Triple Physics
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Formula for acceleration
a = v-u t
Formula for constant acceleration
v2 -u2 = 2ax
Newton’s first law
An object at rest will stay at rest unless a force acts upon it.
Newton’s second law
F = m x a / the larger the resultant force, the more the object accelerates.
Formula for weight
Weight (N) = mass (kg) x gravitational field strength
Describe the experiment carried out to investigate F = ma
1) Measure the mass of the trolley, the unit masses and the hanging hooks.
2) Raise the ramp until the trolley starts to move to balance out the effect of friction.
3)Make sure the trolley travels the same distance every time.
4) Attach the trolley to the hanging mass and hold the trolley in place until you want to let go of it.
5) Each light gate will measure the acceleration of the trolley.
6) You then move mass from the trolley onto the hanging hook and redo the 4th step and record the acceleration.
7) You repeat the experiment 3 times and record the acceleration.
Newton’s third law
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Formula for momentum
P = m x v
What is the law of momentum
Total momentum before is equal to total momentum after.
Formula for change in momentum
Force (N) = change in momentum change in momentum = mv - mu time (s)
Formula for stopping distances
thinking distance + braking distance = stopping distance
8 energy stores
1) Kinetic
2) Thermal
3) Chemical
4) Gravitational Potential energy
5) Elastic Potential
6) Electrostatic
7) Magnetic
8) Nuclear
Formula for kinetic energy
KE = ½ x m x v2
Formula for gravitational potential energy
GPE = m x g x h
4 Energy Transfers
1) Mechanical
2) Electrical
3) By heating
4) By radiation
Equation for efficiency
Efficiency = Useful energy transferred by device (J) Total energy supplied to device(J)
What diagrams show energy transfer
Sankey
How do you decrease energy transfer
Lubrication and insulation
List 4 renewable energy resources
1) Wind Power
2) Solar cells
3) Hydro-electricity
4) Tidal Barrages
Definition for transverse waves
They are waves that oscillate perpendicular to the direction the wave travels.
Definition of longitudinal waves
Waves that oscillate parallel to the direction the wave travels.
Equation to calculate wave speed
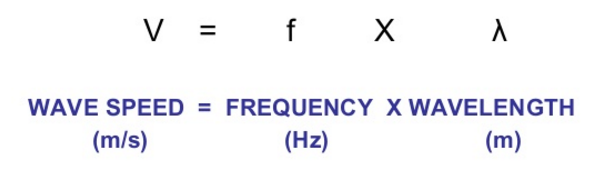
How to measure the speed of water ripples
1) Use a signal generator to produce a certain frequency.
2) Dim the lights and turn on a strobe light, the wave patterns will be made visible.
3) Alter the frequency of the strobe light until the waves seem to ‘freeze’
4) The distance between each shadow is equal between the wave length.
5) Use the equation for speed to figure out the speed.
What for things can a wave do at a boundary
1) Be absorbed
2) Be transmitted
3) Be reflected
4) Be refracted
How does a light depending on the density of the other side of the boundary
If the second material is denser than the first it move towards the normal.
FAST
S-waves
S-waves are transverse and can’t travel through liquids this shows the earth has a liquid core.
P- waves are longitudinal and travel through liquids and solids.
How does total internal refraction occur
When the incident angle is equal or greater than the critical angle it is totally internally reflected and no light comes out.
Why does an apple look red
Since the apple absorbs every colour but red since it reflects red and so we see the colour red as red.
How do colour filters work
They only allow certain wave lengths of light through.
How does a converging lens work
Converging lenses bend light into a focus point where all the light rays bend towards. It rotates the image and makes a real image.
How do diverging lenses work
They spread out light rays. It produces a virtual image.
How does an electron get deexcited?
It absorbs the energy from EM radiation causing it to excite and move up but if its not enough to leave the nucleus it would deexcite and emit EM radiation. If it does leaves it becomes ionised.