Leaves
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Human Uses of Leaves
food; tea from small evergreen shrubs and herbal teas; seasonings from mint family like basil, thyme, etc
perfumes; dyes; fibers; medicines; waxes
Eudicot Leaf Structures
blade: broad, flattened part of the leaf
petiole: the stalk/stem-like structure that attaches the leaf to the node
axillary buds:
sessile leaves: leaves with no petiole; are directly attached to node
primary veins diverge from one another in various ways
(recall that eudicots are plants that have two embryonic leaves)
Monocot Leaf Structures
leaves usually narrow and long; leaves attach to stem with sheath
primary veins/venation are/is parallel to one another
Conifer Leaf Structure
needle-like leaves
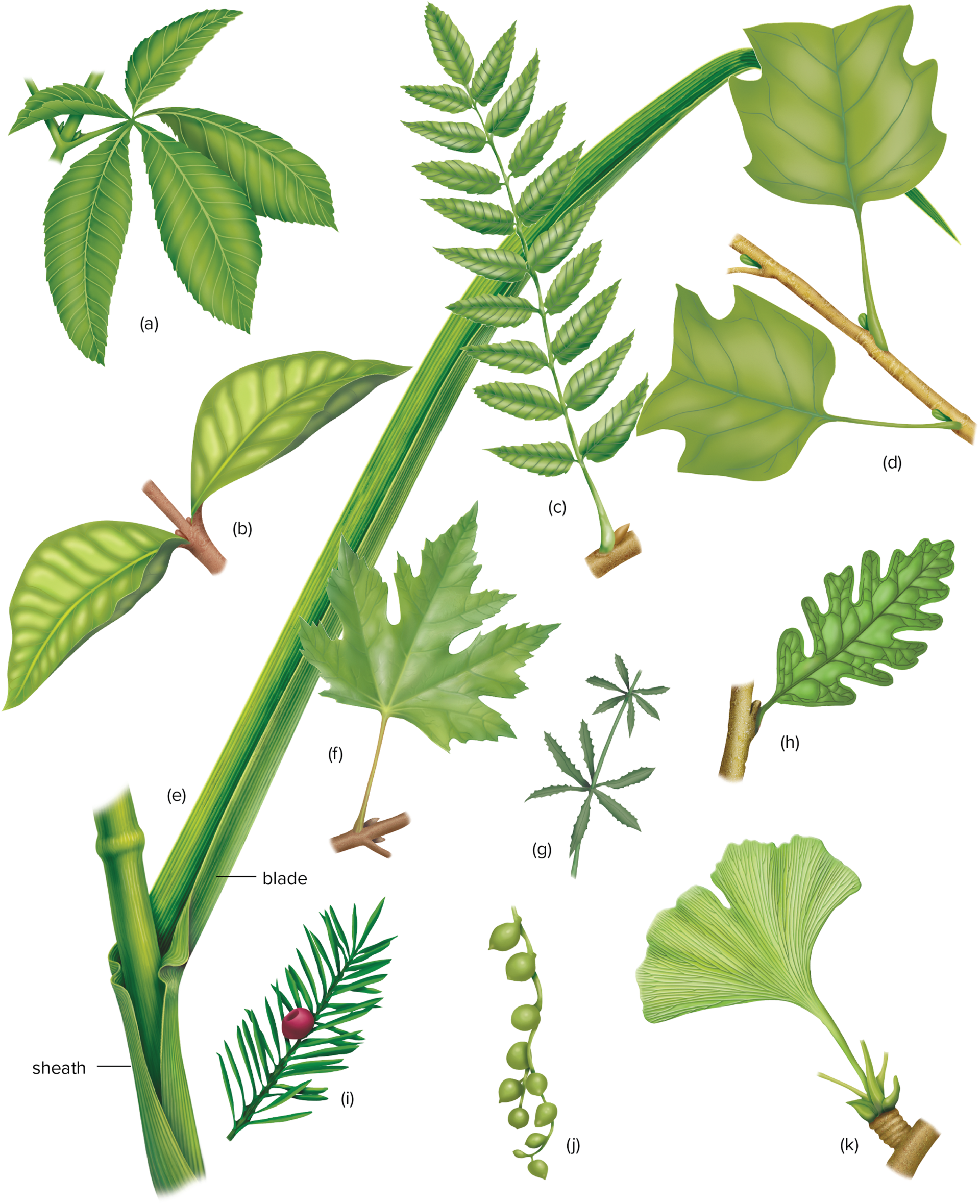
Leaf Characteristics
a: palmate leaf of buckeye
b:opposite
c: pinnately compound
d: alternate, simple but lobed leaves
e: parallel-veined leaf of grass
f: palmately veined of maple
g: whorled leaves
h: pinnately veined, lobed leaf of oak
i: linear leaves of a yew
j: globe-shaped succulent leaves
k: fan-shaped leaf of ginko showing dichotomous venation

Leaf Margins/Edges
smooth: very few indentations or serration
toothed/serrated: jagged back and forth texture, appears sharp
lobed: leaf tissue wraps closer to veins of leaf
Quercus Lobata (Valley Oak)
native to central valley
Leaf Venation
monocot: veins are parallel to one another
dicot: netted veins that branch
pinnate: one central vein with other major veins branching off from it (similar to feather)
palmate: several major veins branching off from a common point (like a palm with fingers radiating out)
Simple vs Compound
simple: only one leaf blade
compound: two or more leaflets in a blade
pinnate: leaflets arranged along a central axis
palmate: leaflets arise from a common/central point at the end of petiole
(leaflets do not have axillary buds)
Leaf Positioning on Stems
alternate: one leaf per node; usually offset by a certain number of degrees
opposite: two leaves per node; rotated usually about 90 degree with respect to leaves above and below
whorled: three or more leaves per node
(the positioning helps the plants to maximize exposure to sunlight)
Epidermis Structure & Function
outer cell layer that covers upper and lower surfaces
mostly non-photosynthetic; translucence allows light to pass to underlying tissues
provide support for leaf and prevents water loss by secreting waxy waterproof material called cutin to form cuticle
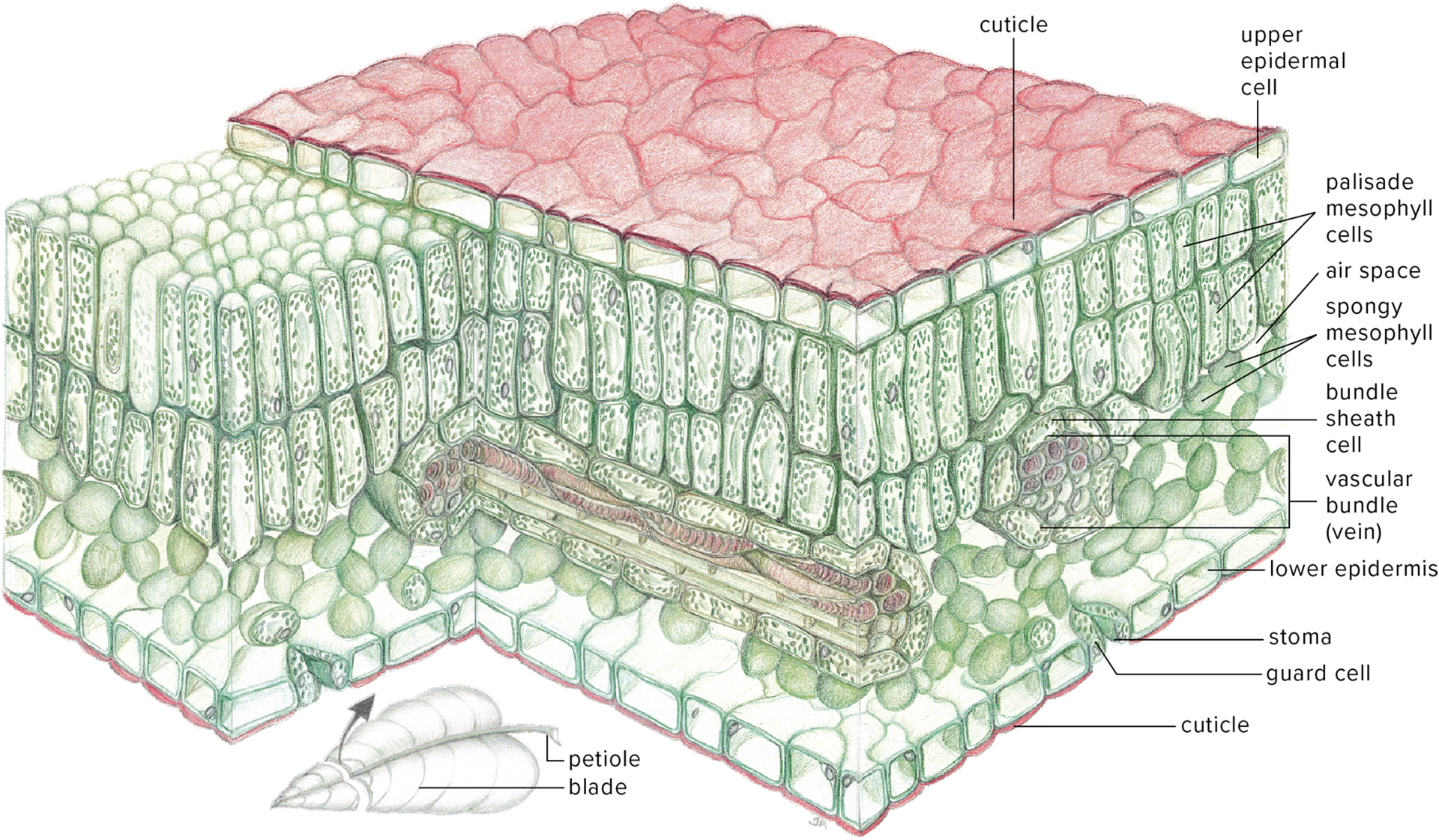
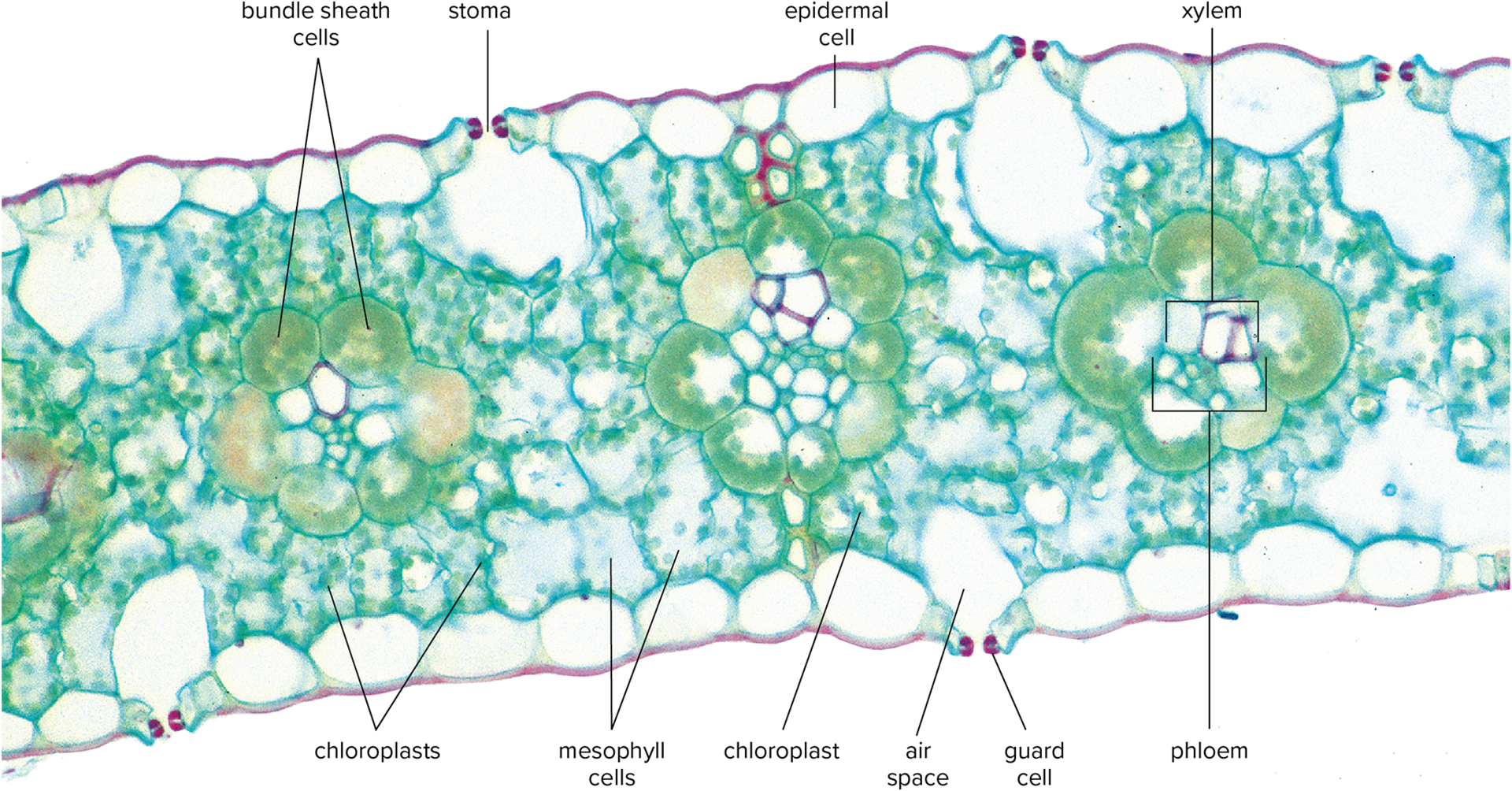
Stomata
a pore/opening in the epidermis of leaves that is flanked by two guard cells that regulate its opening and closing and thus regulate gas exchange and transpiration
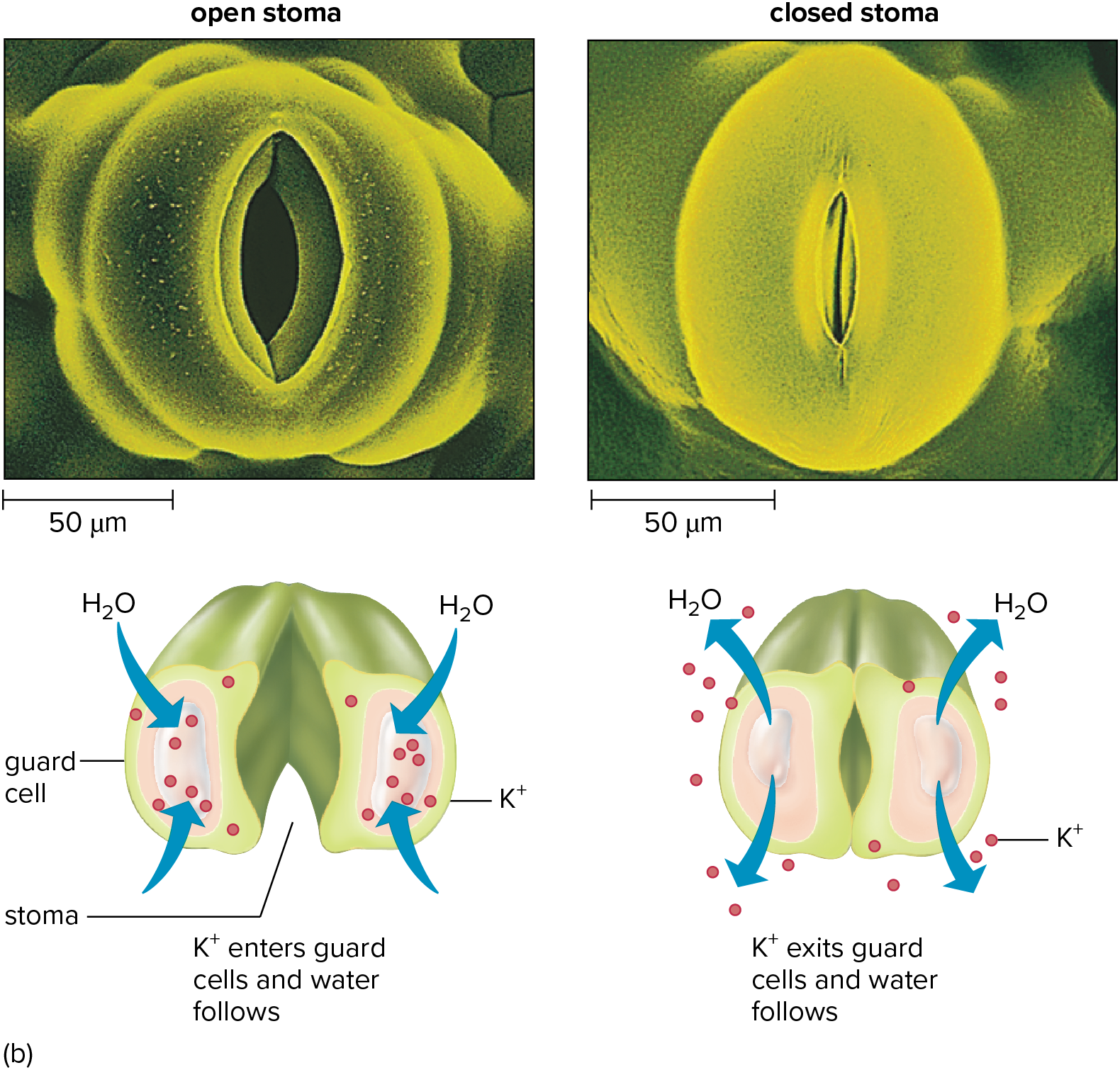
Guard Cells
a pair of specialized cells surrounding a stoma
when water is low, guard cells are limp and close
when water is high, guard cells become turgid and open the stoma
Trichomes
specialized “hairs” on leaves that absorb water and minerals in epiphytes and deter predators
Mesophyll Tissue
a parenchyma (chlorenchyma) tissue between the upper epidermis and the lower epidermis
Mesophyll Tissue Anatomy
palisade parenchyma: columnar cells usually in the upper side of leaf; most photosynthesis occurs here
spongy mesophyll: irregularly shaped cells, usually in lower side of leaf, have open areas between cells that facilitate gas exchange
hydrophytes: large air spaces for gas exchange and flotation (called aerenchyma)
*mesophyll layer in monocots all looks the same; it is not differentiated into palisade or spongy
Bundle Sheath Cells
parenchyma cells that surround xylem and phloem
book def: the parenchyma and/or sclerenchyma cells surrounding a vascular bundle
Kranz Anatomy
leaves have two forms of chloroplasts: large chloroplasts with few to no grana and small chlorophylls in mesophyll
Transpiration
quantities of water evaporate from leaves through stomata
moist cells are exposed to absorb CO2 and release O2, but some O2 moisture evaporates from mesophyll
book def: loss of water in vapor form; most transpiration takes place through stomata
Positive Effects of Transpiration
cools plant as water evaporates
forces water up from roots
produces water vapor and rain for other plants in area
Cohesion Tension
happen in xylem
as water evaporates from mesophyll of leaves water from other cells and from xylem from roots, water gets pulled upward
Stomatal Movements
in sunlight K+ ions are pumped into guard cells; this causes water to move into guard cells by osmosis and become turgid; turgid cells bend because they are attached to each other at both ends
remember that water follows solute
Tendrils
long threadlike structures, develop from leaves
Bud Scales
modified waxy leaves that protect young buds, contain growth inhibitor, prevent growth until spring
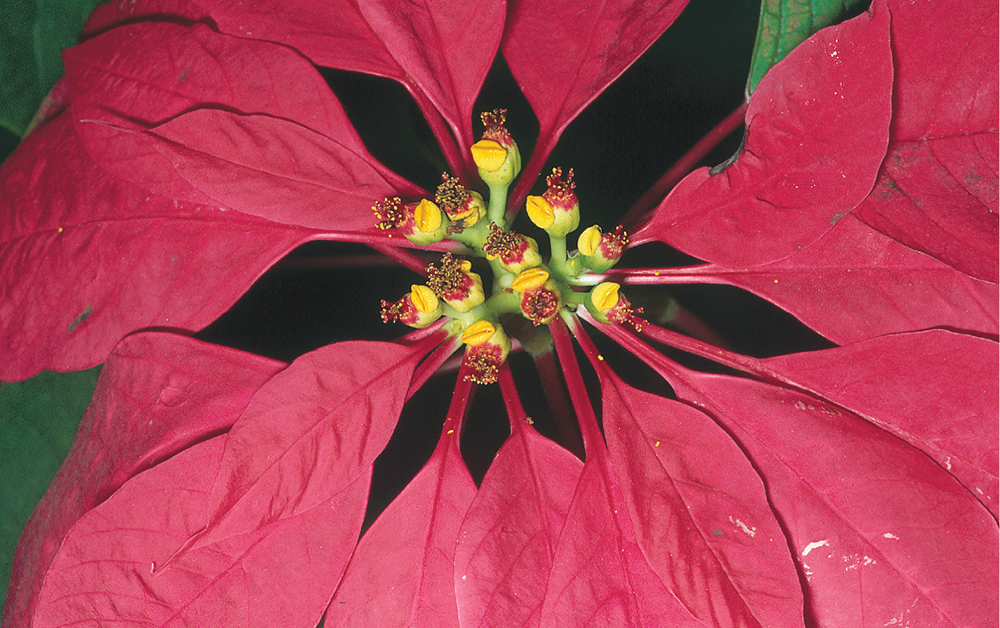
Bracts
colorful, modified leaves, attract pollinators
ex: poinsettia

Other Functions of Leaves
water storage: thickened leaves to store water; cuplike structures to catch rainwater
food storage: onion, cabbage leaves
defense: sharp, non-photosynthetic spines on cacti
capture prey: carnivorous plants; trichome hair in venus fly trap trigger plant to shut
Spines, Thorns, & Prickles
spines: modified leaves
thorns: modified stems
prickles: epidermal extensions of the stem
Sundew Plant
parasitic
grows in nitrogen poor soil
hair-like trichomes w bio-adhesive mucilage containing nanofibers and digestive enzymes (chitinases and proteases)
(charles darwin’s favorite plant)
Senescence
series of irreversible changes and breakdown of cell components that leads to cell death
in annuals: occurs in plant as a whole
in perennials: occurs only in parts of plants- flowers senesce after pollination and some xylem cells die; leaves senesce before dry and cold seasons
Leaves Changing in Fall
chlorophyll is broken down, leaving xanthophylls, carotenoids, and anthocyanins
avoids leaves getting weighed down with snow etc
(example of planned senescence)
Leaf Abscission
complex process that leads to dropping of leaves
abscission zone: separation layer at base of petiole; thin walled cells will form
cork layer: suberized cells that help to seal wound along abscission layer; seals completely when leaf falls
ethylene hormone: promotes abscission