pulmonary blood flow and VQ mismatch
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
pulmonary circulation
low pressure → low vascular resistance → thin blood vessel walls → less smooth muscles in blood vessel walls
Factors that affect pulmonary vascular resistance: passive regulation
cardiac output, lung volume, hydrostatic pressure of blood vessels
Cardiac output
increase cardiac output → increase blood flow → recruitment (opening of closed capillaries) and/or distention (increase in diameter of open capillaries) → decrease pulmonary vascular resistance
Lung volume
low: compressed lung tissue → decrease blood vessel diameter → increase pulmonary vascular resistance
high: inflated alveoli → decrease blood vessel diameter → increase pulmonary vascular resistance
hydrostatic pressure of blood vessels
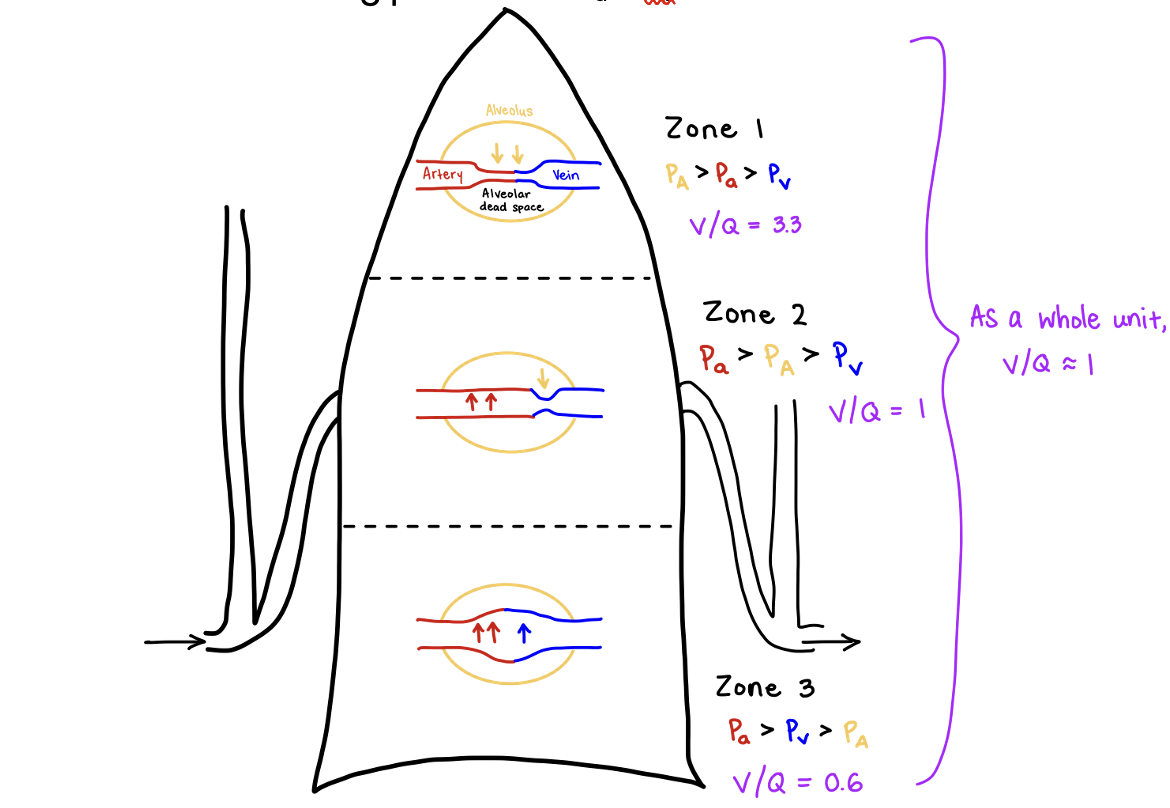
distribution of blood flow in the lung is uneven
blood flow decreases as it travels toward apex because of gravity → less hydrostatic pressure
Zone 1: little blood flow, P Alveoli > P artery > P venous, V/Q =3.3
Zone 2: driving pressure= P artery - P alveoli, P artery > P Alveoli > P venous, V/Q=1
Zone 3: driving pressure = P artery - P venous, P artery > P venous > P Alveoli, V/Q= 0.6
As a whole unit, V/Q=1
Factor that affect pulmonary vascular resistance: active regulation
reduction in alveolar P O2 → hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction (HPV)
HPV: small pulmonary arteries constrict, increasing PVR, and decreasing blood flow
Blood flow is directed away from poorly ventilated areas of lung → pulmonary edema
Extensive pulmonary artery constriction → pulmonary hypertension
V/Q mismatch
High V/Q: oxygen but less/no blood flow
Alveolar dead space: ventilation of lung units without perfusion (V/Q= infinity) caused by cardiovascular shock, emphysema, pulmonary edema
Low V/Q: blood flow but less/no oxygen→ shunt
Shunt: abnormal connection between pulmonary and systemic circulations
-Left to right: “back-lead” of blood from systemic to pulmonary circulation → increase pulmonary flow → development of pulmonary hypertension
-Right to left: deoxygenated blood flows directly from pulmonary to systemic circulation to cause hypoxemia (V/Q =0), patients do not respond to 100% oxygen treatments because of perfusion limitation
Cause of hypoxemia
V/Q mismatch (most common) caused by COPD, asthma, chronic bronchitis, pulmonary edema, pneumonia
hypoventilation (increase P a CO2)
decrease PiO2 (extreme high altitude)
shunt
diffusion limitation (decrease DL CO)
All causes of hypoxemia can be corrected by giving 100% O2 except shunt
A-a gradient normal
Cause of hypoxemia: hypoventilation → increasing PaCO2, low PiO2 → extremely high altitude
A-a gradient increase
Cause of hypoxemia: V/Q mismatch, shunt, impaired diffusion → decrease DLCO → can be corrected via 100% O2