Cell Physiology: pt.2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/69
Last updated 3:41 AM on 12/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1
New cards
glycoprotein
Integral proteins with attached carbohydrate groups
2
New cards
phospholipids
Molecules that form the membrane bi-layer
3
New cards
glycocalyx
A sticky coat formed over the cell surface
4
New cards
cholesterol
Forms pate-like wedges that help keep the membrane fluid
5
New cards
glycolipid
Lipids with carbohydrates attached
6
New cards
peripheral protein
proteins, not embedded in the lipid bi-layer, some of which are enzymes
7
New cards
integral protein
proteins that are firmly embedded in the lipid bi-layer
8
New cards
osmosis
The movement of water molecules across a membrane, from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
9
New cards
dialysis
The separation of small molecules from larger ones by passing a solution through an artificial, semipermeable membrane
10
New cards
simple diffusion
The movement of substances from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration
11
New cards
facilitated diffusion
The transport of substances across the plasma membrane with the help of carrier molecules
12
New cards
filtration
The movement of solvents and solutes across a semipermeable membrane by mechanical pressure
13
New cards
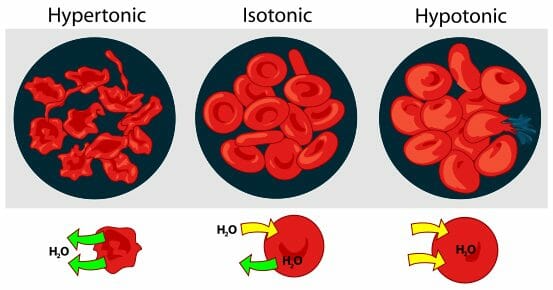
hypertonic- H2O leaves; becomes shriveled
isotonic- stable; H2O going in & out
hypotonic- H2O is filling it causing it to grow; cell will rupture
isotonic- stable; H2O going in & out
hypotonic- H2O is filling it causing it to grow; cell will rupture
Explain red blood cells in hypertonic, isotonic, and hypotonic solutions
14
New cards
pinocytosis
The uptake of tiny droplets of extracellular fluid
15
New cards
phagocytosis
Process in which large, solid particles are taken in by the cell
16
New cards
receptor-mediated endocytosis
The active uptake of specific substances from the extracellular environment
17
New cards
phagocytosis
The disposal of germs, including viruses and bacteria from the body tissues may occur via the process of ____
18
New cards
pinocytosis
The acquisition of molecules or ions dissolved in the extracellular fluid is called ___
19
New cards
invagination
The folding of the plasma membrane resulting in the formation of a vesicle called ____
20
New cards
pinocytosis- PM pinches inward (imagination)
phagocytosis- PM pinches outward (pseudopods)
phagocytosis- PM pinches outward (pseudopods)
What is the difference, in terms of vesicle formation, of pinocytosis and phagocytosis?
21
New cards
RME- receptors bind to specific molecules called ligands (invagination is present)
phagocytosis- PM pinches outward (pseudopods)
phagocytosis- PM pinches outward (pseudopods)
What is the difference, in terms of vesicle formation, of receptor- mediated endocytosis and phagocytosis?
22
New cards
amino acids
The building blocks units used to construct a protein
23
New cards
codon
A three letter code word for individual amino acids located on a mRNA molecule
24
New cards
alpha-helix
A spiral-shaped type of secondary protein
25
New cards
replication
The duplication of DNA
26
New cards
primary structure
The sequence of amino acids that make-up a protein
27
New cards
transcription
The construction of a strand of mRNA
28
New cards
tertiary structure
A functional form of a protein
29
New cards
secondary structure
A specific shape of a polypeptide region that results from the interactions between amino acids
30
New cards
beta-sheet
A type of secondary protein structure that has the shape of a fan-folded piece of paper
31
New cards
transcription
The production of mRNA from DNA is called ____
32
New cards
true
A phospholipid bi-layer forms the basis of the plasma membrane
33
New cards
true
The plasma membrane is kept fluid by the presence of cholesterol wedged between phospholipids
34
New cards
true
Most integral proteins pass entirely through the phospholipid bi-layer of the plasma membrane
35
New cards
false
Peripheral proteins are most often found attached to integral proteins
36
New cards
true
The plasma membrane is permeable to CO2 and O2
37
New cards
true
The plasma membrane is permeable to H2O
38
New cards
false
The plasma membrane is permeable to ions and most nutrient molecules
39
New cards
true
The rate of diffusion can be affected by temperature
40
New cards
false
A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of water molecules than a hypotonic solution
41
New cards
true
Blood cells placed in a hypertonic solution will crenate
42
New cards
false
It takes about 1 hour to complete a good session of hemodialysis
43
New cards
true
Simple sugars, such as fructose, galactose, and glucose, are moved across the plasma membrane by the transporter protein GLUT-1
44
New cards
false
Glucose transport via GLUT-1 is an active transport process
45
New cards
true
The uptake of tiny droplets of extracellular fluid is termed pinocytosis
46
New cards
false
In the process of phagocytosis, the plasma membrane invaginates
47
New cards
false
The role of ribosomes in protein synthesis is to carry out transcription
48
New cards
true
Genes describe how to make proteins by putting the correct amino acids into a long chain in the correct order
49
New cards
false
The nitrogen base uracil is never found in RNA
50
New cards
true
The sequence of amino acids determines the function of a protein
51
New cards
true
A "STOP" codon signifies the end of an amino acid sequence
52
New cards
fluid mosaic
The ____ ____ model is used to describe the structural organization of the plasma membrane
53
New cards
aquaporins
The movement of water through membranes is facilitated by transport proteins called ____
54
New cards
concentration gradient
A ____ ____ represents that physical difference in concentration of a substance between two regions
55
New cards
diffusion
_____ is the net movement of substances along a concentration gradient such that equilibrium is achieved
56
New cards
glycocayx
Glycoproteins and glycolipids form a sticky coat over the cell surface called ____
57
New cards
antigen and antibodies
The immune system can distinguish body cells from foreign cell by the presence of ____ and ____ located on the cell surface
58
New cards
size, ionization, presence of carrier molecules, solubility in a lipid temperature
The rate of simple diffusion is affected by 5 factors. They are ____ ____ ___ ____ and ____
59
New cards
lipids, O2, CO2
Materials that move through membrane by simple diffusion include:
60
New cards
glucose, polar molecules, ions
Materials that move through membrane by facilitated diffusion include:
61
New cards
exocytosis
The movement of materials out of a cell, involving the formation of vesicles is called _____
62
New cards
endocytosis
The movement of materials into a cell, involving the formation a vesicles is called ____
63
New cards
phagocytosis
Certain white blood cells engulf and remove bacteria from body tissue via ___
64
New cards
hypertonic
A solution that has a higher solute concentration is called ____
65
New cards
hypotonic
A solution that has a lower concentration of solute is called ____
66
New cards
dialysis
____ removes waste products from the body by passing it out of the body through a filtering system (dialyser) and returning it, to the body
67
New cards
genes
Pieces of DNA that describe how to make a protein are called ___
68
New cards
tRNA
Amino acids are transported to the ribosome for protein synthesis by ____
69
New cards
methionine
The first amino acid in the formation of any protein is ____
70
New cards
"A"- first binding site in the ribosome
"P"- second binding site for the tRNA
"P"- second binding site for the tRNA
Explain what the "A" site and "P" sites are regards to protein synthesis :