maths things to remember
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
n(A)
number of elements in set A
A ⊂ B
A is a proper subset of B
all elements in set A are in set B, but not all elements in set B are in set A
∅
empty set (the set with no elements)
a^-1
1/a
a^1/2
√a
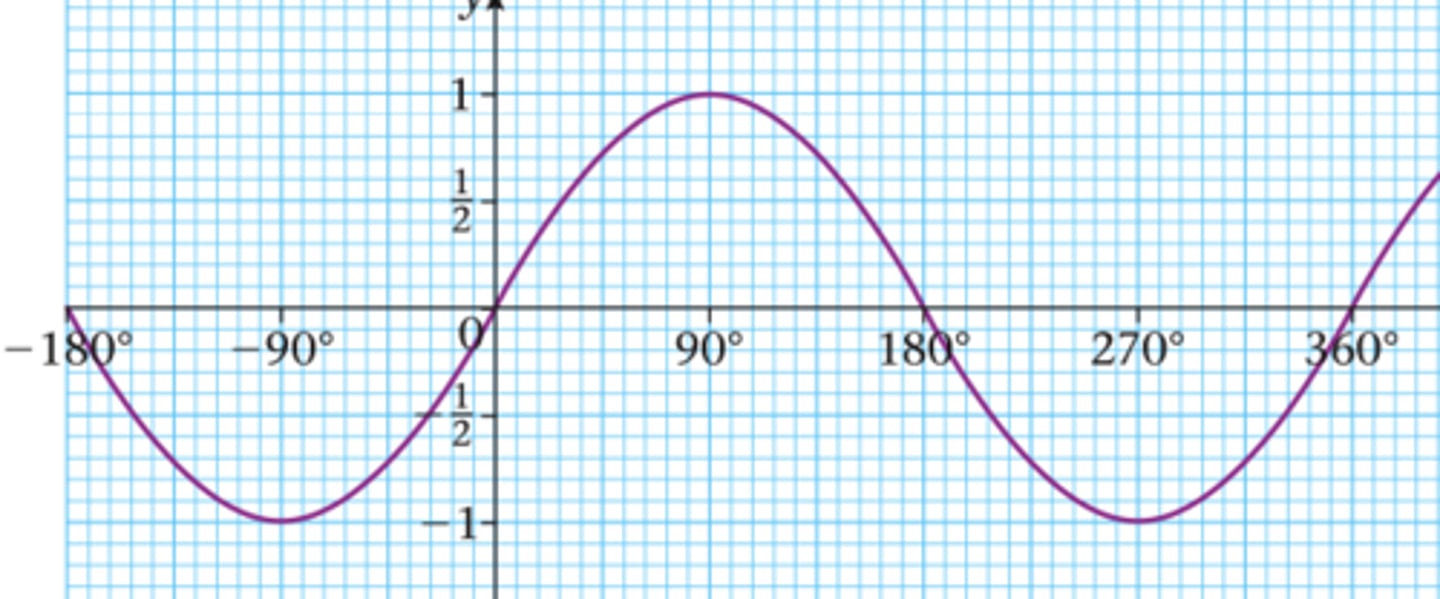
sin graph
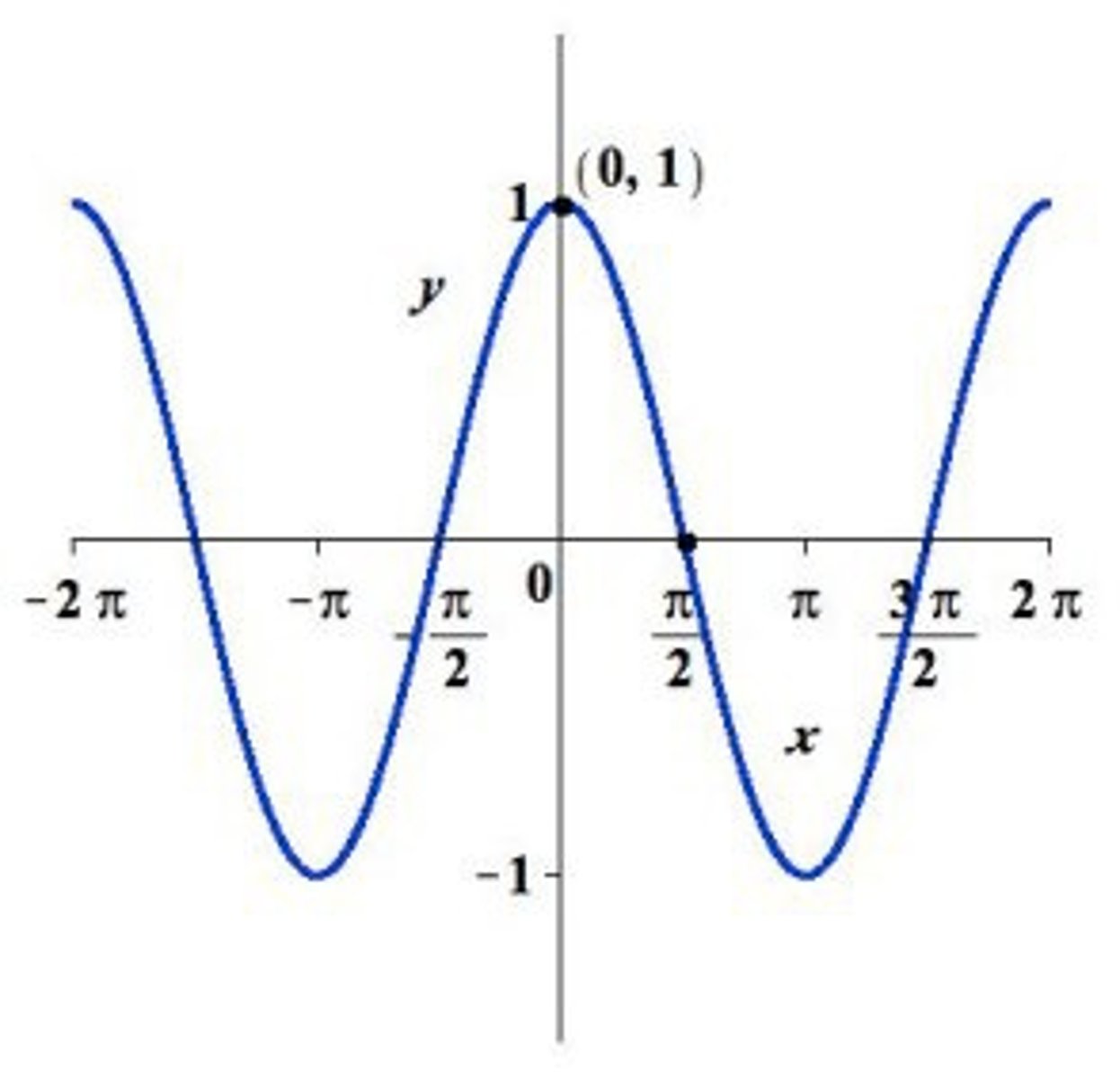
cos graph
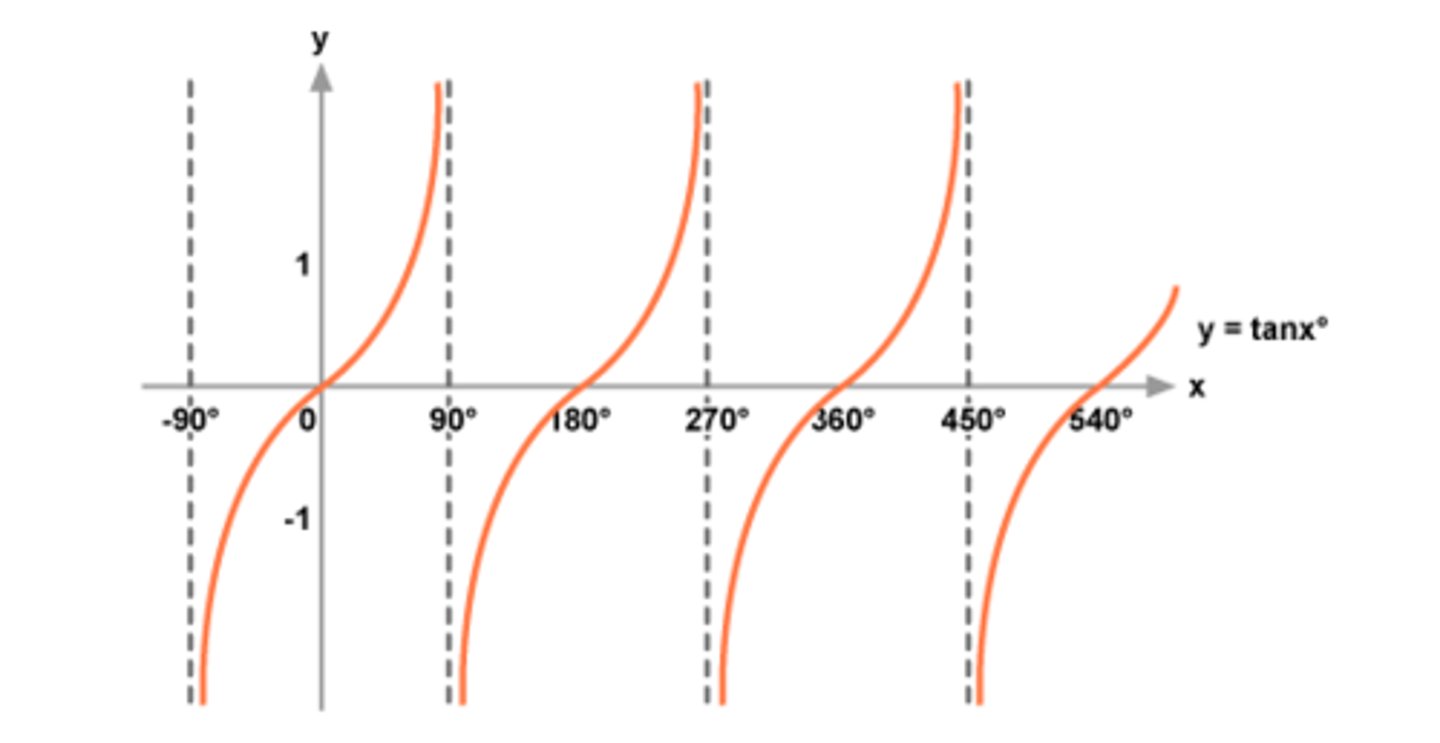
tan graph
area of segment
= area of sector-area of triangle
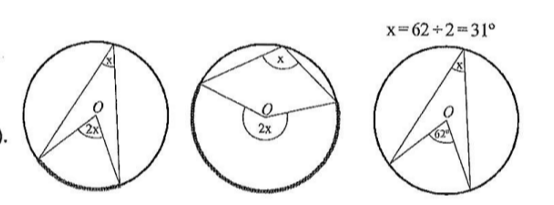
angle at the centre
the angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference
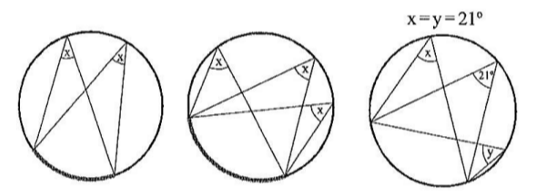
angles on the same arc
angles on the same arc are equal
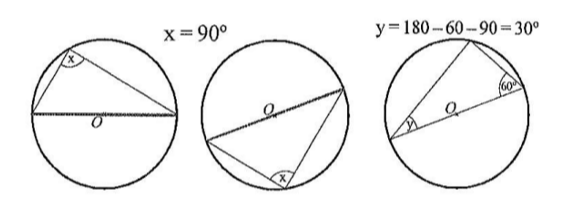
angles in a semicircle
angles at the circumference standing on a diameter are equal to 90
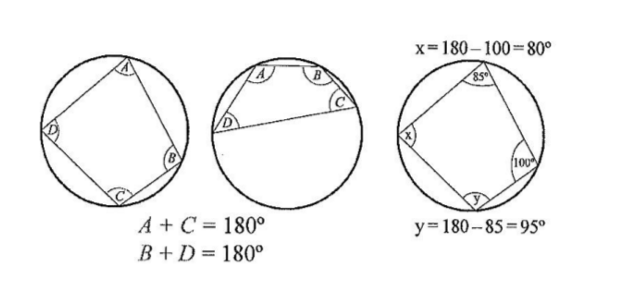
cyclic quadrilateral
opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral add up to 180
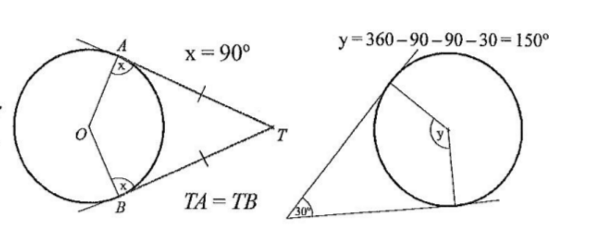
tangent to a circle
tangent to a circle always perpendicular to radius at point of contact
two tangents drawn from same point are equal in length
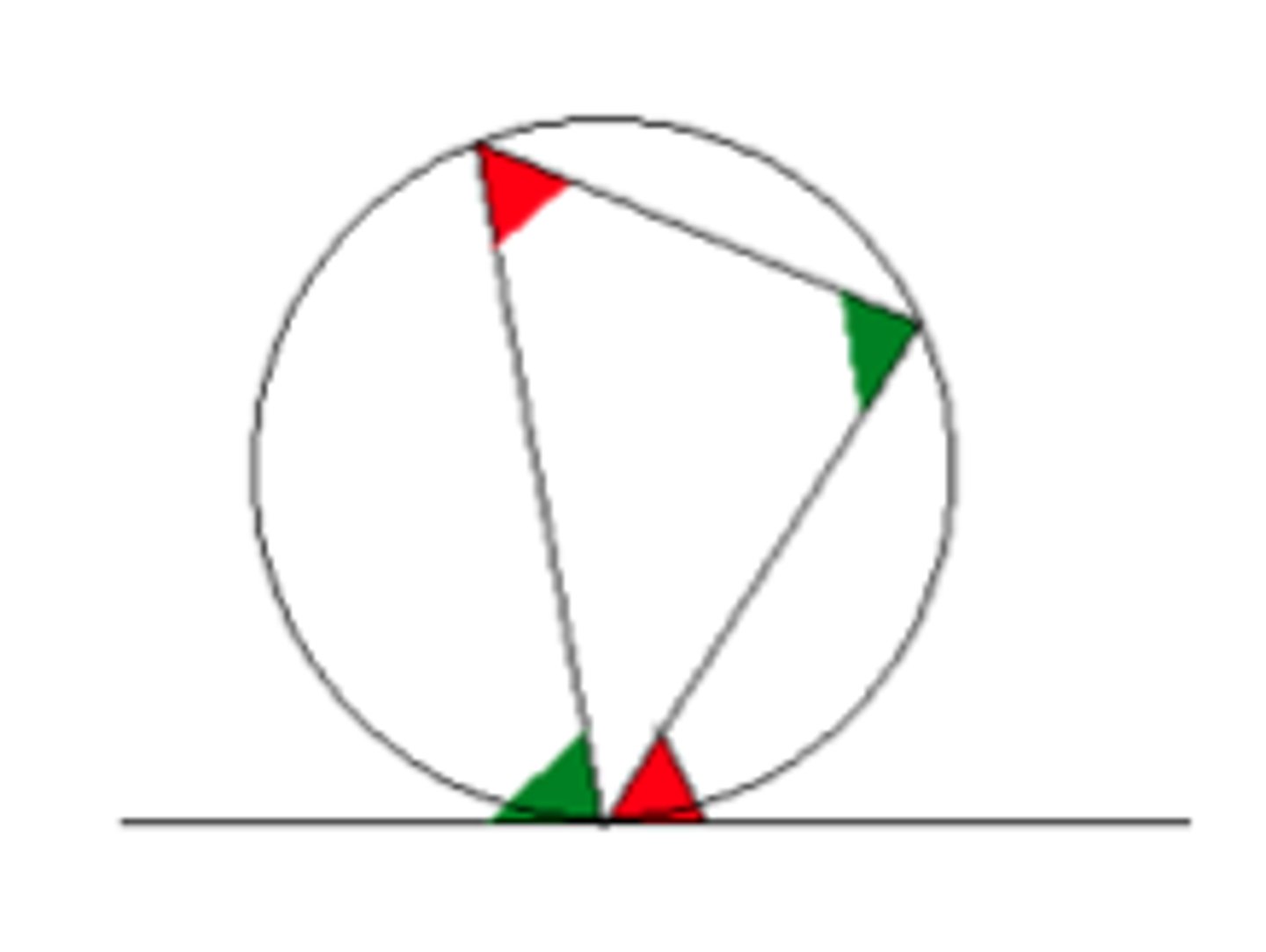
alternate segment
angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to any angle made by that chord in the alternate segment
direct proportion
y∝x
y=kx
inverse proportion
y∝1/x
y=k/x
domain
what is put in to a function
range
what you get out of a function
frequency density =
Frequency/class width
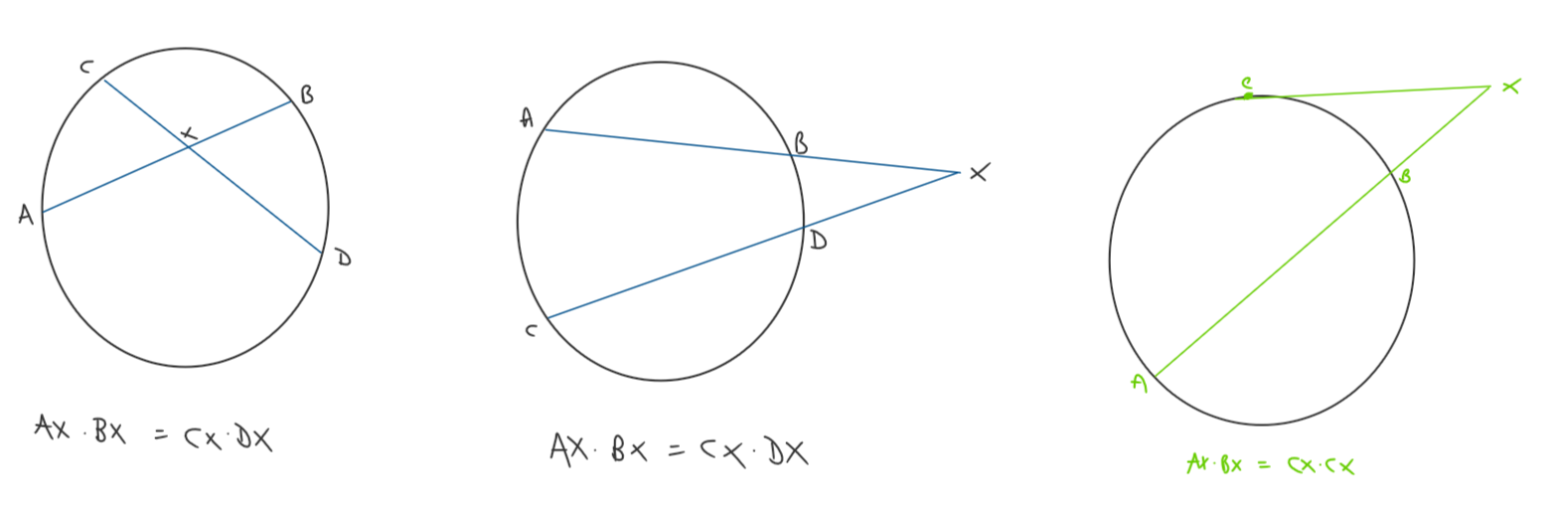
intersecting chord theorems
f(2x)
horizontal shrink by 1/2
2f(x)
vertical stretch by 2
y=-f(x)
reflection in x axis
y=f(-x)
reflection in y axis
f(x)+b
change in y by b
f(x+a)
change in x by -a