ORGMED LAB ACT 1
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
ALKANES
CnH2n+2
Aliphatic compounds
Saturated hydrocarbons
Carbon–carbon single bonds (C-C)
insoluble
Alkanes and cycloalkanes are_______in water.
increase in carbon–chain length or ring size
The boiling points of continuous chain alkanes and cycloalkanes increase with an_______________.
5 to 17 carbon atoms
Continuous-chain alkanes containing________are liquids.
17 carbon atoms
Alkanes that have_______are solids at room temperature
COMBUSTION
Chemical reaction between a substance and oxygen (usually from air) that proceeds with the evolution of heat and light (usually as a flame).
Oxidation reaction
HALOGENATION
Chemical reaction between a substance and a halogen in which one or more halogen atoms are incorporated into molecules of the substance.
ALKENES
CnH2n
an acyclic unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon– carbon double bonds.
has fewer hydrogen atoms than alkane.
olefins
alkenes are also called as?
ALKYNES
CnH2n-2
Carbon with multiple bond
carbon–carbon triple bonds (C≡C)
acyclic unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon–carbon triple bonds.
insoluble in water , less than that of water , with molecular mas
Alkynes are_________but soluble in organic solvents, have densities________, and have boiling points that increases______.
- triple bonds move , - carbon chains move
Constitutional isomers are possible for alkynes, in Positional isomers the while in Skeletal isomer the________.
ADDITION REACTION
chemical reaction in which atoms or groups of atoms are added to each carbon atom of a carbon–carbon multiple bonds in a hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative
Alkene, Alkane
product of addition reaction?
HYDROGENATION
addition reaction in which hydrogen atoms are incorporated into molecules of an organic compound.
presence of a catalyst (usually Ni or Pt).
To speed up chemical reaction
HALOGENATION
addition reaction in which two halogen atoms are incorporated into molecules of an organic compound.
no catalyst is needed.
chlorination and bromination.
Usually halogenation occurs in_______.
HYDROHALOGENATION
addition reaction in which a hydrogen halide (hydrogen + halogen=HCl, HBr, or HI) is incorporated into molecules of an organic compound.
No catalyst is needed.
One carbon atom receives halogen and the other carbon atom receives hydrogen.
HYDRATION REACTION
addition reaction in which H2O is incorporated into molecules of an organic compound
Completely miscible with water
Unsubstituted C1 to C4 monocarboxylic acids are?
1.) water soluble
2.) not water soluble
Short-chain dicarboxylic acids are also________.
Aromatic acids are___________________.
liquids that have strong, sharp odors
Unsubstituted saturated monocarboxylic acid containing up to nine carbon atoms are?
are waxy solids that are odorless
carboxylic acids that have 10 or more carbon atoms in an unbranched chain are?
nitriles
Carboxylic acids can be prepared from_________on heating with aqueous acid or base
SN2 reaction
Nitriles are made by_______ of a primary or secondary alkyl halide with CN2
metal carboxylate,
The reaction of a Grignard reagent with CO2 yields a_____________followed by protonation to give a carboxylic acid.
DEPROTONATION
Oxygen takes the electron of hydrogen which breaks the bond of hydrogen to the carboxylic acid leaving a free lone pair of electrons.
REDUCTION
Alpha Substitution Reaction aka Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky (HVZ)
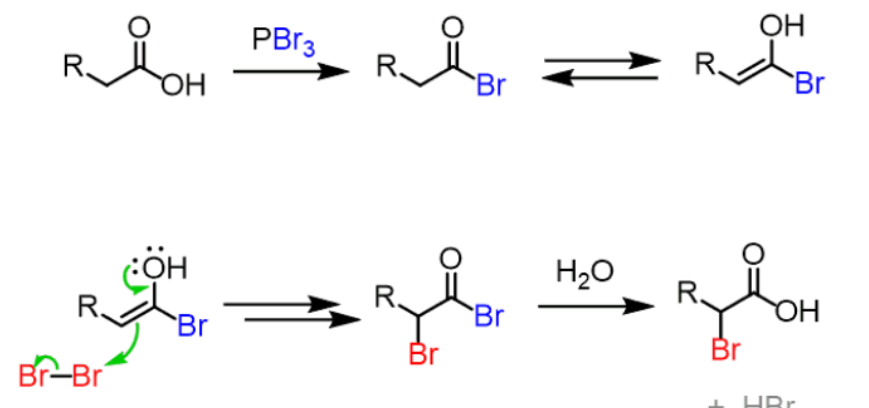
Carboxylic acid to Ketone.
Keto-Enol tautomerism.
Enol Tautomer reaction with Dihalide
Reaction with Water.
Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction in for steps?
ESTERS
have lower boiling points than carboxylic acids, and they are also volatile
very insoluble in water
Large esters are____________ but soluble in organic solvents
Alcoholysis
When acid chloride is reacted with alcohol, its OR group of alcohol will displace Cl group since the OR group has higher affinity.
Then the chloride group will be cleaved and will bond to the remaining hydrogen in the alcohol. This will form an ester.
Fischer Esterification
So when benzoic acid is reacted with the OR group of ethanol, the OR group will displace the hydroxyl group of benzoic acid and replace it. And the hydroxyl group will bind to the hydrogen atom left of ethanol when the OR group leaves.
HYDROLYSIS
Conversion of Esters into Carboxylic Acids
In basic solution is called saponification
REDUCTION
Conversion of Esters into Alcohols
AMINOLYSIS
Conversion of Esters into Amides
Esters react with ammonia and amines to yield amides
GRIGNARD REACTION
Conversion of Esters into Alcohol
ALDEHYDES
an organic compound in which the carbonyl group is attached to a carbon atom at the end of a carbon chain.
The R group may be a hydrogen atom or any length carbon chain.
C3 to C11
aldehydes that has C1 and C2 are gasses at room temperature. ______saturated aldehydes are liquid at room temperature.
carbonyl oxygen atom.
Aldehydes can form weak hydrogen bonds with water through the_______.
have pleasant odors
Lower carbon atoms have pungent odors, while many higher aldehydes (C8 and above)_______.
FORMALDEHYDE (METHANAL)
Sold as formalin
Manufacture of Bakelite, a hard plastic with high chemical and electrical resistance.
ACETALDEHYDE (ETHANAL)
Widely found in nature
Fuel combustion emissions, immediate product of alcohol fermentation, and metabolism of sugar in the body.
PROPIONALDEHYDE OR PROPANAL
Clear colorless liquid
Overpowering fruity-like odor
Less dense than water
Metabolite found in or produced by Escherichia coli (strain K12, MG1655)
KETONES
have a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two carbon atoms.
The carbonyl carbon has trigonal planar geometry.
It forms sigma bonds with adjacent carbons and a pi bond with oxygen.
higher boiling points
Ketones have_______and are polar, making them soluble in water to a degree
carboxylic acids , secondary alcohols
Ketones can be oxidized to____________or reduced to____________.
ACETONE (Dimethyl ketone)
it is used in chemical peeling and for acne treatments.
Note: The presence of ______ in urine is a sign of diabetes.
In household, it is used as a major component of some nail polish removers and paint thinner
METHYL ETHYL KETONE
A colorless, flammable liquid with a sharp, sweet odor, soluble in water and alcohol
Boils at a higher temperature and has a slower evaporation rate than acetone
CYCLOHEXANONE
A clear, colorless to pale yellow liquid with a mint or Acetone-like odor
Less dense than water but its vapors are heavier than air
Miscible in both ethanol and ether
antihistamines.
Cyclohexanone in pharmaceutical industry, its derivatives are used in the synthesis of?
adipic acid and caprolactam,
Cyclohexanone in nylon industry, its derivatives are oxidized to produce________precursors for nylon 6.
ALCOHOL
Organic compound with a hydroxyl (OH) functional group on an aliphatic carbon atom.
increase in the number of carbon atoms
The boiling point of alcohol increases with the____________, as stronger van der waals forces start acting in between the molecules.
Primary Alcohol (RCH2OH)
are those alcohols where the carbon atom of the hydroxyl group (OH) is attached to only one alkyl group.
Secondary Alcohol (R2CHOH)
are those where the carbon atom of the hydroxyl group is attached to two alkyl groups on either side.
Tertiary Alcohol (R3COH)
are those which feature a hydroxyl group attached to the carbon atom which is connected to 3- alkyl groups.
DEHYDRATION REACTION
The reaction removes the OH group from the alcohol carbon atom and a hydrogen atom from an adjacent carbon atom in the same molecule
Catalysts: 180 degrees Celsius & Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
catalyst of dehydration reaction?
aldehydes and carboxylic acids
Primary alcohols can be oxidized to form
ketones.
Secondary alcohols can be oxidized to give
Oxidation of Alcohols
These are catalysts for what reaction?
Catalysts: Potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇), Chromic acid (H₂CrO₄), Chromium trioxide (CrO3)
good bases and nucleophile
sodium alkoxides are both
weak acids
___________ don’t protonate alcohols to any significant extent
ETHER
Organic compound that consists of oxygen atom bonded to two aryl or alkyl groups.
Two carbon atoms bonded to an oxygen
alkanes.
Boiling points of ethers are similar to those of?
Higher boiling point
Ether has__________of the alcohol.
unstable hydroperoxides and peroxides
Ethers react slowly with oxygen from the air to form____________.
SN1 mechanism
When using HBr or HI, the acidic cleavage of ethers with tertiary, benzylic, or allylic substituents tend to occur by an__________.
SN2 reaction
It is important to note that a phenyl substituent on an ether is not capable of participating in the______of an acidic cleavage.
false, alcohol is denser than ether
t or f
alcohol is less dense than ether?
APROTIC SOLVENTS
ETHER IS USED IN
AMIDE
is an organic molecule with a functional group made up of an acyl group (R–C=O) linked to a nitrogen atom.
soluble
AMIDES are typically________in polar solvents like water due to their capacity to establish hydrogen bonds with water molecules
hydrolysis reactions
AMIDES can undergo______under acidic or basic conditions
Primary amide
in which the only substituent on the amide’s nitrogen atom is hydrogen.
Secondary amide
In which the amide’s nitrogen atom is linked to a hydrocarbon substituent
Tertiary amide
one in which the amide nitrogen atom is linked to three carbon atoms
FORMAMIDE
Simplest carboxylic acid amide
Formed by heating CO2 and NH3 under pressure
Uses: feedstock in manufacture of formate esters, ionizing solvent, and tissue preservation
ACETAMIDE
Acetic acid amide or Ethanamide
Simplest amide derived from acetic acid & naturally found in red beetroot
Uses: plasticizer, explosive, and penetrating agent
BENZAMIDE
Simplest amide derivative of benzoic acid
Found in the herbs of Berberis pruinosa.
Uses: organic synthesis, manufacture of benzonitrile
AMINES
Organic derivative of ammonia (NH3) in which one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl or aryl groups have replaced ammonia hydrogen atoms
are liquids at room temperature
Primary amines with 3 OR 4 carbon atoms_____________.
soluble in water
Lower aliphatic amines are
ANILINE
primary amine in which the nitrogen atom is attached directly to a benzene ring
BENZYLAMINE
primary amine compound having benzyl as the N-substituent
DOPAMINE
Drug of choice for Cardiogenic shock
Parkinson’s disease
ex: Sinemet
NOREPINEPHRINE
Drug of choice for Septic shock
Constricts blood vessels
ex: Levophed
SEROTONIN
Involved in sleep, sensory perception and regulation of body temperature
Based on tryptamine core
EPINEPHRINE
Drug of choice for anaphylactic shock
Produced by adrenal glands from norepinephrine
ARENES
are a type of aromatic hydrocarbons.
These are hydrocarbons with sigma bonds and delocalized pi electrons between carbon atoms forming rings.
eight carbon atoms
Arenes up to_____________are colourless liquids with characteristic odor.
Arenes are insoluble in water
Fairly soluble in organic solvents
active pharmaceutical ingredients
arenes are used as________in new drug synthesis since the stability of the aromatic ring provides resistance against metabolic degradation
specific histamine receptors,
Arene block works by binding to________thereby preventing histamine from attaching to these receptors and triggering an allergic response
ELECTROPHILIC SUBSTITUTION REACTION
a chemical reaction in which the hydrogen atom attached to a compound is replaced by an electrophile.
EPOXIDES
It is a cyclic ether that contains three atom rings.
Exist as a colorless, non polar, and volatile compound.
ethylene oxide and propylene oxide
Some of the most common examples of epoxides are
Regioselectivity
bond forming in a specific location of a molecule
Alcoholysis
reaction where alcohol is the reactant which later on, becomes part of the reaction