Science Quiz - Rocks + Minerals
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Why is color alone not enough information to classify a rock?
lots of rocks are the same color, color can change and be affected by environment
What are rocks made of?
minerals and sediment (particles of dirt, sand, and organic matter/living things)
What three characteristics do scientists use to identify rocks/properties of rock classification?
mineral composition (type of minerals), texture (grain size/shape), and color
What are sedimentary rocks?
rocks formed of sediments that layer and compact over time
What are igneous rocks? What do most of them have?
rocks formed from cooling and hardening of magma in the Earth or lava on Earth’s surface. Crystals
What are metamorphic rocks?
rocks that are squished with heat and pressure
Where does the name igneous come from?
Latin word for fire, ignis.
Why are igneous rocks very useful? What have they been used for?
Used as tools, building materials, cleaning, and cutting in cooking. used throughout history, with Native Americans. hard, dense, durable
In igneous rocks, what is the relationship between the cooling rate and grain size?
The faster the cooling rate, the finer the grain. The slower the cooling rate, the coarser the grain.
In igneous rocks, what is the relationship between cooling rate and the environment the rock was formed in?
The faster the cooling rate, the closer the environment is to the surface. The slower the cooling rate, the farther down the environment is.
What are the two types of igneous rock? What are they? What types of grain do they have and why?
extrusive - formed from lava that cools and hardens ON Earth’s surface, cools faster so has fine or no grain.
intrusive - formed from magma that cools and hardens below Earth’s surface, cools slower so has coarse grain
What does metamorphic mean?
to change form because meta = change and morphosis = form in Greek.
What are two ways in which metamorphic rocks form?
By heat or pressure deep under Earth’s surface or out of igneous, sedimentary, other metamorphic rocks.
If a sedimentary rock with hard grains of sediment in random places is about to be changed into a metamorphic rock through pressure, what would the grains of the rock look like in the transformed rock?
very thin layers
What does foliated mean?
parallel layers and thin, flat layering in METAMORPHIC rocks!
What are some important uses of metamorphic rocks?
Building, sculpture, flooring, roofing, architecture
What is erosion?
particles/fragments carried away from source by water/wind
What is deposition?
movement of sediment out of the water/wind that’s carrying it.
What is compaction?
process that presses sediment together
What is weathering?
chemical and physical processes that break down rock at Earth’s surface
What is sediment?
small solid pieces of material that come from rocks or organisms
What two forces commonly carry sediment?
water and wind
Why are certain types of sedimentary rock useful to use as building materials?
some are soft enough to easily be cut into blocks, and hard rocks can be shaped and carved.
What is one notable building made of sedimentary rock? What type of sedimentary rock is it made of?
White House, sandstone
What sedimentary rock is used to produce energy for humans? Why is this rock referred to as a fossil fuel?
COAL - made of dead swamp plants
Do rocks last forever? WHY?
Yes, the atoms of a rock never go away, they just change form. Rocks are never created nor destroyed, they are recycled.
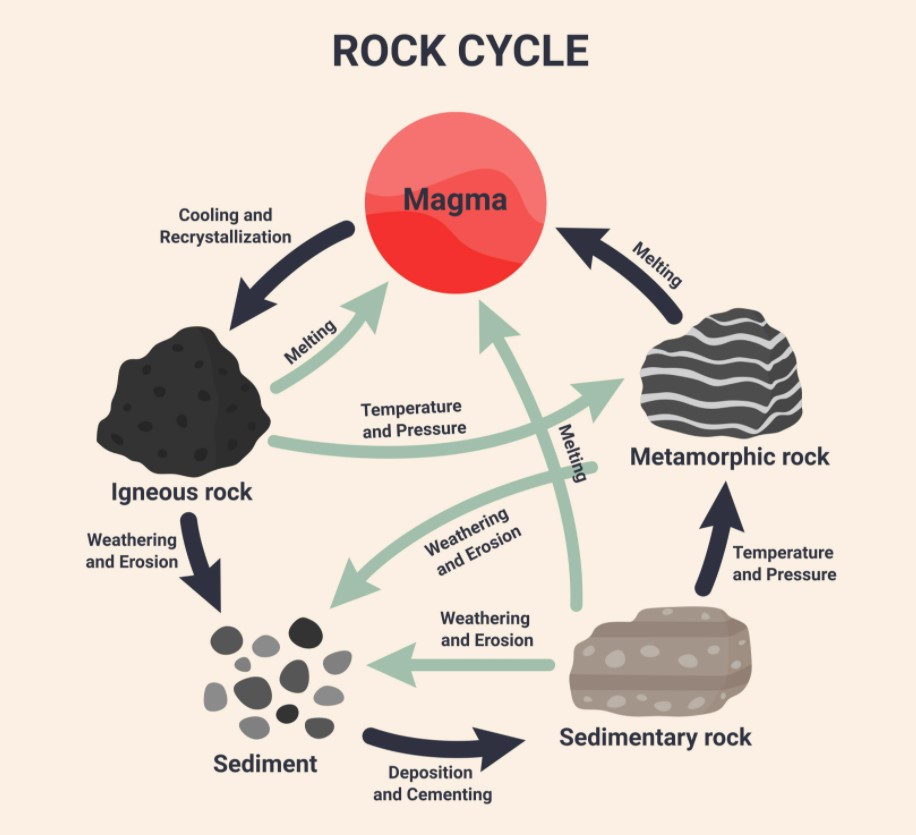
What are the 5 main components of the rock cycle?
sediment, sedimentary rock, magma, igneous rock, metamorphic rock
Is there only one path to the rock cycle? Do all rocks move through the cycle at the same pace? Does the rock cycle have a beginning or end?
NO!
Where does the energy that causes the rock cycle to continue come from?
energy from Earth’s core, energy from sun (indirectly - sun causes wind, temp, and air pressure changes)
DRAW a diagram of the rock cycle! (you need paper)
!
What is organic sedimentary rock?
type of sedimentary rock created with remains of dead animals/plants
What is a foliated metamorphic rock?
metamorphic rock where there is a banded arrangement of grains
What are the properties of minerals?
hardness, luster, color, density, cleavage and fracture
What does inorganic mean?
no carbon, not formed from living things or their remains
What is the formula for mineral density?
mass/volume
What is luster?
The way a mineral reflects light (metallic or nonmetallic)
How can minerals be used by humans?
Gemstones (jewelry), source of metal (copper), medicine, fertilizer, building,
What are five characteristics necessary for a substance to be a mineral?
must be naturally occuring, solid, have a crystal structure, inorganic, and have definite chemical composition
What three characteristics do geologists observe when studying a rock sample?
texture, mineral composition, color
How do people determine the five properties of minerals (what do they do to test them)?
hardness- do scratch test
color- see mineral surface
luster- see how mineral reflects light
density- find mass/volume
cleavage and fracture - break mineral apart to see if it splits along flat surfaces
What is the difference between cleavage and fracture?
Cleavage is the property of splitting easily along flat surfaces, fracture is when a mineral breaks apart in an irregular way
What is Mohs hardness scale?
ranking of minerals from softest to hardest