Anatomy and Physiology Honors | Control and Coordination - The Nervous System
The ultimate control center of the body that oversees all communication among the organs.
What is the main function of the nervous system?
Sensory Input
It receives stimuli via millions of sensory receptors throughout the body.
1/101
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
The ultimate control center of the body that oversees all communication among the organs.
What is the main function of the nervous system?
Sensory Input
It receives stimuli via millions of sensory receptors throughout the body.
Integration
It processes the input stimuli and decides what should be done.
Motor Output
It activates effector organs to cause a response.
Nervous Tissue
The nervous system is composed of what?
Neurons (nerve cells) and Neuroglia (glial cells)
Nervous tissue is densely packed with?
Neurons (10%)
Neuroglia (90%)
How many percent does neurons and neuroglia make up in a nervous tissue.
Neurons (nerve cells)
They are excitable cells that respond to stimuli by conducting impulses to transmit signals.
Neuroglia (glial cells)
They are supportive cells that provide nutrition, insulation, and help with signal transmission.
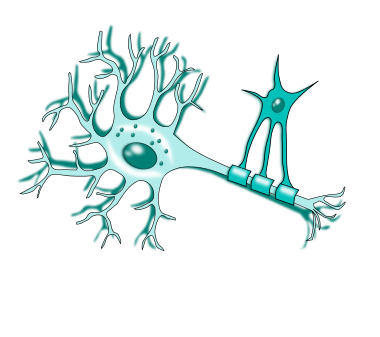
Some (cell body)
They are the life support containing the nucleus and most organelles (such as tons of mitochondria).
Ganglion
They are a collection of nerve cell bodies located n the body (just not the brain or spinal cord).
Nerve
They are bundles of axons that extend from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body.
Processes
They are extensions from the cell body
Dendrites
The min receptor of signals; input region.
Axon
Generates and transmits nerve impulses; the conducting region; also known as the nerve fiber.
Axon terminals
The end of the axon that releases neuron transmitters at a synapse when a nerve impulse is received; the secretary region.
Myelin sheath
It covers long axon (nerve fibers) to protect an electrically insulate them to increase the speed of nerve impulse transmission.
Node of Ranvier
Unmyelinated gaps in the myelin sheath that aid in increasing the veocity of nerve signal conduction.
Multipolar
Bipolar
Unipolar
How are neurons classified structurally as well as based on their number of processes?
Multipolar
99% of neurons are __ (structural classification)
Bipolar
They are rare and found in only a few special sense organs. (structural classification)
Unipolar
They are found in the ganglia in the PNS. (structural classification)
Ganglia
These are a group sensory neurons.
Sensory Neurons
Motor Neurons
Interneurons
How are neurons classified functionally as well as based on the way an impulse travels through a neuron with regards to the brain and spine?
Sensory Neurons
They are also called afferent neurons.
Sensory Neurons
They transmit info from sensory receptors to the CNS
Sensory Neurons
They are mostly unipolar. (functional classification)
Motor Neurons
They are also called efferent neurons.
Motor Neurons
They transport info from the CNS to the rest of the body.
Motor Neurons and Interneurons
Most are structurally multipolar to send impulse to multiple places. (functional classification)
Interneurons
They are also called association neurons.
Interneurons
They housed in the CNS and transport info between the sensory and motor neurons.
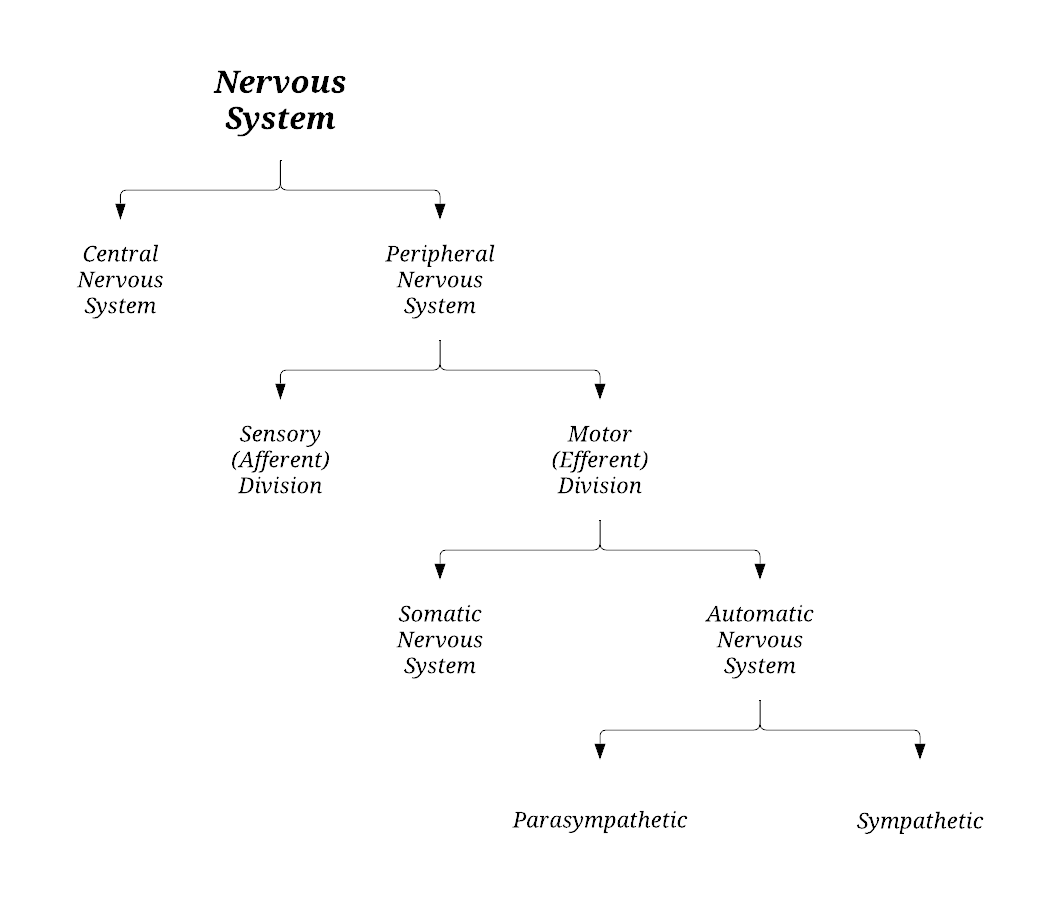
Label the following organization diagram of the nervous system.
Integration and control center of the brain and spinal cord.
What is the main function of the central nervous system (CNS)?
It is protected by the skull and surrounded by layers of tissue called the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid that cushions the brain from injury.
How is the brain protected?
Ventricles
They are hollow fluid-like cavities within the brain that contains the choroid plexus which makes cerebrospinal fluid.
Choroid Plexus
It is made up of ependymal cells and makes cerebrospinal fluid.
After puberty
When does the brain fully develop?
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Brain Stem
What are the three (3) main parts of the brain?
Cerebrum
It is the largest part of the brain, making up 83%.
Cerebrum
Part of the brain that is made up of the left and right hemispheres.
Cerebrum
Part of the brain that is divided into four (4) lobes.
Learning
Emotion
Speech
Hearing
Reasoning
Vision
Fine movements
What are the functions of the cerebrum?
Cerebral Cortex
Surface
It is located under the cerebrum.
Where is the cerebellum located?
Maintains POSTURE and BALANCE
Coordinates TIMING and PATTERNS for smooth and agile SUBCONSCIOUS movements
What are the functions of the cerebellum?
Base of the cerebrum
Anterior to the cerebellum
Where is the brainstem located?
Medulla Oblongata
Midbrain
Pons
What are the parts of the brainstem?
Brainstem
Part of the brain that relays info between the rest of the brain and the spinal cord.
Coordinates automatic functions:
Body Temperature
Digestion
Sleep
Swallowing
Respiration
Circulation
What are the functions of the brainstem?
It is composed of the spinal and cranial nerves and serves as the communication system between the CNS and the rest of the body.
What is the main function of the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
Motor nerve fibers
They send out information from the brain to effector organs lie muscles (so they will contract) and glands (so they will secrete).
Somatic motor, voluntary
nerve fibers innervate skeletal muscles to control movements.
Preganglionic Axon
First (1st) neuron’s cell body in the CNS
Postganglionic Axon
Second (2nd) neuron’s axon terminals in the effector organ
Cardiac and smooth muscles, gonads, involuntary
Muscle fibers innervate as well as to control movements.
norepinephrine (NE), acetylcholine (ACh), stimulatory, inhibitory
Neurotransmitter is released in the sympathetic nervous system, while is released in the parasympathetic; both can be and .
Parasympathetic Division
Craniosacral nerves (they start at the based of your brain) and they help calm you down.
Parasympathetic Division
Ganglia are far from the spinal cord, right next to or inside of effector organs.
Parasympathetic Division
“rest and digest” division, helps maintain your body and conserves energy for later.
Parasympathetic Division
It is set up to communicate to 1 effector organ at a time
Parasympathetic Division
Preganglionic cells are longer than postganglionic
Parasympathetic and Sympathetic Division
Uses neurotransmitter norepinephrine (NE) and hormones for stimulation and inhibition
Neurotransmitters
These are chemicals released from neurons to cross synapses.
Hormones
They are chemicals released form glands into the bloodstream.
Sympathetic Division
Thoracolumbar nerves (they start between the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae) and they excite you
Sympathetic Division
Ganglia are in the spinal cord and send signals far distances to effector organs.
Sympathetic Division
“fight or flight” division; focuses on what your body needs to do right now.
Sympathetic Division
Set up so that 1 stress signal → responses in multiple organs at once
Sympathetic Division
Preganglionic cells are shorter than postganglionic
Sympathetic Division
It is antagonistic to the parasympathetic division, but they can work cooperatively.
Dilate Pupils
Increase Heartbeat
Inhibit Stomach Activity
Inhibit Intestine Activity
Relax Airways
Give examples of sympathetic nerves.
Constrict Pupils
Constrict Airways
Slow Heartbeat
Stimulate Stomach Activity
Stimulate Intestine Activity
Give examples of parasympathetic nerves.
Sensory nerve fibers
They receive sensory stimuli to send back to the CNS/brain.
Somatic sensory fibers
Carry info from the skin, skeletal muscles, and joints
Visceral sensory fibers
Carry info from the visceral organs
Mechanoreceptors
mechanical force; vibration, pressure, stretch, and touch
Thermoreceptors
change in temperature
Photoreceptors
light
Chemoreceptors
cehmicals
Nociceptors
pain
Stimulus → received by receptor → transmission through the nerves → spinal cord → brain
What is the process of the sensory division?
Reflex
An automatic response to stimuli.
Innate (Intristic)
Learned (acquired)
A reflex can either be or .
Reflex Arc
Reflexes occur over highly specific neural pathways are called __.
Receptor
site of stimulus
Sensory neuron
transmits impulse from PNS to CNS
Integration center
“decodes” the signal at a synapse (or multiple synapses)
Motor neuron
conducts impulses to an effector organ
Effector
responds by contracting (if a muscle cell) or secreting (if a gland)
CNS
Where is the location of astrocytes?
CNS
Where is the location of ependymal cells?
CNS
Where is the location of microglial cells?
CNS
Where is the location of oligodendrocytes?
PNS
Where is the location of satellite cells?
PNS
Where is the location of schwaan cells?
Astrocytes
They travel from mitochondria to neurons and are the most abundant of all glial cells. They help regulate blood flow, supply nutrients, and form the physical structure of the brain.
Ependymal Cells
They play an important role in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) homeostasis, brain metabolism, and the clearance of waste from the brain.
Microglial Cells
They repair brain injury and maintain neuronal networks.
Oligodendrocytes
They maintain the generation of the myelin sheath.