Final GenChem
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
1. A/An ________ is made up of two or more pure substances which may be in any ratio.
a. mixture
b. element
c. molecule
d. atom
a. mixture
2. Which of the following is a unique element and does not truly belong to any family?
a. Nitrogen
b. Radium
c. Hydrogen
d. Helium
c. Hydrogen
3. What is the orbital geometry of sp2 hybridization?
a. Trigonal planar
b. Spherical
c. Tetrahedral
d. Trigonal bipyramidal
a. Trigonal planar
4. Explain the difference between bonding angle in NH3 (107) and CH4 (109.5):
a. The lone pairs on N repels making bonding angle become smaller while CH4 does not have any lone pairs of C
b. Because NH3 is trigonal pyramidal while CH4 is tetrahedral
c. Because N-H bonds are stronger than C-H bonds
d. Because of Hydrogen bondings between NH3 molecules
a. The lone pairs on N repels making bonding angle become smaller while CH4 does not have any lone pairs of C
5. Hypothetically, there are two elements A and B, with respective electronegativities of 3.09 and 2.85. What is the most likely type of bond between them?
a. Polar covalent
b. Nonpolar covalent
c. Ionic
d. Metallic
b. Nonpolar covalent
3,09 - 2,85 = 0,24 < 0,4
6. A molecule of water contains hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:8 ratio by mass. This is a statement of ________.
a. the law of multiple proportions
b. the law of constant composition
c. the law of conservation of mass
d. the law of conservation of energy
b. the law of constant composition
7. Chemical equations must be balanced to satisfy the _____.
a. Law of definite proportions
b. Law of multiple proportions
c. Law of conservation of mass
d. Principle of Avogadro
c. Law of conservation of mass
8. Isotopes are atoms that have the same ________ but different ________.
a. atomic masses, charges
b. mass numbers, atomic numbers
c. atomic numbers, mass numbers
d. charges, atomic masses
c. atomic numbers, mass numbers
mass num = pro + neu ; atomic num = pro
9. Atomic radius generally increases as we move ________.
a. down a group and from right to left across a period
b. up a group and from left to right across a period
c. down a group and from left to right across a period
d. up a group and from right to left across a period
a. down a group and from right to left across a period
↓←
10. What is true about VSEPR model:
a. It gives information about shape of molecules
b. It gives bond length
c. It gives chemical formula
d. It detects the chemical properties of molecules
a. It gives information about shape of molecules
11. How many electrons can a single p-orbital hold?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 4
d. 6
b. 2
12. Calculate the formal charge of the carbon atom below
O=C=O
a. 0
b. +1
c. +2
d. -1
a. 0
FC = V – L – B/2 = 4 – 0 – 8/2 = 0
13. Which of the following molecules have the same hybridization as NH3 at the central atom (In this case, it’s Nitrogen):
a. CH4
b. CO2
c. HCl
d. SF4
a. CH4
14. Which of the following statements about the Pauli Exclusion Principle is correct?
a. It states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same spin.
b. It applies only to s-orbitals.
c. It states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers.
d. It is responsible for the quantization of energy levels.
c. It states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers.
15. When the following equation is balanced: KClO3(s)→KCl(s)+O2(g), the coefficient of KClO3 is:
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
b. 2
2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2
16. Which rule states that electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first?
a. Pauli Exclusion Principle
b. Hund’s Rule
c. Aufbau Principle
d. Octet Rule
c. Aufbau Principle
17. A precipitate is formed in a reaction when:
a. A gas is produced
b. A solid is formed from a solution
c. A liquid evaporates
d. A color change occurs
b. A solid is formed from a solution
18. Which rule do Lewis symbols obey?
a. Hund’s rule: Every atom prefers to be surrounded by 8 electrons
b. Octet rule: Every atom is surrounded by 8 electrons
c. Octet rule: Every atom (except H) prefers to be surrounded by 8 electrons
d. Rule of 4th: Every atom prefers to be surrounded by 4 pairs of electrons
c. Octet rule: Every atom (except H) prefers to be surrounded by 8 electrons
19. Predict the shape of SO2Cl2.
a. Tetrahedral
b. Bent
c. Trigonal bipyramidal
d. Square pyramidal
a. Tetrahedral
20. Which one of the following is a metalloid?
a. Si
b. S
c. Cl
d. Li
a. Si
21. In general, as you go across a period in the periodic table from left to right: (1) the atomic radius ________; (2) the electron affinity becomes ________ negative; and (3) the first ionization energy ________.
a. decreases, increasingly, increases
b. increases, decreasingly, decreases
c. increases, increasingly, increases
d. decreases, decreasingly, increases
a. decreases, increasingly, increases
22. The atomic mass unit is presently based on assigning an exact integral mass (in amu) to an isotope of ________.
a. hydrogen
b. oxygen
c. sodium
d. carbon
d. carbon
23. Of the following elements, ________ has the most negative electron affinity.
a. S
b. Cl
c. Se
d. Br
b. Cl
24. Which of the following is an isoelectronic series?
a. B5−, Si4−, As3−, Te2−
b. F−, Cl−, Br−, I
c. Si2−, P2−, S2−, Cl2−
d. O2−, F−, Ne, Na+
d. O2−, F−, Ne, Na+
all 10 electrons
25. What happens when the number of electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals (MOs) equals the number of electrons in bonding MOs?
a. It becomes unstable and may not exist.
b. It exists normally.
c. The molecule has stronger and shorter bonds.
d. The bond order increases.
a. It becomes unstable and may not exist.
26. Neutralization is a reaction between:
a. An acid and a base
b. A metal and an acid
c. A non-metal and a base
d. An acid and a salt
a. An acid and a base
27. Which of the following molecule is most likely going to have different physical properties compared to the rest?
a. CH3COOH
b. NaCl
c. HF
d. CO2
b. NaCl
28. Why does the energy of an electron increase as it moves to higher orbitals?
a. The electron is farther from the nucleus and experiences less attraction.
b. The electron gains more mass as it moves farther from the nucleus.
c. The electron absorbs energy from the nucleus.
d. The electron is shielded by other electrons in lower orbitals.
a. The electron is farther from the nucleus and experiences less attraction.
29. What are pure substances classified as?
a. Elements and Atoms
b. Molecules and Compounds
c. Elements and Compounds
d. Atoms and Molecules
c. Elements and Compounds
Bonding within the diamond (an allotrope of carbon) is:
a. Covalent
b. Ionic
c. Metallic
d. Coordination
a. Covalent
In principle, the electrical conductivity of a metal will increase if:
a. Decreasing the metal temperature.
b. Increasing the metal temperature.
c. Adding a non-metal impurity such as carbon inside the metallic structure.
d. Exciting the metal by visible light (400 - 700 nm).
a. Decreasing the metal temperature.
In principle, the metallic bond strength will increase if: (more than 1 correct ans)
a. Number of valence electrons of metal increases.
b. Number of valence electrons of metal decreases.
c. Atomic radius of metal increases.
d. Atomic radius of metal decreases.
a. Number of valence electrons of metal increases.
d. Atomic radius of metal decreases.
Geometry (shape) of SnCl−3 anion is
a. Tetrahedral
b. Trigonal planar
c. Trigonal pyramidal
d. Square planar
c. Trigonal pyramidal
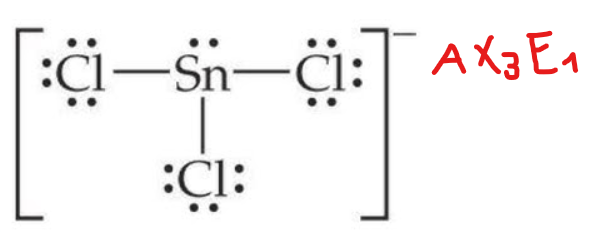
Predict the hybrid orbital of C atom within Diamond.
a. sp
b. sp2
c. sp3
d. sp3d
c. sp3
Chemical bonds within the CO2 molecule are:
a. Covalent bonds.
b. Ionic bonds.
c. Metallic bonds.
d. A mixture of ionic and metallic bonds.
a. Covalent bonds.
Among the following molecules, which atom does not obey the octet rule:
CO2,H2,NO,O2
a. H2
b. CO2
c. O2
d. NO
d. NO
Bonding within the NaCl crystal is:
a. Covalent
b. Ionic
c. Metallic
d. Coordination
b. Ionic
Which of the following compounds would have the largest H-X-H bond angle (X = C, N, or O)?
a. CH4
b. NH3
c. H2O
a. CH4
(no non-bonding e)
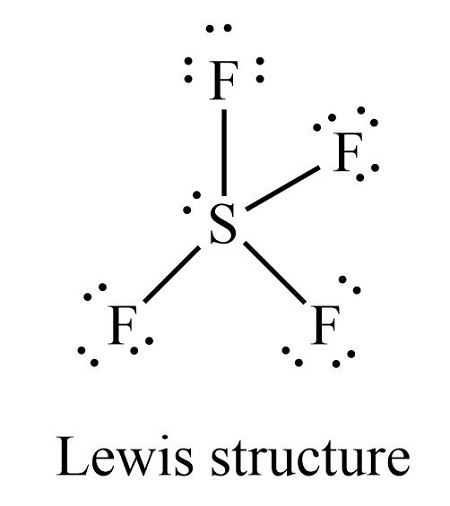
Geometry of SF4 molecule is:
a. Square plane
b. Tetrahedral
c. Seesaw
d. Octahedral
c. Seesaw
(4 bond 1 non-bond)
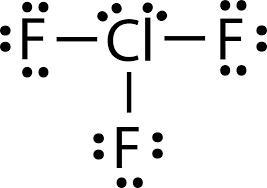
Geometry of ClF3 molecule is:
a. Trigonal planar
b. Trigonal pyramidal
c. T-shape
d. Tetrahedral
c. T-shape
(3b 2nb)
Which of the following hybridization of a Sulfur atom is invalid?
a. sp3d
b. sp3d3
c. sp3
d. sp2
b. sp3d3
In which of the following compounds would hydrogen have an oxidation state of zero?
a. HI
b. NaH
c. Ca(OH)2
d. H2
d. H2
Which VSEPR formula is not accounted for a linear shape?
a. AX2E2
b. AX2E3
c. AX2E0
d. AX2E4
a. AX2E2
Which of the following order is a correct representation of bond strength in non-aqueous condition.
a. Nonpolar covalent > Ionic > Polar covalent
b. Ionic < Polar covalent < Nonpolar covalent
c. Ionic > Polar covalent > Nonpolar covalent
d. Nonpolar covalent < Ionic < Polar covalent
c. Ionic > Polar covalent > Nonpolar covalent
Which change is classified as a physical change?
a. The burning of palm tree woods
b. The digestion of protein in our stomach
c. The dissolution of organic compounds in benzene
d. The electrolysis of water
c. The dissolution of organic compounds in benzene
Which change is classified as a chemical change?
a. The coagulation of protein in egg yolk
b. The melting of candle wax under constant burning
c. The crystallization of salt from a solution
d. The breaking of a glass cup
a. The coagulation of protein in egg yolk
Of the following, the smallest and lightest subatomic particle is the ________.
a. neutron
b. proton
c. electron
d. nucleus
c. electron
Which of following compounds will have fixed volume and shape?
A. Oxygen
B. Water
C. Diamond
D. Ethanol
C. Diamond
Atom is known as the building block of all matters. Atom is named by inspiring the Greek word ATOMOS. What does ATOMOS mean:
A. Understandable
B. Complicated
C. Divisible
D. uncut, indivisible
D. uncut, indivisible
Arrange following ions in order of increasing ionic radius: O2-, F, Na+, Mg2+, Al3+
A) O2- < F- < Na+ < Mg2+ < Al3+
B) Na+ < Mg2+ < Al3+ < O2- < F
C) Al3+ < Mg2+ < Na+ < F- < O2-
D) Al3+ < Mg2+ < Na+ < O2- < F-
C) Al3+ < Mg2+ < Na+ < F- < O2-