engineering data analysis
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Identify and create the appropriate dataset
Perform computation to learn
Required rules, pattern and relations
Output the decision
What is machine learning
Supervised learning
In _____, we need some thing called a Labelled Training Dataset
Supervised learning
Given a labelled dataset, the task is to devise a function which takes the dataset, and a new sample, andproduces an output value.
Classification
If the possible output values of the function are predefined and discrete/categorical, it is called _________
Predefined classes
_______ _______ means, it will produce output only from the labels defined in the dataset. For example,
even if we input a bus, it will produce either CAR or BIKE
Regression
If the possible output values of the function are continuous real values, then it is called _______
Supervised
The classification and Regression problems are both _______
Experience
The characteristics of the ground truth labels or values present in the dataset, which we define as experience
unsupervised learning
[ In the , we do not need to know the labels or Ground truth values ]
Reinforcement Learning
Learning from trials and errors
Classification
is supervised learning from examples.
Unsupervised learning
Class labels of the data are not given or unknown
Unsupervised learning
Given a set of data, the task is to establish the existence of classes or clusters in the data
Decision tree learning
is one of the most
widely used techniques for classification
Ross Quinlan
C4.5 by ______ ______ is perhaps the best
known system. It can be downloaded from
the Web.
information theory
provides a mathematical
basis for measuring the information content
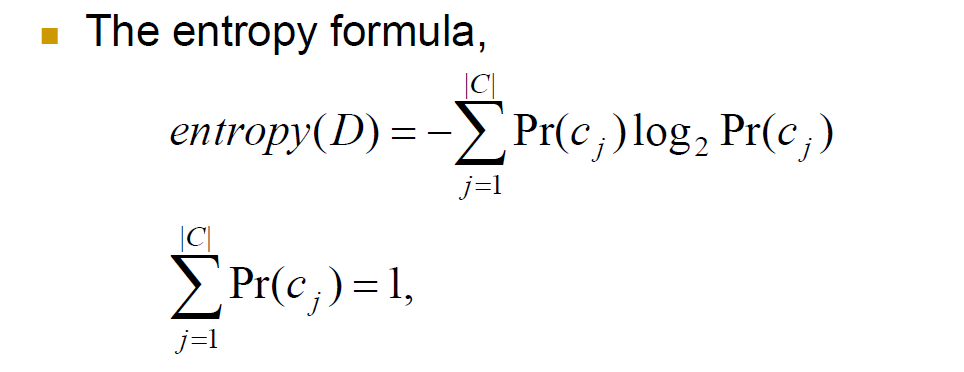
The entropy formula
entropy
We use ________ as a measure of impurity or disorder or uncertainty of data set D (or, a measure of information in a tree)
Overfitting
A tree may ______the training data
Good accuracy on training data but poor on test data
Symptoms: tree too deep and too many branches, some may reflect anomalies due to noise or outliers
Pre-pruning
Halt tree construction early
Difficult to decide because we do not know what may happen subsequently if we keep growing the tree.
Post-pruning
Remove branches or sub-trees from a “fully grown” tree.
This method is commonly used. C4.5 uses a statistical method to estimates the errors at each node for pruning.
A validation set may be used for pruning as well.
Predictive accuracy
Accuracy = Number of correct classifications / total number of test cases
Holdout set
The available data set D is divided into
two disjoint subsets
Holdout set
This method is used when the data set D is large.
n-fold cross-validation
The available data is
partitioned into n equal-size disjoint subsets.
Validation set
the many cases, the available data
is divided into three subsets
Validation Set
is used frequently for estimating
parameters in learning algorithms.
The parameter values that give the best accuracy on the validation set are used as the final parameter values
Positive Class
The class of interest is commonly called the
_______ _______
Precision and recall measures
Used in information retrieval and text classification.
Precision p
is the number of correctly classified
positive examples divided by the total number of
examples that are classified as positive
Recall r
is the number of correctly classified positive
examples divided by the total number of actual
positive examples in the test set
ROC Curve
It is a plot of the true positive rate (TPR) against the false positive rate (FPR).
Sensitivity
Same as TPR (or recall)
Specifity
Also called True Negative Rate (TNR) (negative recall)