Crime & Deviance: Functionalist & Subcultural theories of crime
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/11
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
1
New cards
Functionalism & Crime
While too much crime is destabilising, crime is inevitable in society and performs some positive functions.
\
The perfect amount of crime will keep society healthy and avoid anomie (Normlessness)
\
The perfect amount of crime will keep society healthy and avoid anomie (Normlessness)
2
New cards
Positive functions of crime (Functionalist, Durkheim)
1. Boundary maintenance
2. Adaptation and change
3
New cards
Other functions (Functionalist, Davis)
Safety Valve- prostitution acts as a safety valve for the release of men’s sexual frustrations without threatening the monogamous nuclear family.
4
New cards
Other functions (Functionalist, Cohen)
**Warning devices**– theft, drug use and truancy alert us to other social problems in society/that institutions aren’t working effectively.
5
New cards
Critiques (Durkheim)
1. How much deviance is functional?
2. Why does crime happen?
6
New cards
Strain theory (Functionalist, Merton)
Strain to anomie.
\
Goals that a culture encourages individuals to achieve VS what the institutional structure of society allows them to achieve legitimately (goals vs means)
\
An individual’s position in the social structure determines how they adapt or respond to this strain.
\
Goals that a culture encourages individuals to achieve VS what the institutional structure of society allows them to achieve legitimately (goals vs means)
\
An individual’s position in the social structure determines how they adapt or respond to this strain.
7
New cards
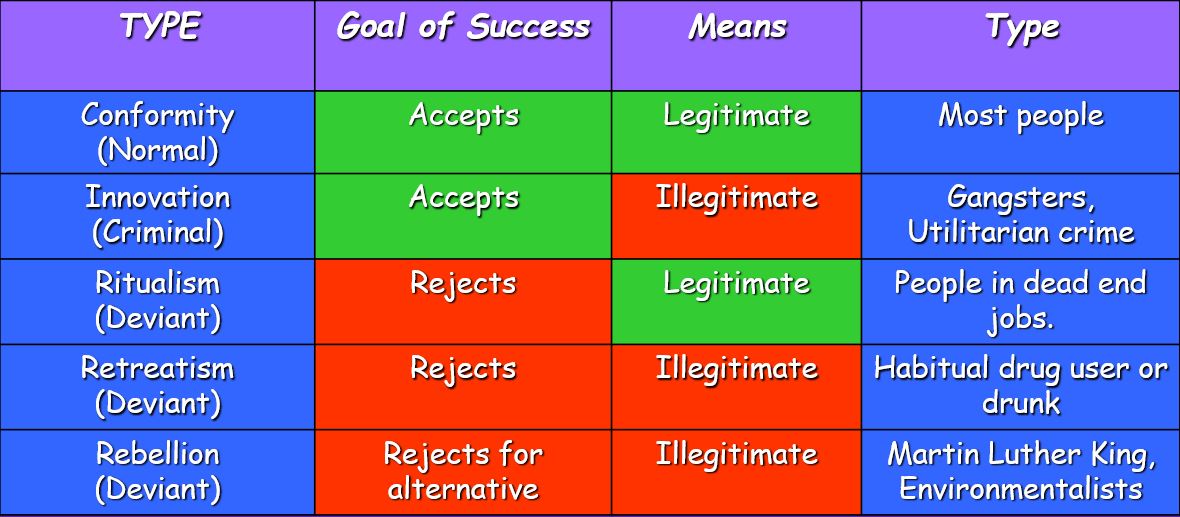
Conformity (Response to strain, Merton)
People that accept culturally approved goals and strive to achieve them legitimately (mostly among middle-class).
8
New cards
Innovation (Response to strain, Merton)
Individuals who accept the goals but use illegitimate means to achieve them as they lack the legitimate means.
9
New cards
Status frustration (Sub-cultural. A.K Cohen)
Status frustration.
Agrees w/Merton but looks at subculture response rather than individual and explains non-utilitarian crime through the alternative status hierarchy.
1. w/c taught m/c norms and values
2. w/c children can’t achieve m/c norms and values legitimately
3. this causes status frustration.
4. so, they reject m/c norms and values and want to seek revenge
5. form delinquent subcultures w/others in the same position and an alternative status hierarchy begins
6. offers an alternative route to gain success by inverting the values of school and society (vandalism and truanting)
Agrees w/Merton but looks at subculture response rather than individual and explains non-utilitarian crime through the alternative status hierarchy.
1. w/c taught m/c norms and values
2. w/c children can’t achieve m/c norms and values legitimately
3. this causes status frustration.
4. so, they reject m/c norms and values and want to seek revenge
5. form delinquent subcultures w/others in the same position and an alternative status hierarchy begins
6. offers an alternative route to gain success by inverting the values of school and society (vandalism and truanting)
10
New cards
Three subculture responses (Subcultural, Cloward and Ohlin)
Agrees with Merton but notes not everyone turns to innovation, different subcultures respond in different ways to the lack of legitimate opportunities.
There is also unequal access to illegitimate opportunity structures.
__The subculture responses:__
1. criminal subcultures
2. conflict subcultures
3. retreatist subcultures
There is also unequal access to illegitimate opportunity structures.
__The subculture responses:__
1. criminal subcultures
2. conflict subcultures
3. retreatist subcultures
11
New cards
Critiques (Cloward and Ohlin)
1. south – boundaries are too sharply drawn between these- drug use is also common in both conflict and criminal subcultures
2. matza – most delinquents are not strongly committed to their subculture and will merely drift in and out of delinquency
12
New cards
Strain theory responses (Functionalist, Merton)
__Responses:__
1. Conformity
2. Innovation
3. Ritualism
4. Retreatism
5. Rebellion
1. Conformity
2. Innovation
3. Ritualism
4. Retreatism
5. Rebellion