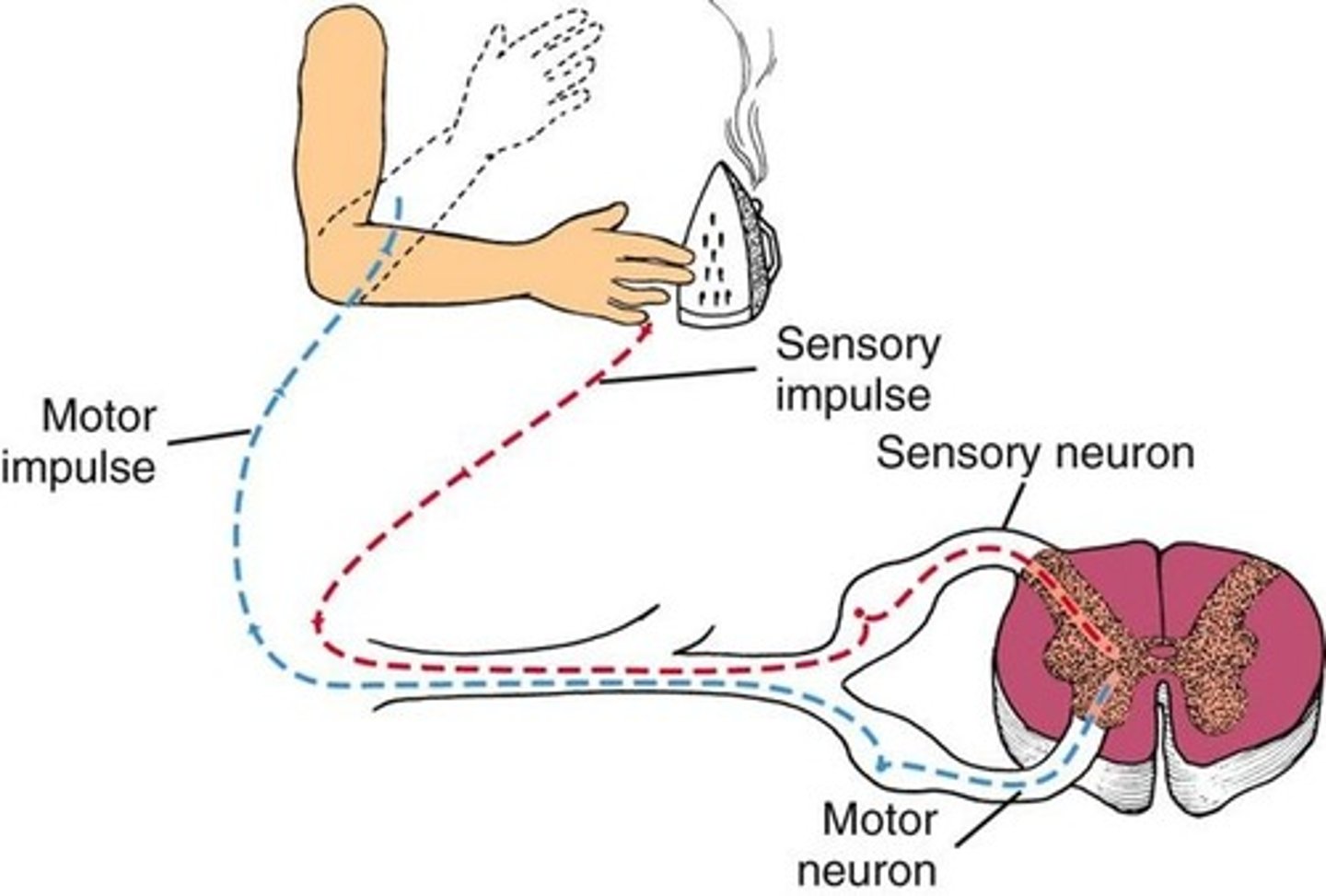
Order of Stimulus (from sensory to effector)
1. Stimuli: physical or chemical signal (ex. hot room)
2. Nerve impulse (ex. sends signal to brain)
3. Effectors: muscle & glands react (ex. sweat glands start sweating)
Stimulus
Things that initiate nerve impulses (ex. hot room)
Effector
Response (ex. Sweating)
Motor Functions
Complex muscle-and-nerve acts that produce movement (walking, writing, typing running etc.)
"Electrochemical"
A nerve impulse is partially electric (change in polarity/charge) and partially chemical (neurotransmitters)
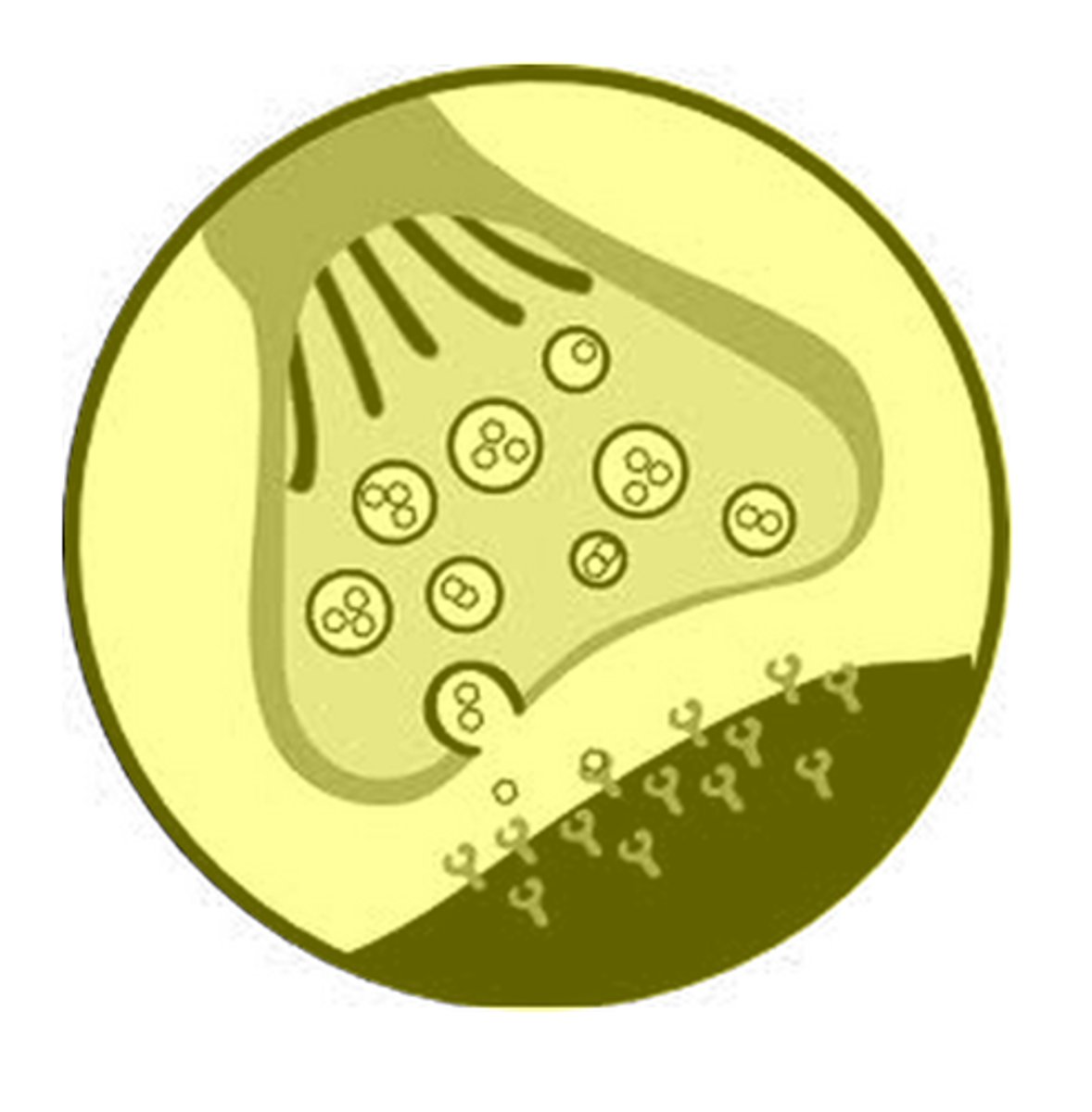
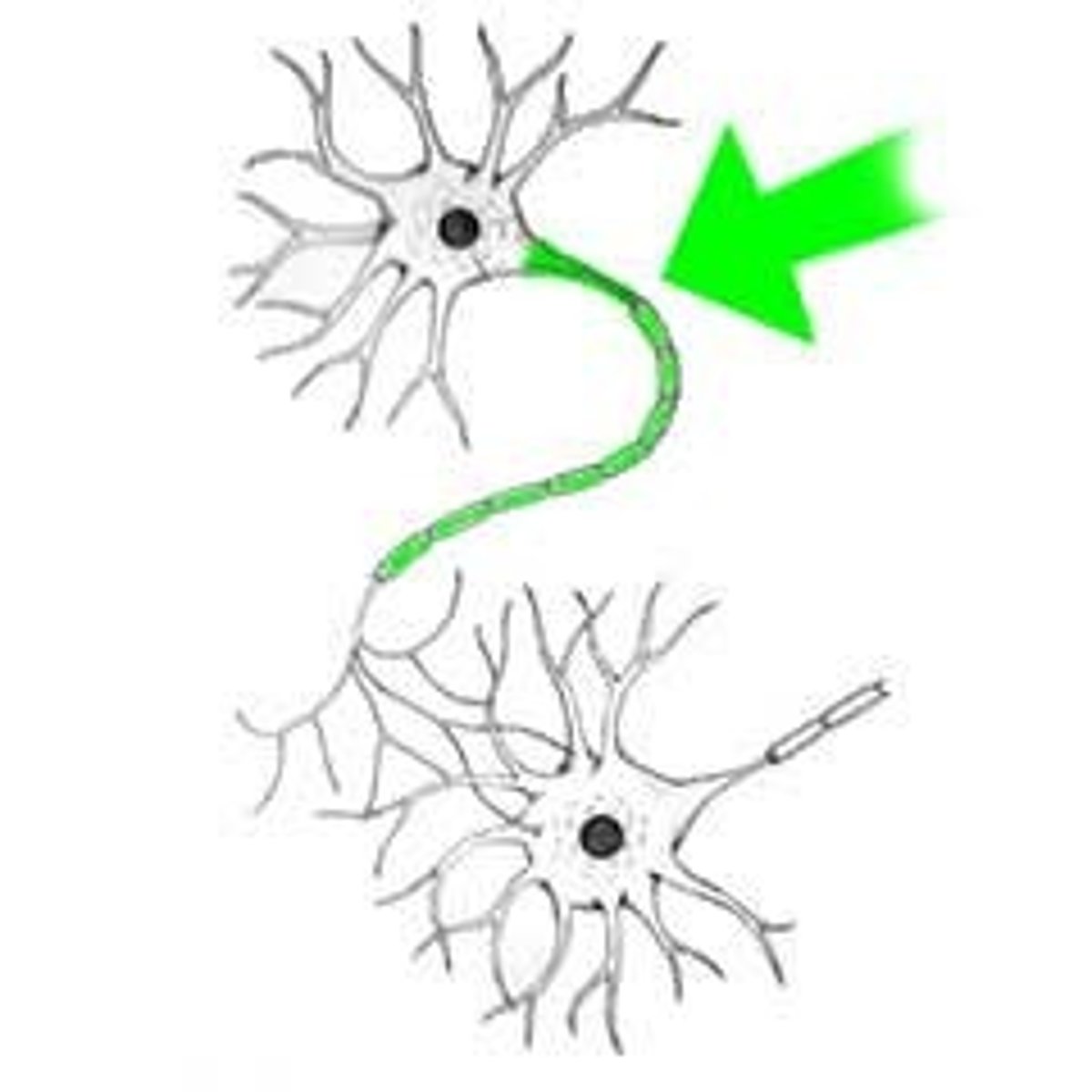
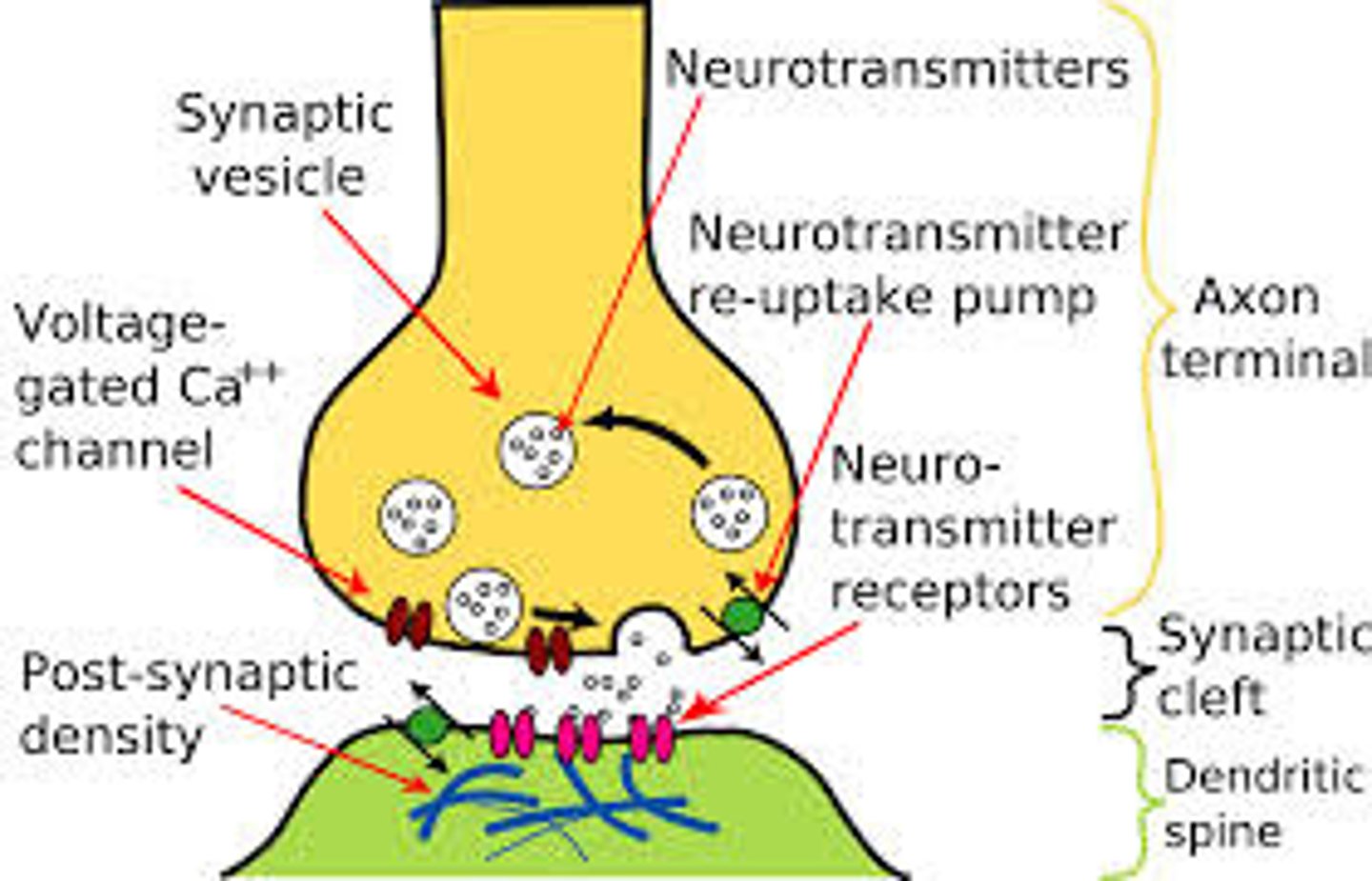
Synapse
Where the nerve impulse is sent (connection of 2 neurons) .
Action Potential changes the charge of the synapse (causes electricity) and Neurotransmitters are sent.
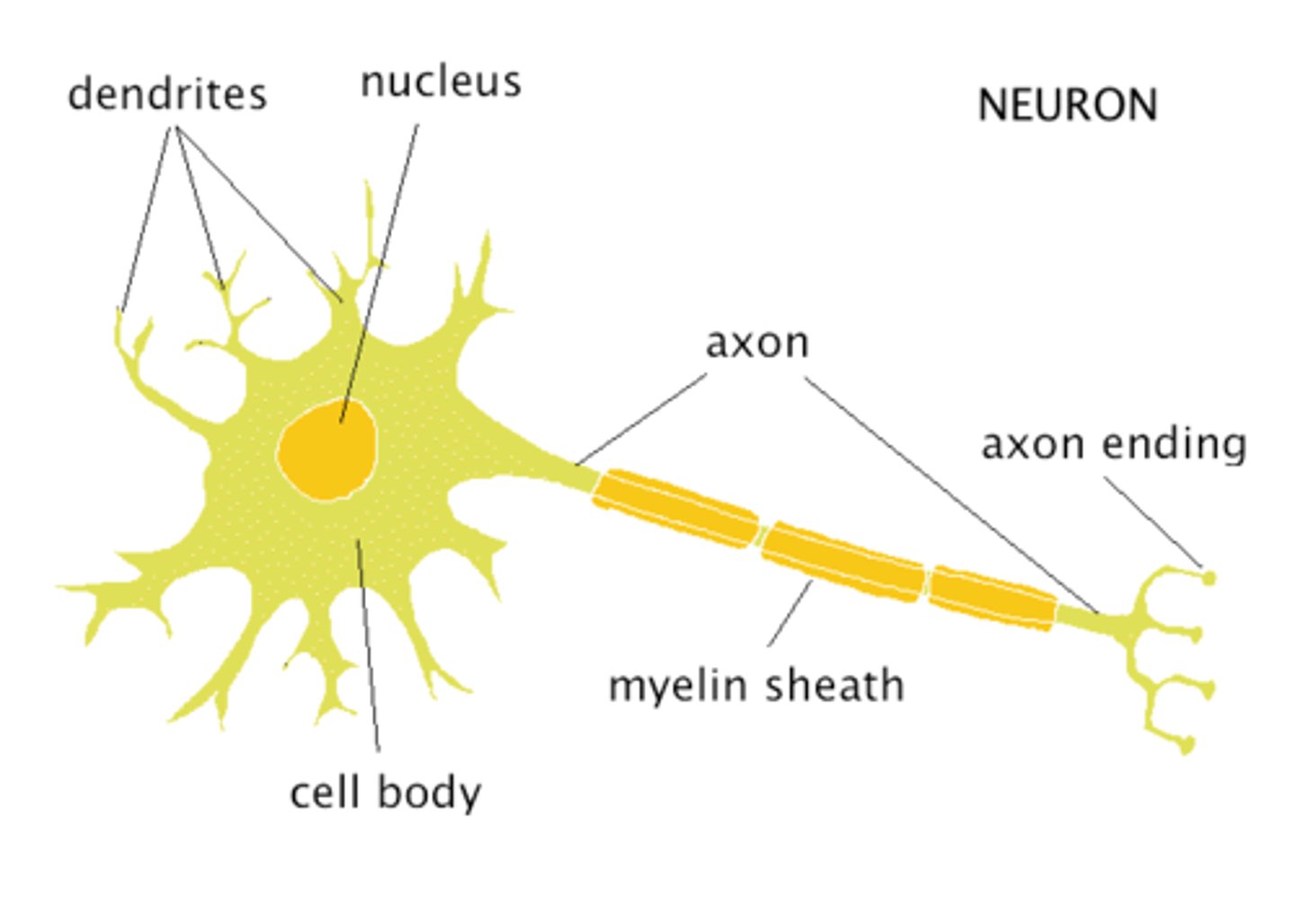
Myelin Sheath
Covering of Schwann Cells, Speeds up nerve impulses.
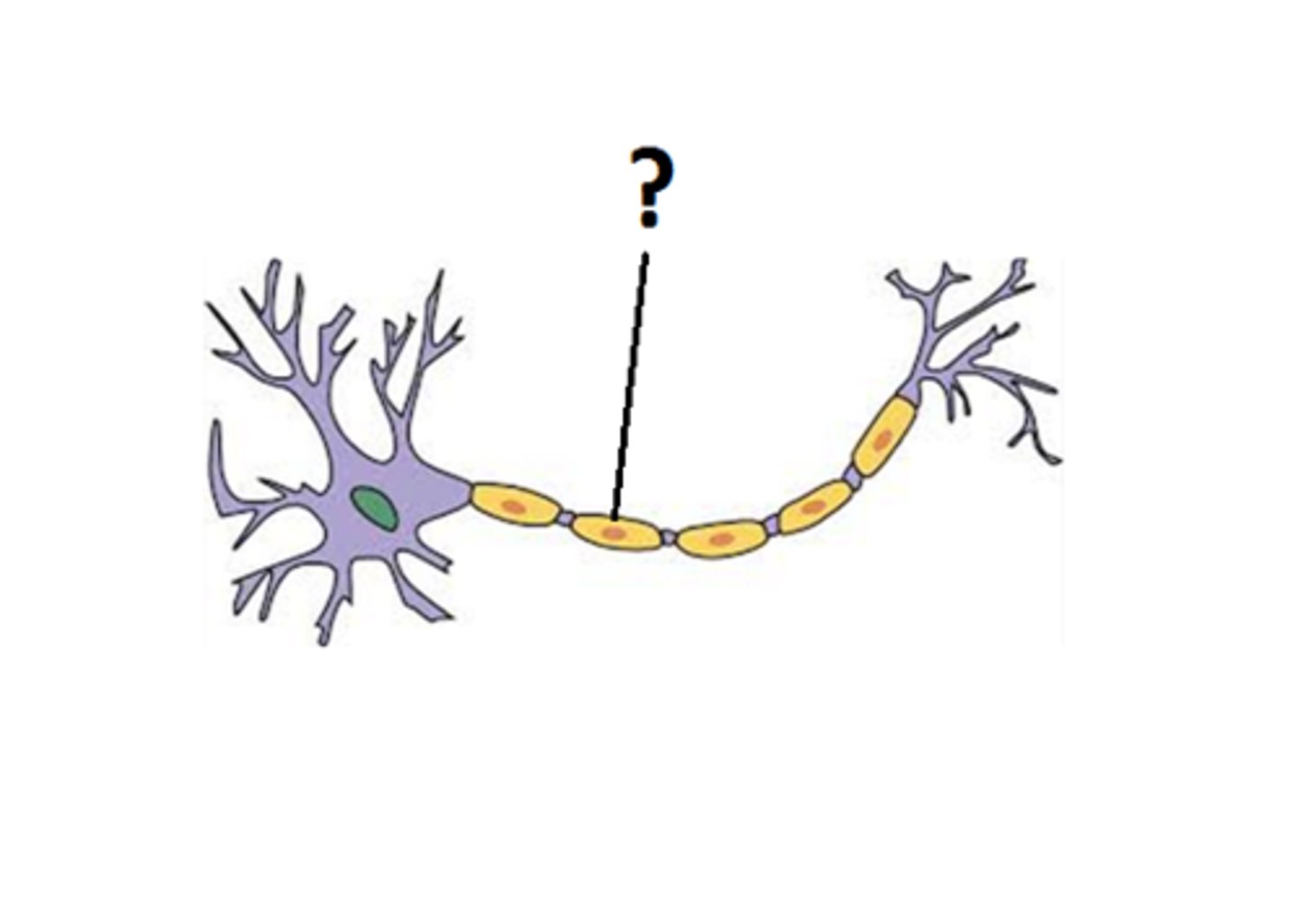
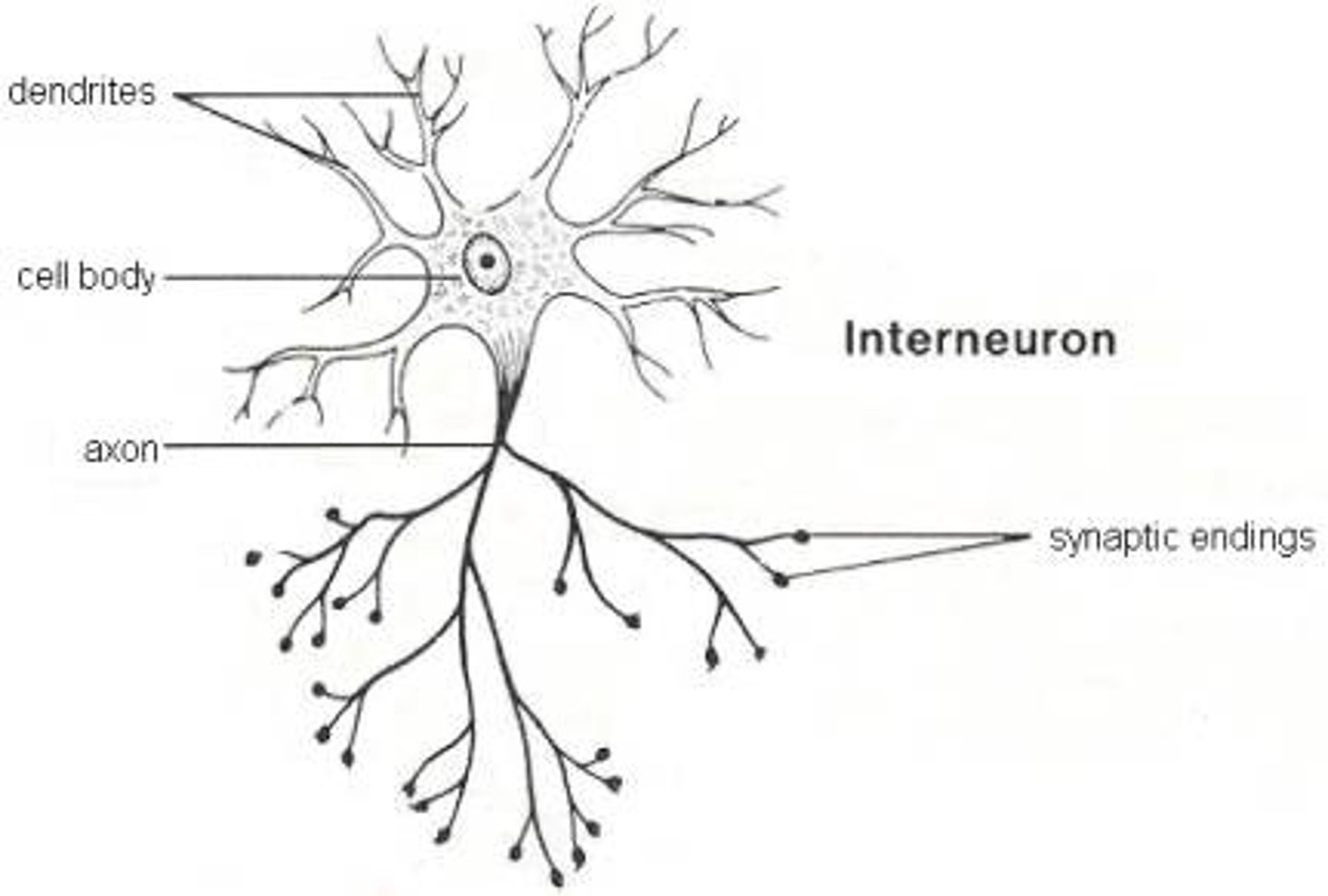
Axon
The long threadlike part of a nerve cell that carry the nerve impulse
Dendrites
Branch like extensions on a neuron that GET signals and connect to the synapse
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit signals across a synapse from one neuron to another 'target' neuron
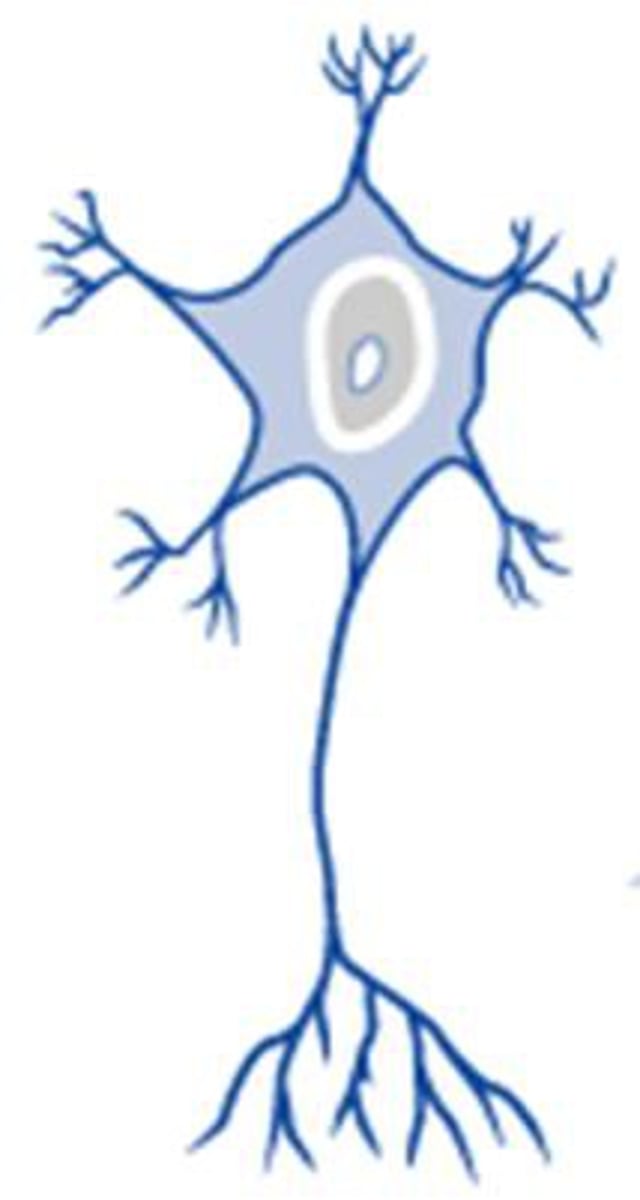
Multipolar Neuron
Most of the brain/spinal cord & is mylinated
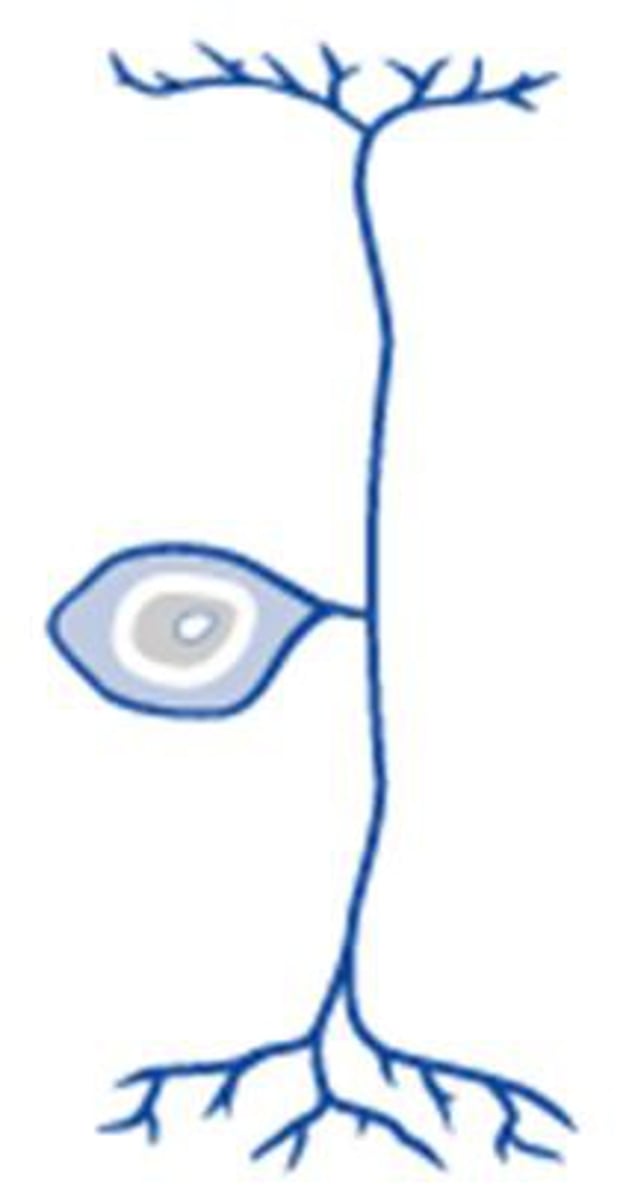
Bipolar Neuron
Found in eyes, nose, and ears
Classified as an "Interneuron": connects PNS to CNS
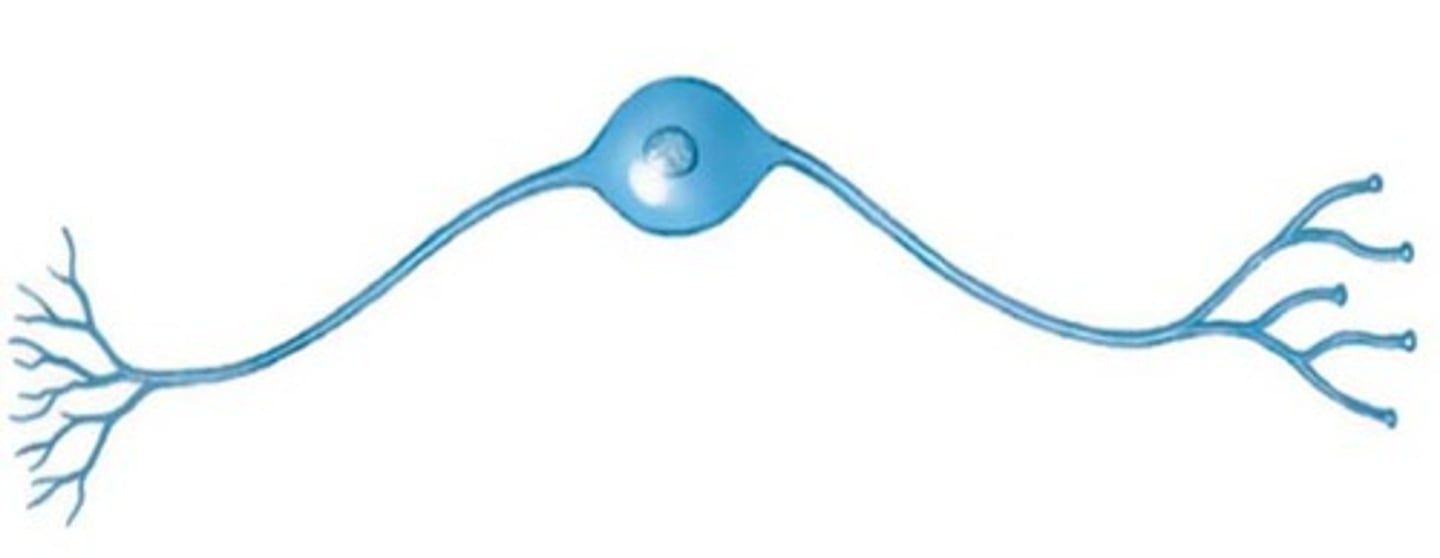
Unipolar Neuron
Accepts Sensory messages (feelings & senses)
Found outside of the brain and spinal cord
Sensory Neuron
Nerve cells that transmit sensory information (sight, smell, sound etc.)
Unipolar shaped Neurons
Interneuron
Nerve cells that serve as that connection between Peripheral Nerves to Central Nervous System.
Bipolar shaped Neurons
Motor Neuron
Nerve cells responsible for making an action or movement happen.
Multipolar Shaped Neurons
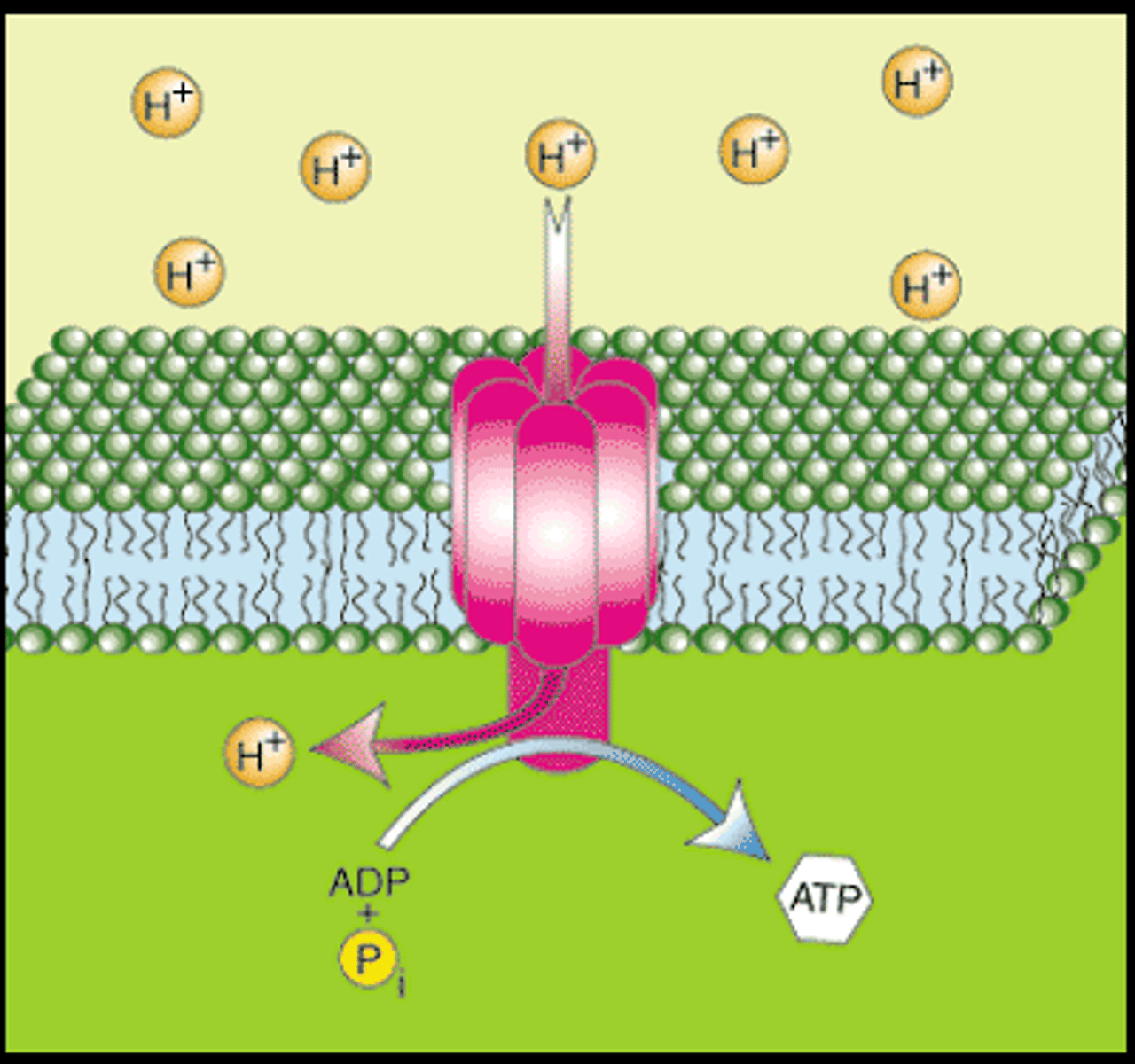
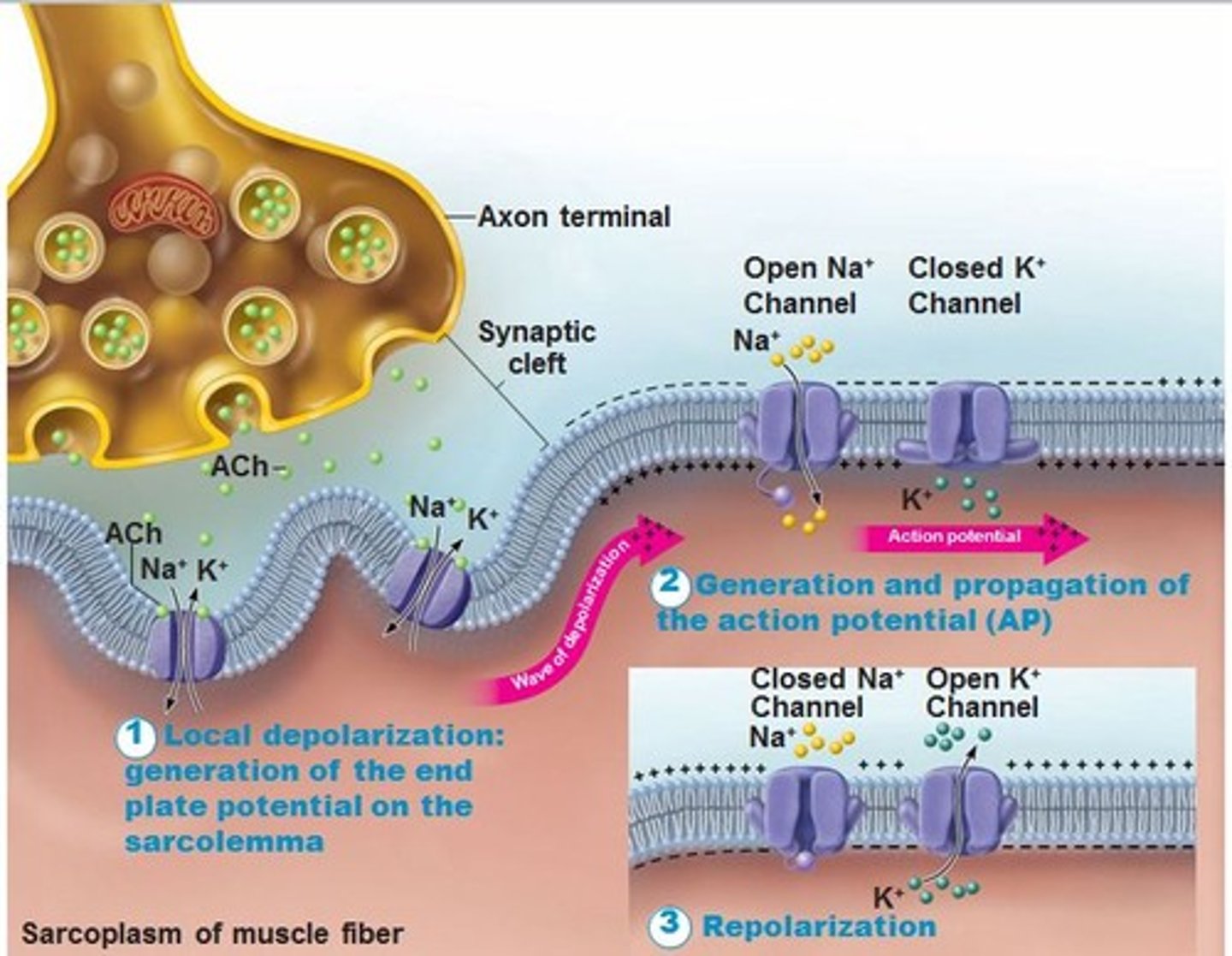
Sodium Potassium Pump
A protein on the outside membrane of a neuron at the Synapse.
Changes the charge (aka. polarity) of the neuron.
Moves sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane to change the "electricity" of the neuron.
The order of events during an Action Potential caused by the Sodium Potassium Pump
1.) Sodium Channel Opens
2.) Sodium Channel Closes
3.) Potassium Channel Opens
4.) Potassium Channel Closes
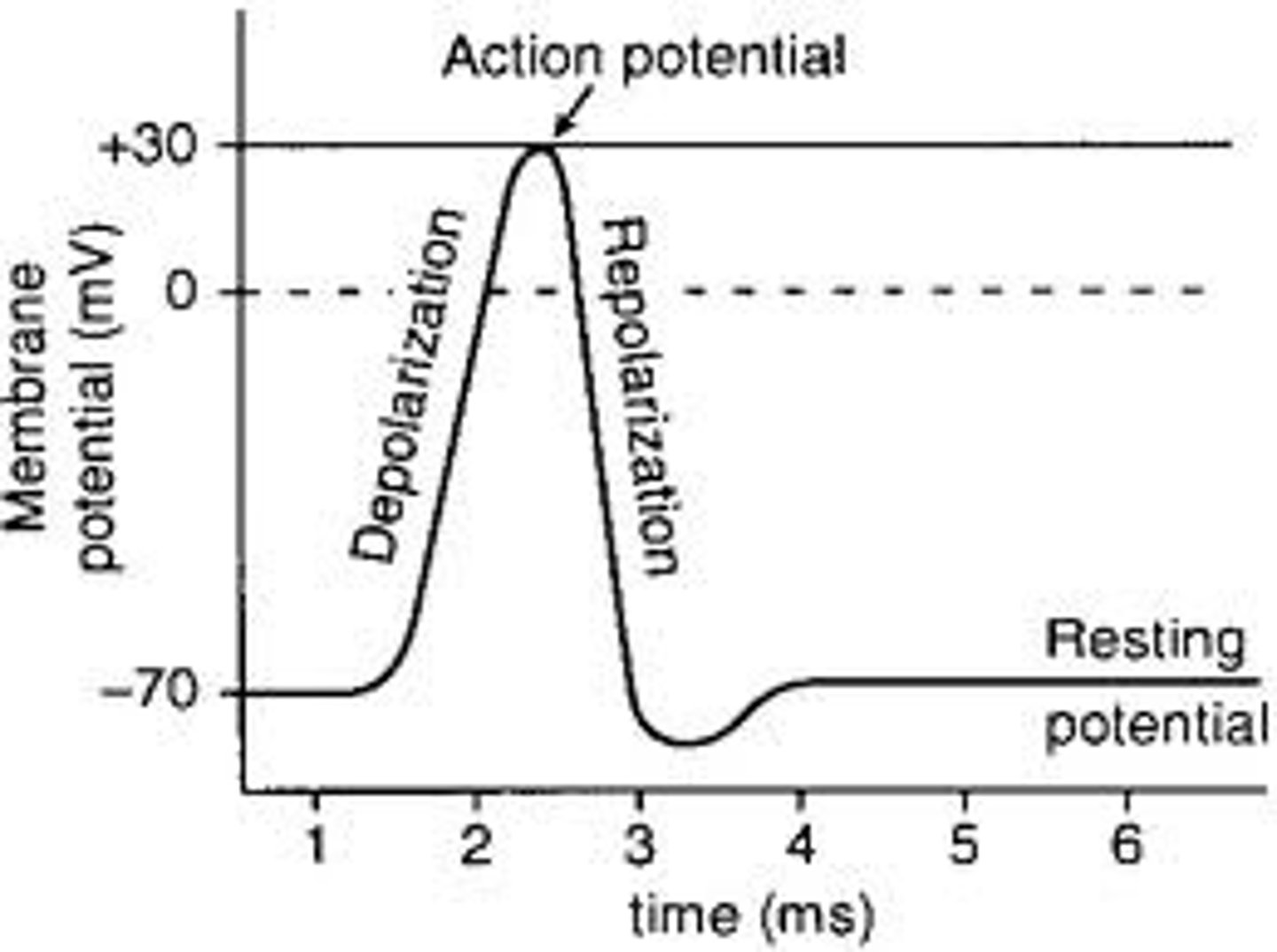
Depolarization
During nerve impulse, electrical charge increases to Action Potential (30mV)
Repolarization
During nerve impulse (Action Potential), electrical charge decreases to Resting Potential (-70mV)
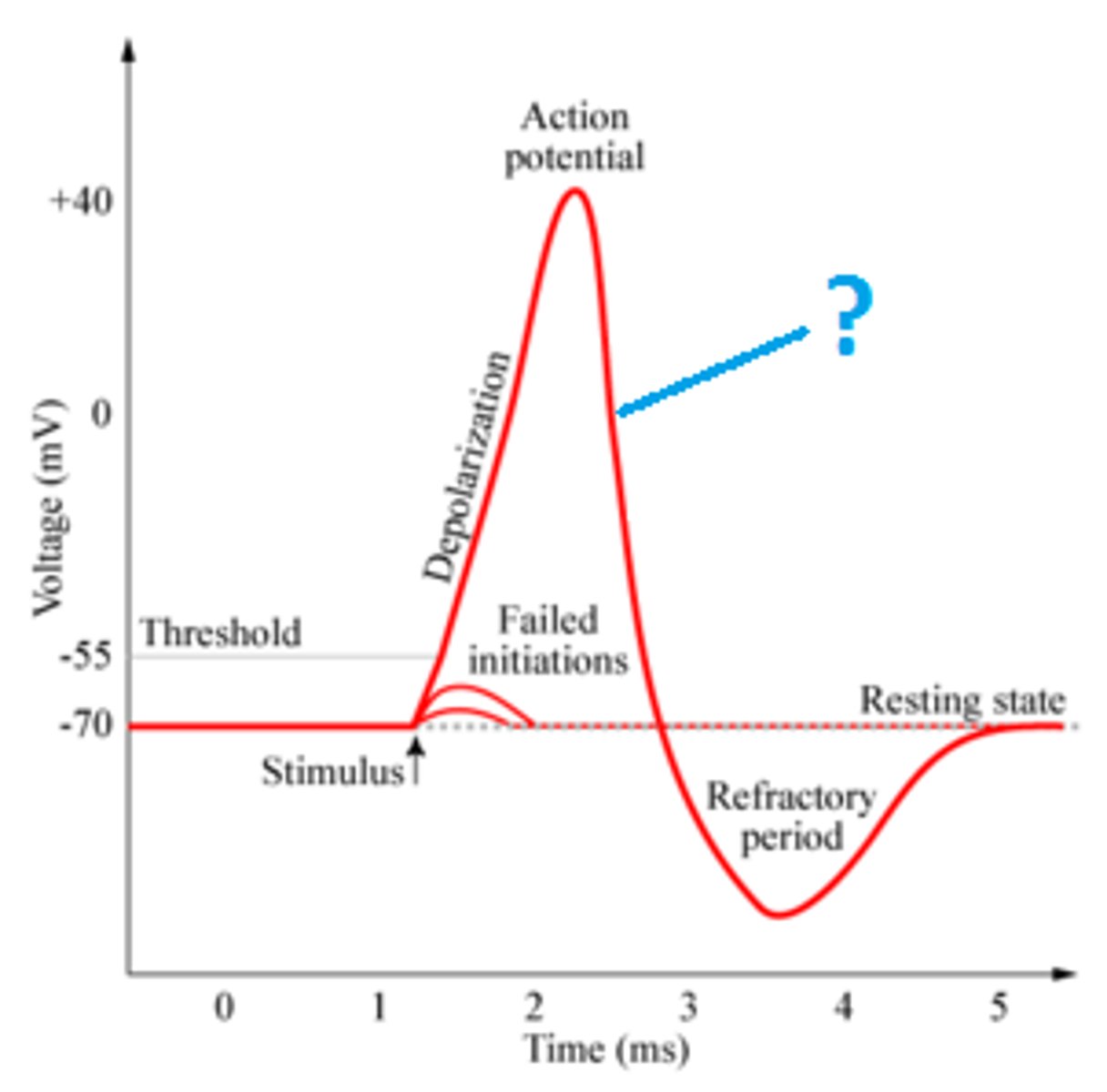
Significance of 30mV
Action potential- highest charge
Significance -70mV
Resting Potential
(both the start and end in Sodium Potassium Pump)
Resting Potential
Non-active state of a neuron (not sending an impulse)
Action Potential
Highest charge of a neuron, 30mV (caused by Sodium Potassium Pump) -- causes a Nerve Impulse
Threshold Potential
Starts an action potential.
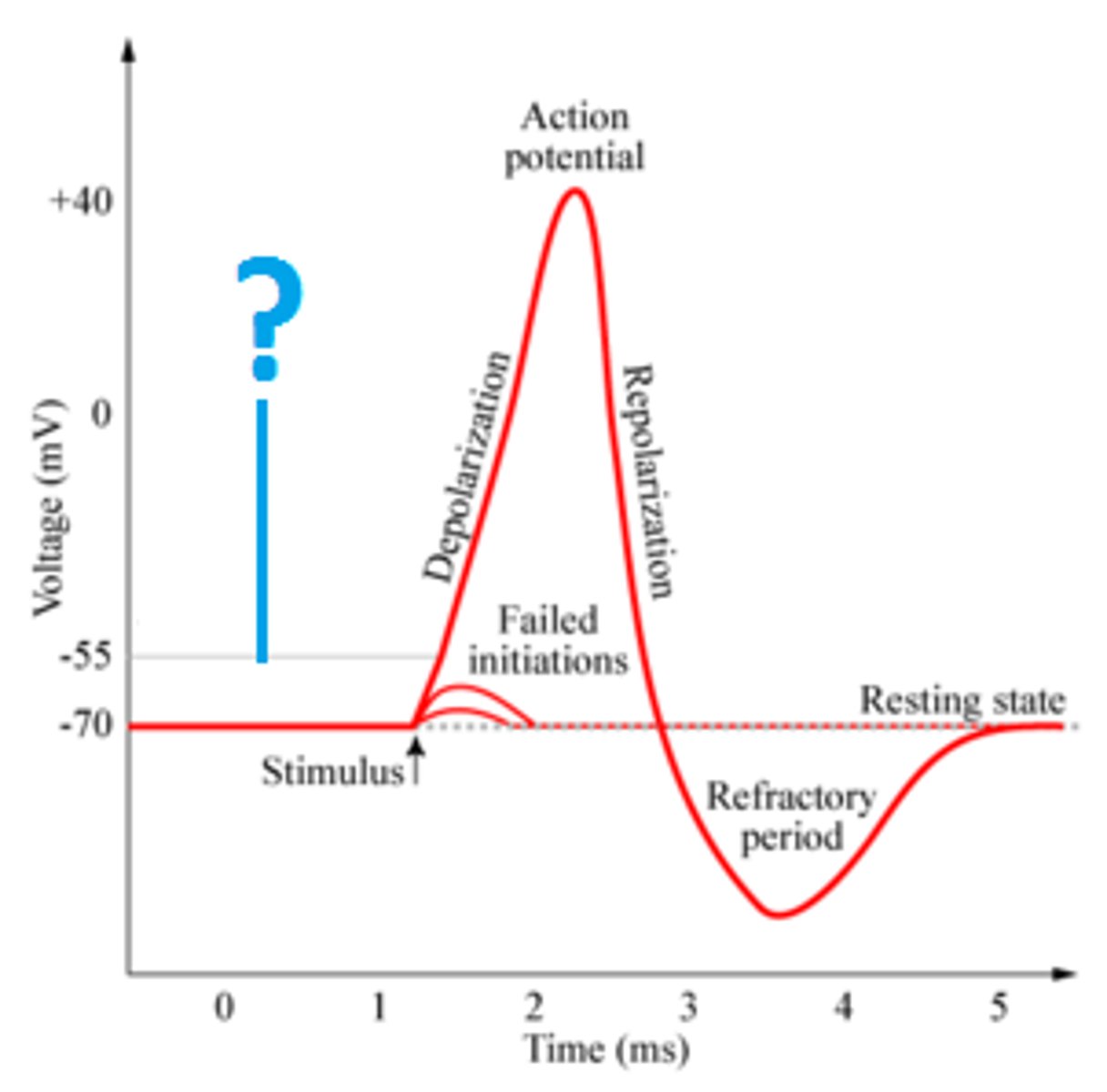
5 milliseconds
Time it takes to send a nerve impulse (Action Potential of Sodium Potassium Pump)
4 Major Brain Structures
1. Cerebellum
2. Cerebrum
3. Diencephalon
4. Brainstem
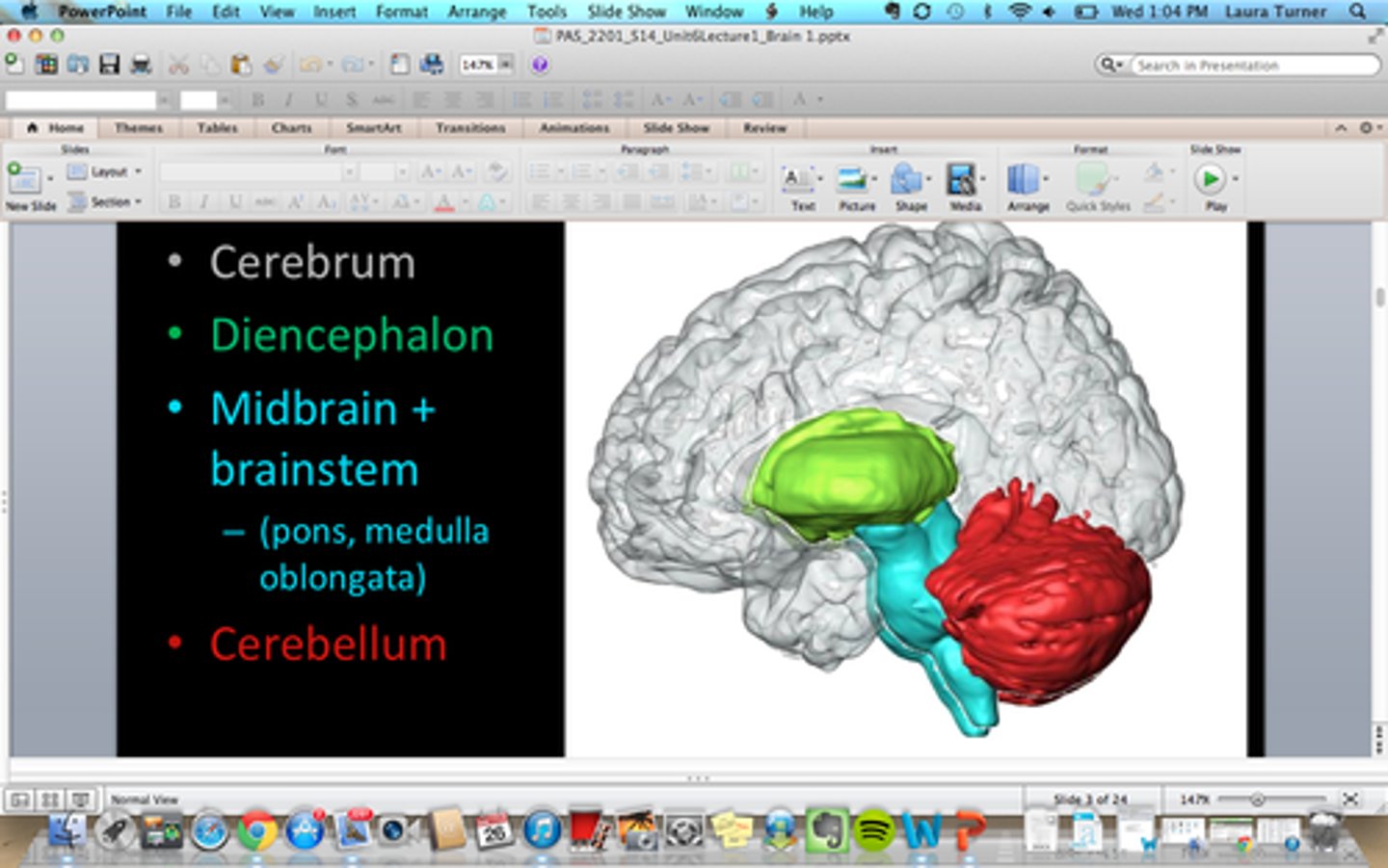
Cerebrum
"Brain" area
Divided into Right and left hemispheres, connected by the Corpus Callosum
Diencephalon
"Middle of brain"- in between Cerebrum & Brain Stem
Consists of:
1. Hypothalamus
2. Thalamus
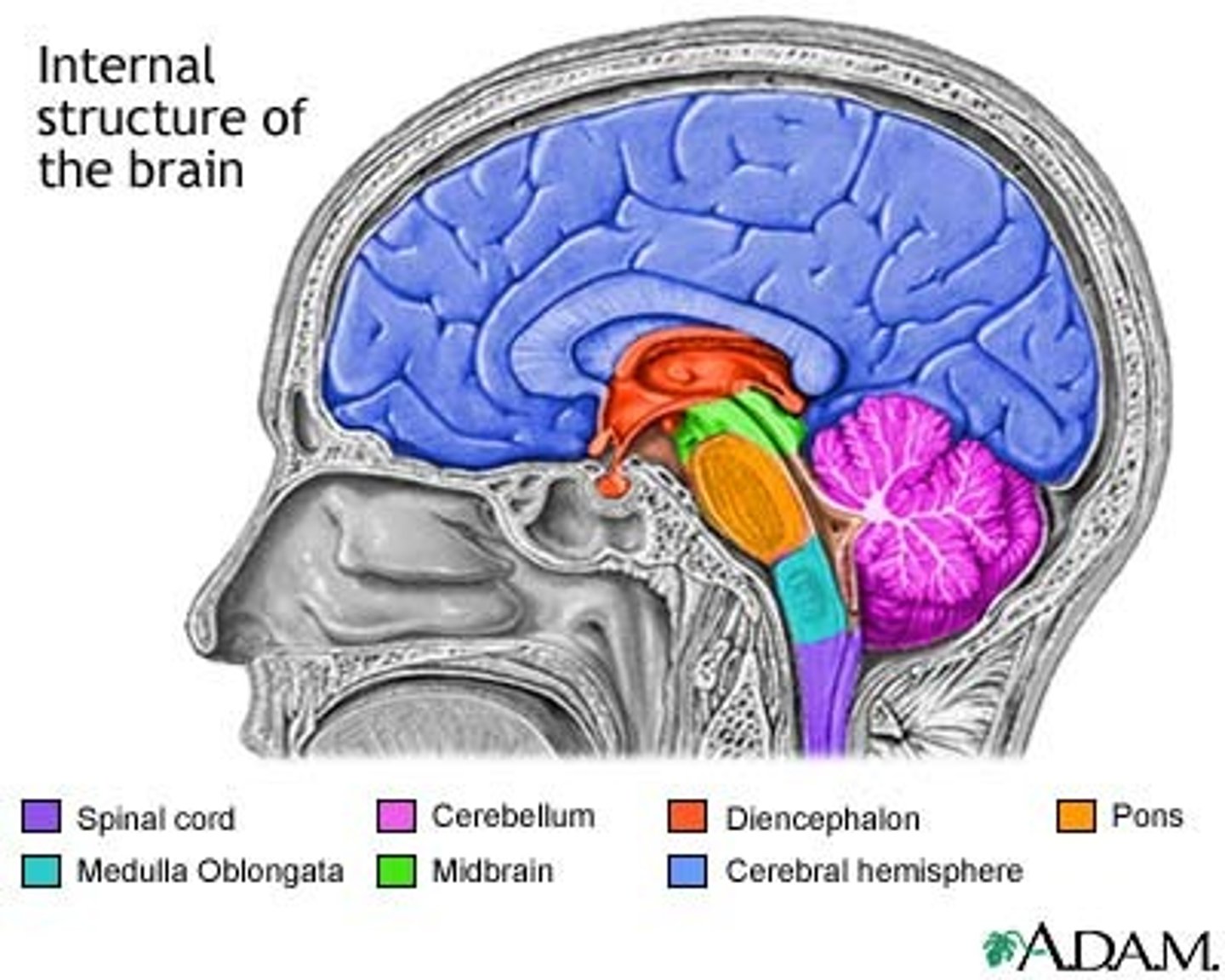
Cerebellum
Coordinates voluntary movements such as posture, balance, coordination, and speech, resulting in smooth, balanced muscular activity
-
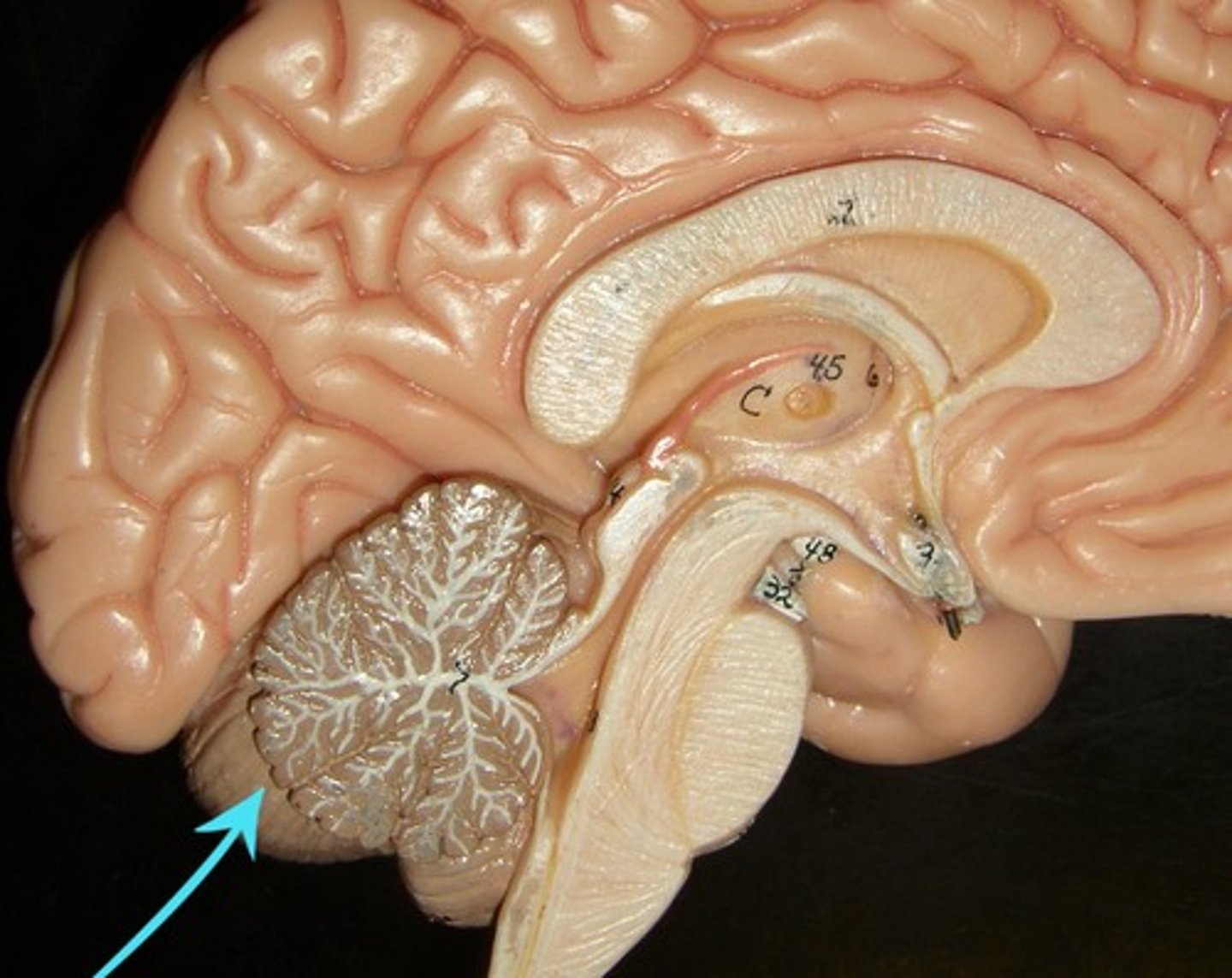
Injury to the Cerebellum leads to this...
Tremors or movement issues.
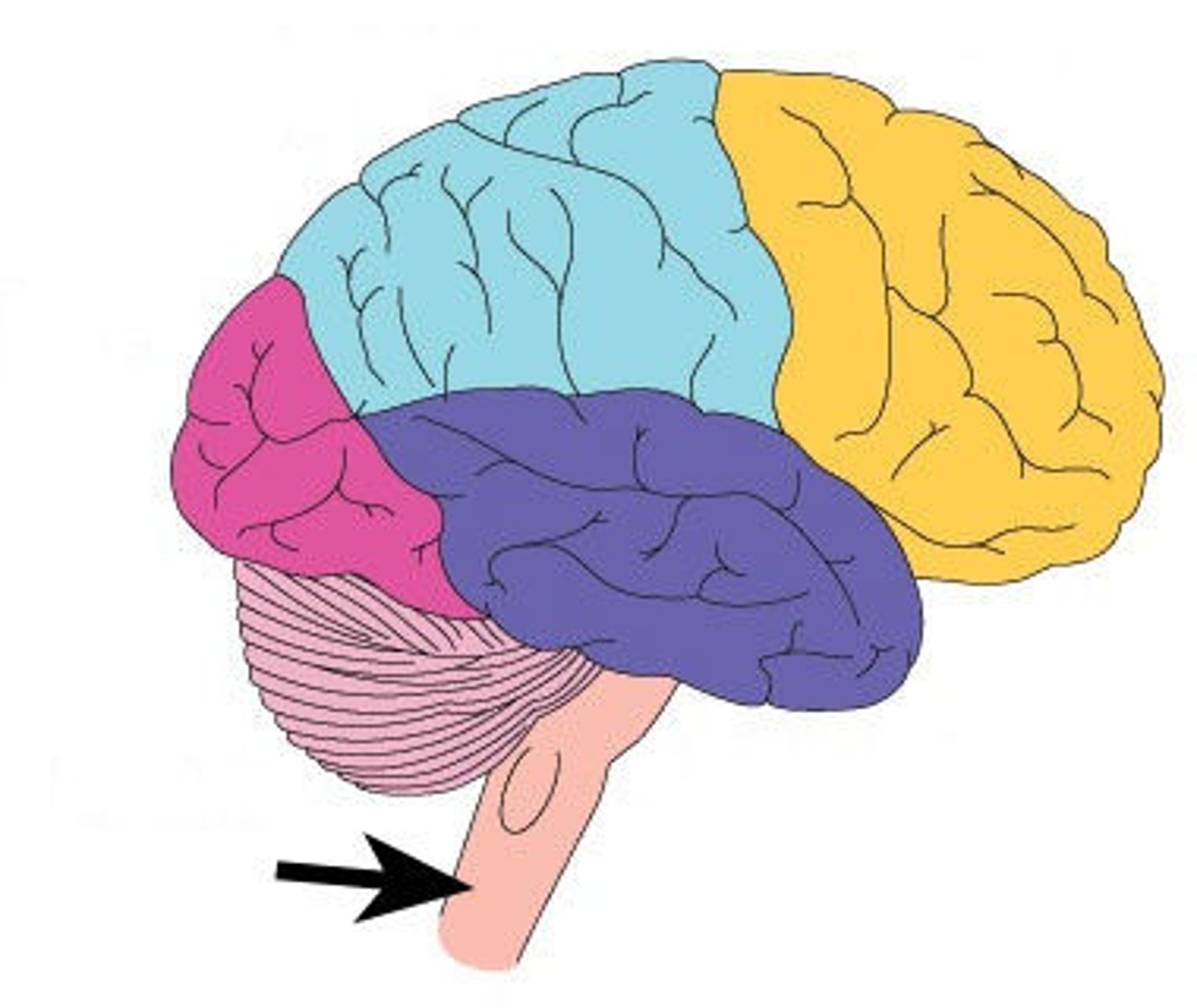
Brain Stem
Connects brain to spinal cord
Made up...
1. Midbrain
2. Pons
3. Medulla Oblongata
Right Cerebral Hemisphere
Controls left body,
Creative, Visual, facial recognition, visual, and musical traits
Left Cerebral Hemisphere
Controls Right Body
Logical, Math, Calculations, Organized traits
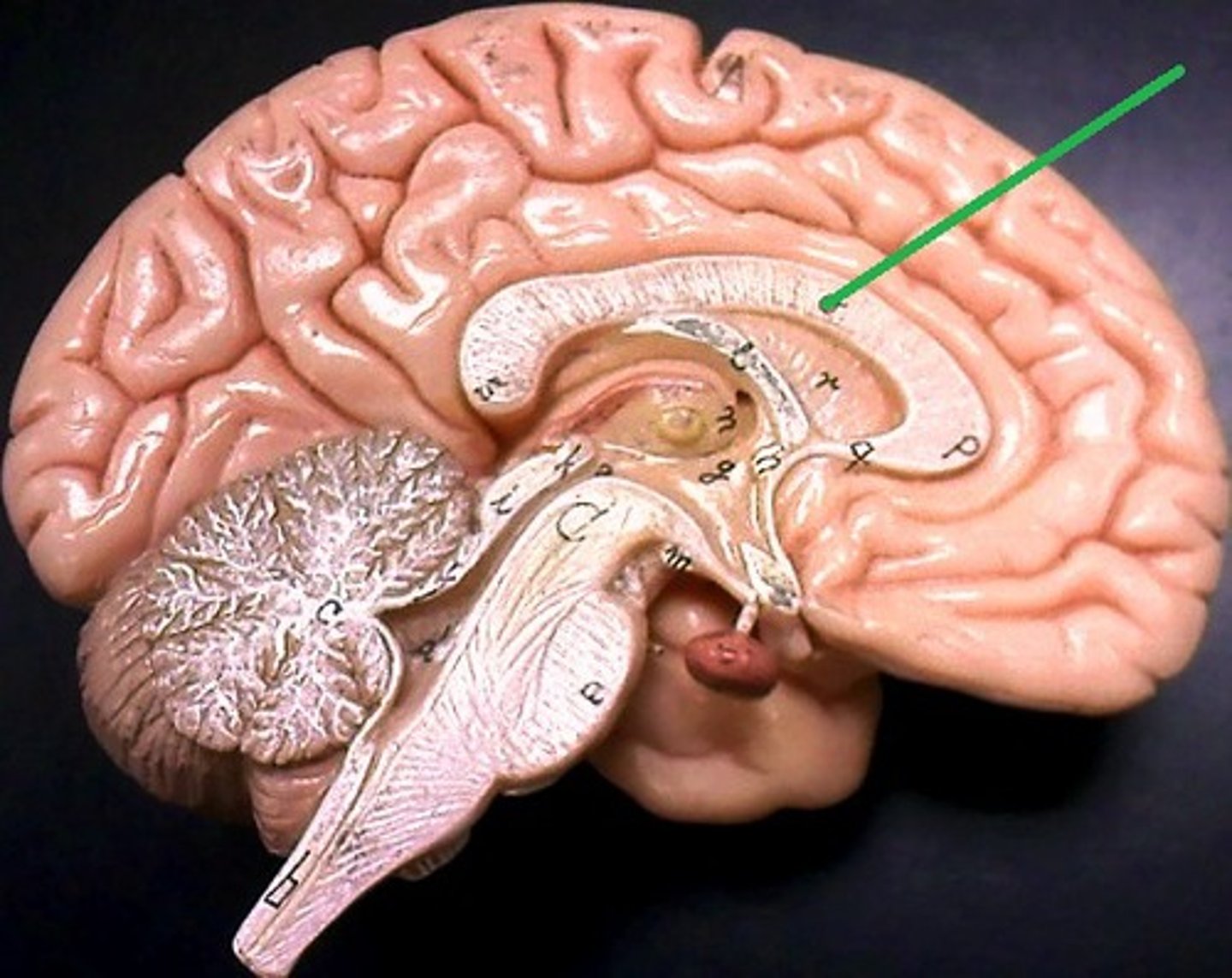
Corpus Callosum
Connects the left and right hemispheres(sides) of the brain
Gyri
Brain ridges or Brain wrinkles
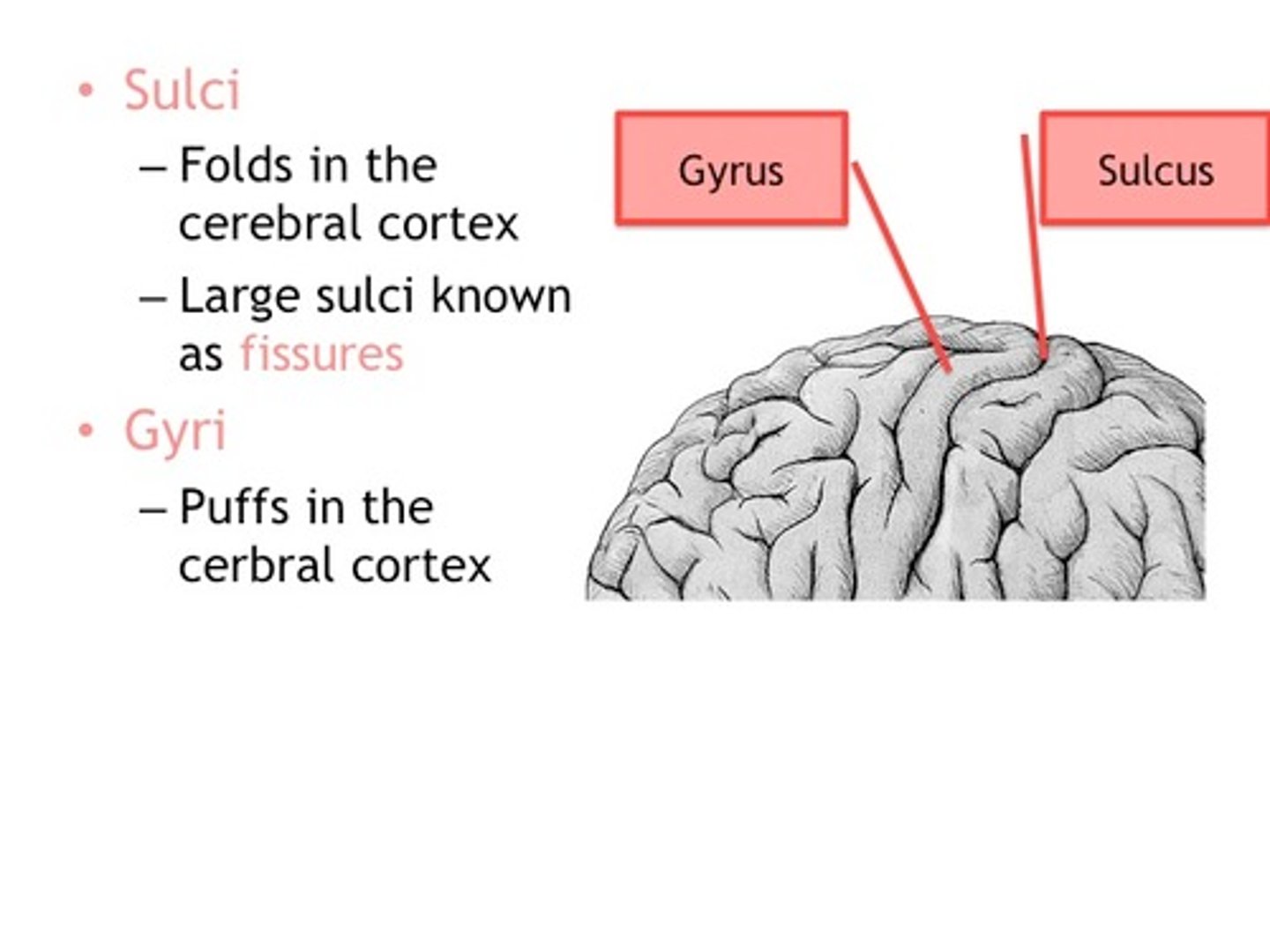
Sulcus
Shallow wrinkles of the brain
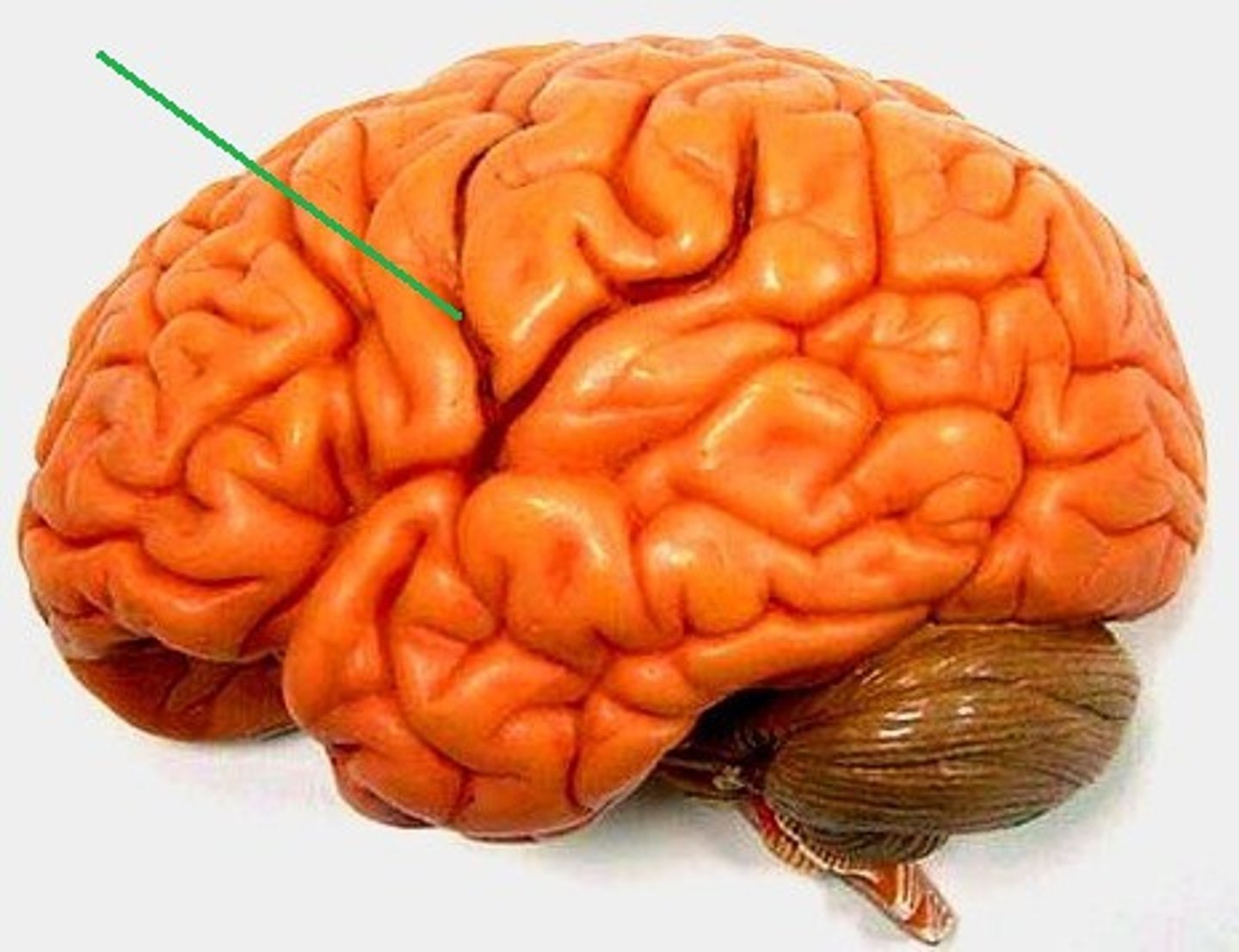
Fissure
Deep groove of the brain
Split Brain Experiment (1981)
An experiment that discovered differences in the right and left brain hemispheres; won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
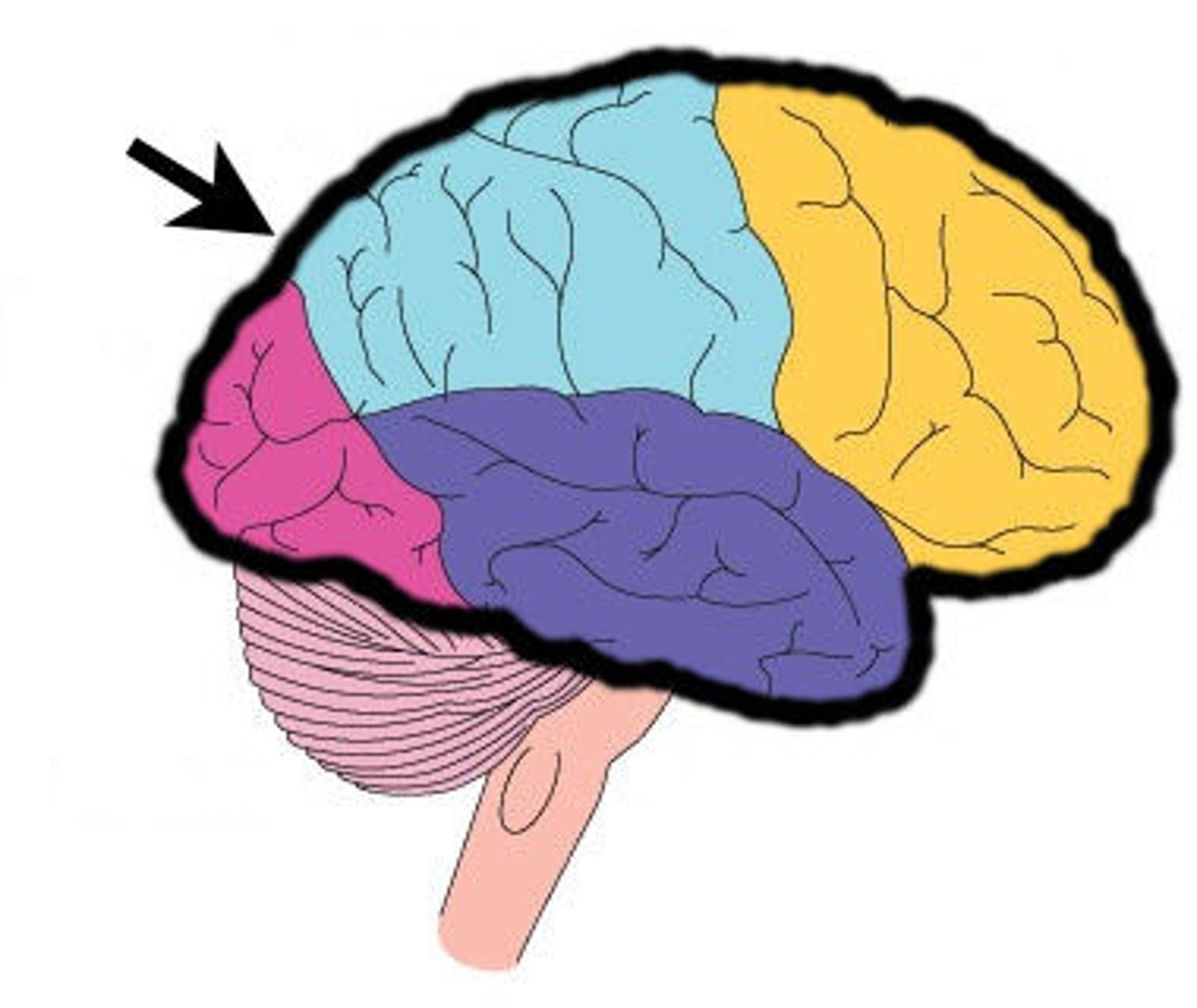
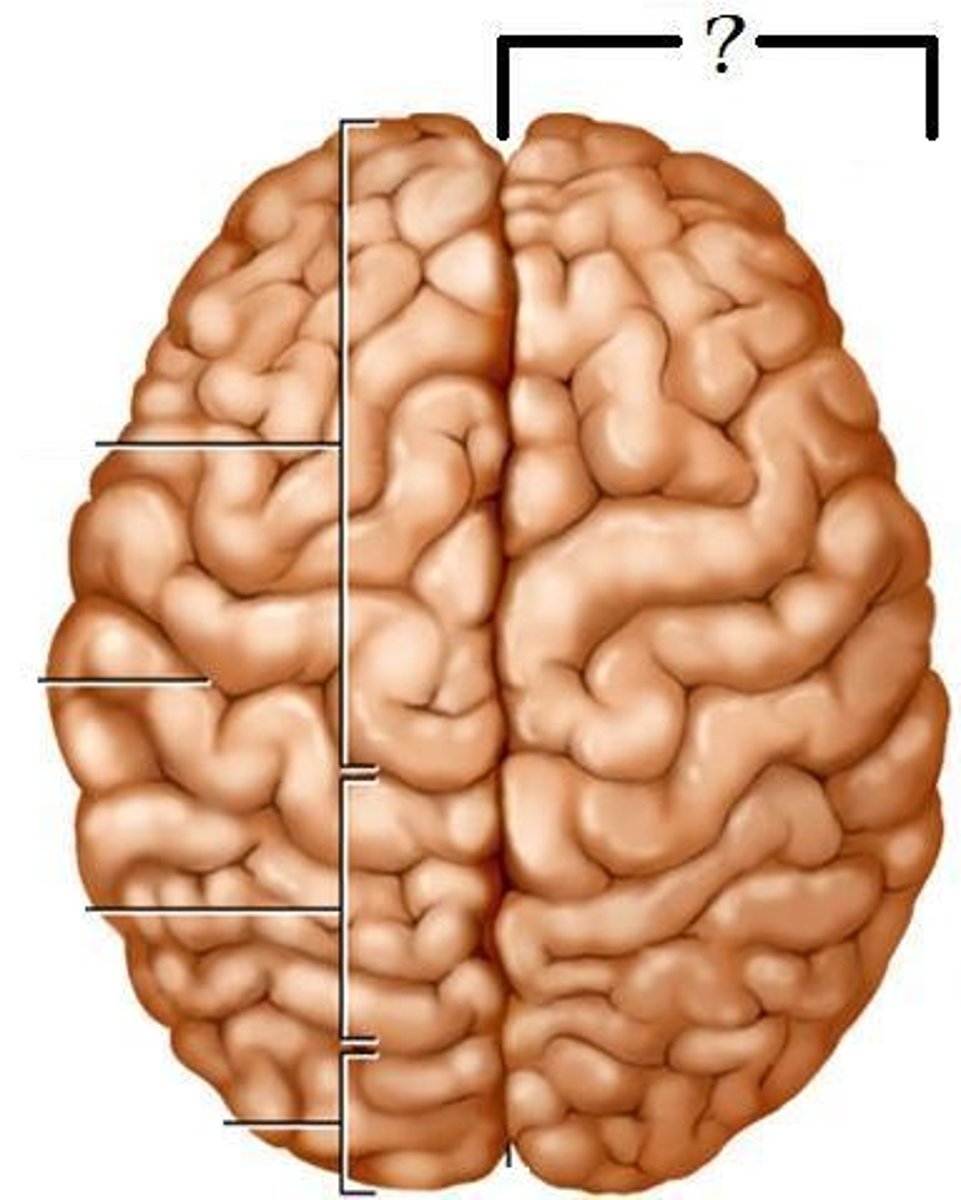
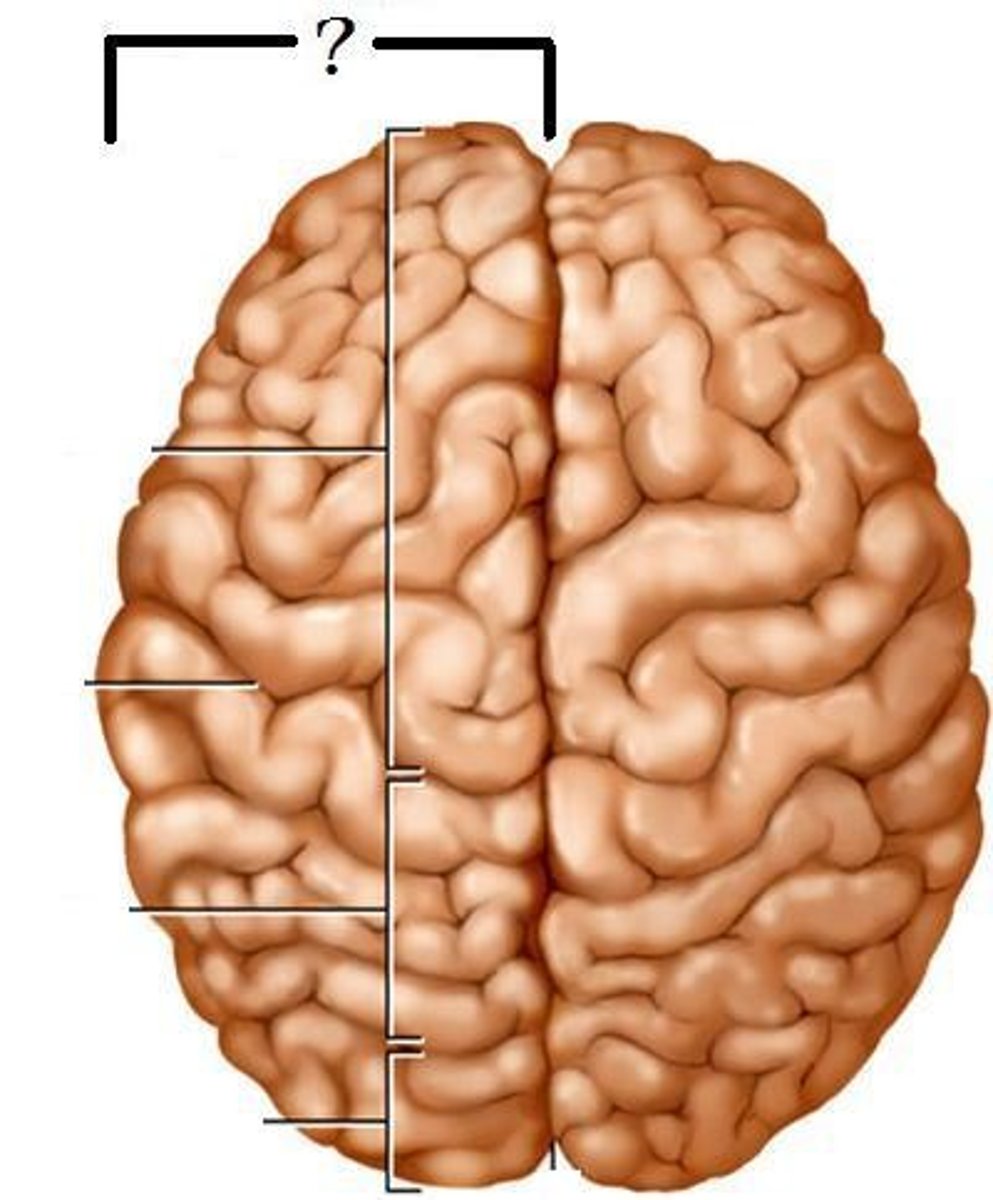
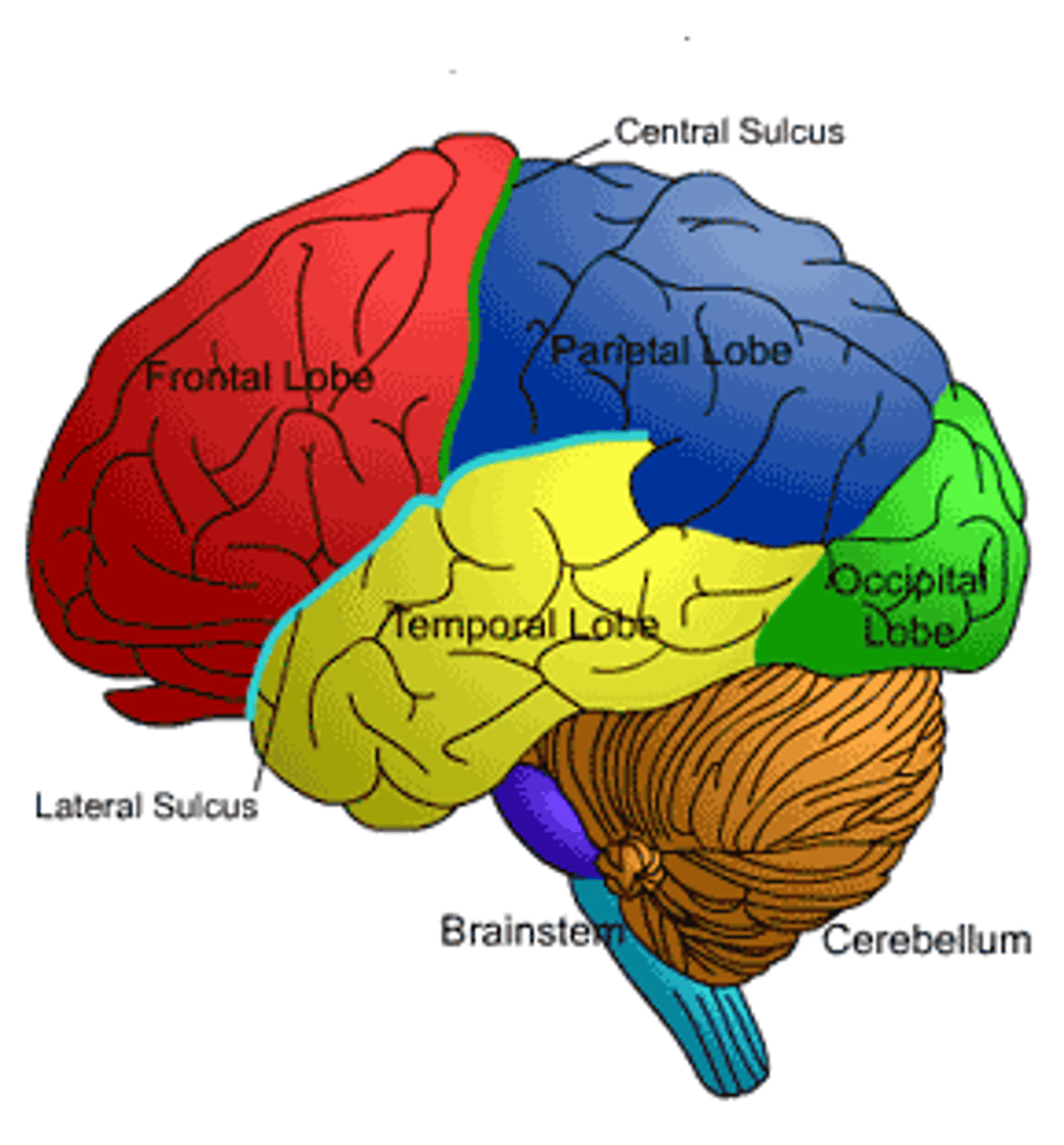
Frontal Lobe
Controls your logic, decision making, concentration, and personality
Parietal Lobe
Touch, pressure, temperature, pain
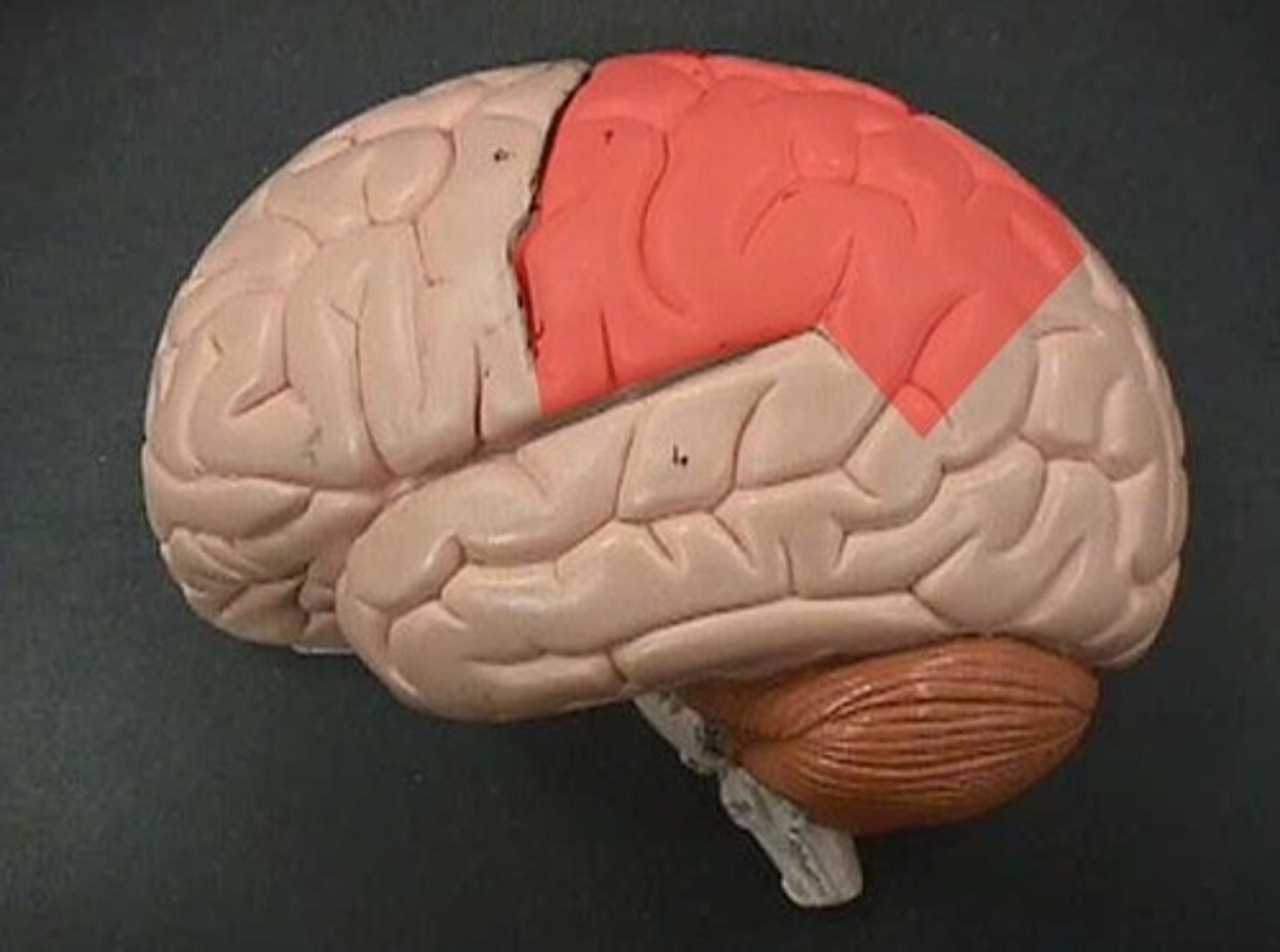
Temporal Lobe
Controls your hearing & memory.
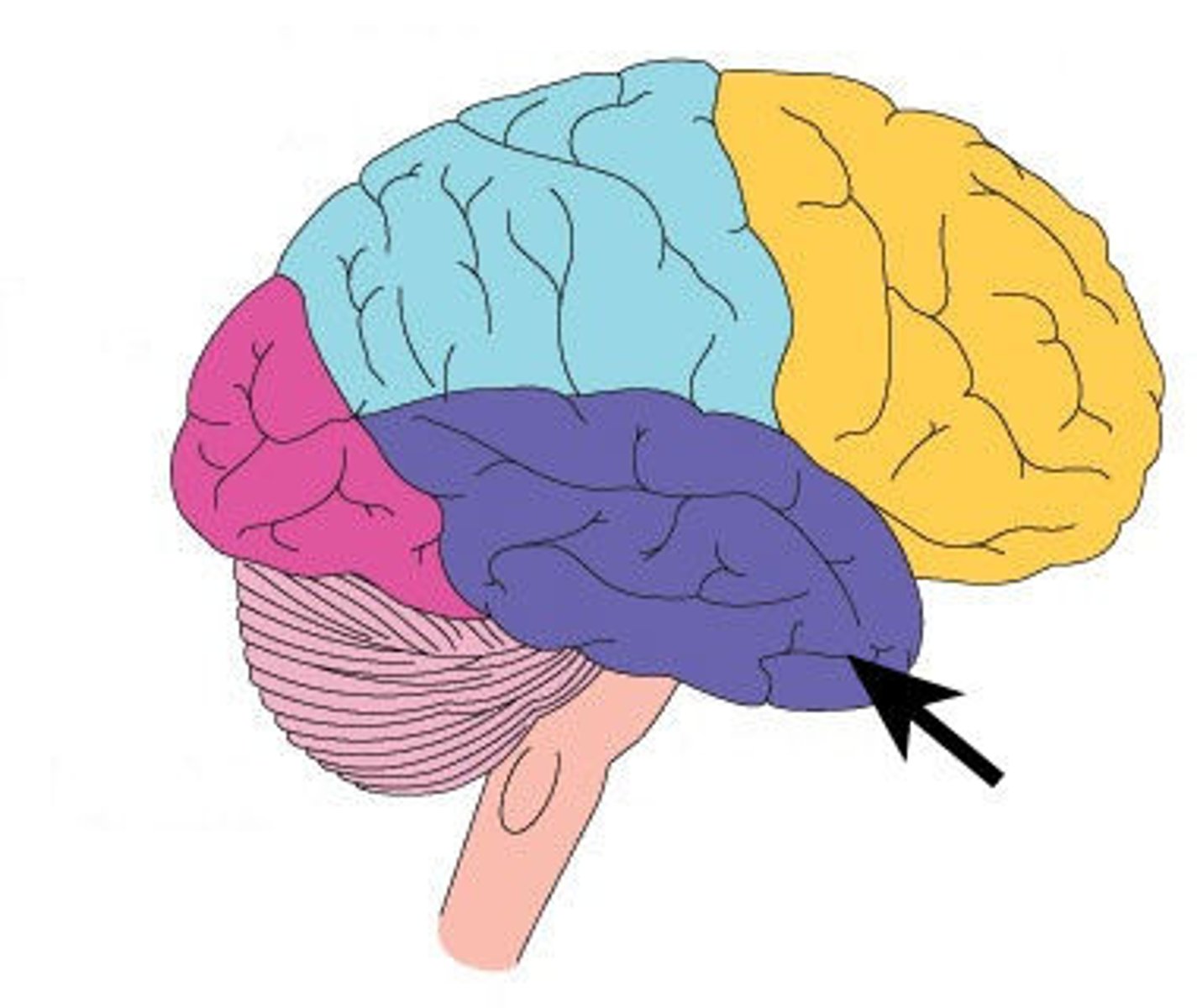
Occipital Lobe
Controls vision/sight
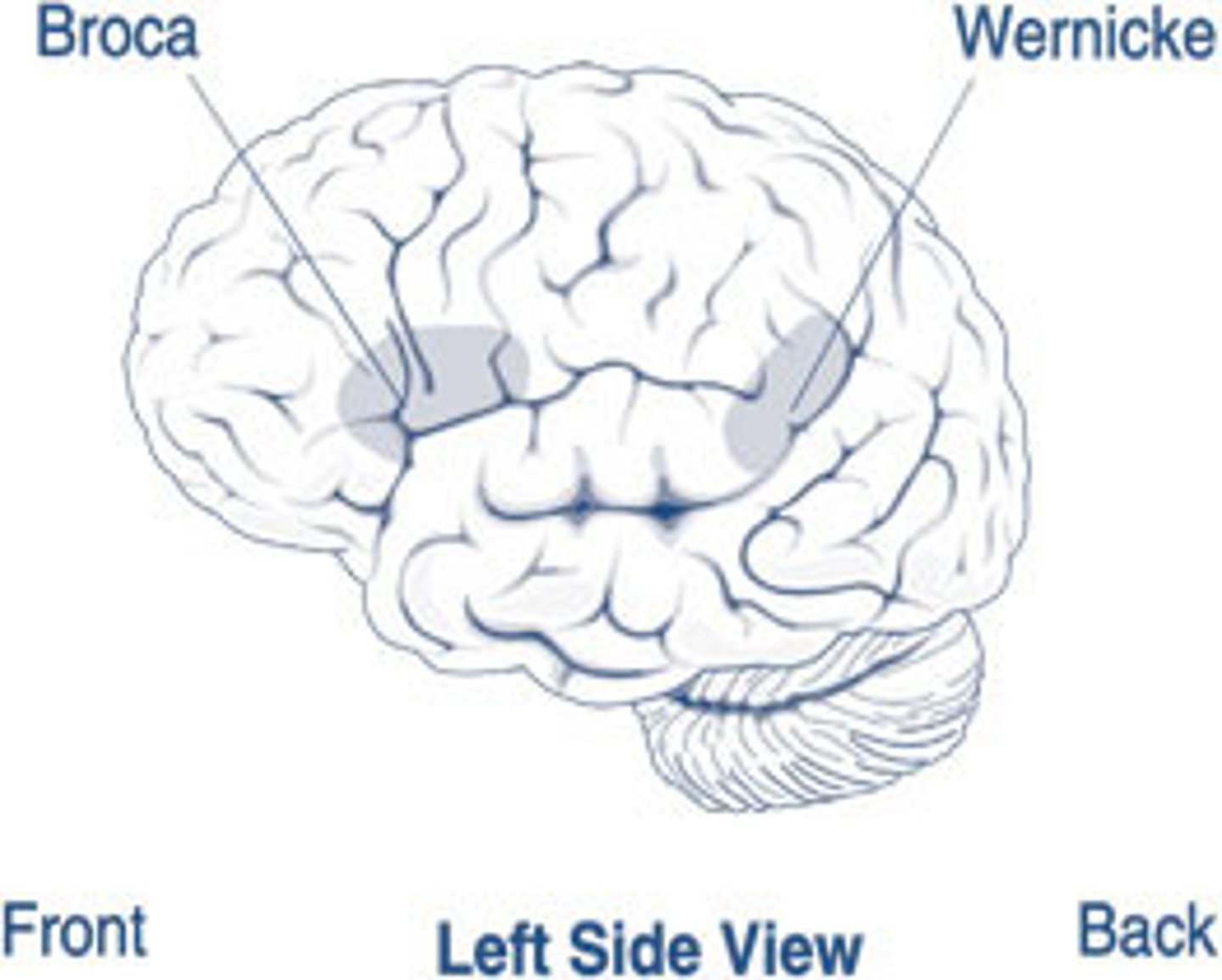
Brocas & Wernicke's Area
Controls Language and Speech
Brocas: hearing and interpreting speech
Wernickes's: writing
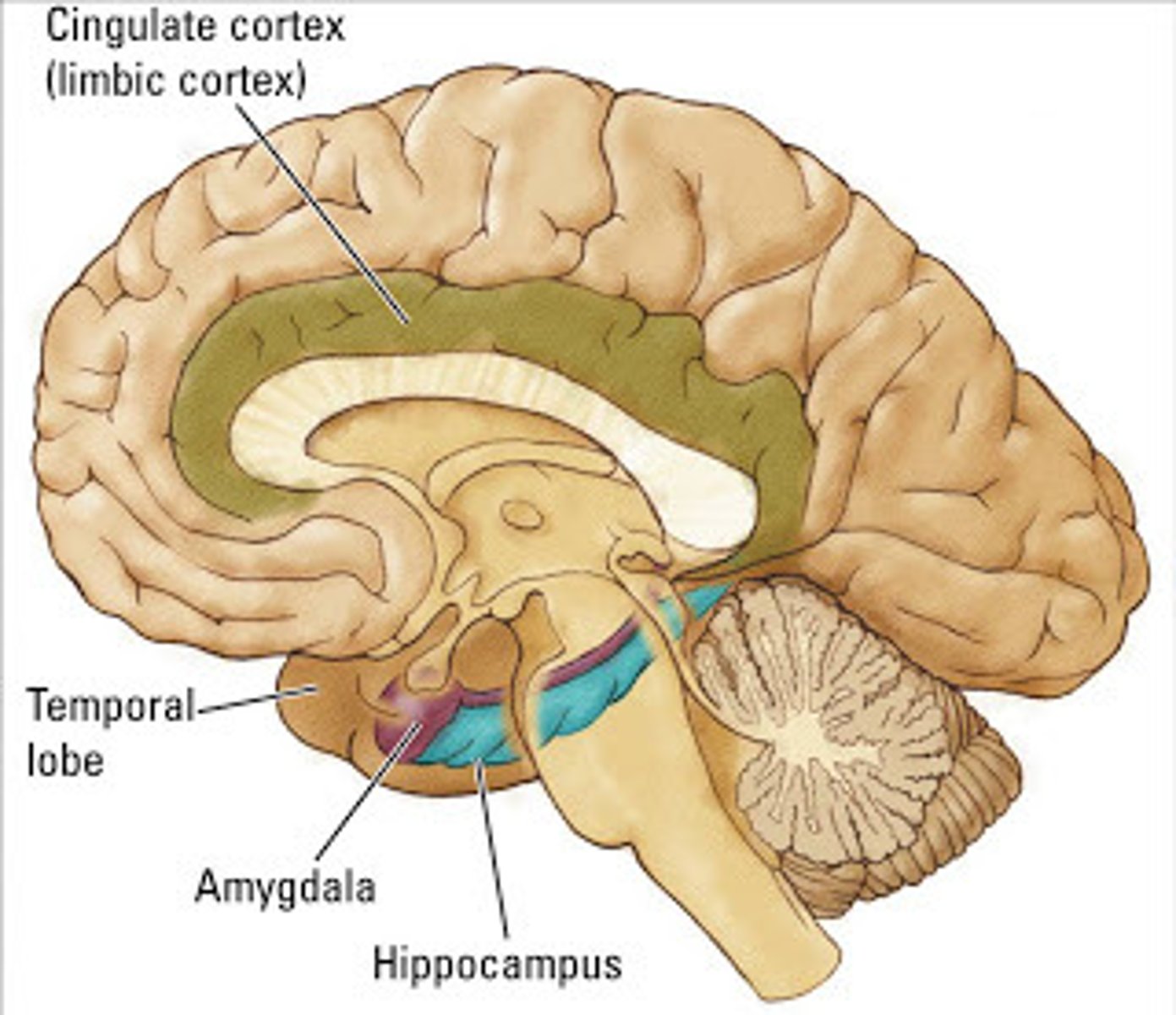
Hippocampus
Controls Memory
important in forming new memories and connecting emotions and senses, such as smell and sound, to memories.
Thalamus
Accepts sensory messages
Hypothalamus
Takes messages from the Thalamus and sends signals to glands.
Helps regulate body temperature, certain metabolic processes and other autonomic activities
Amygdala
Controls Emotions
"almond" shaped
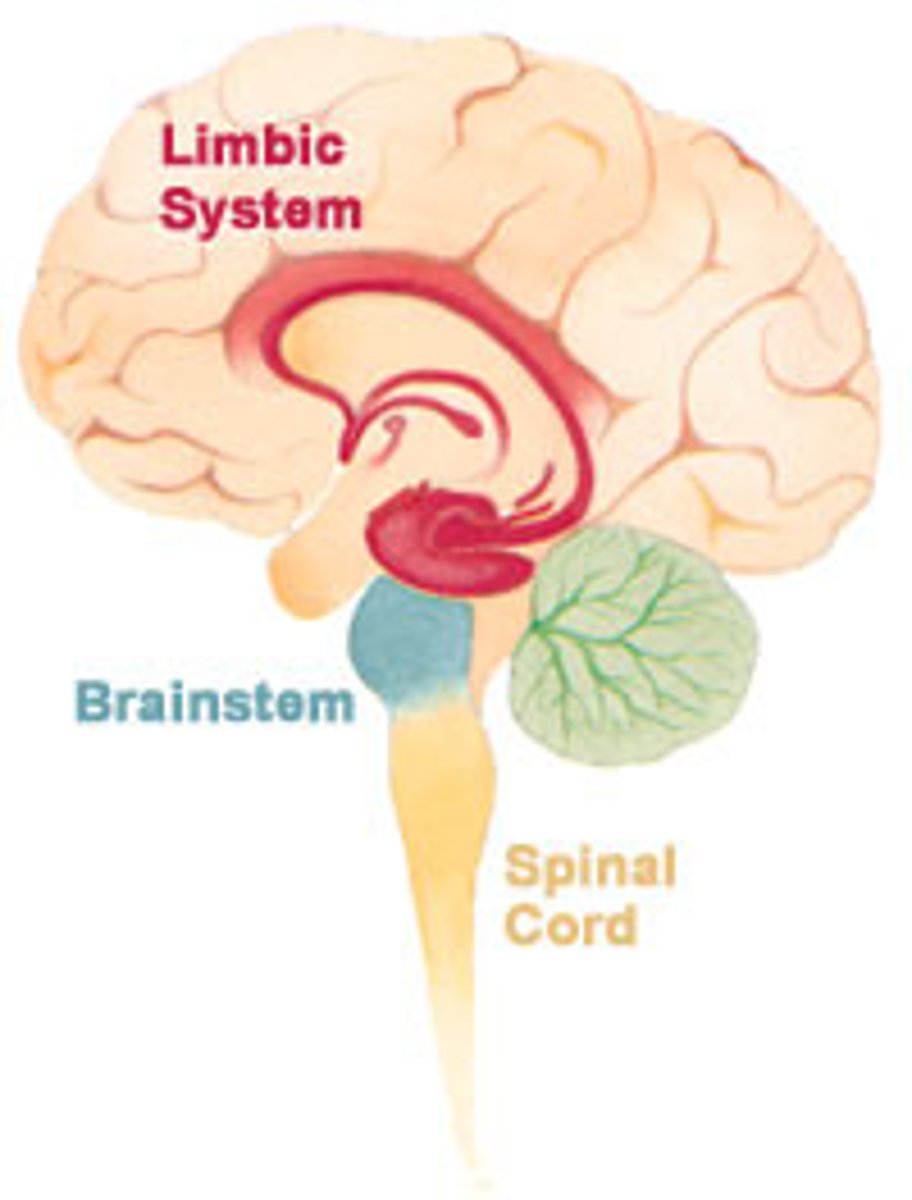
Limbic System (and the organs that make up the Limbic System)
Controls Emotion.
Includes:
1.Thalamus & Hypothalamus
2. Amygdala
3. Hippocampus
4. Olfactory bulbs.
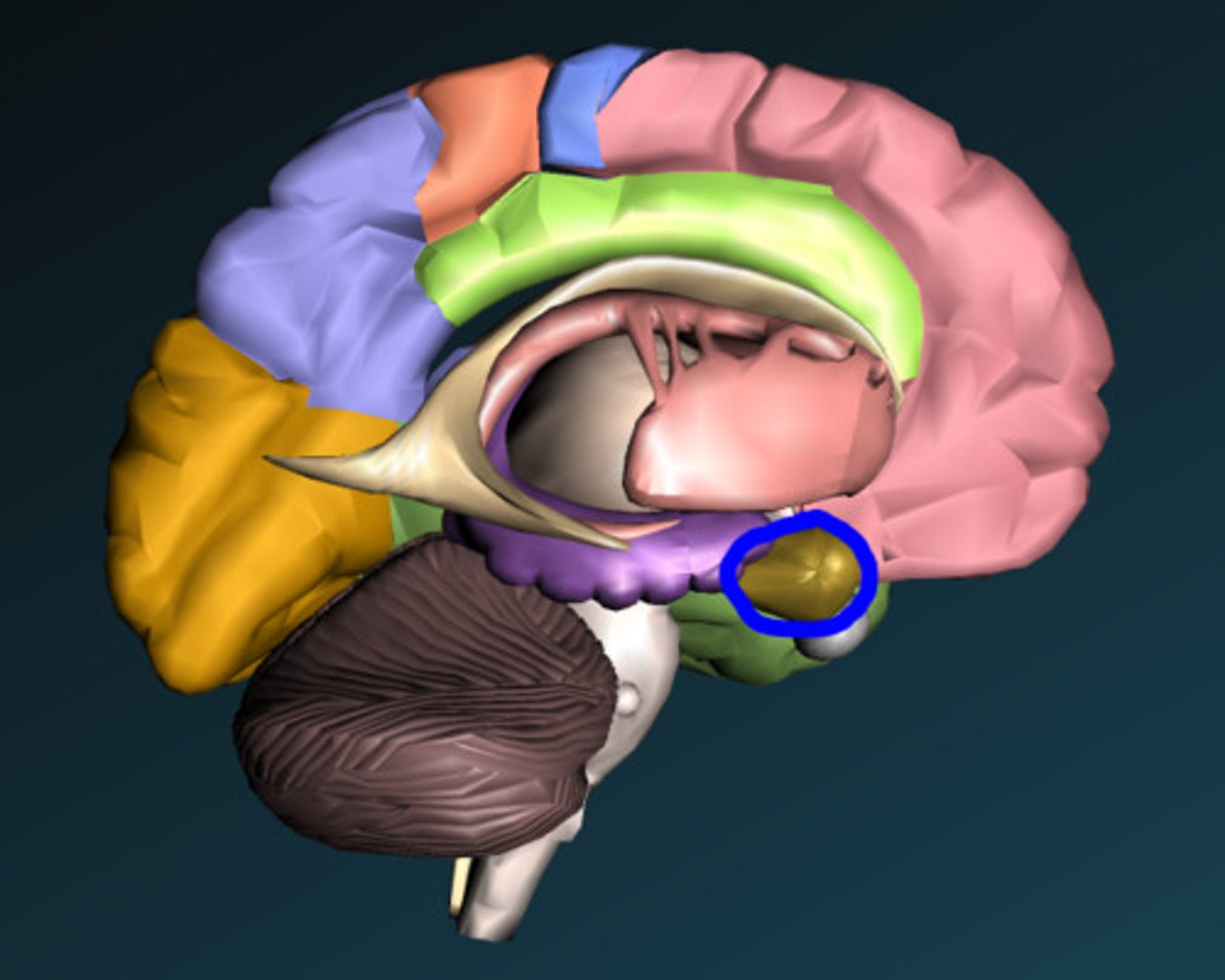
Midbrain
A portion of the Central Nervous System controls reflexes
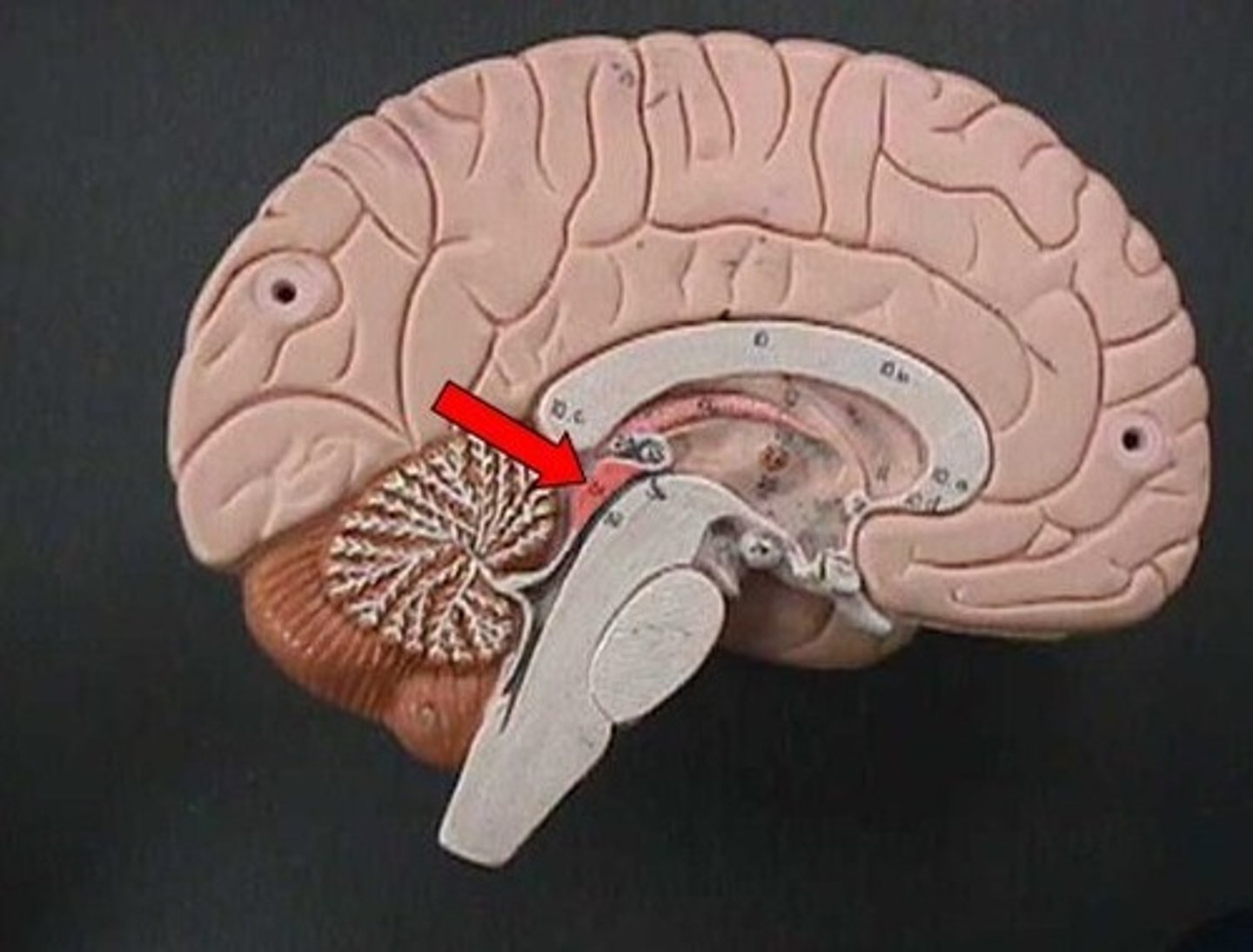
Medulla Oblongata
Transfers messages along the spinal cord.
Located below the pons
Controls some autonomic functions (ex. breathing, swallowing)
Autonomic functions
Regulate involuntary actions like the intestines, heart, and glands.

Reticular Formation
Mediates the overall level of consciousness
During Sleep: Reticular Formation off
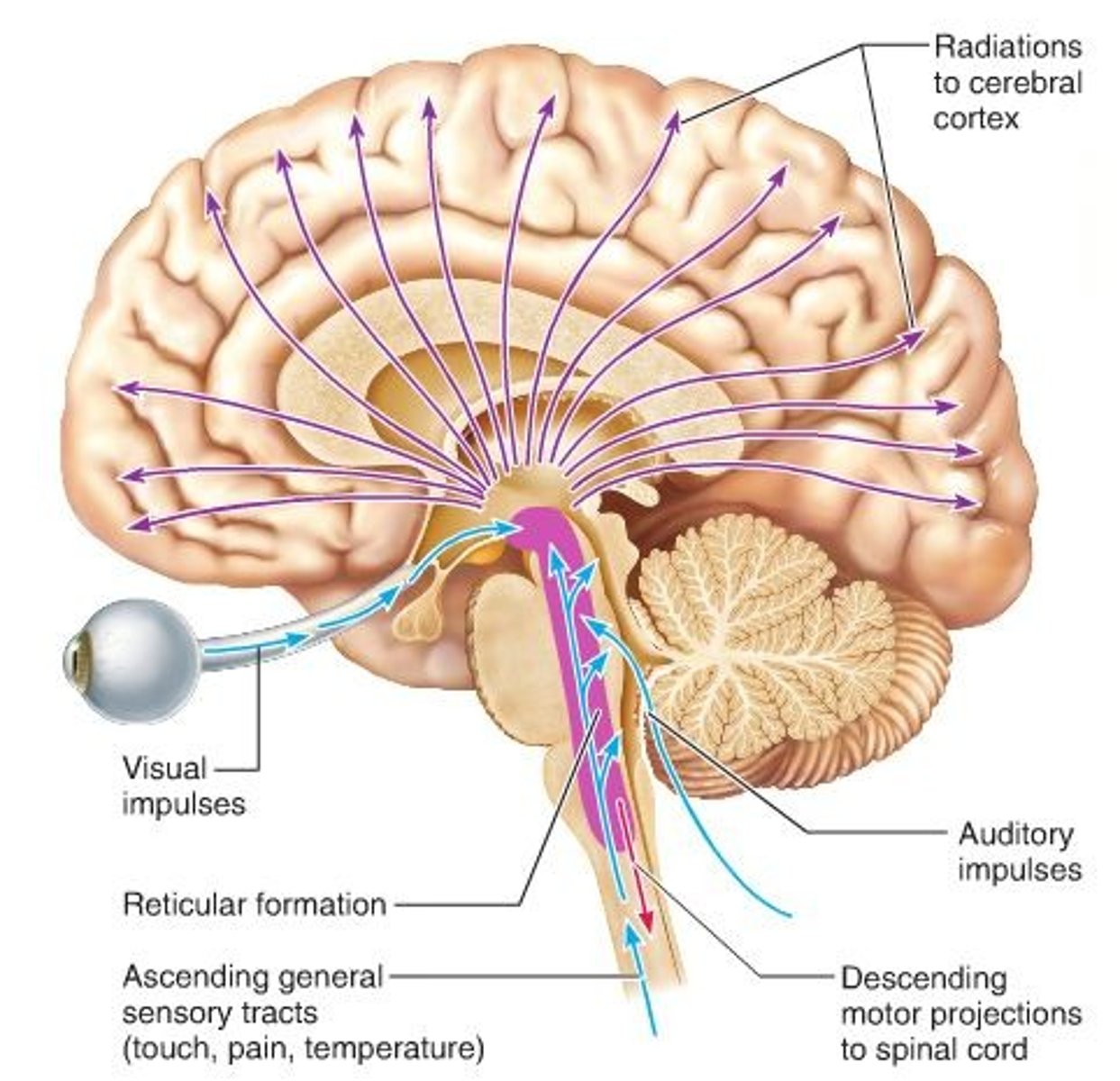
Comatose
Damage to Reticular Formation leads to...
Effect of consistent Barbituate Drug use (depressants like alcohol, Xanax) on Reticular Formation
Decreases Reticular Formation (ability to turn brain on or off)
Meninges
The protective covering over the brain & spinal cord.
Meningitis
Infection of meninges, causes of infection include bacteria, viruses, cancer, and brain injury
meningitis
Spinal Tap can test for this...
Ascending Nerves
A nerve pathway that goes upward from the spinal cord toward the brain carrying sensory information
Descending Nerves
Nerves pathway going down the spinal cord
Cervical Plexus
The first four cervical spinal nerves. (C1-C4)
Brachial Plexus
A network of nerves that send signals to your spine, shoulders, arms, and hands. (C5-T1)
Intercostal Nerves
Network of nerves found in between the thoracic region of the spine. (T1- T11)
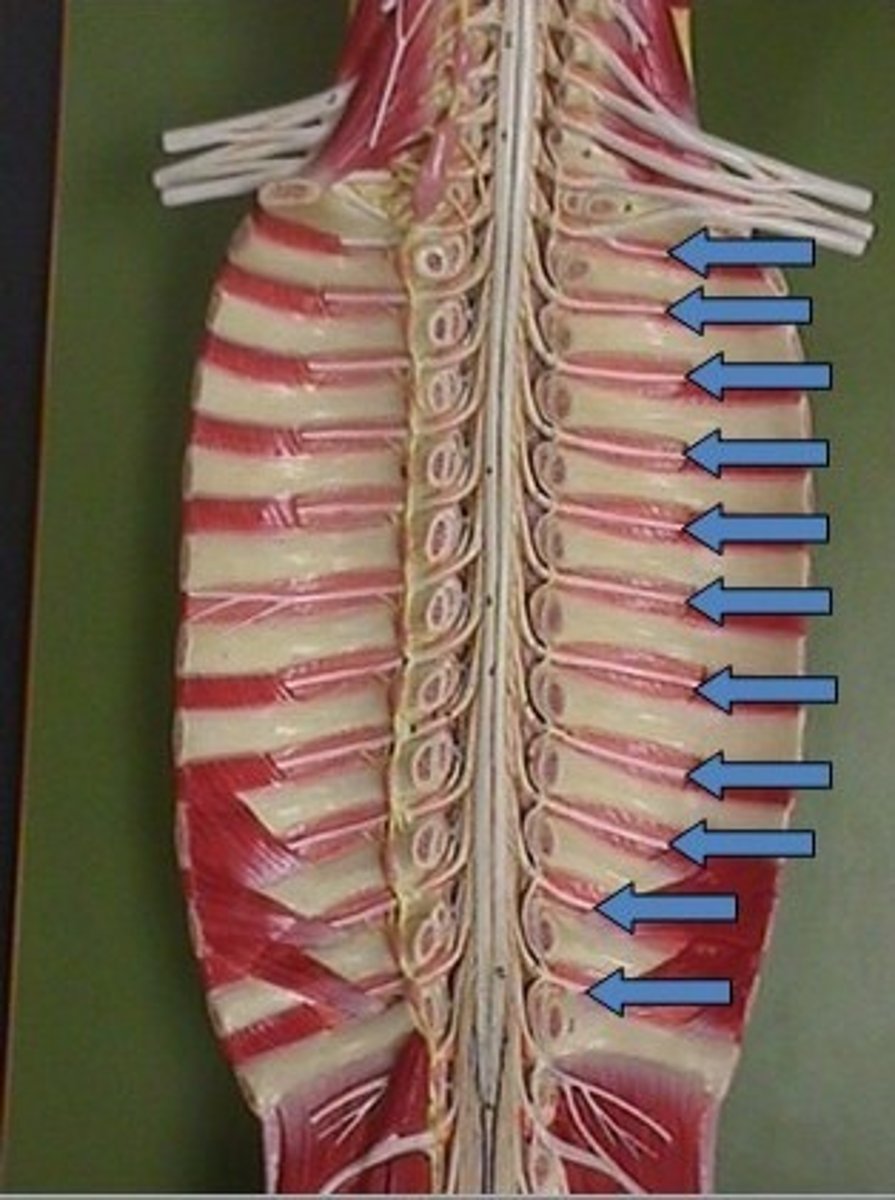
Lumbosacral Plexus
Network of nerves found at base of spinal cord (T11 - S5)
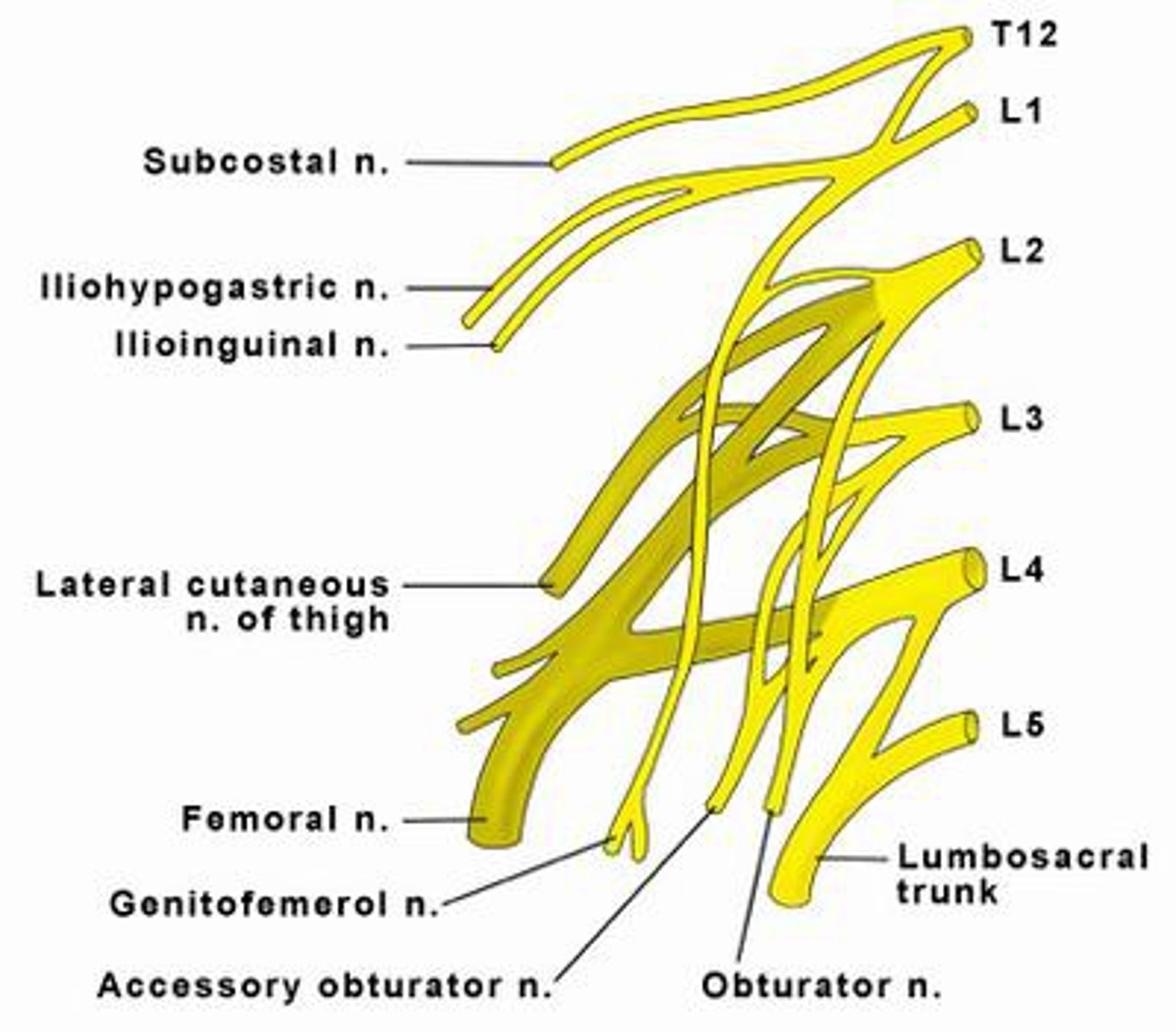
Sciatic Nerve
A major nerve extending from the lower end of the spinal cord down the back of the thigh, and dividing above the knee joint.
It is the nerve with the largest diameter in the human body
Common Injury
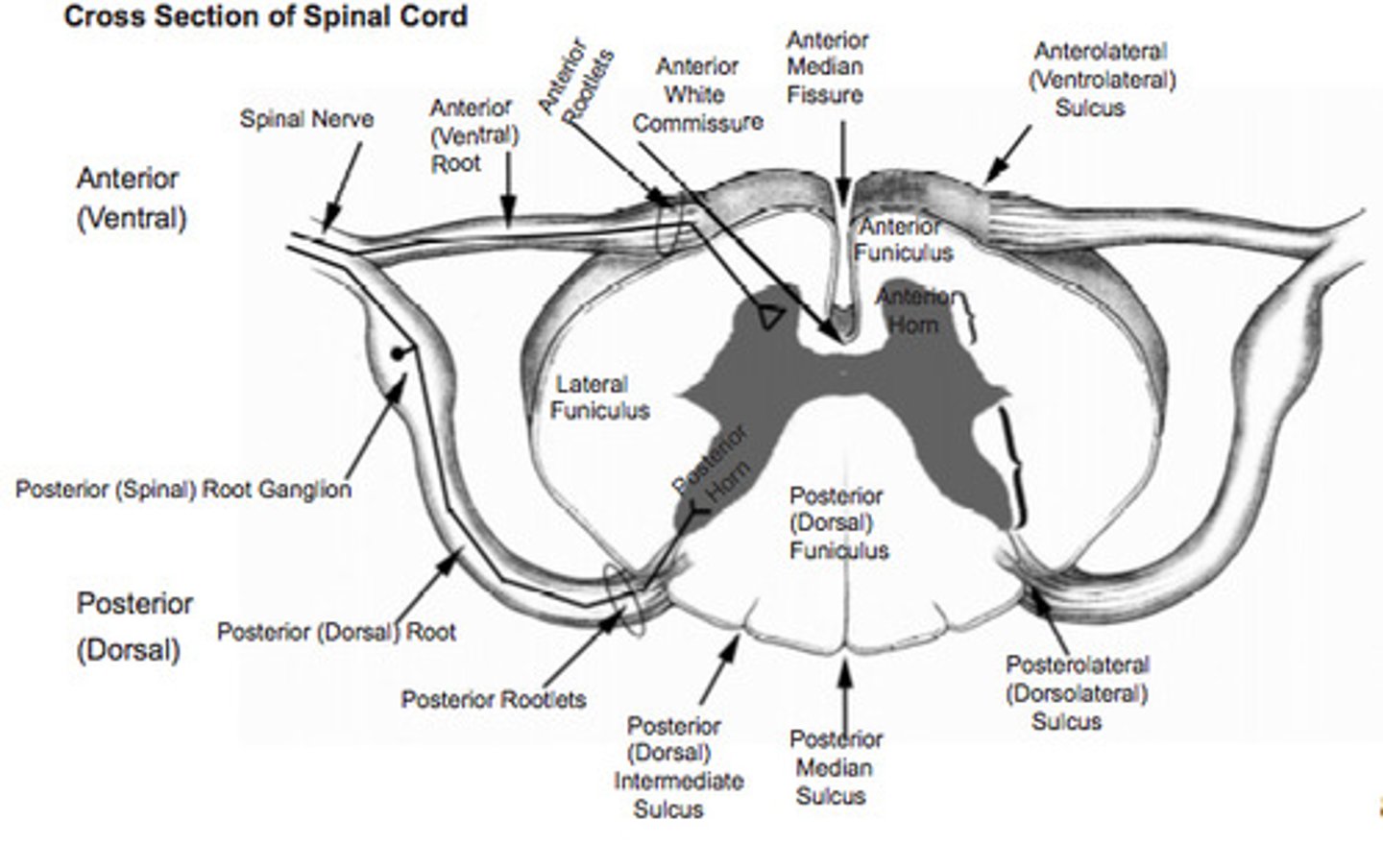
Spinal Cord cross section
Excitatory Neurtransmitters
Starts up (stimulates the brain)
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Calms the brain and helps create balance
Acetylcholine
Neurotransmitter, skeletal muscle contractions
Endorphins
Neurotransmitter, Reduces pain, fight or flight
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter, feel good
(low amounts: depression)
Dopamine
Neurotransmitter, feel good
Regulates attention, cognition, movement, pleasure, and hormonal processes
(Low amounts: Parkinson's)
Serotonin
Neurotransmitter, that causes the feeling of sleepiness
(Low amounts: Aggression)
Why are Personality Disorders difficult to treat?
There is not one cure for any type of personality disorder. Every person is different and must be treated differently
Since there is a personality issue, drugs do not necessarily fix the issue
Symptoms begin to show around age 18 in men and age 25 in women.
The worst symptoms begin to show from ages 25-40
What age do those suffering from Schizophrenia typically begin to show symptoms
Olfactory Bulb
Sense Smell
Linked to the Hippocampus (the reason why smell is so related to memory)